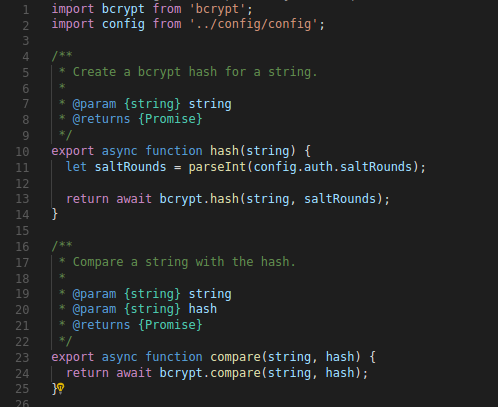
Javascript
(66 Hours)
1. Web Technology to know the concept of web
2. Core JavaScript for the depth knowledge of JavaScript
3. ReactJS for Front End Purpose
4. NodeJS for Back End Purpose
5. PostgreSQL Database
6. Express Server
Welcome
Teaching you what you want to learn.
About you!!!
1. Why are you Here?
2. What are you expectations?
3. What are your goals?

Web Development
(3 Hours)
1. What is Internet ? Differences between web server, web page, web browser and search engine.
2. Understanding Client and server and DNS (Domain Name server) servers.
3. How internet works?
4. Understading HTML and DOM (Document Object Model)
5. Anatomy of HTML element.
6. HTML attributes.
Internet
1. Internet
2. Protocols
3. TCP/IP
4. Packets
5. Routers
6.DNS
Web Browsers/ Web Page/ Web Servers/ Search Engines
Internet
-
The internet is a network of linked computers from around the globe. Each of these computers communicate with each other in a specific format.
-
Protocols: A set of rules governing the format of data sent over the internet.
-
TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol are communication protocols that define how data should travel across the web.
-
Packets are the information of the internet. Packets are sent from the sender to the receiever in a specific format which contains all the information needed to communicate.
-
A webpage is the page you look at in your browser
-
A web server is the computer that has the code for how the webpage should look and act.
-
A web browser is a program on a computer that displays the web page.
-
A search engine is a web server that searches all other web servers for information. A user can then pull up the webpage on their web browser and search for a site.
-
A client is the computer or internet device that requests information from the server.
-
A server is the computer that receives requests (as packets) from the client and responds with the appropriate data.
-
DNS Servers are the "phone book" of the internet. They translate IP addresses into domain names.
Http/Https
Hypertext Transfer Protocols is an application protocol that defines a language for clients and servers to speak to each other.
Encryption in Seucre Socket Layers/ Transport Layer Security.
SSL certificates.
How internet works!!
How search Engines works!!
How is web page build from HTML ?
- The rendering engine : responsible for displaying requested content. For example if the requested content is HTML, the rendering engine parses HTML and CSS, and displays the parsed content on the screen.
- JavaScript interpreter. Used to parse and execute JavaScript code.
How is web page build from HTML ?
Rendering Engines
Safari uses WebKit. Chrome and Opera (from version 15) use Blink, a fork of WebKit.
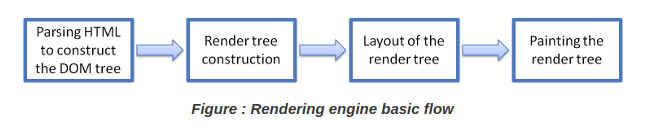
DOM Tree

Planning a basic website.
Git Setup
HTML/CSS
Tomorrow's Topic
- clear/cls
- pwd - present working directory
- cd - change directory
- mkdir - make directory
- touch - makes file
- sudo - super user privilege
- cp/copy - copy files and folders
- mv/move - move/rename files and folders
- rm/rmdir - remove/delete file and folders
Command line
Lets HTML
1. <!DOCTYPE html>
2. Head (title, meta, script, style, link) : Information that browser will use but not necessarily display to the user.
3. Body
4. ID and Class
5. Heading
6. Block Vs Inline
7. Whitespace and Character entities.
8. Link tags
9. Responsive
10. Deprecated Html Tags (Font, marquee, strike)
Lets CSS
1. Inline/ Internal/ Extrenal Css.
2. How to apply our first css.
3. Padding vs margin.
Design
1. Design is solution to the problem.
2. Identify KiKi and BoBo.
3. UI is looks and UX is usability.
- Design product such that it can be used without user manual.

Principle of Design
- Uniform
- Alignment
- pixel perfect
- Proximity
- visual connection
- Space
- let the content breath
- Balance
- Contrast
- juxtaposition of opposing element
Good vs Bad Design
1. Selection of chair.
2. Change shape in case of different products. (Shampoo/Conditioner).

3. Dont change conceptual model.
4. Themes should define sites.
Element of design
- Line
- link/highlights -> a
- header -> h1
- list/menu/table -> ul/li/table
- seperator (different topic) -> hr
- panel
- Shape
- menu, radio, checkbox, tabs, textarea, textbox, dropdown, layout
- Size
- Texture
- Color
GIT (Version Control Systme)
(2 Hours)
1. What is GIT?
2. Setup a first git repo.
3. How to use GIT ?

- git init - initalized an empty Git repo
- git status - shows the status of repo
- git add - Adds file to be tracked
- git commit - commits a file or locks a version of a file
- git log - shows you the logs
- git checkout - change your branch or head
- git remote add origin - adds a remote point
- git remote -v - shows the available remotes
- git push origin - pushes the commits to the remote branch
- git diff - shows the changes since last commit
Git/GitHub
Git is a revision control system, a tool to manage your source code history.
GitHub is a hosting service for Git repositories.
Git with SSH
List your SSH Key.
- https://putty.org/
- download puttygen
-install and generate
-save
vs code
Ctrl +c
Ctrl + D
Alt + Down
Alt + Up
Ctrl + I Select current line
Shift + Ctrl Select and move the cursor
Alt + PageDown Move to second page
Ctrl + Home/End Move to first and last line.
Ctrl +/ Comment/uncomment
Core Javascript
(16 Hours)
1. Javascript core concept.
2. Playing with javascript .
3. Writing first ES6 syntax and features.
4. Writing professional code with good programming practice.
5. Developing a small game using plain javascript.
6. Presentation
.
What is JS?
1. A programming language that is used to make web pages interactive.
2. Interpreted language.
3. Runs on the client's computer/browser.
.
Why JS?
1. Game Development.
2. Server Application.
3. Web Application.
4. Native Mobile Application.
5. Desktop Application.
5. Typescript.
6. Frameworks before core javascript???
.
JS
1. Dynamically Typed Language.
2. Case sensitive.
3. Whitespace are ignored.
4. Variables much not be a keyword.
.
How JS works
1. Syntax parser
Your code => Compiler => Run at your computer
2. Reads each characters one by one.
3. Js object are name value paired.
4. Execution context
-Creation phase
- Execution code
.
How JS works
1. Single Threaded
2. Synchronous.
3. Invocation
.
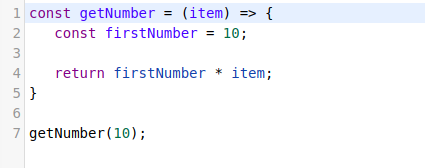
Basics
1. Declarations
-var
-let
-const
2. Declaring variables.
3. Variable Hoisting.
4. Function Hoisting.
5. Declaring const.
.
Hoisting
Text

Data Types
1. Boolean.
2. null
3. undefined
4. Number
5. String
6. Object
7. How to know data types ??
.
"1" to 1
1. parseInt()
2. parseFloat()
3. +
.
Conditional Statement
1. if ... else statement.
.

1. Switch statement

Loops and iteration
1. For statement
2. do..while statement
3. while statement
4. for...in statement
Functions
function name(parameter1, parameter2, parameter3) {
code to be executed
}
var result = getFirstName('Hari prasad');
function getFirstName(firstName) {
return 'Mr.' + firstName;
}
Array
1. concat()
2. map()
3. filter()
4. includes()
5. indexOf()
6. toString()
7. pop()
8. push()
9. reduce()
10. splice() // start how many
11. sort()
12. slice() //start end
Object
1. A JavaScript object is a collection of named values.
2. Creating an object.
3. Updating an object.
4. JavaScript variables are not mutable not object and array.
HTML with JS
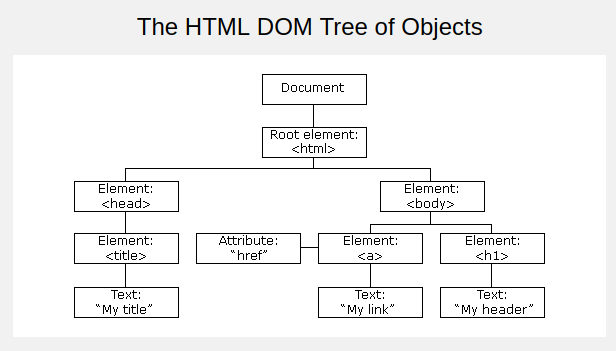
How JS understand HTML???
1. The DOM allows us to use our javascript code to access parts of the web page.
Accessing DOM
1. getElementById
2. getElementByTagName
3. getElementByClassName
Changing Elements using getElementById
- innerHTML
-style
-value
-validation
-events
4. querySelector
document.querySelector('input[name=gender]:checked').value
Accessing DOM
1. previousElementSibling
2. nextElementSibling
3. parentElement
Separation of Concerns
<JS/>
<button id='btn' onclick='function()'>Click Me</button>
Vs
var btn = document.getElementById('btn');
1. btn.onclick = function
2. btn.addEventListener('click', function);
Js utils
1. new Date()
- getDay()
- getDate()
- new Date().toLocaleTimeString()
- new Date().toLocaleDateString()
2. setTimeout()
setTimeout(function, milliseconds)
3. setTimeInterval()
-setInterval(function, milliseconds)
4. JSON.stringify()
5. window
6. try...catch
window
1. window.location
2. window.localStorage
3. window.onload
Math
1. Math.PI ;
2. Math.sqrt()
3. Math.pow()
4. Math.round()
5. Math.random()
Regex
A regular expression is an object that describes a pattern of characters.
Single Character
\d => 0-9
\w => A-Z a-z 0-9
\s => whitlespace
. => any character
Regex
Quantifier
+ => 1 or more
? => 0 or 1
{n}
{min,max}
Position
^ => beginning
$ => end
\b => word boundary
Character Class
[]
Regex
/pattern/modifiers;
alert and route
ES6 and Class
Object Literal
let book = {
title: 'Ramayan',
author: 'Balmiki'
getSummary: function() {
return this.title + 'was written by' + this.author
}
}
Object.value(book)
Object.key(book)
Constructor
function Book(title, author) {
this.title = title,
this.author = author
}
let book1 = new Book('ramayan', balmiki')
Inheritance
function EBook(title, author, link) {
Book.call(this, title, author)
this.link= link,
}
let book1 = new Book('ramayan', balmiki')
let eBook = new EBook('ramayan', 'balmikli', 'www.www.com')
Class
class Book {
constructor(title, author) {
this.title = title,
this.author = author
}
getSummary() {
return this.title + 'was written by' + this.author
}
}
let book1 = new Book('ramayan', balmiki')
Class
class Ebook extends Book {
constructor(title, author, link) {
super(title,author);
this.link = link;
}
}
let book1 = new Book('ramayan', balmiki')
let ebook = new EBook('ramayan', 'balmiki', 'www.google.com')
JS version
ECMAScript 6 is also known as ES6 and ECMAScript 2015
* String- Template.
const myString = `This is a string`;
const myString `This is a ${val}`;
* Arror function.
* Object destruction.
var car = {name:'McF', model: 'A303', color:'black', price: 334}
const {name, color, model, price} = car
Callback and promise
JavaScript statements are executed line by line. However, with effects, the next line of code can be run even though the effect is not finished. This can create errors.
To prevent this, you can create a callback function.
A callback function is executed after the current effect is finished.
Npm
1. Package Manager used by JS developer to share the code to solve the problem.
2. Reuse
3. Package : Directory with one or more files.
4. Package should be small and should solve the problem.
React JS
(20 Hours)
1. Introduction of JSX.
2. Components and Props.
3. State and Lifecyle.
4. Handling Events.
5. State-full vs State-less Components.
6. Build application in react.
7. Presentation

What Is React?
React is a declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It lets you compose complex UIs from small and isolated pieces of code called “components”.
Declarative Vs Imperative
Declarative allows you to control flow and state in your application by saying "It should look like this".
An imperative style turns that around and allows you to control your application by saying "This is what you should do".
Go to kitchen
Open fridge
Remove chicken from fridge
...
Bring food to table
In a declarative world, you would simply describe what you want
I want a dinner with chicken.
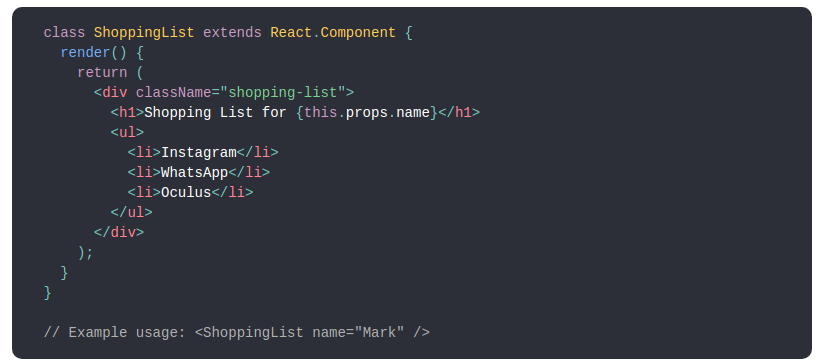
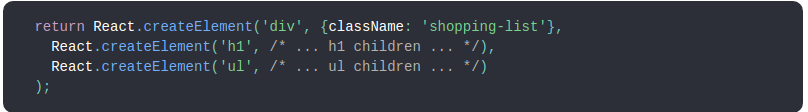
React Element
In simple words, react element are the JSX code or user defined component.


JSX
It is a syntax extension to JavaScript.It describe what the UI should look like.

Variables in JSX
You can put any valid JavaScript expression inside the curly braces in JSX. For example, 2 + 2, user.firstName, or formatName(user) are all valid JavaScript expressions.
JSX Prevents Injection Attacks: By default, React DOM escapes any values embedded in JSX before rendering them.
- Components
1. Components are like JavaScript functions. They accept arbitrary inputs (called “props”) and return React elements describing what should appear on the screen.
2. Class and Function Component
3. Try to split component into smaller pieces.
-Passing props in our components.
1. Props are read only.
<Header/>
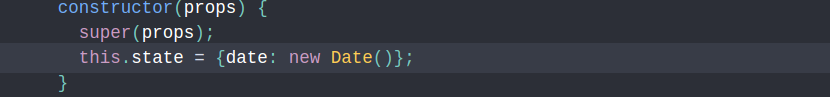
- State
1. State is similar to props, but it is private and fully controlled by the component.
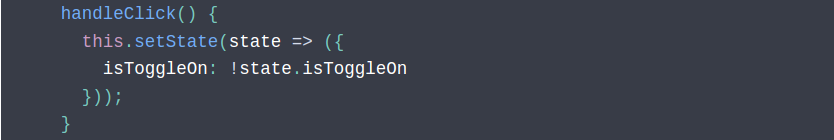
2. Stateless vs Stateful
3. Declare and update state.
- Handler Events
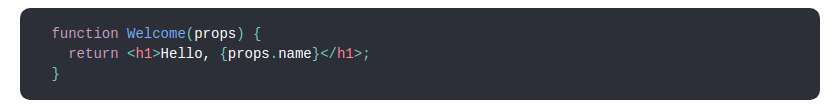
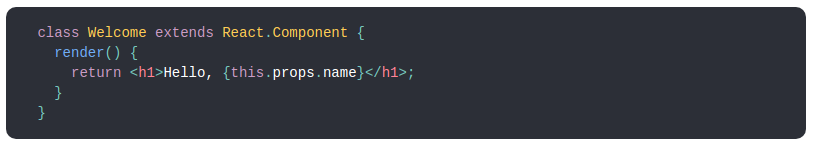
Function which accepts only data as props and returns JSX elements is functional component.
ES6 class extending React component is called class component.
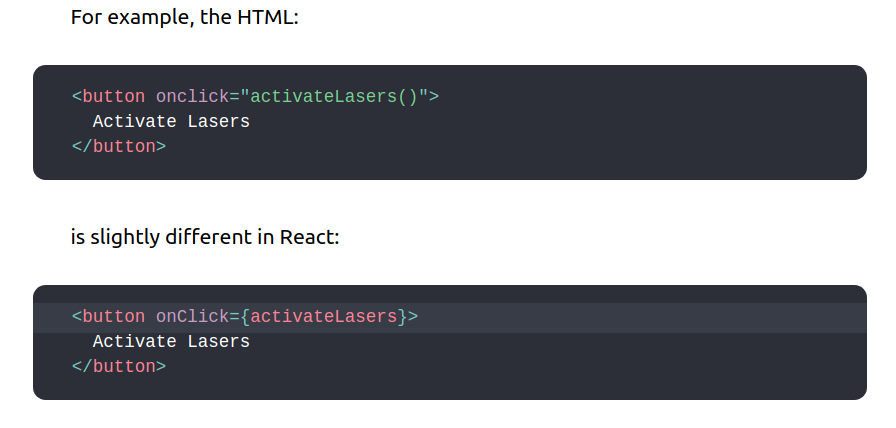
Event Handlers
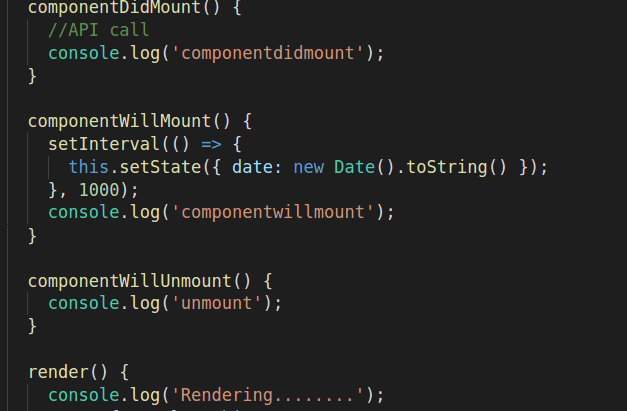
In applications with many components, it’s very important to free up resources taken by the components when they are destroyed.
Playing with other react packages.
-react-bootstrap
-react-router-dom
React-router-dom
- npm install --save react-router-dom
- import {BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link} from 'react-router-dom';
Router
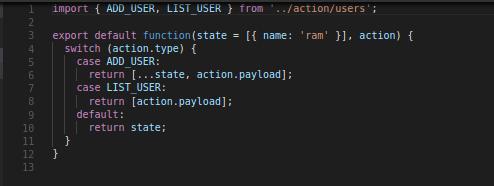
Redux
1. yarn add redux.
2. create store.
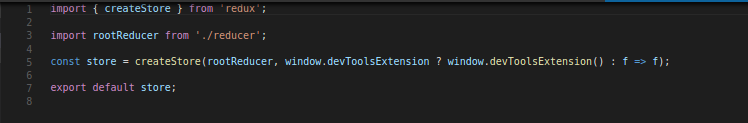
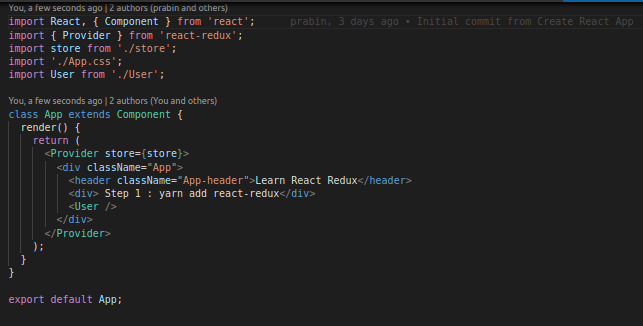
3. Wrapping our App with store.
4. yarn add redux-actions
5. Adding structure for store
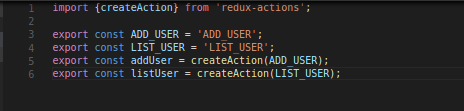
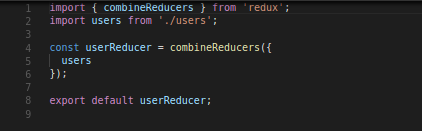
6. Adding reducers
Database
(6 Hours)
1. Setup postGre Sql in our machine.
2. Creating users, database and tables.
3. Playing with tables.

PostGre SQL
Object oriented relational database (RDMS).
Big company such as instragram uses majority of data.
Download link : https://www.enterprisedb.com/downloads/postgres-postgresql-downloads#windows
Port : 5432
Create Database :
CREAE DATABASE learnjs
List of database : \l
Select database : \c learnjs
Table description: \d+ tablename
Drop db :
DROP DATABASE learnjs
Quit: \q
Datatype size :
smallint ( for id ) 32767 max
integer 2.14Billion
bigint 9Trillion
numeric decimal
real decimal upto 4 float
smallserial auto increament
Create table:
CREATE TABLE users(id int primary key not null, name text not null, roll int not null, address char(50));
\d Descript schema for the table
Insert Table :
INSERT INTO user(id, name, roll, address) VALUES (1, 'tester', 1, 'patan');
INSERT INTO user(id, name, roll, address) VALUES (1, 'tester', 1, 'patan'), (1, 'tester', 1, 'patan');
Select Table :
Select id from users;
SELECT 2+3;
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id=4 AND id=5 AND id=6;
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id<>4 AND name='test';
SELECT * FROM users WHERE name isnull;
SELECT * FROM users WHERE name like 't%';
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age in(20,30,40);
SELECT * FROM users WHERE age between 23 AND 32
Comment
--This is my query
/* Even this is comment */
Expression:
SELECT name as firstname FROM users;
SELECT count(*) from users;
SELECT MAX(age) from users; /MIN
SELECT SUM(fees) FROM users; /AVG
SELECT current_timestap;
Constraint
Check condition which should satisfy before inserting.
CREATE TABLE items( id int, price numeric CHECK (price>0));
UNIQUE and NOT NULL
CREATE TABLE items (id int, name text, UNIQUE(name));
Primary key:
Its unique and not null
Foreign Key:
Its a primary key mapped with other primary key.
CREATE TABLE order (
id int primary key,
item_no integer REFERENCES items(id)
)
Alter
ALTER TABLE users ADD gender char(1);
ALTER TABLE users DROP COLUMN gender;
ALTER TABLE users ADD CONSTRAIN pmy PRIMARY KEY(id)
ALTER TABLE user DROP CONSTRAINt pmy
Update
UDPATE users SET name='ram' WHERE id=3;
DELETE FROM users where name='ram'
Limit and Offset
SELECT * FROM users limit 10;
SELECT * FROM users LIMIST 10 OFFSET 10
GROUP and HAVING
Finding similary data from the table forming a group.
SELECT age, count(*) FROM users GROUP BY age;
SEELCT age, count(*) FROM users GROUp BY age HAVING MAX(age) > 20;
ORDER BY
SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY name DESC ASC;
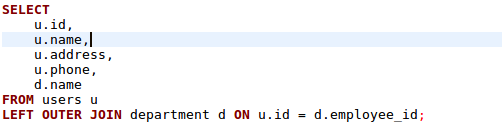
Joins
Combining common field
Cross :
Match each and every row of first table with each and every rows with second table.
Inner :
Make a new table with common fields in two or more tables.
Outer:
Extension of inner join
Left Outer join :
Views:
Multiple uses of same data.
CREATE VIEW fetch_users as
SELECT name from users;
Truncate
TRUNCATE TABLE users;
Subqueries
Query within another query.
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id in(SELECT id from users where id <4)
Node JS
(18 Hours)
1. What is Node JS and what can it do?
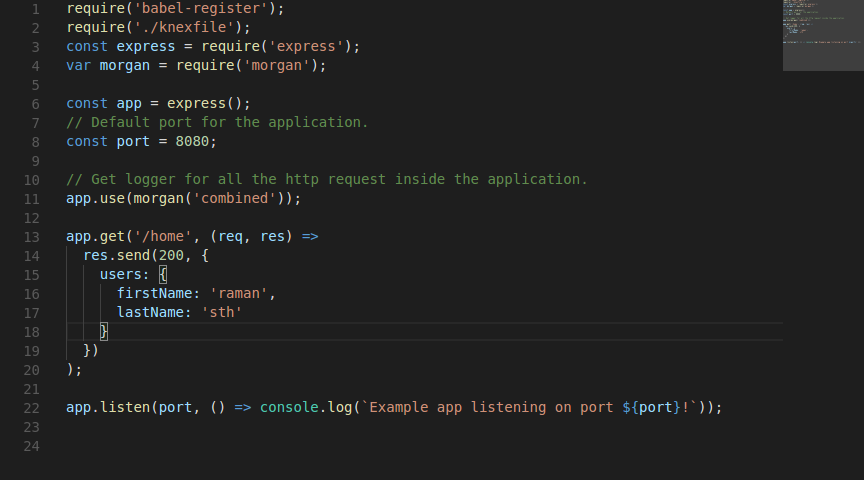
2. Create our first server.
3. What is express js ?
4. Restful API's (Application Program Interface) using express js. (Representational State Transfer)
5. Making a API calls from react app.
6. Final Presentation.

Init package.json
Install express
install nodemon
install morgan
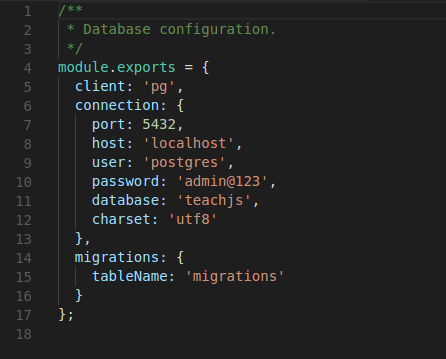
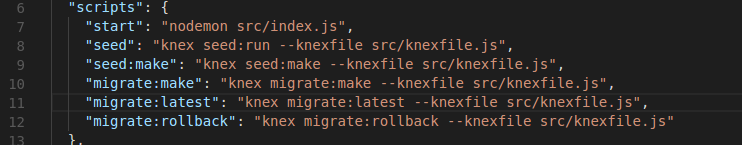
Knex configuration and scripts
Knex : Query builder
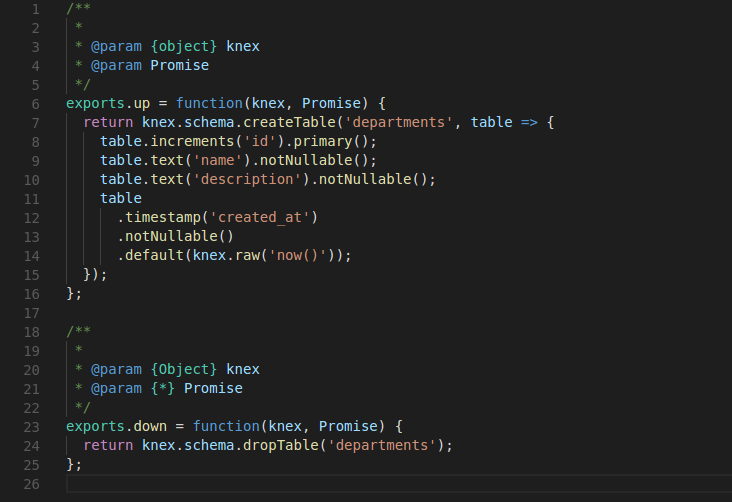
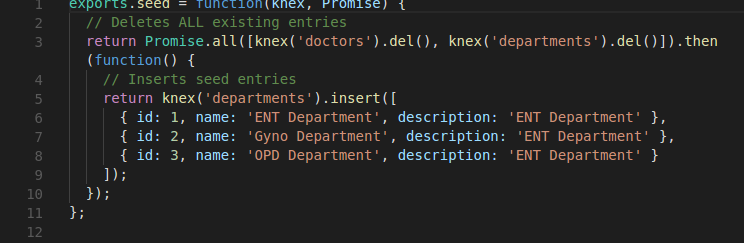
Migration and Seed
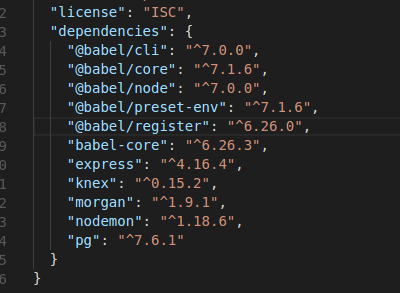
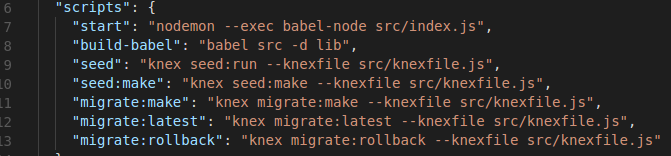
ES6 babel compiler
Knex : Query builder
Select:
query: "Select * from tbl_name";
knex.raw(query);
Syntax: knex(tbl_name)
Example: knex('user')
query : "Select * from tbl_name where id=1"
knex(tbl_name).where('id',1)
query: Insert into tbl_name(id) values(1);
knex(tbl_name).insert({id: 1})