PHP for Absolute Beginners
"Hello, World!" and Beyond
Follow along:
Created by Juan Manuel Torres / @onema


Juan Manuel Torres
Born and raised in Bogotá Colombia
Software Engineer
MS Computer Science SDSU, 6+ years of experience

Started using PHP in 2000
Started programming in 1999


How this presentation works
- Use the link to follow the presentation http://bit.ly/1JsOgJC
- Use the orange links to access resources
- Follow my instructions!
- If you see this icon, you can see working code example



Overview
- Create a GitHub Account
- Create a Cloud 9 Account
- What is a computer program?
- What is PHP?
- Writing your first script "Hello, World!"
- Variables in PHP
- Data types in PHP
- Operators in PHP


Create a GitHub Account
What is GitHub?
- GitHub is a hosted Git service (version control system)
- It is very popular for hosting Open Source projects
- It is used to "Sign in with GitHub" to a lot of development Tools



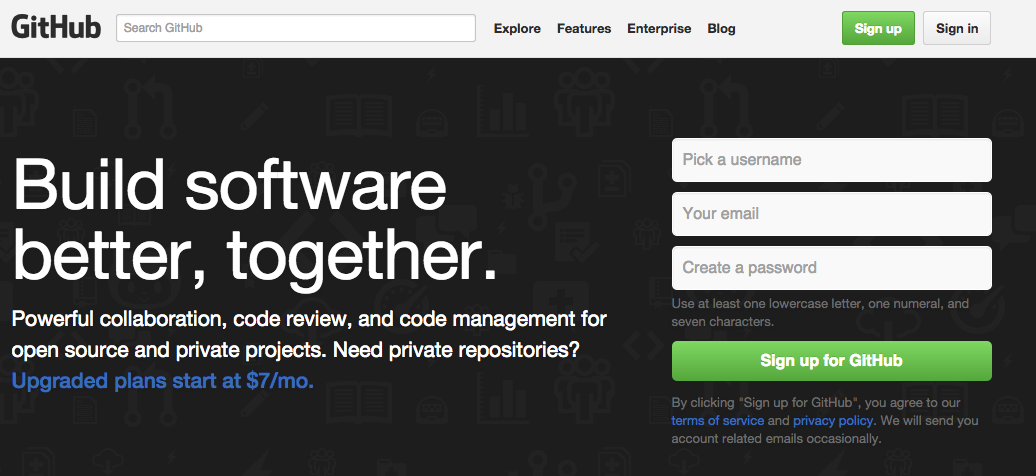
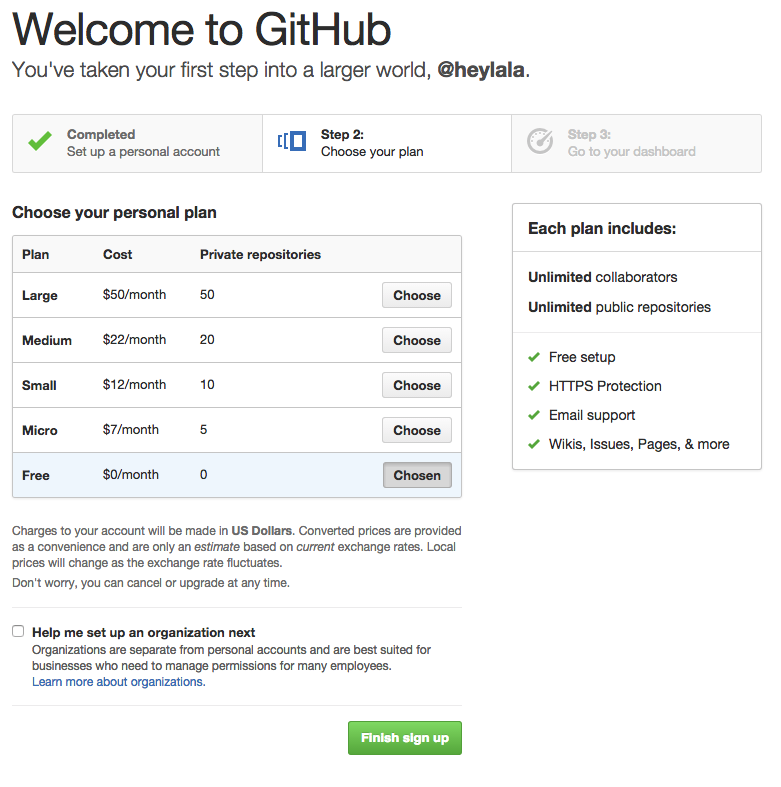
Create a GitHub Account
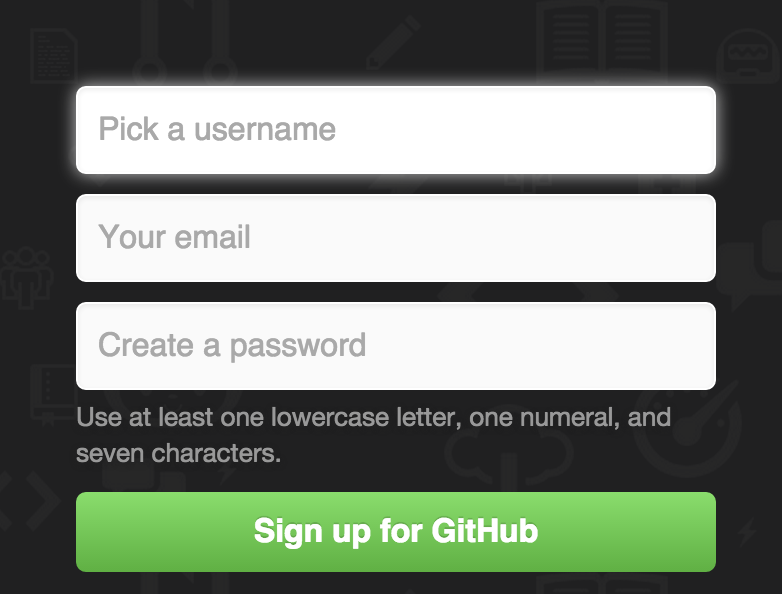

Pick a Username / Password & SELECT A FREE ACCOUNT



Fork the Repository


Create a Cloud 9 Account
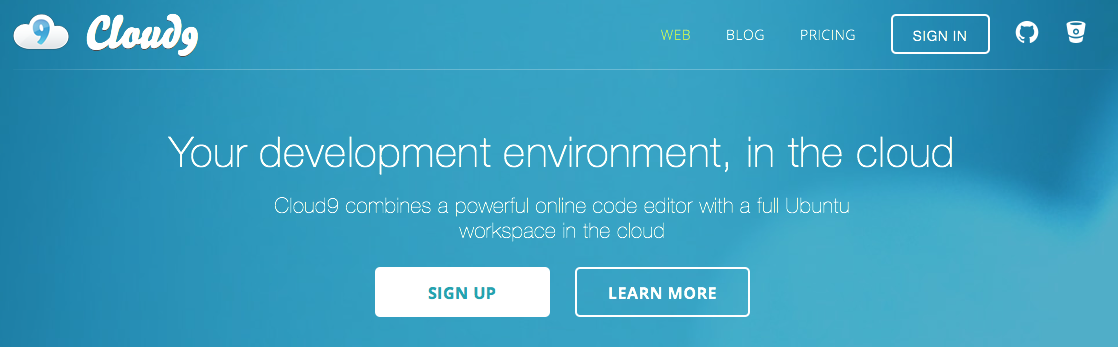


Create a Cloud 9 Account
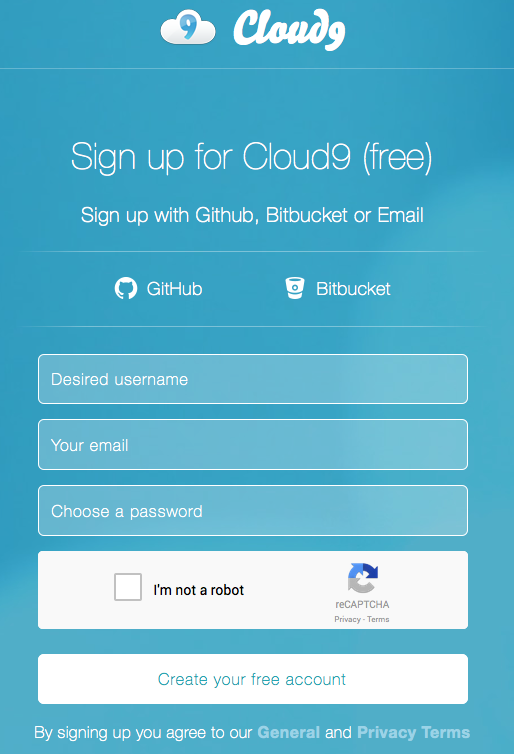


Create a Cloud 9 Project

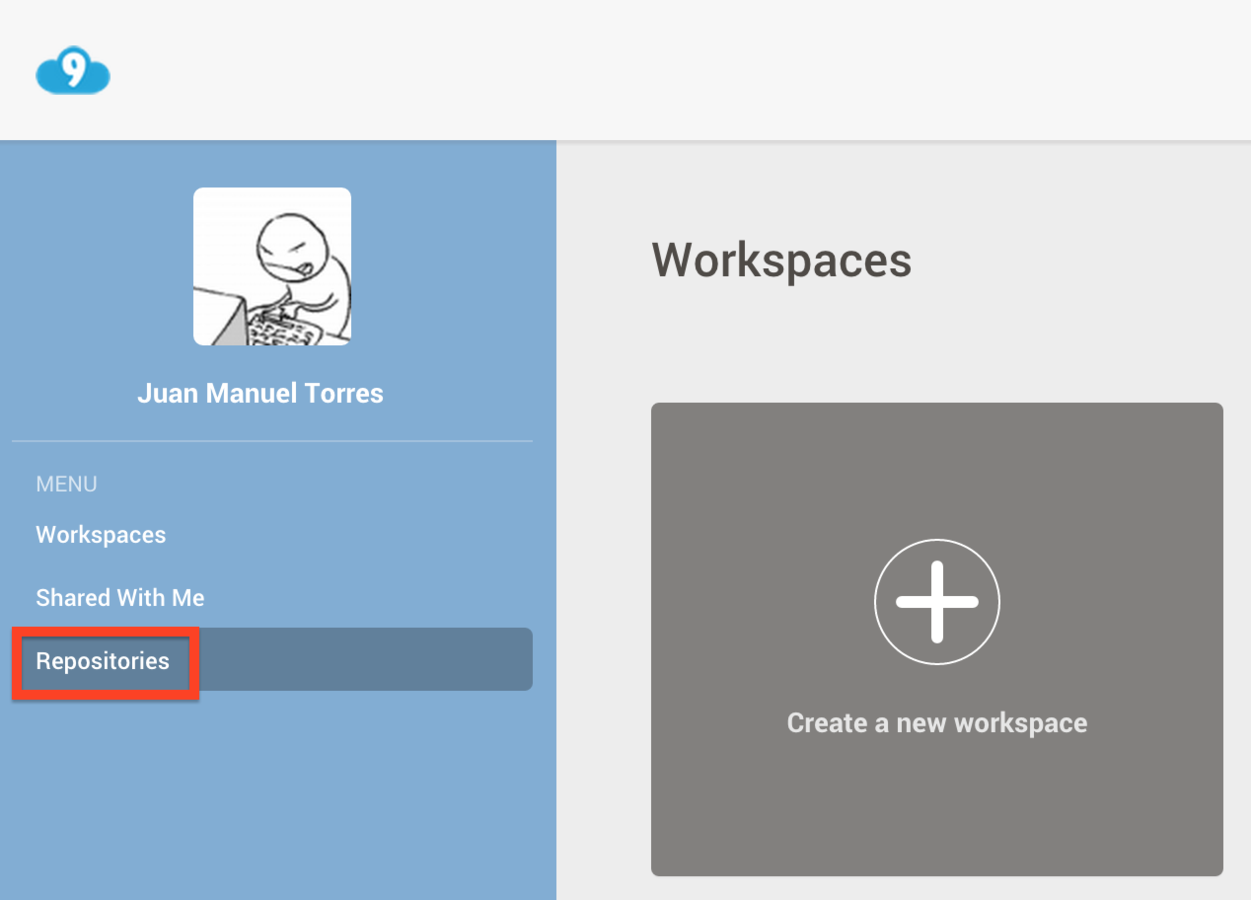

Create a Cloud 9 Project

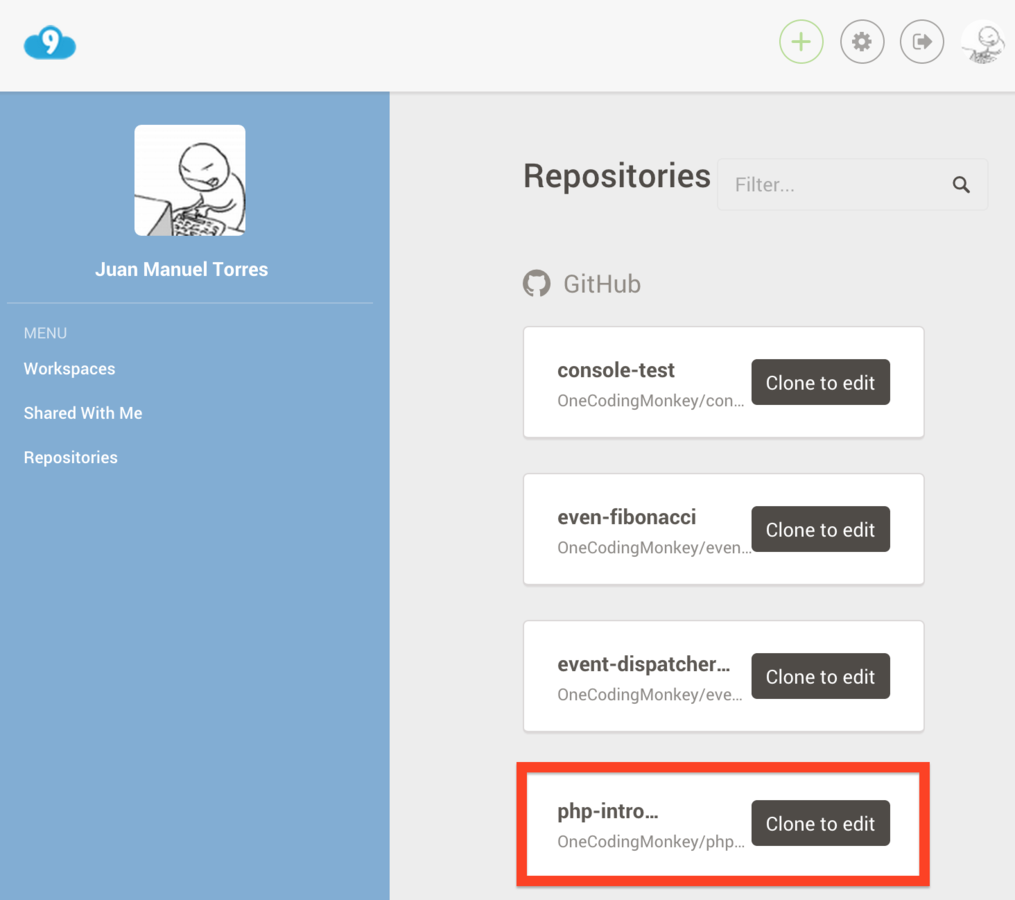

Create a Cloud 9 Project


What is a Computer Program?
Computer programs are collections of instructions that tell a computer how to interact with the user, the computer hardware or process data [1]



What is PHP?
PHP (recursive acronym for PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development [2]
Unlike other scripting languages that run directly in your computer, PHP will almost always run on a server.


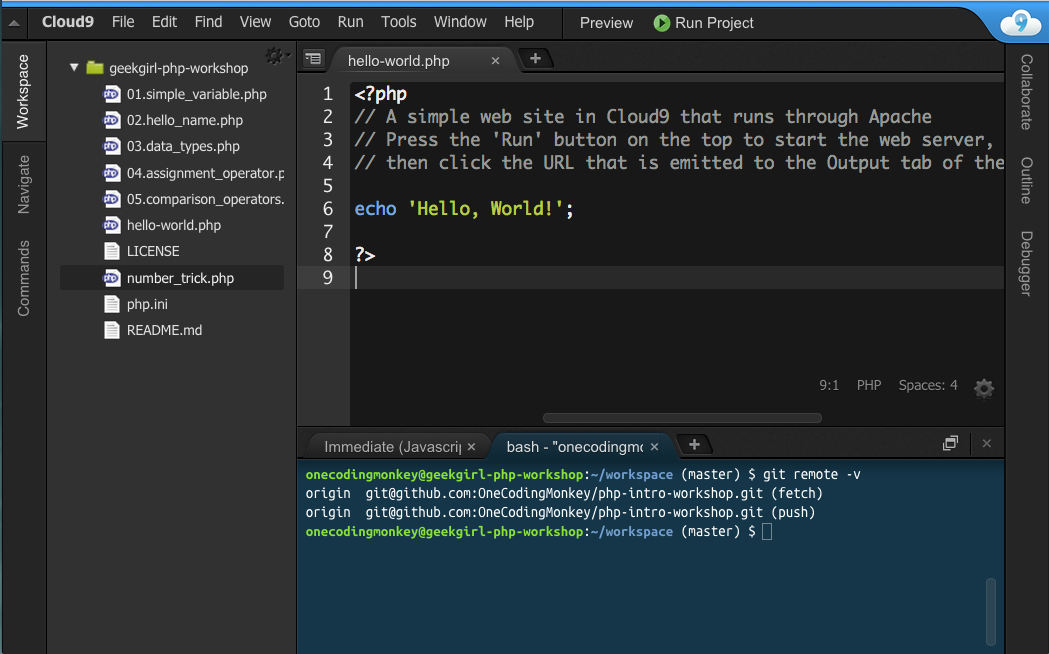
Writing our first program
"Hello, World!"
The "Hello, World!" program is the simplest program you can write in any programming language. All it does is output "Hello, World!" [3]


Writing our first program
"Hello, World!"
<?php
// THESE ARE COMMENTS AND
// WILL BE IGNORED BY PHP
/*
USE THE "/*" FOR
MULTILINE COMMENTS
*/
print 'Hello, world!';
?>With our "php-intro-workshop" project there is a sample hello-world.php file
PHP Open tag: tells the computer where the php program starts
- "echo" or "print" to the screen
- Anything in the quotes is a "string"
- the ';' tells php the end of the command
PHP only files do not require a closing php tag


Variables
A variable is a storage location associated with a name. Variables contain an unknown quantity or information called value [4]
<?php
// 01.simple_variable.php
$name = 'Juan';
$x = 30;
$y = 1.123;
// print the values below
print "";

Rules for PHP Variables [5]
- A variable starts with the $ sign, followed by the name of the variable.
- A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character.
- A variable name cannot start with a number.
- A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _ )


Using PHP Variables [5]
<?php
// 02.hello_name.php
$name = 'Juan';
print "Hello, $name!";
/**
* This will output:
* Hello, Juan!
*/

Data Types
A Data Type Is classification identifying one of various types of data [6]


Data Types
PHP Defines eight data types [7]
- Four scalar types:
- Two compound types:
- And finally two special types:


Data Types
<?php
// 03.data_types.php
print gettype(true) . PHP_EOL; // bolean
print gettype(12345) . PHP_EOL; // integer
print gettype(1.2345) . PHP_EOL; // double
print gettype("Hello") . PHP_EOL; // string
print gettype([1, 2, 3]) . PHP_EOL; // array
print gettype(new stdClass()) . PHP_EOL; // object
print gettype(null) . PHP_EOL; // NULL
PHP_EOL is a constant that represents the "End Of Line" symbol.


Operators
An operator in a programming language is a symbol that tells the [computer] to perform specific mathematical, relational or logical operation and produce final result. [8]
An operator is something that takes one or more values (or expressions, in programming jargon) and yields another value. [9]


Arithmetic Operators
| -$a | Negation | Opposite of $a. |
| $a + $b | Addition | Sum of $a and $b. |
| $a - $b | Subtraction | Difference of $a and $b. |
| $a * $b | Multiplication | Product of $a and $b. |
| $a / $b | Division | Quotient of $a and $b. |
| $a % $b | Modulus | Remainder of $a divided by $b. |
| $a ** $b | Exponentiation | Result of raising $a to the $b'th power. |


Assignment Operator
<?php
// 04.assignment_operator.php
$a = 1;
$b = 2;
$three = $a + $b;
print $three;
The assignment operator "=" is used to assign a value to a variable. It is not used to compare!


Comparison Operators
| $a == $b | Equal | TRUE if $a is equal to $b |
| $a === $b | Identical | TRUE if $a is equal to $b |
| $a != $b | Not equal | TRUE if $a is not equal to $b |
| $a !== $b | Not identical | TRUE if $a is not equal to $b |
| $a < $b | Less than | TRUE if $a is strictly less than $b . |
| $a > $b | Greater than | TRUE if $a is strictly greater than $b . |
| $a <= $b | Less than or equal to | TRUE if $a is less than or equal to $b . |
| $a >= $b | Greater than or equal to | TRUE if $a is greater than or equal to $b . |


Comparison Operator
<?php
// 05.comparison_operators.php
var_dump(1 == 2); // FALSE
var_dump(1 < 2); // TRUE
var_dump(1 <= 2); // TRUE
var_dump(2 > 2); // FALSE
var_dump(2 >= 2); // TRUE
var_dump(1 == true); // TRUE - same as (bool)1 == TRUE
var_dump(1 === true); // FALSE - same as (int)1 === FALSE
var_dump(0 == false); // TRUE - same as (bool)0 == FALSE
var_dump(0 === false); // FALSE - same as (int)0 === FALSEThe assignment operator "=" is used to assign a value to a variable. It is not used to compare!


Let's write some code!
Write a program that does the following:
- Choose a number between 1 and 10
- Assign that number to the variable $x
- Add five to $x
- Double the result
- Subtract 4
- Divide by 2
- Subtract the original number


Conclusion
- While you learn do not waste time setting up dev environments, use C9
- PHP is a general purpose scripting language often used for the web
- Variables are used to store data
- Operators (assignment and arithmetic) are used to make transformations to the data
- Comparison operators along with flow control statements are used to add logic to your programs


practical Advice [10]
- Plan your code before you write it
- Write a lot of code
- Ask others to review your code
- Learning how to program takes time; take the time to learn
- There are a lot of free resources, but don't be afraid to invest in your education (books, trainings, conferences, subscriptions )


RESOURCES

questions?
THE END
Juan Manuel Torres | @onema

References

