Introduction to Python Programming
Program
A computer program is a set of instructions that causes a computer to perform some kind of action. It isn't the physical parts of the computer-like the wires,microchips,cards, hard drive and such- but the hidden stuff running that hardware.
A computer program, which I'll usually refer to as program, is the set of commands that tell that dumb hardware what to do.
Installation
A python interpreter , version 2.7.
For People with a mac, Python comes inbuilt.
For People with a mac, Python comes inbuilt.
"Hello World!"
Well ! Let's try our first code!
print ("Hello World")!
Hello World!
Operators in Python
python has the following set of basic operators.
Addition :+
Subtraction: -
Multiplication : *
Division : /
A New concept - Modulus!
In Programming, Modulo is defined as the remainder of division of one number by another In Python, the statement is written as a%n
where a and n positive numbers!
Let's try them !
a = 21 b = 10 c = 0 c = a + b print "Line 1 - Value of c is ", c c = a - b print "Line 2 - Value of c is ", c c = a * b print "Line 3 - Value of c is ", c c = a / b print "Line 4 - Value of c is ", c
Data types in Python :
Numerical Data types supported:
- Integers
- Long
- Float
- Complex
Let's see how we can declare variables!
Go back to the program where we implemented various operators!
At the start of the program we declared a = 10, b= 2
This is called variable declaration.
Lets add a modulus to it now!
Comparison operators
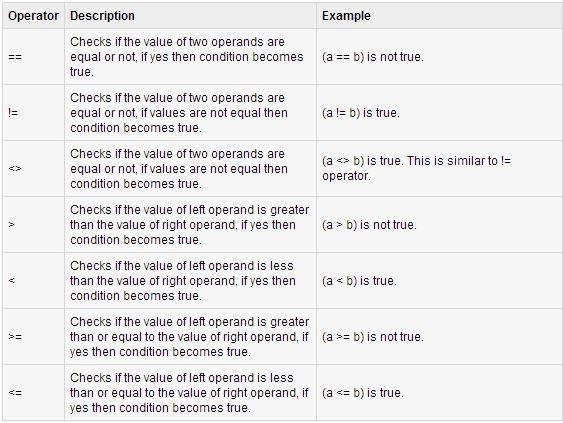
Let's try them out!
Task - 1
Compare two numbers!
We used some thing called If- condition.
Let's see what that is!
Decision Making
If-else condition
"If you have a tail
then you are a Lion!"
Decision Making Continuation :
Nested IF- Else.
Syntax :

Let's do an example!
Loops :D
1) While Loop
2) For loop
3) Nested Loops
While Loop
Syntax :
While expression :
statement(s).
Let's Implement an example.
For loop
for i in range(10): print('Hello')
Nested Loops!
Now try putting while inside a while!
And a for inside a while!
Functions in Python.
A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action. Functions provide better modularity for your application and a high degree of code reusing.
As you already know, Python gives you many built-in functions like print(), etc. but you can also create your own functions. These functions are called user-defined functions.
Consider this!
What are the properties you look for, when you go to buy a car?
Defining a Function
You can define functions to provide the required functionality. Here are simple rules to define a function in Python.
Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the function name and parentheses ( ( ) ).
Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these parentheses. You can also define parameters inside these parentheses.
The first statement of a function can be an optional statement - the documentation string of the function or docstring.
The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is indented.
The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing back an expression to the caller. A return statement with no arguments is the same as return None.
Calling a Function
Defining a function only gives it a name, specifies the parameters that are to be included in the function and structures the blocks of code.
Once the basic structure of a function is finalized, you can execute it by calling it from another function or directly from the Python prompt. Following is the example to call printme() function:
Syntax for methods.

Let's see an example.
Lists
The most basic data structure in Python is the sequence. Each element of a sequence is assigned a number - its position or index. The first index is zero, the second index is one, and so forth.
Python has six built-in types of sequences, but the most common ones are lists and tuples, which we would now.
There are certain things you can do with all sequence types. These operations include indexing, slicing, adding, multiplying, and checking for membership. In addition, Python has built-in functions for finding the length of a sequence and for finding its largest and smallest elements.
Dictionary
A dictionary is mutable and is another container type that can store any number of Python objects, including other container types. Dictionaries consist of pairs (called items) of keys and their corresponding values.
Imports !
A module allows you to logically organize your Python code. Grouping related code into a module makes the code easier to understand and use. A module is a Python object with arbitrarily named attributes that you can bind and reference.
Simply, a module is a file consisting of Python code. A module can define functions, classes and variables. A module can also include runnable code.
File I/O
Readig input from the user.
Raw_input.
Input
Before you can read or write a file, you have to open it using Python's built-in open()function. This function creates a file object, which would be utilized to call other support methods associated with it.
SYNTAX:
file object = open(file_name [, access_mode][, buffering])
file_name: The file_name argument is a string value that contains the name of the file that you want to access.
access_mode: The access_mode determines the mode in which the file has to be opened, i.e., read, write, append, etc. A complete list of possible values is given below in the table. This is optional parameter and the default file access mode is read (r).
buffering: If the buffering value is set to 0, no buffering will take place. If the buffering value is 1, line buffering will be performed while accessing a file. If you specify the buffering value as an integer greater than 1, then buffering action will be performed with the indicated buffer size. If negative, the buffer size is the system default(default behavior).
file operations:
| file.closed | Returns true if file is closed, false otherwise. |
| file.mode | Returns access mode with which file was opened. |
| file.name | Returns name of the file. |
| file.softspace | Returns false if space explicitly required with print, true otherwise. |
Modes of opening a file.
