再戰 React Concurrent Mode
Concurrent Mode 的第一站:Fiber
在 Fiber 出現之前:
-
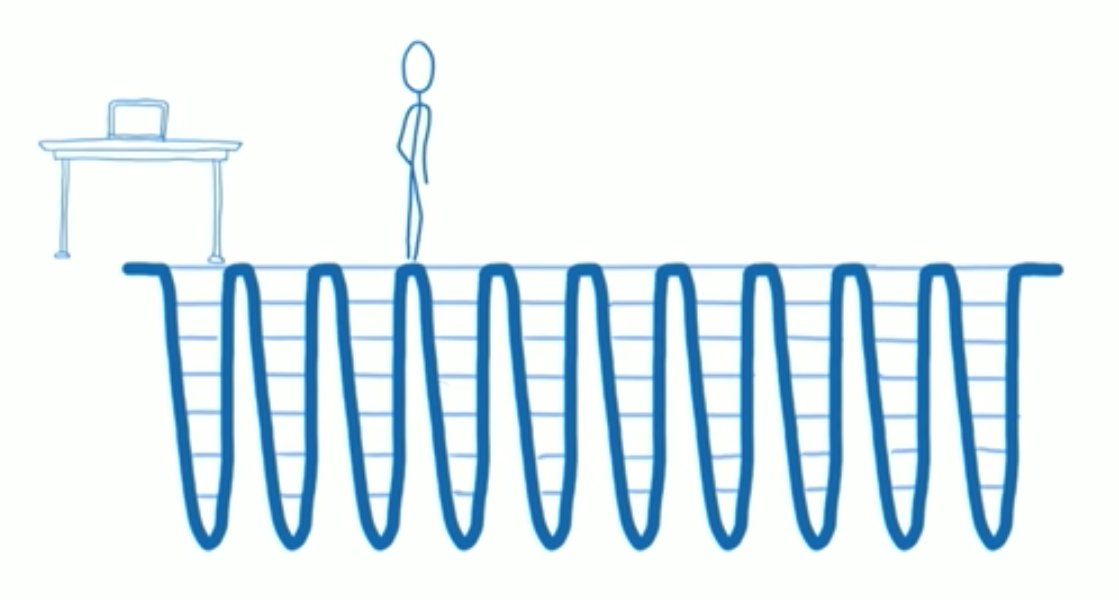
瀏覽器是單線程操作
- 一次性大量更新時
main thread 就會卡住。
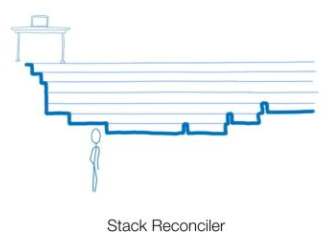
Fiber:
-
把一次性更新拆分成 一個個小更新
- 每次更新之間的空檔去處理別的事情
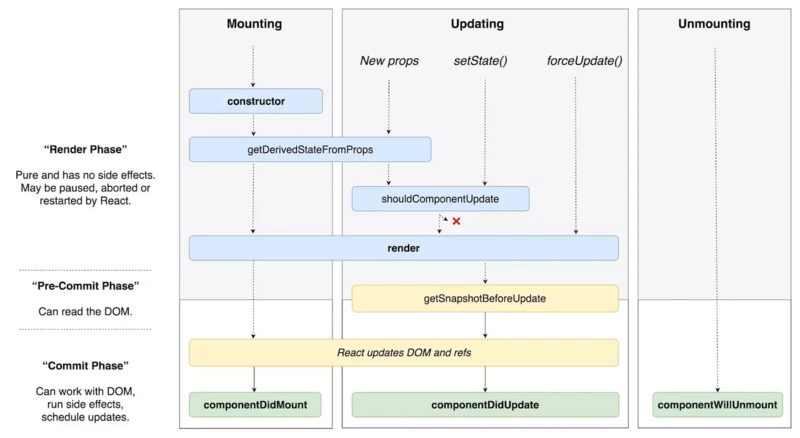
偵錯:componentDidCatch 和 getDerivedStateFromError
getDerivedStateFromError
componentDidCatch
更進一步 的 Concurrent Mode
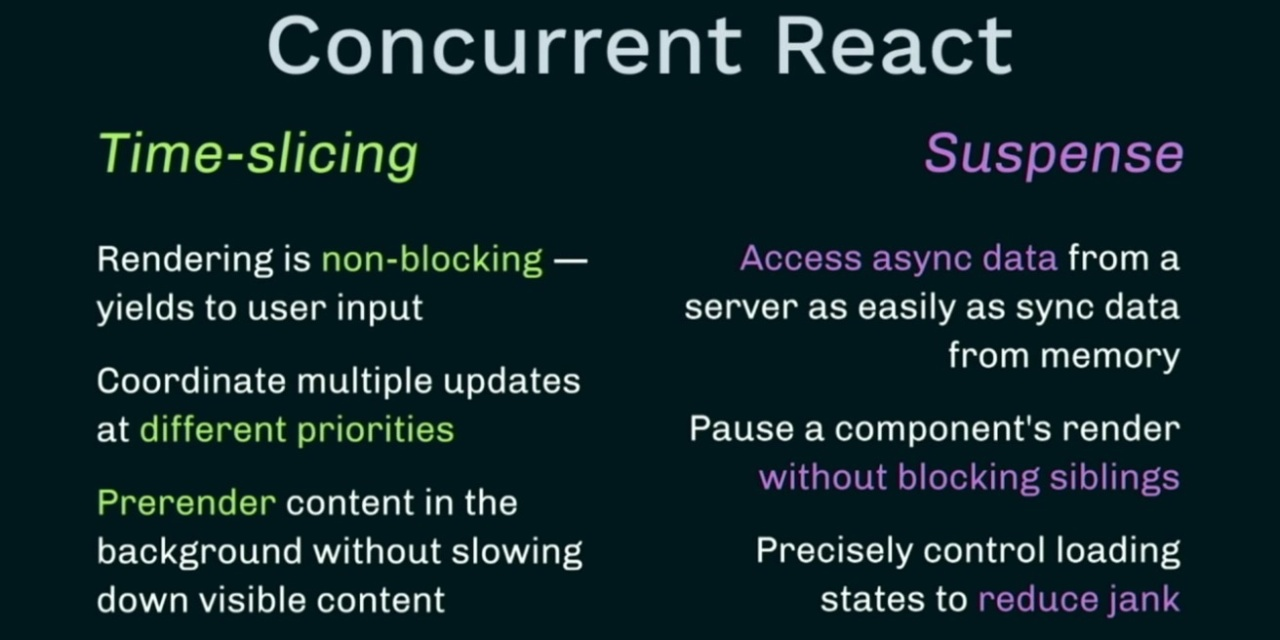

不同裝置的體驗
不同網速的體驗
useTransition
Suspense
Suspense for Data fetching
💡「延遲」 非同步操作,等非同步操作同步後,才開始 Render。
import {unstable_createResource as createResource} from 'react-cache';
const resource = createResource(fetchDataApi);
const Foo = () => {
const result = resource.read();
return (
<div>{result}</div>
);
// ...
<Suspense>
<Foo />
</Suspense>};實作原理
const wrapPromise = promise => {
let status = "pending";
let result = "";
let suspender = promise.then(
r => {
status = "success";
result = r;
},
e => {
status = "error";
result = e;
}
);
return {
read() {
if (status === "pending") {
throw suspender;
} else if (status === "error") {
throw result;
}
return result;
}
};
};
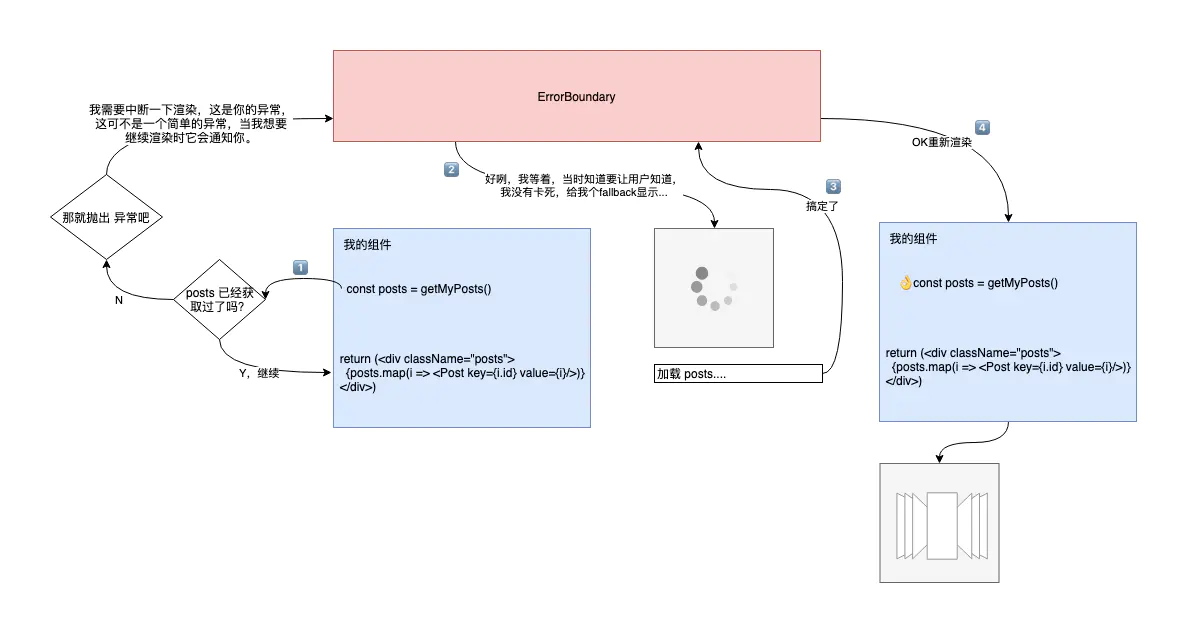
Suspense
ErrorBoundary
- 捕捉 Promise 回傳的 Error
- 包在 Suspense 外層,Literally 像個邊界
- 以 Class Component 的方式實現
import React from "react";
export class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
state = { hasError: false, error: null };
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true, error };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
console.log(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return (
<div>
Something went wrong: {this.state.error.message}
</div>
);
}
return this.props.children;
}
}<ErrorBoundary>
<Suspense fallback={null}>
<ComponentThatThrowError />
</Suspense>
</ErrorBoundary>SuspenseList
<SuspenseList tails="collapsed" revealOrder="together">
<Suspense fallback={<h1>loading num...</h1>}>
<ComponentOne />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<h1>loading person...</h1>}>
<ComponentTwo />
</Suspense>
</SuspenseList>- revealOrder 實現 載入順序
- 如:forwards、backwards、together
- tail 管理 fallback 狀態
- 強制關閉其下的 fallback ( loading state )
- 壓縮他們。
Normal
forwards
together
tail: collapsed
why useTransition?
Default : Receded → Skeleton → Complete
useTransition : Pending → Skeleton → Complete
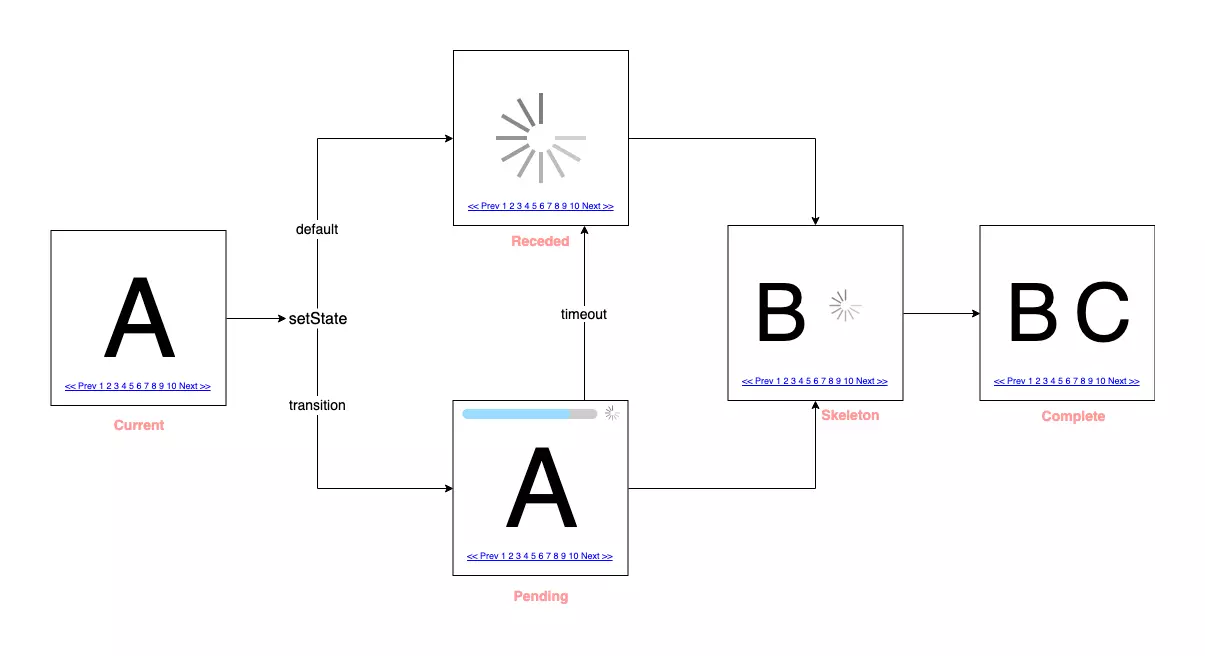
Default
useTransition
再進一步延遲 : useTransition
集中 管理 和 延遲 頁面 更新
(其實在後台繼續 render 但延遲 commit 到真正畫面上的時間)
function ProfilePage() {
const [
startTransition,
isPending
] = useTransition({
// Wait 10 seconds before fallback
timeoutMs: 10000
});
const [resource, setResource] = useState(
initialResource
);
function handleRefreshClick() {
startTransition(() => {
setResource(fetchProfileData());
});
}
return (
<Suspense
fallback={<h1>Loading profile...</h1>}
>
<ProfileDetails resource={resource} />
<button
onClick={handleRefreshClick}
disabled={isPending}
>
{isPending ? "Refreshing..." : "Refresh"}
</button>
<Suspense
fallback={<h1>Loading posts...</h1>}
>
<ProfileTimeline resource={resource} />
</Suspense>
</Suspense>
);
}流程:
1. 將 Suspense 變更為 Pending 狀態
2. 為 Pending 狀態的更新都會被延遲
(此時都還在上一個畫面)
3. 拉完資料 or 超時( 進入 fallback )
4. Render 新畫面
實作原理
function updateTransition(
config: SuspenseConfig | void | null,
): [(() => void) => void, boolean] {
const [isPending, setPending] = updateState(false); // = useState
const startTransition = updateCallback( // = useCallback
callback => {
setPending(true); // pending: true
// 調降執行的優先級
Scheduler.unstable_next(() => {
// 設定 suspenseConfig
const previousConfig = ReactCurrentBatchConfig.suspense;
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.suspense = config === undefined ? null : config;
try {
// 還原 pending: false
setPending(false);
// 執行 fetch OR sth else...
callback();
} finally {
// 還原 suspenseConfig
ReactCurrentBatchConfig.suspense = previousConfig;
}
});
},
[config, isPending],
);
return [startTransition, isPending];
}- unstable_next : 調降更新的優先次序
- suspenseConfig : 計算自己的優先次序
- scheduler : React 內部的更新順序
useDeferredValue
相較於 useTransition 是延遲更新
useDeferredValue 則是取上一個值
function ProfilePage({ resource }) {
const deferredResource = useDeferredValue(
resource,
{
timeoutMs: 1000
}
);
return (
<Suspense
fallback={<h1>Loading profile...</h1>}
>
<ProfileDetails resource={resource} />
<Suspense
fallback={<h1>Loading posts...</h1>}
>
<ProfileTimeline
resource={deferredResource}
isStale={deferredResource !== resource}
/>
</Suspense>
</Suspense>
);
}實作原理
function useDeferredValue<T>(
value: T,
config: TimeoutConfig | void | null,
): T {
const [prevValue, setValue] = useState(value);
const [startTransition] = useTransition(config)
useEffect(
() => {
startTransition(() => {
setValue(value);
})
},
[value, config],
);
return prevValue;
}
1.用 useEffect 監聽 value 的變化
2. 在 startTransition 中更新 value
小結
- 讓非同步操作看起來像同步
- 依此大幅減少 Loading (等資料) 的“感覺”
- 可以安排頁面載入順序,讓UI更好維護
謝謝大家!
參考資料
- https://www.lizenghai.com/archives/47192.html#SuspenseListuseDeferredValue
- https://medium.com/@chentsulin/%E7%90%86%E8%A7%A3-react-%E7%9A%84%E4%B8%8B%E4%B8%80%E6%AD%A5-concurrent-mode-%E8%88%87-suspense-327b8a3df0fe
- https://juejin.im/post/5c7f6106e51d45055e26df9a
- https://juejin.im/post/5db65d87518825648f2ef899
- https://zh-hant.reactjs.org/docs/error-boundaries.html
- https://juejin.im/post/5dbee8e7e51d4558040f0830
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/268028123/answer/332182059
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34210780
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fTFoBr5LJGE&list=PLN3n1USn4xln7sHUudKJEmMe7gFKtuNww