Introduction
to Programming
in Python
Philo van Kemenade - @phivk
General Assembly London
Hi!
I use Python
& natural language processing
This Workshop
Programming
Python
Syntax
Words
Sentences
Stories
These Slides
Coding
Hammurabi Code Photo
by Gabriele B
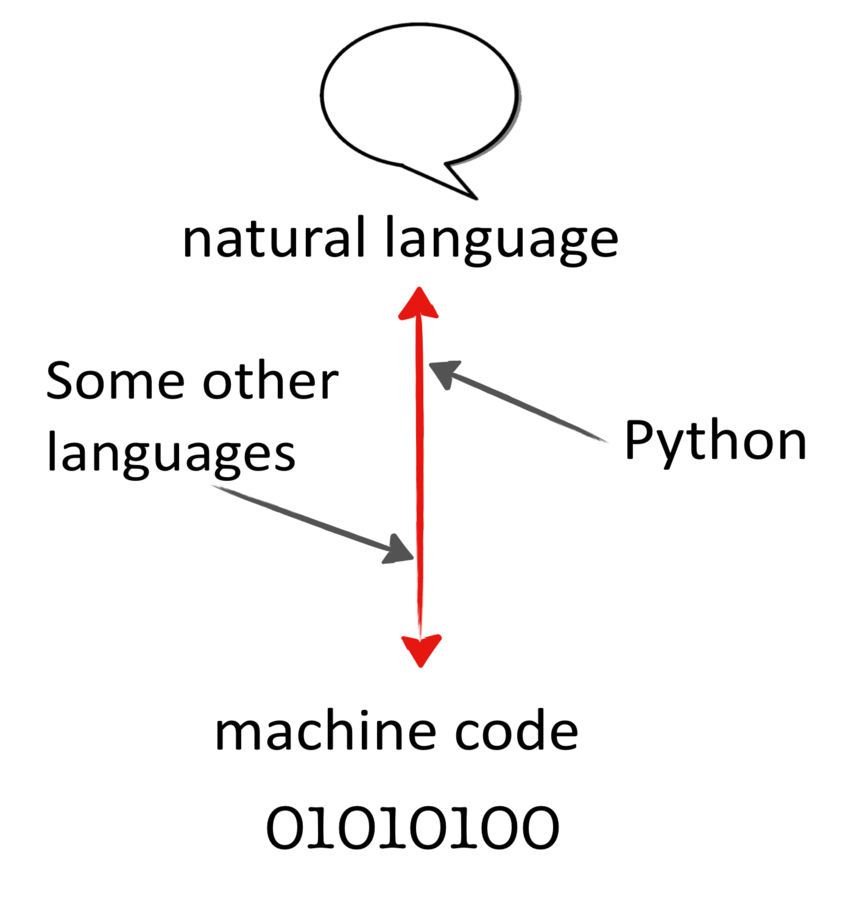
Representation
&
reality
between
Interface
Python
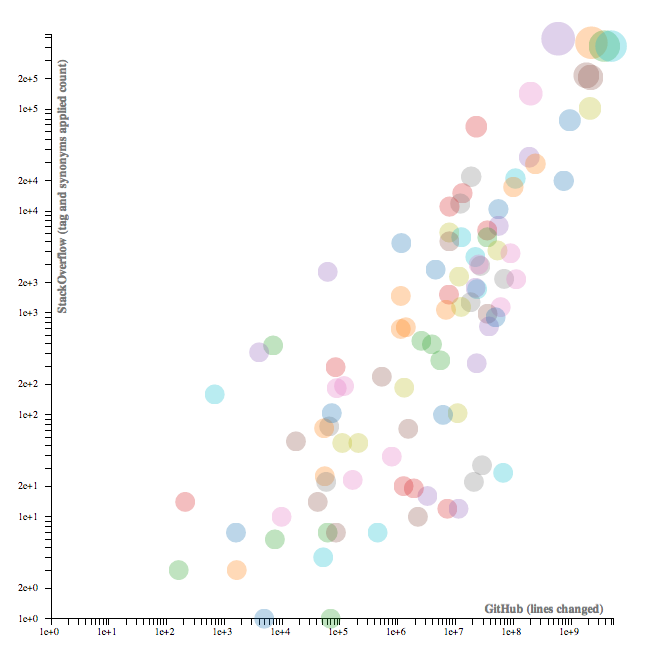
Popularity
Powered by python


Talking Python
Two Modes of Operation
Scripting Mode
- Code in file
- Save & load programs
- More control
Interactive Mode (REPL)
- Terminal-based
- Direct feedback
- Try out code

REPL
Read
Evaluate
Loop
REPL
Read
Evaluate
Print
Loop
Setting Up
Download python 3 from http://python.org/download/
Install Python
Open terminal / cmd window
Type “python3” to start Python in interactive mode

Getting help
>>> help()Syntax
Train Parts Photo by Môsieur J. [version 8.0]

syntax You allready know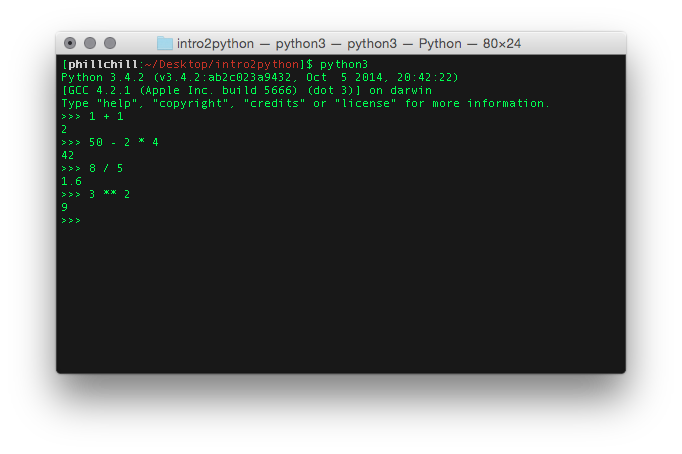
Python as a calculator
LEVELS OF MEANING
Stories
Sentences
WORDS
Words
Earthshaker Pinball Photo
by Chase N.

VARIABLES
variables

assigning Variables in python
name = "Philo"
gender = "male"
height = 1.91 types of Variables
Variables can store values of different types:
string - a sequence of characters, comprising text
”a”, "London", 'X', 'General Assembly'int - an integer, or whole number
1, 5 ,9999, -7 float - a floating point number (using a decimal point)
3.14, 1.68, 1.0bool - boolean; binary true or false values
True, False Changing types
'Casting' a variable to another type
int("42")
float("1.69")
str(1.5) Exercise
(String, Integer, Float, Boolean)
Strings
Integers
Floats
Booleans
Operators
You can process the values in your variables by operators :
| = | assignment: assign a value to a variable |
| == | comparison: are two variables equal? |
| != | comparison: are two variables unequal? |
|
<, >, <=, >= |
less-than, greater-than, less or equal, greater or equal |
| +, -, *, / | mathematical operators |
| and, or | logical operators |
behaviour depends on data type
>>> start = "Lon"
>>> start
'Lon'
>>> end = "don"
>>> start + end
'London'
>>> start + start + end
'LonLondon'
>>> town = 3 * start + end
>>> town
'LonLonLondon'Strings
Integers
>>> 1 + 1
2
>>> cats = 2
>>> cats
2
>>> dogs = 3
>>> cats == dogs
False
>>> cats < dogs
True
>>> dogs + 1
4
>>> dogs
3>>> dogs = dogs + 1
>>> dogs
4>>> pets = cats + dogs
>>> pets
6Questions?
Exercise
Create two string variables:
first for your first name and last for your last name.
Can you make your full name by combining first and last?
Bonus:
What happens if we compare first and last with the ‘<‘ and ‘>’ operators?
Why?
(Cheating encouraged)
Collections
Collections of Values
Lists
Lists
Lists
Lists
We can store multiple values in a list:
>>> l = [1,3,9,4,884328881]
>>> n = ['sex', 'drugs', 'rock', 'roll']
>>> m = l + n
>>> m
[1, 3, 9, 4, 884328881, 'sex', 'drugs', 'rock', 'roll']A list is a ordered sequence of items (between [...]) each with their own index:
>>> m[0]
1
>>> m[8]
'roll' Indices
cool things you can do with lists
>>> l = list(range(10))
>>> l
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> l[1:5]
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> l[:5]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> del l[5:]
>>> l
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4] >>> l.append(5)
>>> l
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> l.reverse()
>>> l
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
>>> 5 in l
True
Bonus
Lists are sequences, and so are Strings
>>> s = "General Assembly"
>>> s[0]
'G'
>>> s[:7]
'General'
Dictionaries
Dictionaries
Dictionaries
Animal Sign Photo by cortneymartin82
Dictionaries
Dictionaries store key:value pairs associatively.
personX = {
'first':'Philo',
'last':'van Kemenade',
'twitter':'@phivk'
}
>>> personX = {'first':'Philo', 'last':'van Kemenade', 'twitter':'@phivk'}
>>> personX['first']
'Philo'
>>> personX['age'] = 30
>>> personX
{'twitter': '@phivk', 'last': 'van Kemenade', 'age': 30, 'first': 'Philo'}some things you can do with Dictionaries
python 3>>> list(personX.keys())
['twitter', 'last', 'first']
>>> list( personX.values())
['@phivk', 'van Kemenade', 'Philo']
python 2
>>> personX.keys()
['twitter', 'last', 'first']
>>> personX.values()
['@phivk', 'van Kemenade', 'Philo']Questions?
Exercise
Form pairs
Create a
dictionary
to represent your neighbour in some attributes
(for example home town, hair colour, favourite film).
Bonus:
Add a list of interests to the dictionary . What do you use as key , what do you use as value ?
(Cheating encouraged)
Sentences
Pinball Photo by Chase N.
Loops
Train Loop Photo by Minnesota Historical Society
For Loops
You use loops to repeat a statement.
A for-loop is useful when you know how many times you want to repeat an action (e.g. for every item in a list)
for item in sequence:
do someting with item
Mind the Indentation
For Loops

For Loops
for example
>>> ages = [18, 21, 16, 12]
>>> for age in ages:
... print(age)
...
18
21
16
12Visualise this code in action
While Loops
While loops

While Loops
for example
>>> gas = 42
>>> while gas > 0:
... print("Vroom!")
... gas = gas - 10
...
Vroom!
Vroom!
Vroom!
Vroom!
Vroom! Conditional Statements
Rail Split Photo by Leonid Mamchenkov
Conditional statements
Conditional statements enable you to deal with multiple options.
A part of your code is executed based on the truth value of a condition. You perform conditional checks with: if, (elif), (else)
if condition:
action
elif other condition: # optional
other action
else: # optional
final action>>> age = 17
>>> if age < 18:
... print("no drinks for you")
...
no drinks for you
conditional statements

Conditional statements
>>> ages = [18, 21, 16, 12]
>>> for age in ages:
... if age >= 18:
... print("come on in")
... elif age >= 16:
... print("not quite yet")
... else:
... print("get outta here")
...
come on in
come on in
not quite yet
get outta hereFunctions
Train Station Photo by luke.baldacchino
Functions
Functions perform a collections of tasks, bundled under a specific name
Take input argument(s), execute statement(s), return output
Input and output can be of all different types
>>> name = "Philo van Kemenade"
>>> length = len(name)
>>> print(length)
18
>>> type(length)
<type 'int'>Built in functions
docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html
Functions
You can define your own functions like this:
def function_name( argument(s) ):
action with argument(s)
>>> def multiply(a, b):
... return a * b
...
>>> multiply(3,4)
12
>>> def greet(name):
... print("hello "+ name)
...
>>> greet('Philo')
hello Philo
Questions?
Train Crash Photo by chrislstubbs
Exercise
Write a function with an appropriate name that:
- takes as input a person (represented as dictionary)
- prints out information about the person
Stories
Earthshaker Pinball Photo
by Chase N.
Modules
>>> import random
>>> random.randint(0,10)
0
>>> random.randint(0,10)
9
>>> random.randint(0,10)
3
Scripts
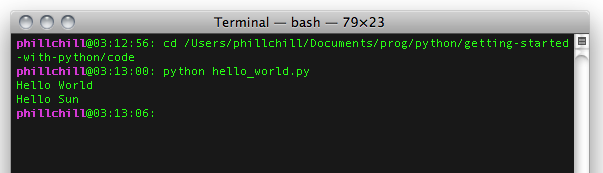
You can also write your code conveniently in a file using your favourite text editor
Such a file is a program or script and can look as simple as this:
print("Hello World") Save your script as “[a_descriptive_name].py”
Navigate in terminal to the location of your file
Run “python [a_descriptive_name].py”
scripts
Or this:
# this is a comment, use them!
'''
Comments can also
span multiple lines
'''
# print() is a very useful function
# mind the quotes
print("Hello World")
# don't forget to greet the Sun
print("Hello Sun")
Questions?
Exercise
Implement your function from the previous exercise in a script,
run it to let it print output
Home work
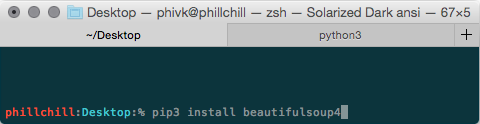
Install the Beautiful Soup module using PIP:
Run in terminal / cmd prompt
(NOT IN THE PYTHON INTERPRETER)
pip install beautifulsoup4or
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
on windows
If windows can't find the pip command, make sure your Python installation folder & Scripts folder are added to your 'PATH'
Follow these instructions:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6318156/adding-python-path-on-windows-7
https://youtu.be/9ocSXl5TL4U?t=2m54s
OR reinstall with this option checked (easy option™)
Next Session
Useful Resources
google; “python” + your problem / question
python.org/doc/; official python documentation, useful to find which functions are available
stackoverflow.com; huge gamified help forum with discussions on all sorts of programming questions, answers are ranked by community
codecademy.com/tracks/python; interactive exercises that teach you coding by doing
wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide/Programmers; tools, lessons and tutorials