Importance Sampling
with Path Guiding:
A Project Proposal
Phillip Thomas
Motivation
The variance of this estimator is \(\mathcal{O}(\frac{1}{N})\). We want to reduce the variance of a Monte Carlo estimator, i.e., image noise when we only have a finite number of samples.
Using a probability distribution for random samples \(\omega_i \) (also the distribution denoted by \(p\)) that is shaped like the integrand, we can reduce the variance of the estimator. This is importance sampling.
Basic idea
Approximating the incoming radiance term by using information collected from past samples is called path guiding.
If we can create a probability distribution \(p\) that has a shape similar to even one term in the numerator, we are eliminating some variance in the estimator.
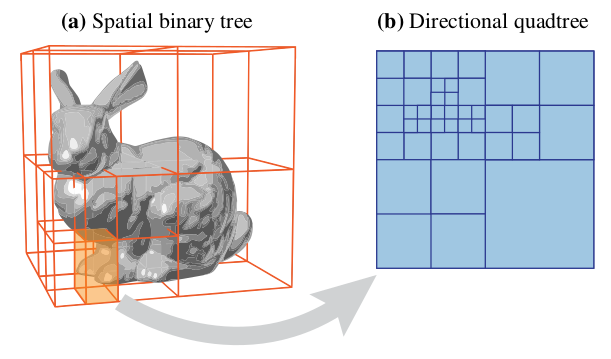
Motivation
Reduce variance of MC estimator.
Basic idea
Learn an approximation of the incoming radiance terms.
My project
Implement this idea (and the details described in the paper) in C++ code.
Reproduce their rendered results.

Two time permitting extensions
- Implement another paper that learns direct illumination separately.
where \(P ( \overline{p}_i)\) gives the amount of radiance scattered over a path \(\overline{p}_i\) with \(i+1\) vertices.
2. Extend the SD-trees to be useful in animated sequences.