Scope Chain
YDKJS
Parminder Singh
Senior Frontend Engineer @ Finder UK
Scope Chain
- Connections between scopes that are nested within other scopes
Scope Chain
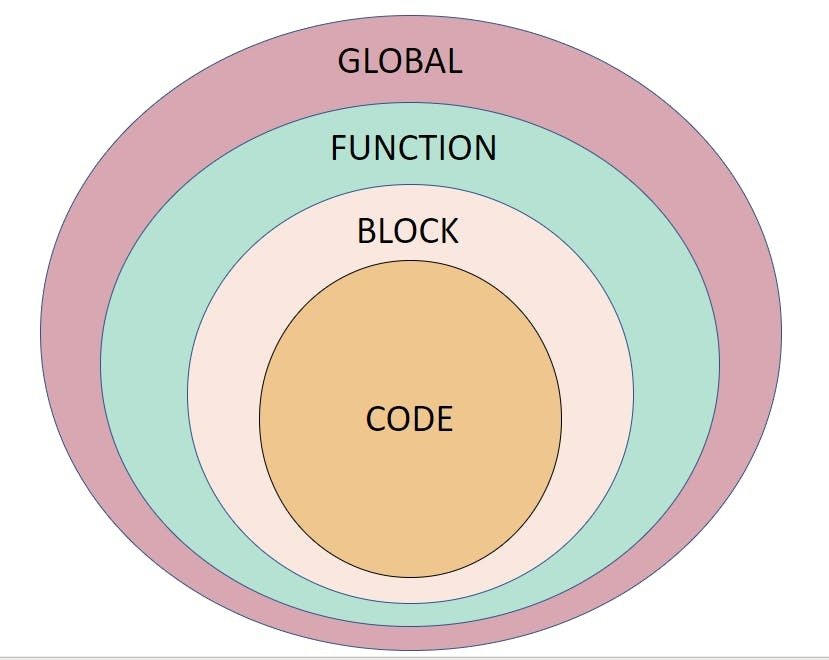
- Path along which variables can be accessed
- Directed chain - the lookup moves upward/outward only
"Lookup" Is (Mostly) Conceptual
"Lookup" Is (Mostly) Conceptual
- "Lookup" - runtime access of a variable
- Runtime lookup process works well for conceptual understanding
- Color of a marble's bucket - "usually determined" during the initial compilation process
- Based on lexical scoping - finalised at that point - nothing will change it later during runtime.
- Since Marble colors are known - immutable - info is stored in variable entry in AST.
- Runtime Engine doesn't need to lookup - already known - optimization benefit of lexical scope.
"Lookup" Is (Mostly) Conceptual
Color of marble is "usually determined" - compile step
<script type="text/javascript" src="ngx-slick-carousel.js"></script>
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/1.7.1/jquery.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>"Lookup" Is (Mostly) Conceptual
What happens when marble is uncolored?
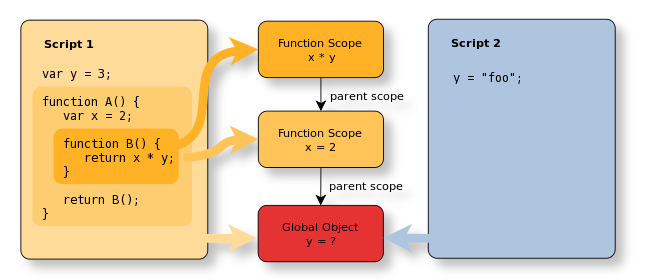
- Consider Variable ref that isn't declared in any lexically available scopes in the current file.
- JS compilation - each file is its own separate program.
- If no declaration is found, that's not necessarily an error.
- Another file (program) in the runtime may indeed declare that variable in the shared global scope.
- Ultimate determination - deferred to the runtime.
- Undeclared is left as an uncolored marble
- Deferred lookup will eventually resolve the color - but only once at runtime - immutable
"Lookup" Is (Mostly) Conceptual
Shadowing
- Two or more variables, each in different scopes, with the same names.
- Single scope can't have multiple variables with the same name, only one is assumed.
- If need to use same name - different scopes (often nested).
- Key aspect of lexical scope behavior
- Impact of shadowing - for inward/downward scope, it's impossible for any marble to be colored as the shadowed variable.
Shadowing
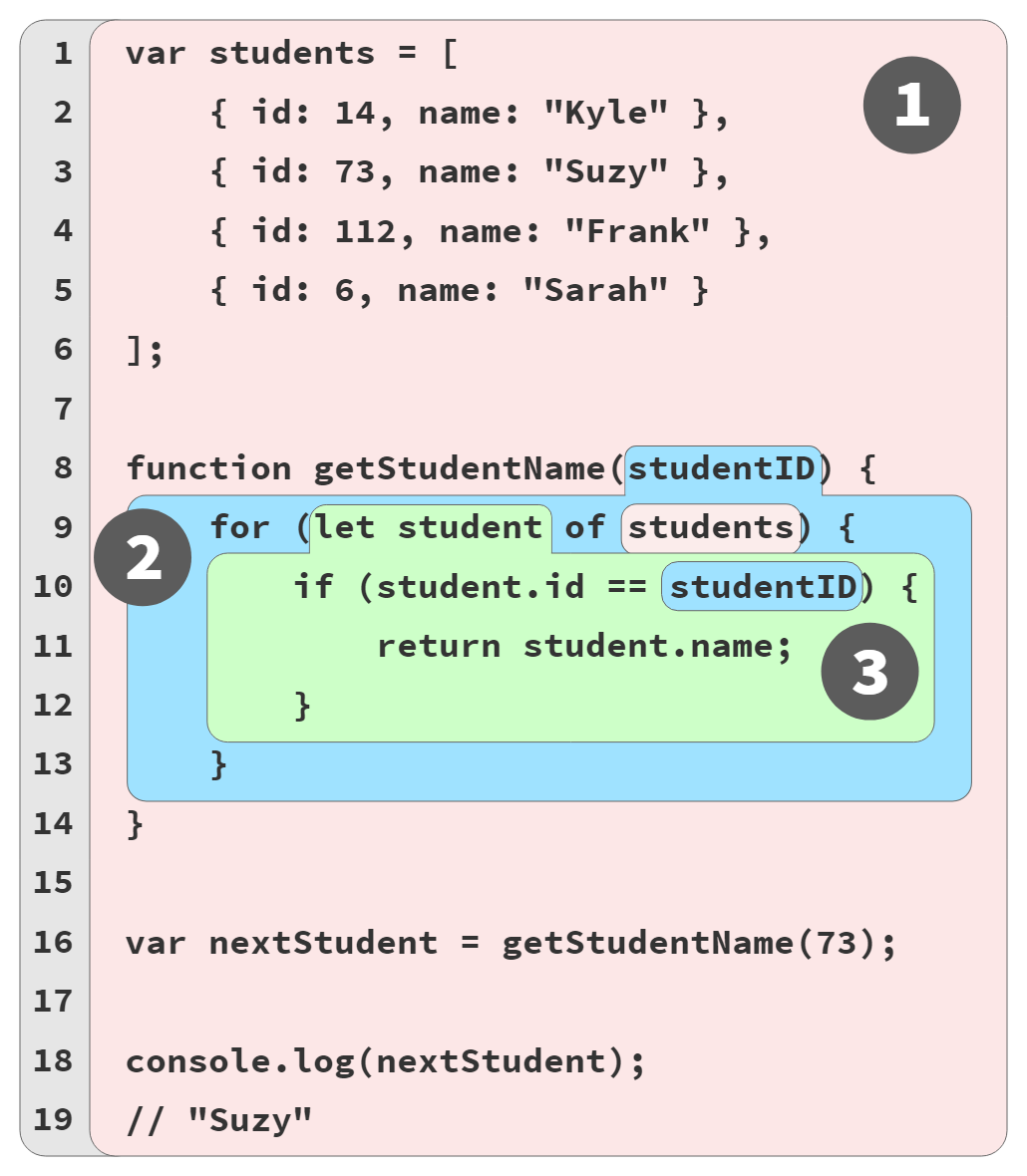
var studentName = "Suzy";
function printStudent(studentName) {
studentName = studentName.toUpperCase();
console.log(studentName);
}
printStudent("Frank");
// FRANK
printStudent(studentName);
// SUZY
console.log(studentName);
// SuzyShadowing
var studentName = "Suzy";
function printStudent(studentName) {
console.log(studentName);
console.log(window.studentName);
}
printStudent("Frank");
// "Frank"
// "Suzy"Global unshadowing trick - anti-pattern
Shadowing
var studentName = "Suzy";
function printStudent(studentName) {
console.log(studentName);
console.log(window.studentName);
}
printStudent("Frank");
// "Frank"
// "Suzy"Global unshadowing trick - anti-pattern
- window.studentName as a getter/setter that accesses the actual studentName variable
- Only works for global scope - not for nested - and only for vars and functions.
Shadowing
var one = 1;
let notOne = 2;
const notTwo = 3;
class notThree {}
console.log(window.one); // 1
console.log(window.notOne); // undefined
console.log(window.notTwo); // undefined
console.log(window.notThree); // undefinedShadowing
var special = 42;
function lookingFor(special) {
// The identifier `special` (parameter) in this
// scope is shadowed inside keepLooking(), and
// is thus inaccessible from that scope.
function keepLooking() {
var special = 3.141592;
console.log(special);
console.log(window.special);
}
keepLooking();
}
lookingFor(112358132134);
// 3.141592
// 42Shadowing
var special = 42;
function lookingFor(special) {
var another = {
special: special
};
function keepLooking() {
var special = 3.141592;
console.log(special);
console.log(another.special); // Ooo, tricky!
console.log(window.special);
}
keepLooking();
}
lookingFor(112358132134);
// 3.141592
// 112358132134
// 42Copying Is Not Accessing
what if I'd used objects or arrays as the values instead of the numbers (112358132134, etc.)? - still can't reassign special parameter
Shadowing
function something() {
var special = "JavaScript";
{
let special = 42; // totally fine shadowing
// ..
}
}
Illegal Shadowing
Shadowing
function another() {
// ..
{
let special = "JavaScript";
{
var special = "JavaScript";
// ^^^ Syntax Error
// ..
}
}
}Illegal Shadowing
let prohibits var to cross the boundaries (or hop over)
Shadowing
function another() {
// ..
{
let special = "JavaScript";
ajax("https://some.url",function callback(){
// totally fine shadowing
var special = "JavaScript";
// ..
});
}
}Illegal Shadowing
Boundary-crossing prohibition effectively stops at each function boundary
Shadowing
Illegal Shadowing
- let (in an inner scope) can always shadow an outer scope's var.
- var (in an inner scope) can only shadow an outer scope's let if there is a function boundary in between.
function something() {
var special = "JavaScript";
{
let special = 42; // totally fine shadowing
// ..
}
}
function another() {
// ..
{
let special = "JavaScript";
ajax("https://some.url",function callback(){
// totally fine shadowing
var special = "JavaScript";
// ..
});
}
}Function Name Scope
function askQuestion() {
// ..
}Function Declaration
Function Expression
var askQuestion = function(){
// ..
};What happens to the name identifier of the function?
var askQuestion = function ofTheTeacher(){
// ..
};Function Name Scope
What happens to the name identifier of the function?
var askQuestion = function ofTheTeacher() {
console.log(ofTheTeacher);
};
askQuestion();
// function ofTheTeacher()...
console.log(ofTheTeacher);
// ReferenceError: ofTheTeacher is not definedFunction Name Scope
What happens to the name identifier of the function?
var askQuestion = function ofTheTeacher() {
console.log(ofTheTeacher);
};
askQuestion();
// function ofTheTeacher()...
console.log(ofTheTeacher);
// ReferenceError: ofTheTeacher is not defined- ofTheTeacher is declared as an identifier inside the function itself
- ofTheTeacher is not exactly in the scope of the function - Implied Scope
Function Name Scope
It's also read-only
var askQuestion = function ofTheTeacher() {
"use strict";
ofTheTeacher = 42; // TypeError
//..
};
askQuestion();
// TypeError- strict-mode, the assignment failure is reported as a TypeError;
- in non-strict-mode, such an assignment fails silently with no exception.
Function Name Scope
Function expression with no name identifier?
var askQuestion = function(){
// ..
};Named function expression
Without name - anonymous function expression.
Arrow Functions
Shorter way to write functions
var askQuestion = () => {
// ..
};- Lexically anonymous
var askQuestion = () => {
// ..
};
askQuestion.name; // askQuestion- Inferred name - but still anonymous
Arrow Functions
Syntactic brevity
() => 42;
id => id.toUpperCase();
(id,name) => ({ id, name });
(...args) => {
return args[args.length - 1];
};Arrow Functions
Claim: Arrow functions somehow behave differently with respect to lexical scope from standard function functions.
Incorrect!
Arrow Functions
Claim: Arrow functions somehow behave differently with respect to lexical scope from standard function functions.
Incorrect!
- Other than being anonymous (and having no declarative form), => arrow functions have the same lexical scope rules as function functions do.
- An arrow function, still creates a separate, inner nested bucket of scope. Variable declarations inside this nested scope bucket behave the same as in a function scope.