Intro to Shaders
(and OpenGL)
Intro
What we'll cover today
- What are shaders and what are they used for?
- What's a GPU? How is it different from a CPU?
- What's OpenGL / WebGL?
- Introduction to GLSL
Before we start
- This is a short intro workshop
- Goal is to teach you enough to keep learning on your own
- Conceptual understanding > shader code specifics
- I'll try not to use any technical terms without defining them
- Please feel free to interrupt me if you don't understand something
Motivation
Inspiration
Applications
- Lighting & materials in 3D engines
- Image Processing
- GPGPU
Where can you use shaders?
- Creative coding
- Processing
- openFrameworks
- p5.js
- Game development
- Unity / Unreal
- Three.js
- Live video performance
- Max/MSP/Jitter
- TouchDesigner
- VDMX
- Machine Learning
- TensorFlow.js
The GPU
CPU vs. GPU
- CPU: a few powerful cores, can run several threads
- GPU: 100s or 1000s of small processors, 1000s of threads
- CPU runs code sequentially
- GPU runs code in parallel
Why compute in parallel?
- A 1080p screen is made up of 1920 x 1080 = 2,073,600 pixels
- Re-drawing the screen at 60 fps requires 124,416,000 calculations a second
- Calculating the color for each pixel one-at-a-time is slow
- Computing all pixels at once is fast
CPU vs. GPU
The Graphics Pipeline
Terminology
- Shader: a program that runs on the GPU
- Texture: an RGBA image stored in the GPU's memory
- Vertex: a point in 2D or 3D space
- Geometry: a 2D or 3D shape made up of multiple vertices
OpenGL / WebGL
- OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a low-level library that lets you send data to and from the GPU
- OpenGL is used for desktop programs, usually written in C++
- WebGL is a JavaScript implementation of OpenGL that is built into web browsers
- Windows also has another competing graphics library called Direct3D
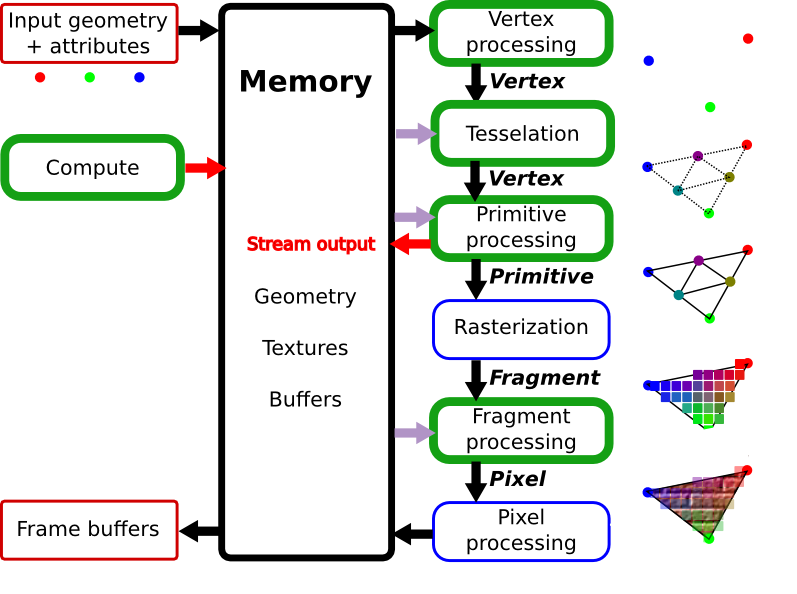
Stage 1: Input
- Your OpenGL code sends the GPU some geometry as an array of 2D / 3D vertices
- You also need to tell the GPU which vertex and fragment shaders to use
- Optionally, you can also pass extra data to your shaders, e.g. a texture that contains an image
Stage 2: Vertex Shader
- The vertex shader converts the position of each vertex to normalized coordinates in "clip space" (-1 to 1 range)
- Optionally, the vertex shader also moves each vertex (e.g. to apply a camera's perspective)
- Runs on all vertices simultaneously
Stage 3: Primitives
- The GPU combines the vertices into simple 2D shapes, e.g. each set of three vertices becomes a triangle
- Primitive types include:
- points (1 vertex)
- lines (2 vertices)
- triangles (3 vertices)
- quads (4 vertices)
- Your OpenGL code tells the GPU which primitive type to use
Stage 4: Rasterization
- The GPU figures out which pixels are covered by primitives
- Only the pixels that are covered will get passed on to the fragment shader
- Assigns each pixel a position in window coordinates (0 to size of screen)
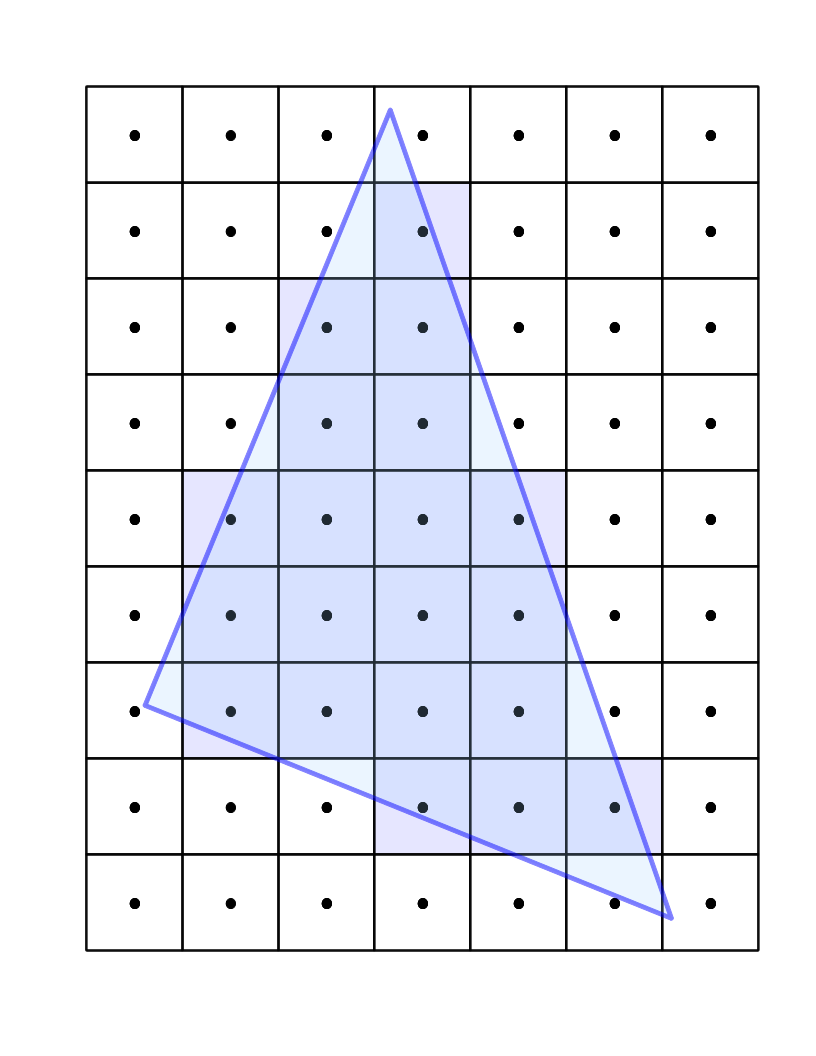
Stage 5: Fragment Shader
- Sets an RGBA color for each pixel from the rasterization stage
- Runs for every pixel simultaneously
- "Fragments" and pixels are technically not the same thing, but don't worry too much about it - you can safely think of them as interchangeable
Shaders
Recap: What's a shader?
- Shaders are programs that run on the GPU
- Vertex shaders change the positions of points that make up a piece of geometry
- Fragment shaders set the RGBA color for every pixel on the screen
- Fragment shaders take an XY pixel coordinate and return a color
Why are shaders difficult?
- The same shader program has to run independently for each pixel
- Each pixel only gets its XY position as input
- Can't keep track of state over time
GLSL
- OpenGL Shading Language
- Programming language for writing shaders
- Syntax is based on the C programming language
- Statically typed