CMS
Week 9
Views - Advanced
Advanced?
Last week
We learned about making simple views: simple lists, grids or tables.
These use either fields or content.
We learned how to create page views and block views, and how they are used.
Useful tidbits
Small things views can do for you.
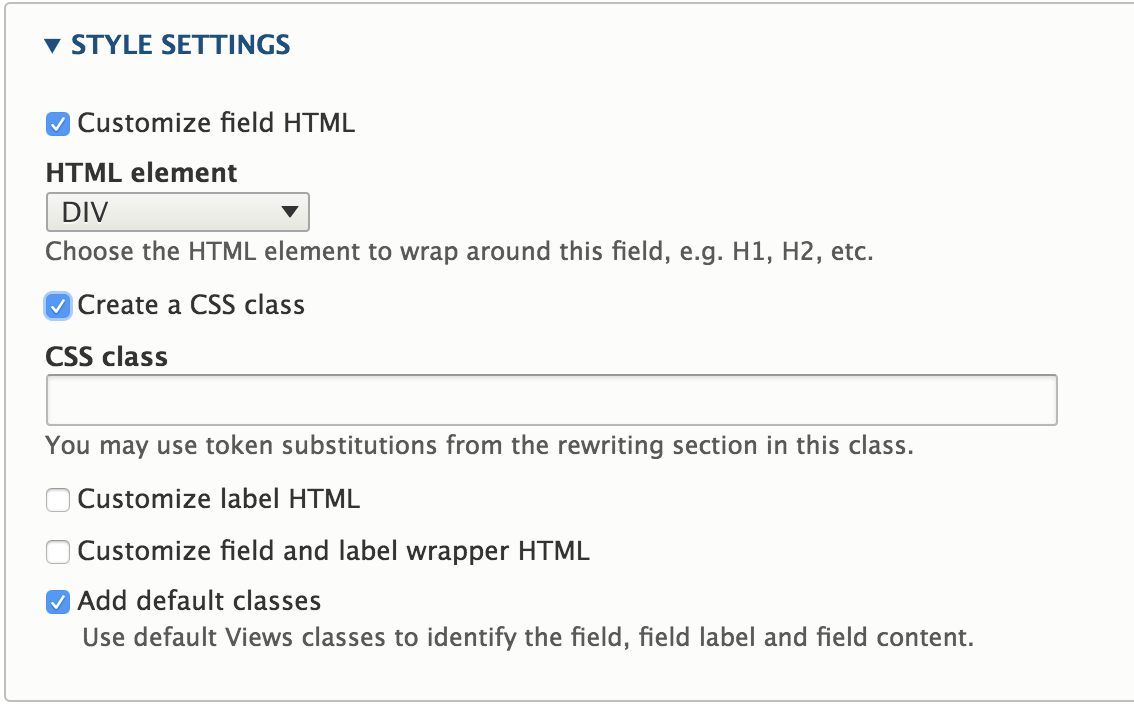
Style settings
Change the markup of your fields.
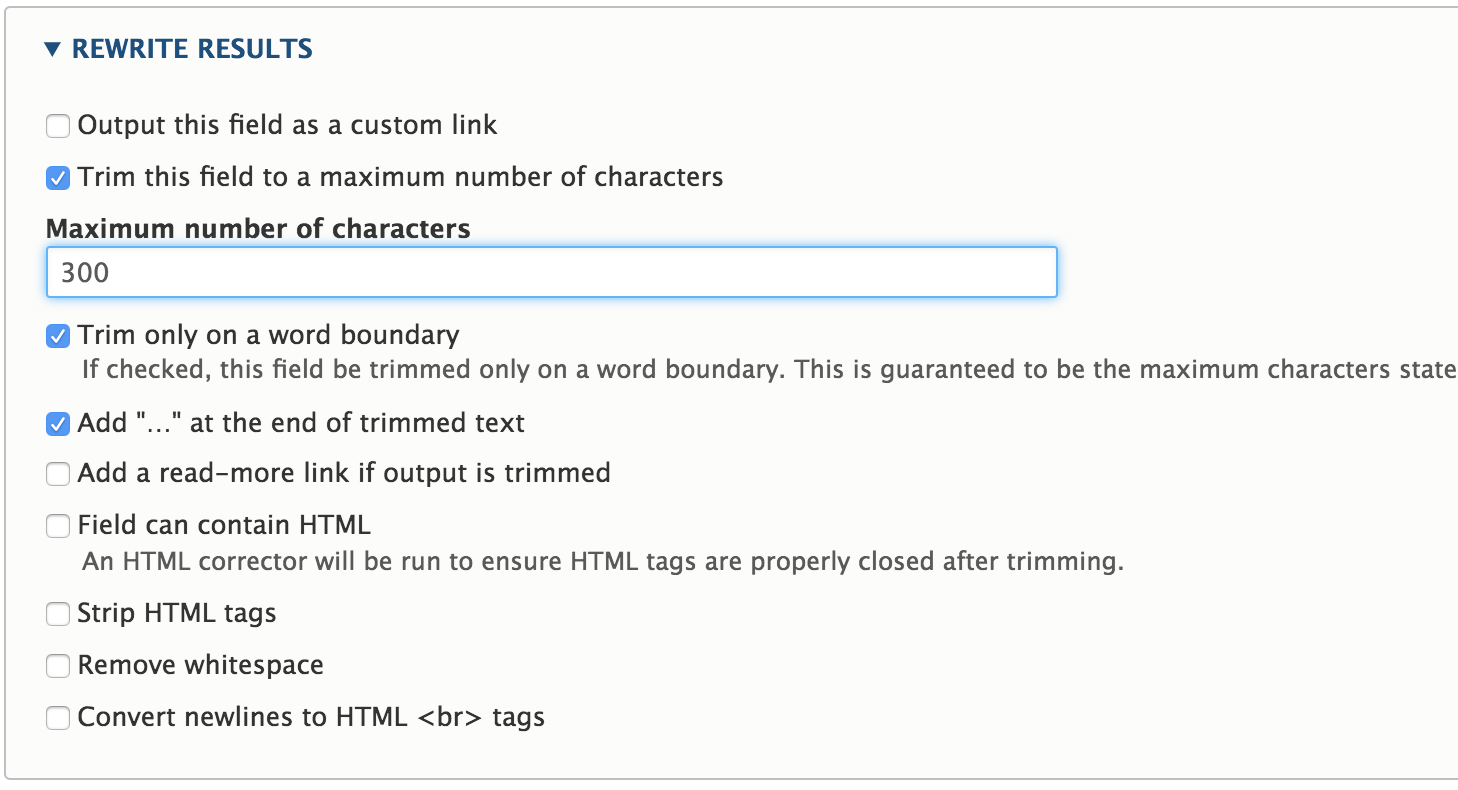
Rewrite results
You can manipulate the field results.
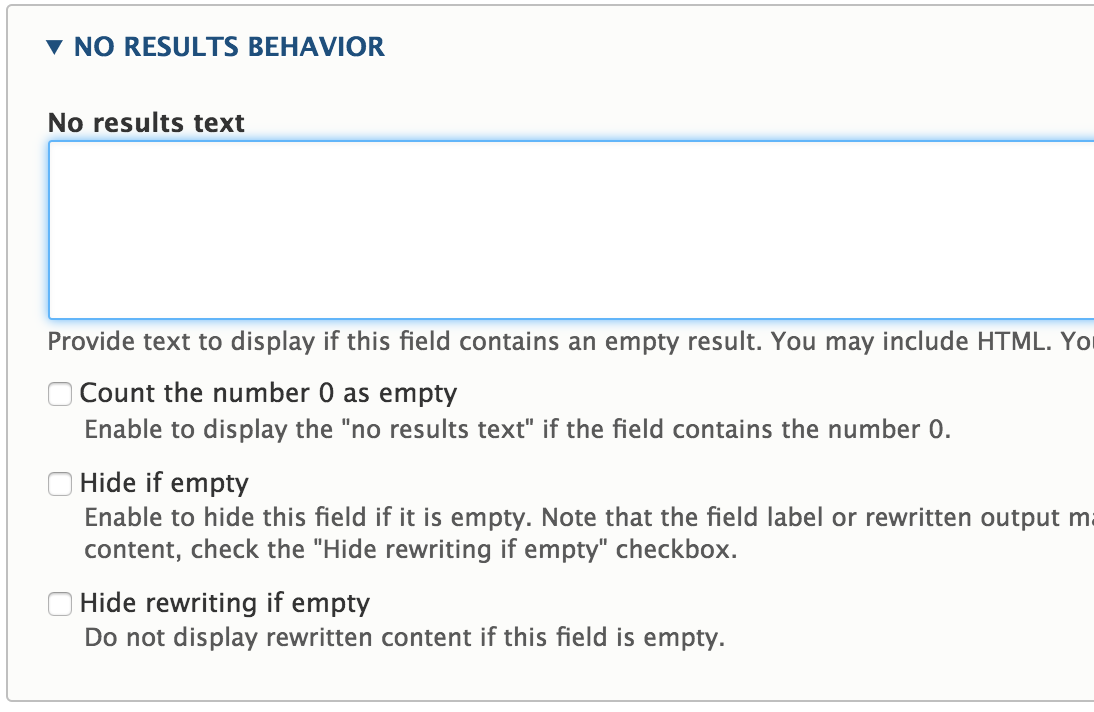
No results behavior
What should the field display if it has no value?
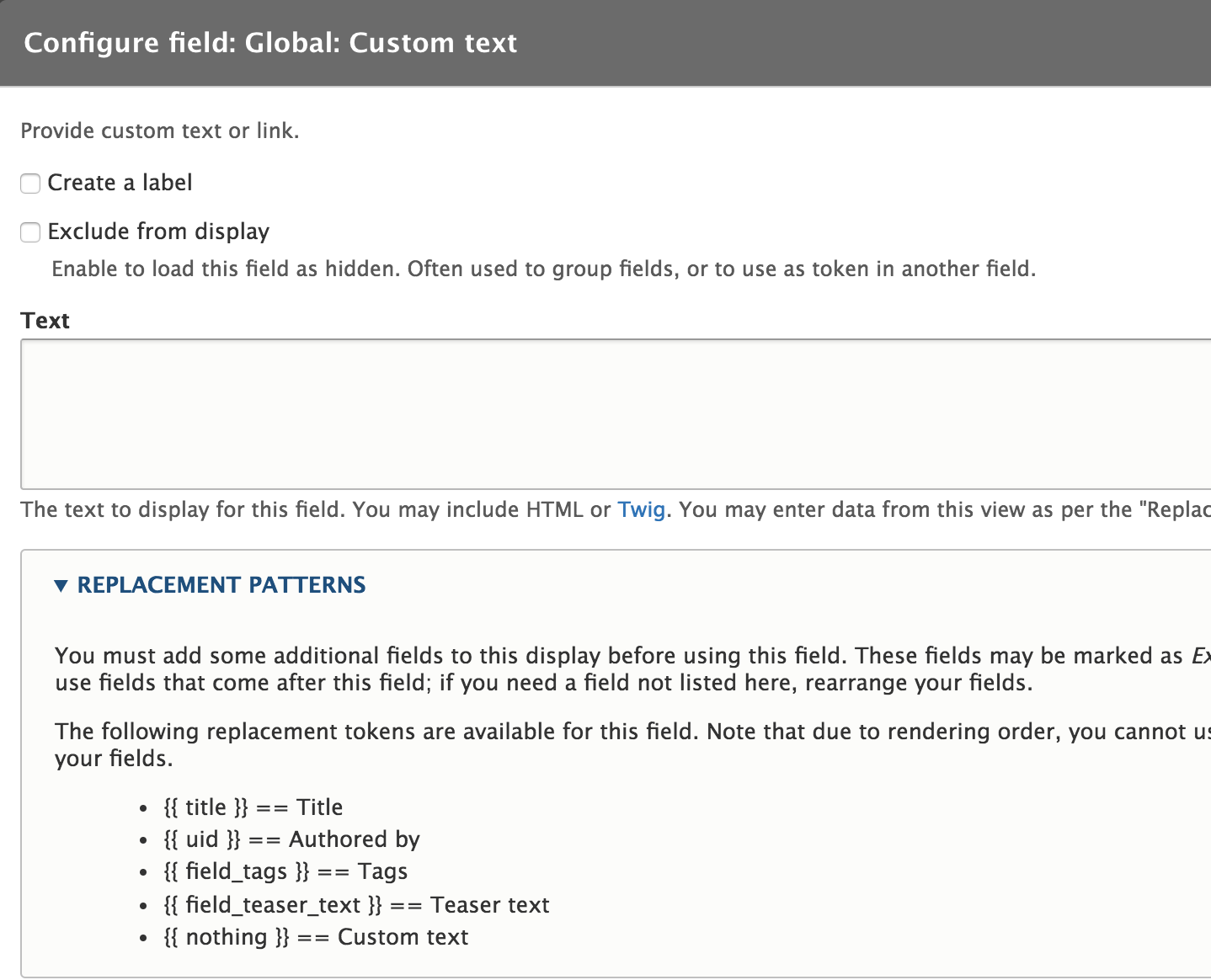
Custom text field
Add some custom html or text, or show fields through tokens.
Exposed filters
Add simple filters.
An example
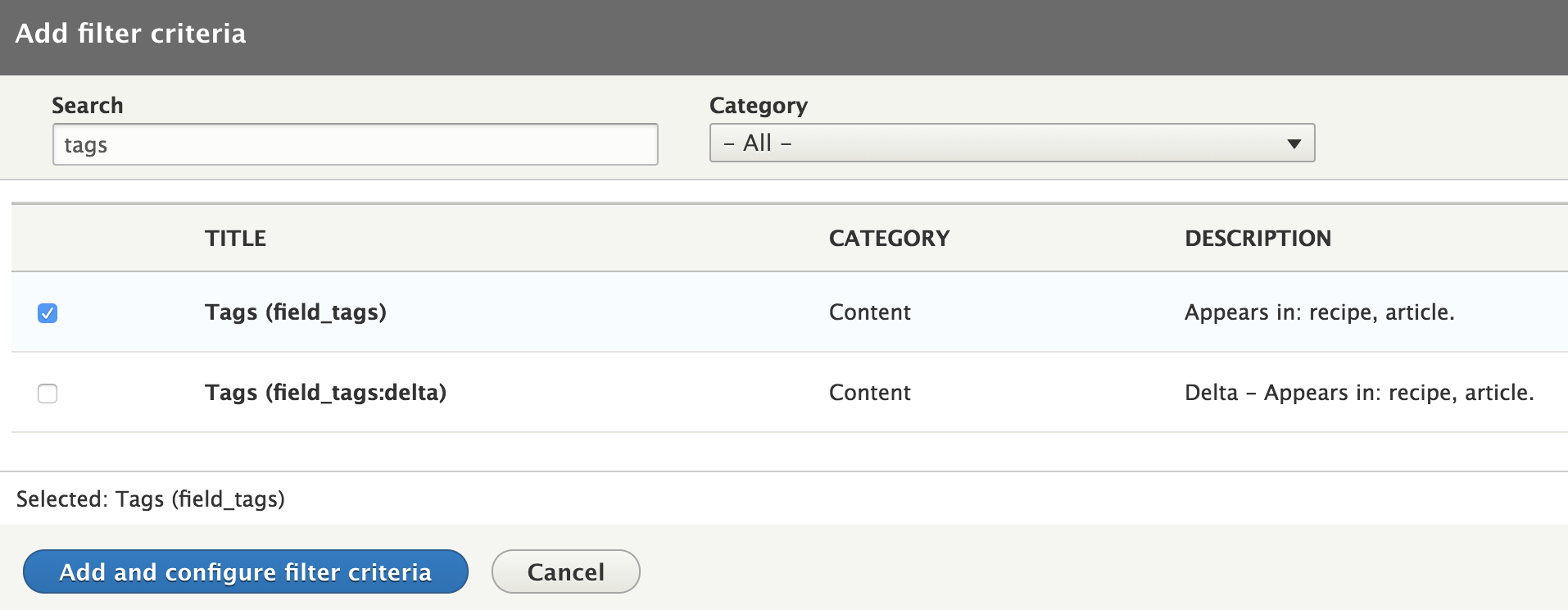
Add tags field
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars
Set filter options
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars
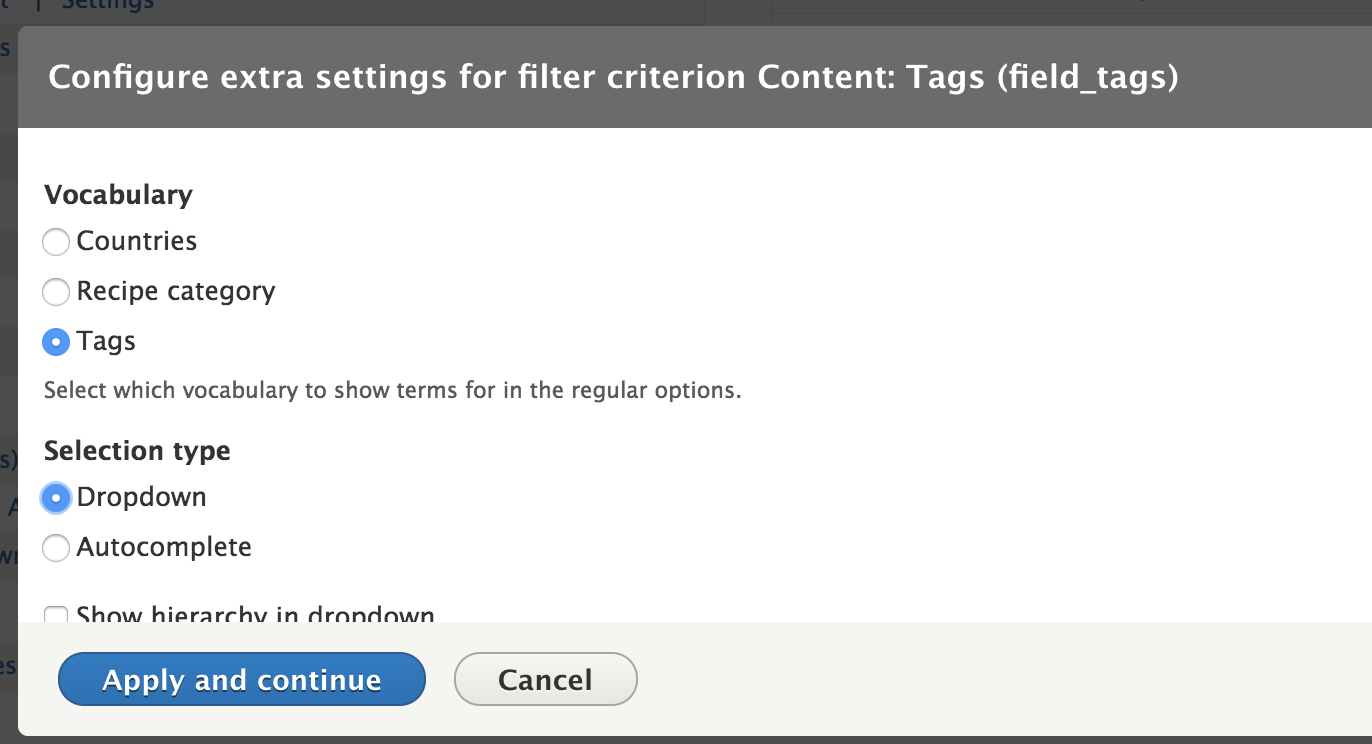
Expose the filter
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars
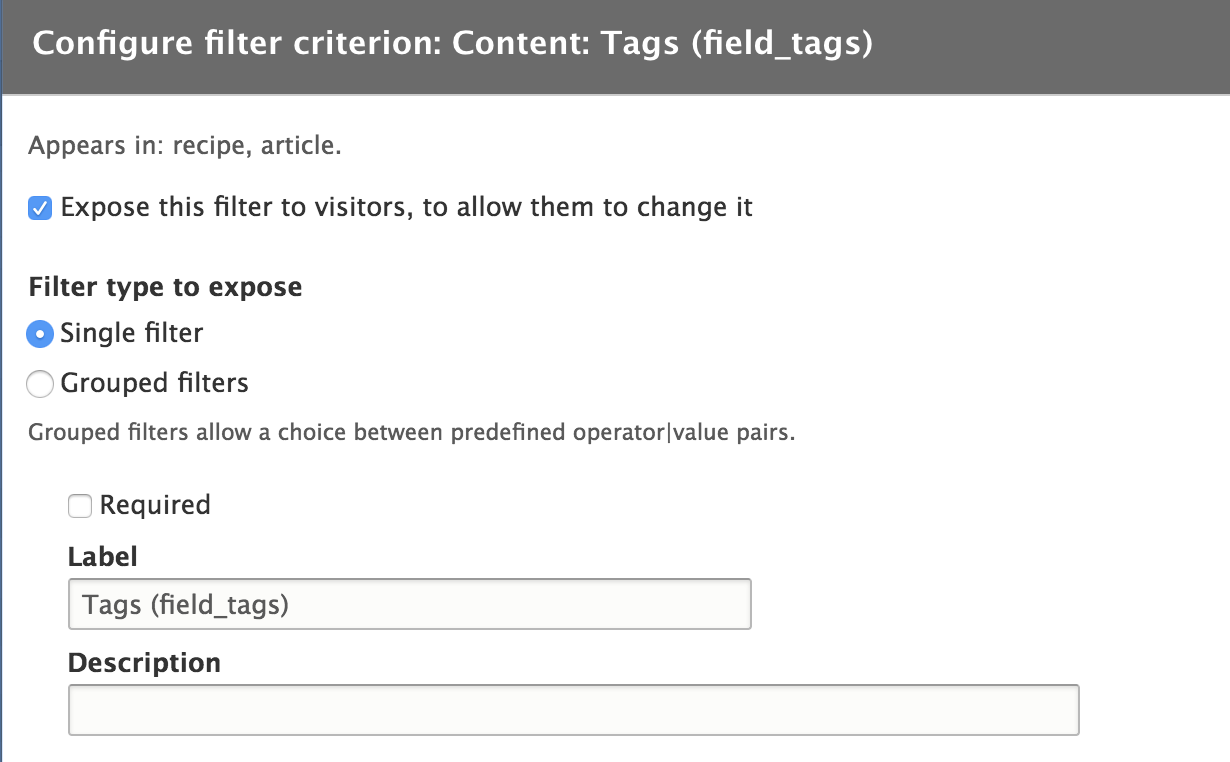
Hello operator
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars

How to
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars

Results
Let's create a new View to display all of our cars.
We will create a Page view to display all of our cars in Teaser form on the url /cars
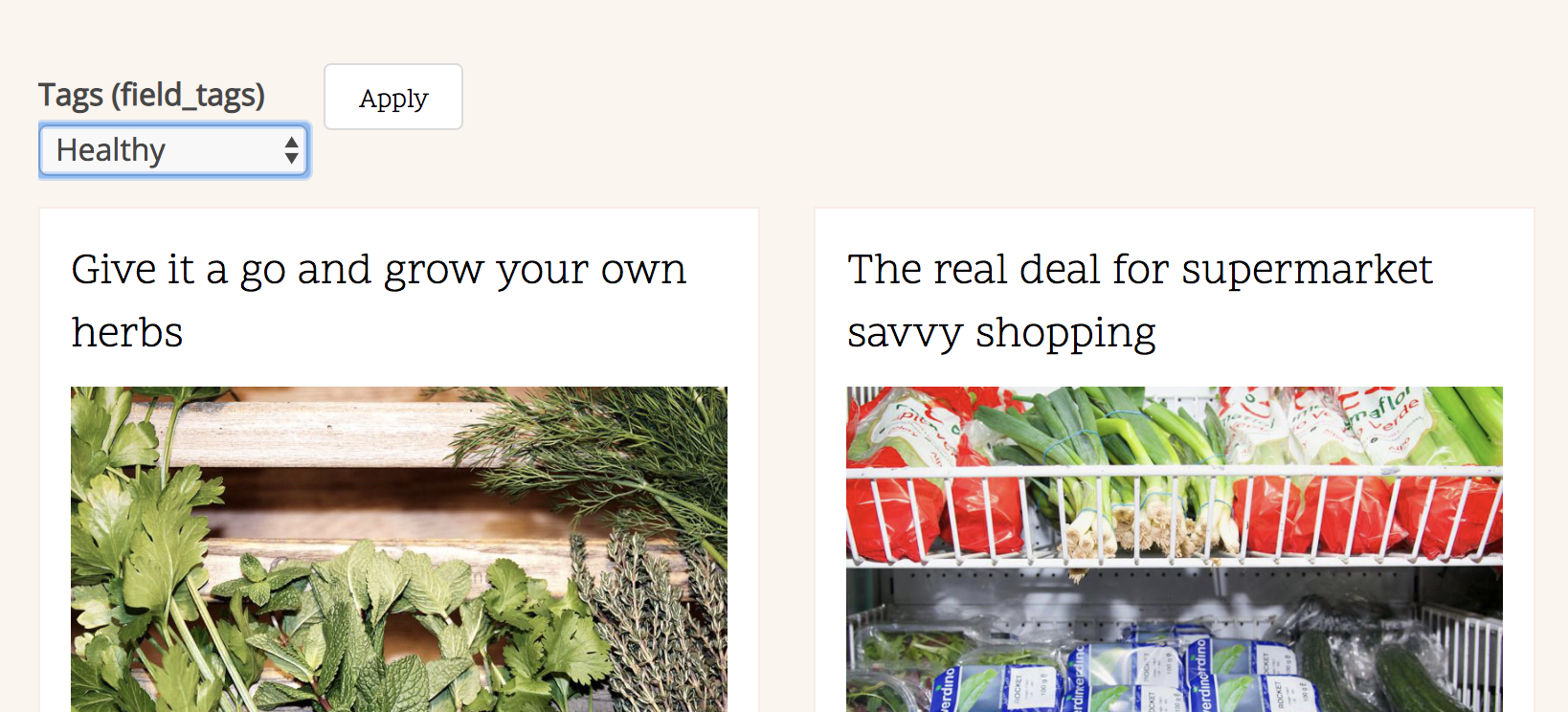
Exercise
Add some filters to the car view:
- Brand
- Fuel type
- Options
- etc
Contextual filters
Create views that show related content.
Contextual filters?
Filter criteria allow us to add filters that the user can manipulate, to narrow the view to only show a specific set of results.
Contextual filters are always applied. They are used to populate a view with content that is related.
Examples:
- Related articles (using same tags, author, ...)
- Related products
- etc.
How to
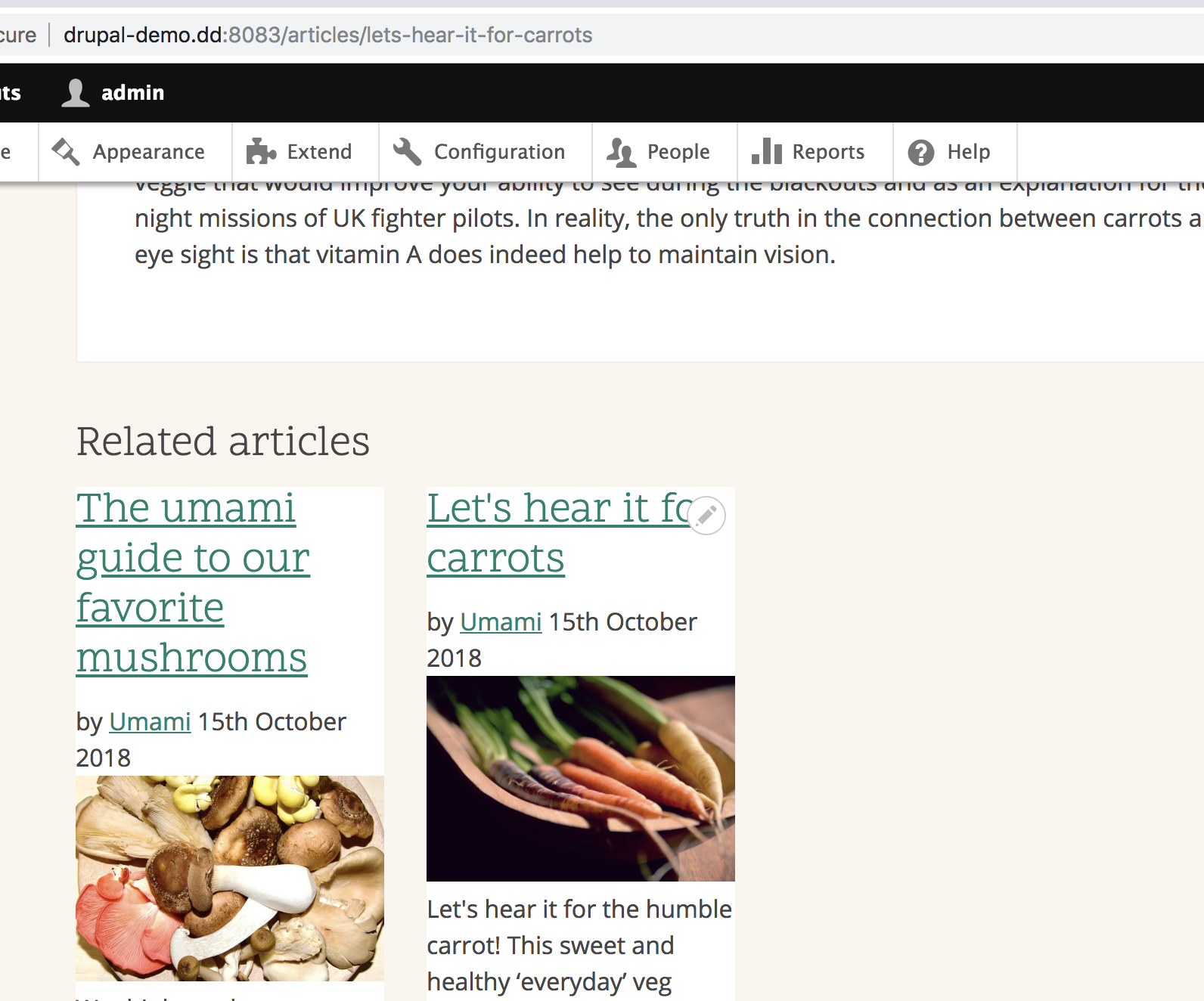
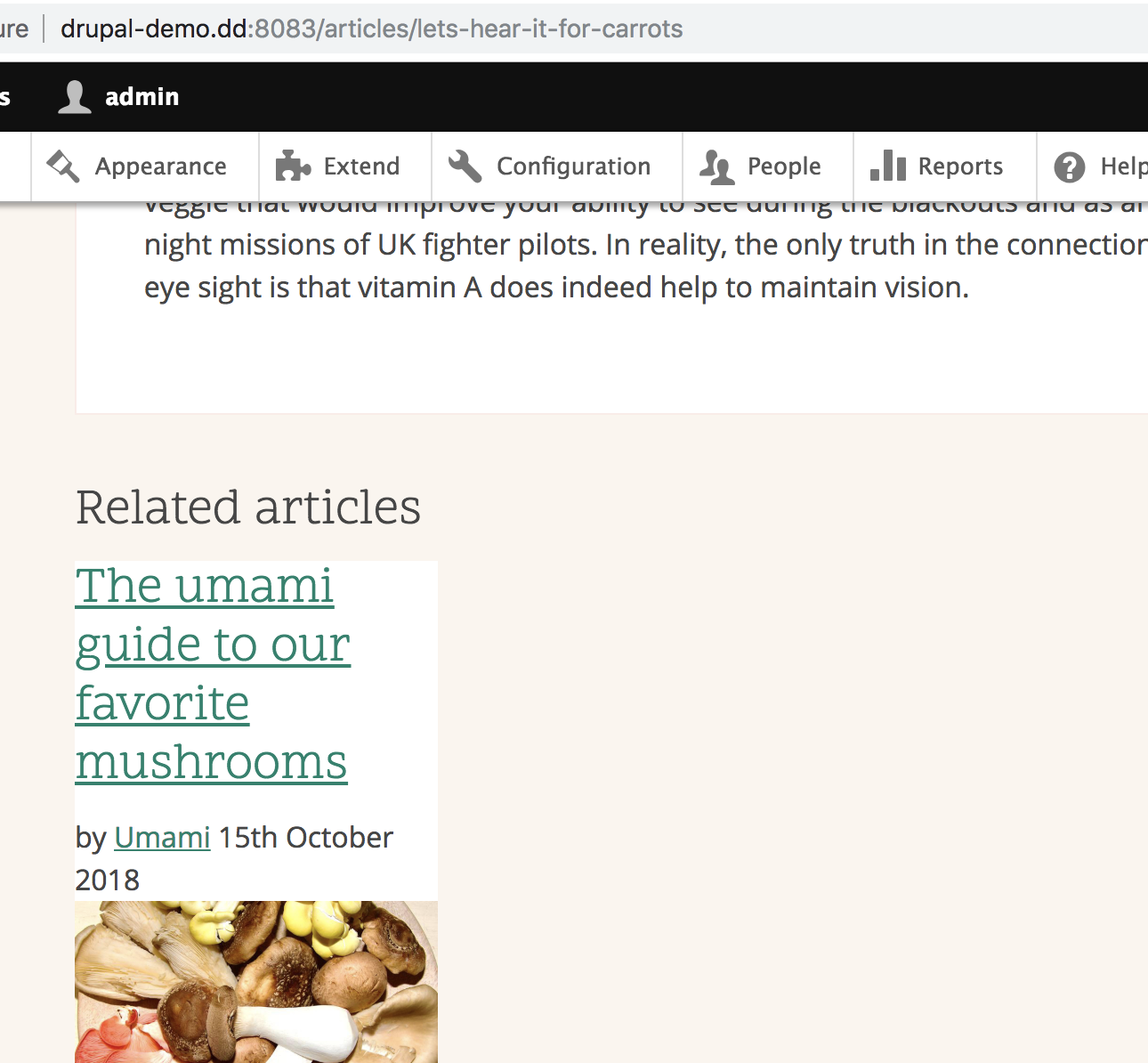
Lets create a view that shows articles using the same tags: Related articles
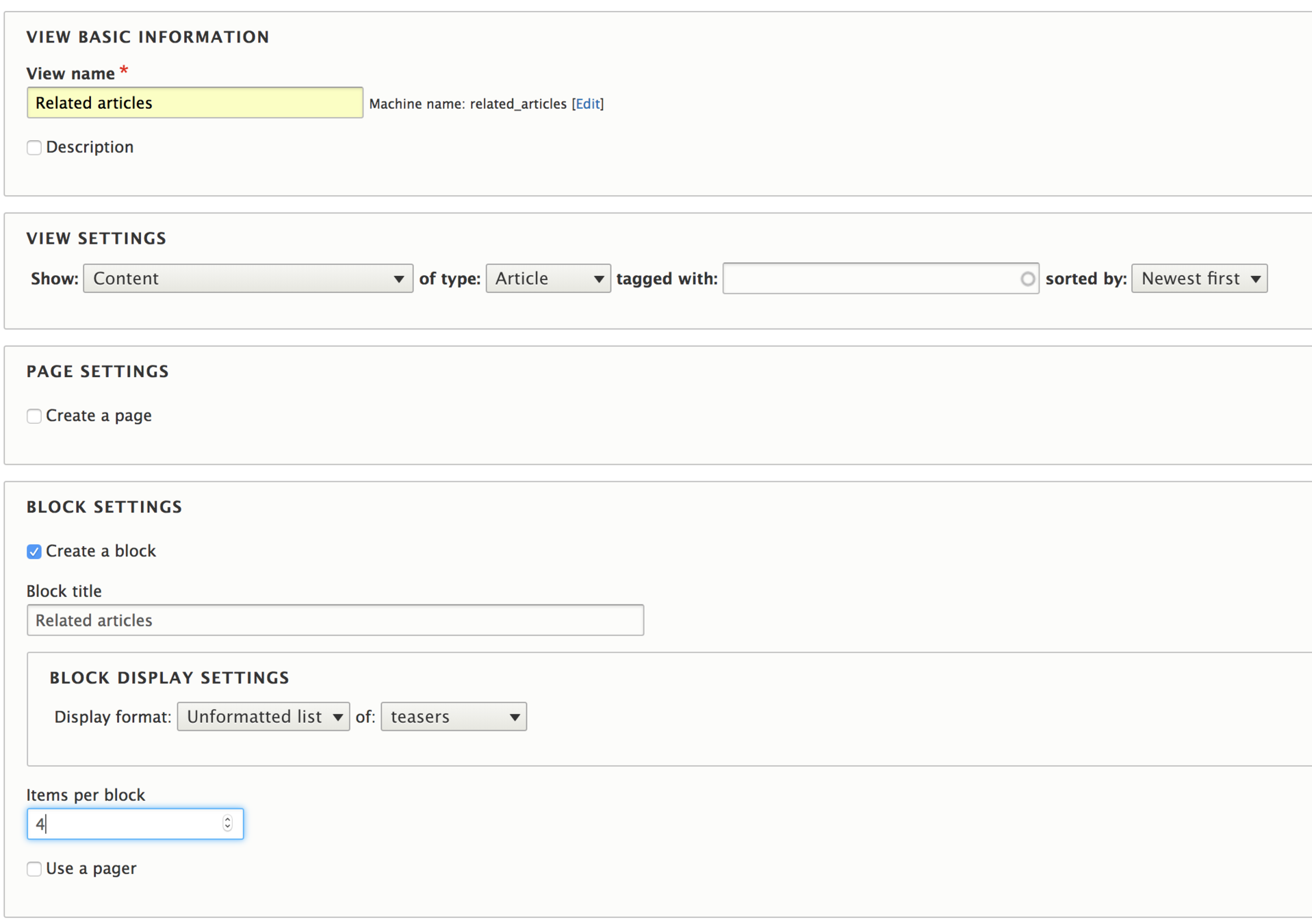
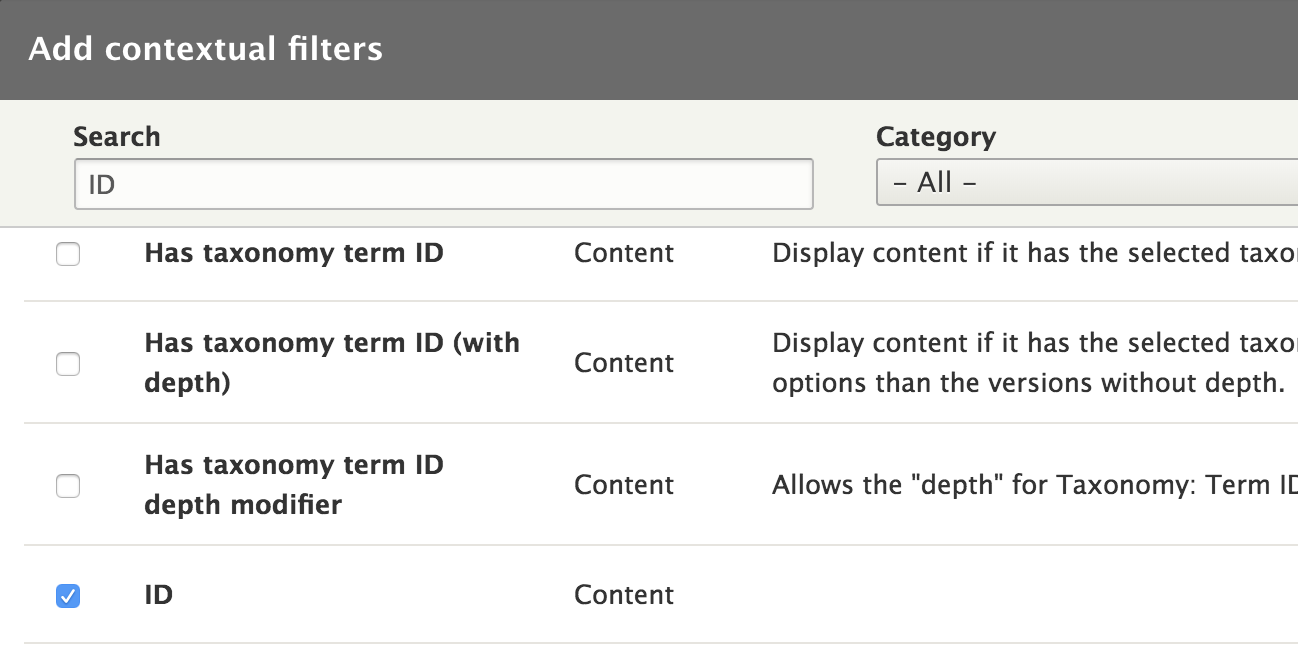
Add the contextual filter
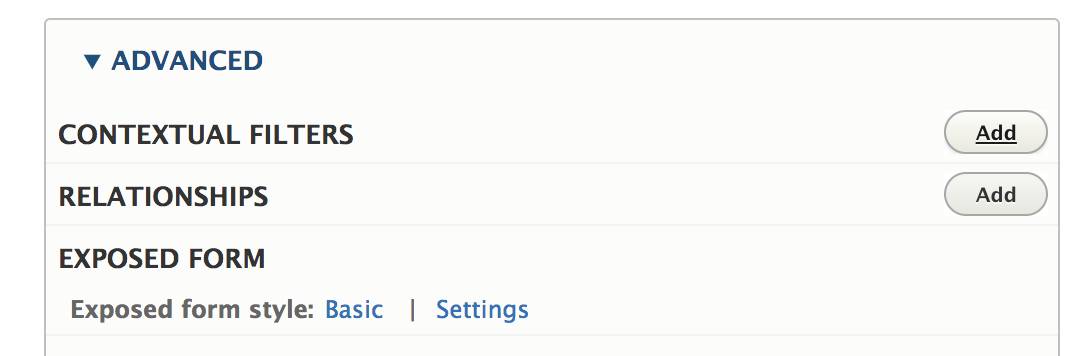
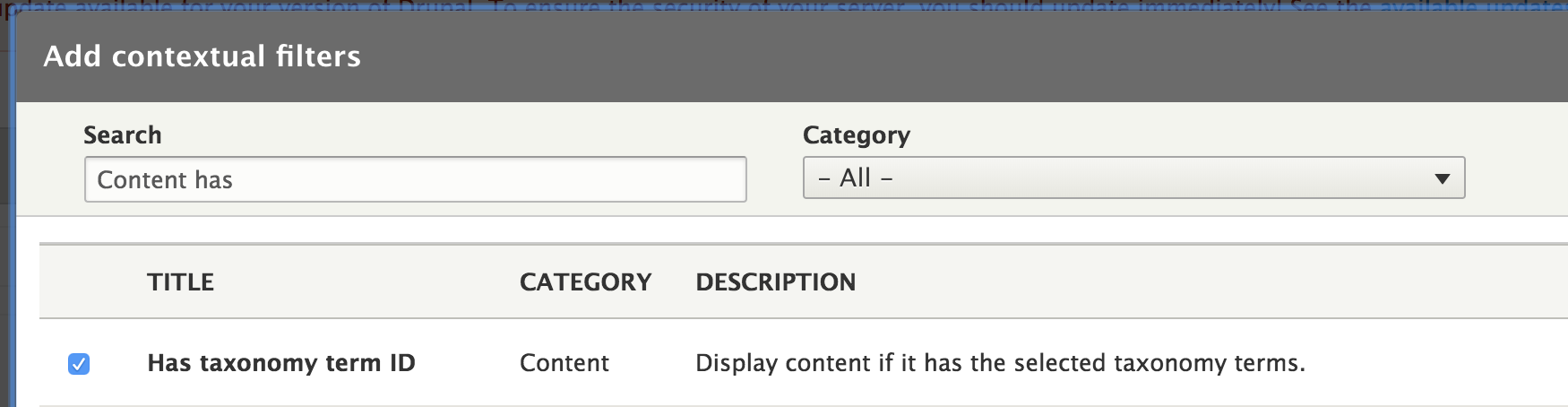
Set the contextual filter
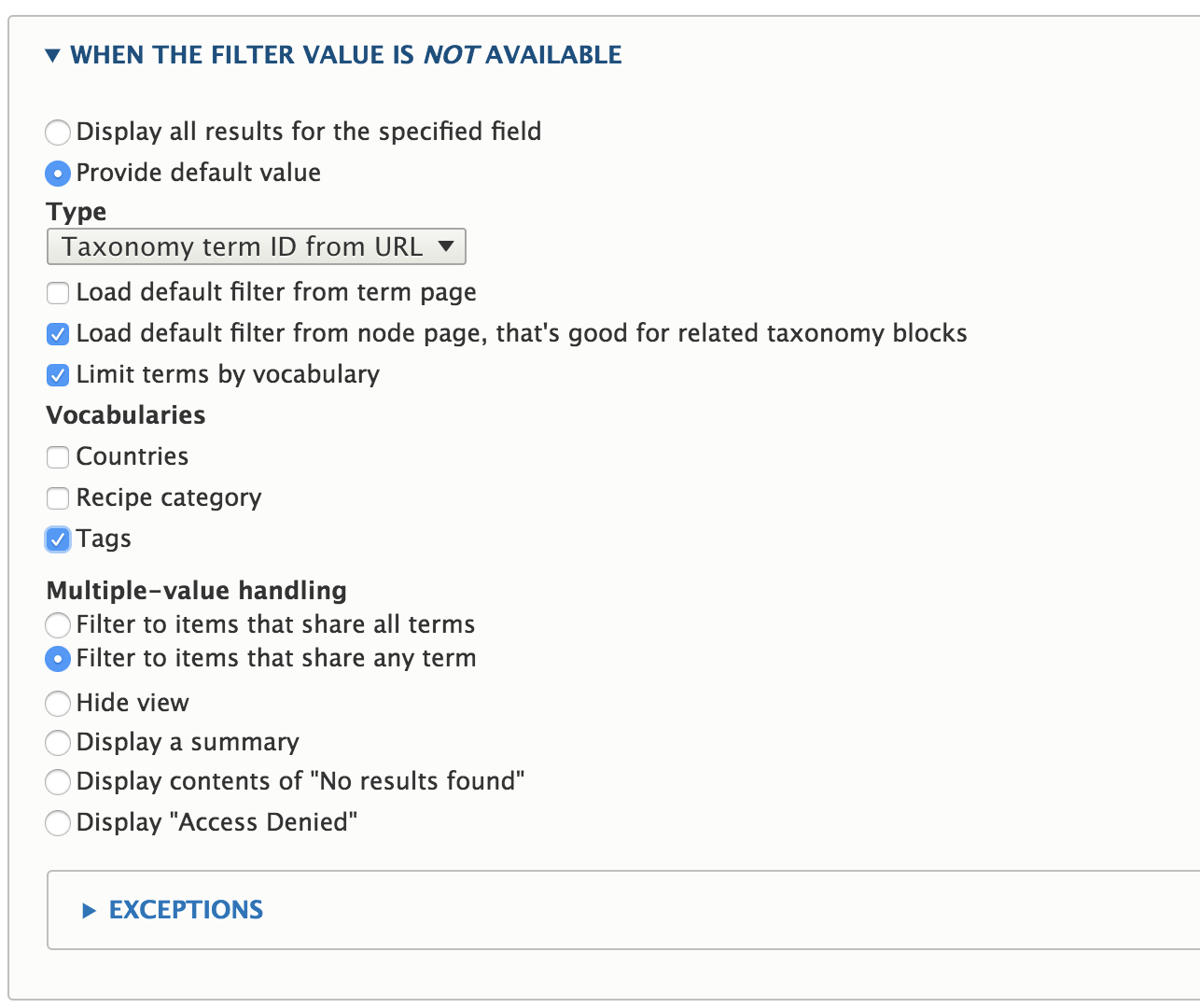
Set the contextual filter

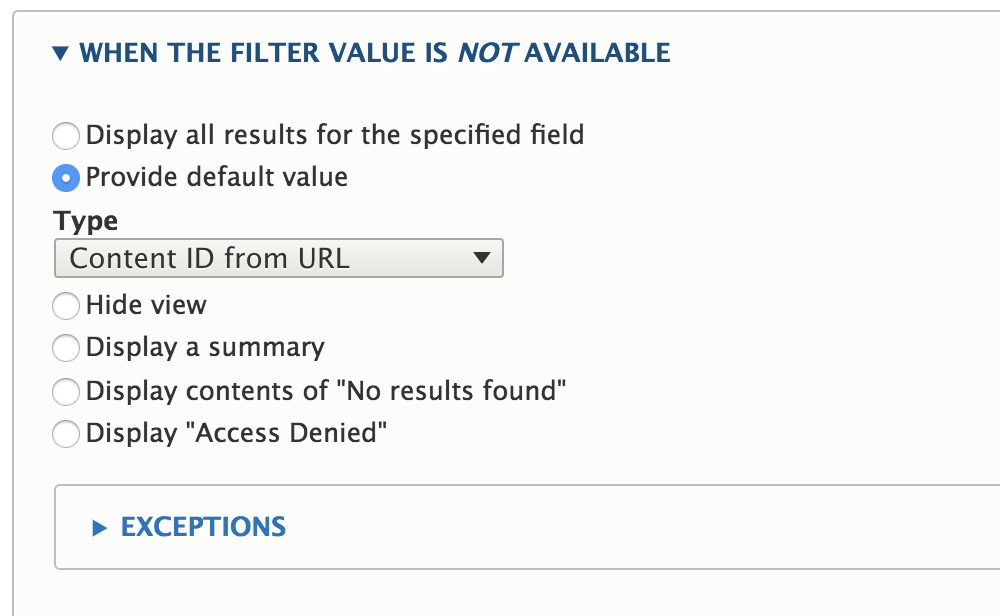
Place block
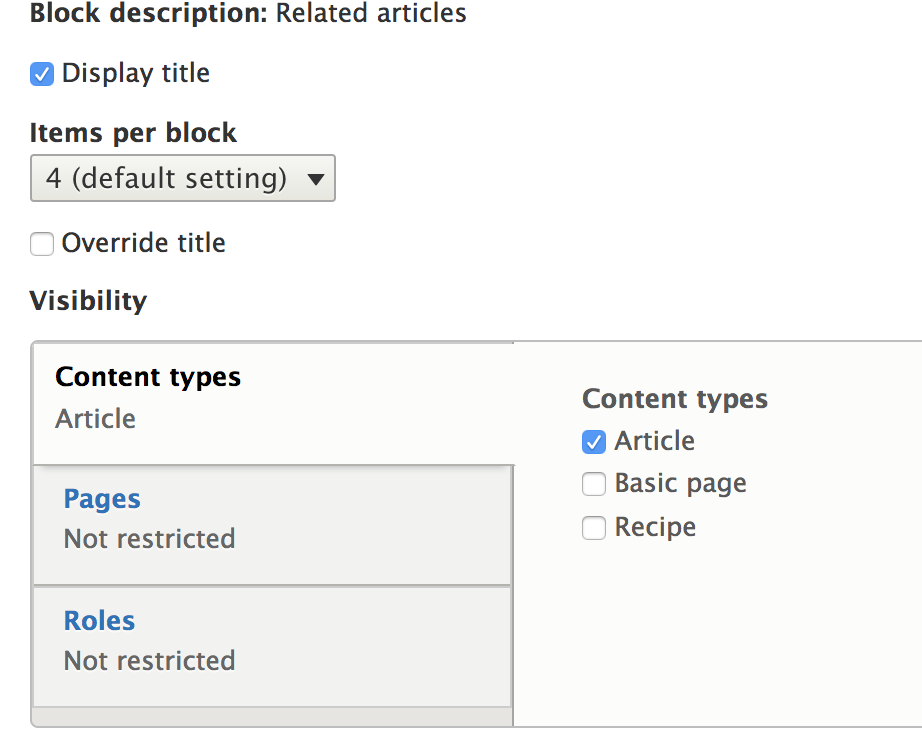
Results
Remove own item
Remove own item
Remove own item

Results
Exercise
Create a related cars view, that shows 4 cars that are similar in options to the selected car.
Show this view on pages that are of the content type car.
Relationships
Include more referenced content.
Relationships?
When you first create a view you select the base table from options such as Comments, Content, and Taxonomy terms. This cannot be changed later. After that selection you will only be able to select fields from that base table.
For example, with a Content view, you can get the User ID of the author, but not the author's username.
To get that information you will need to create a Relationship to join those two tables. With the connection of User ID, you can get the author's username from the User table.
How to
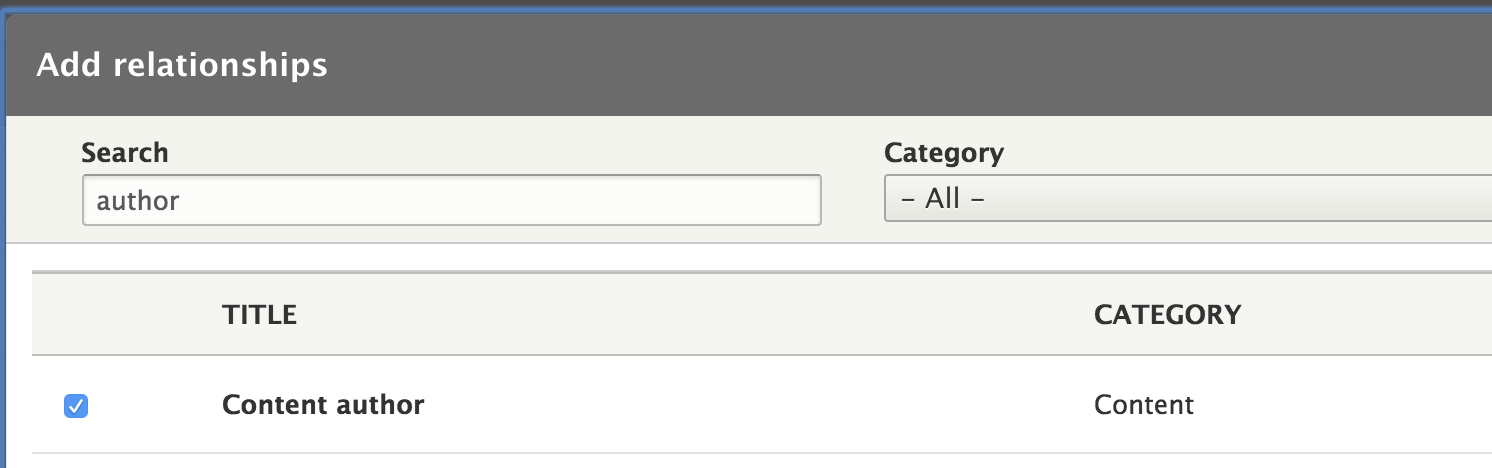
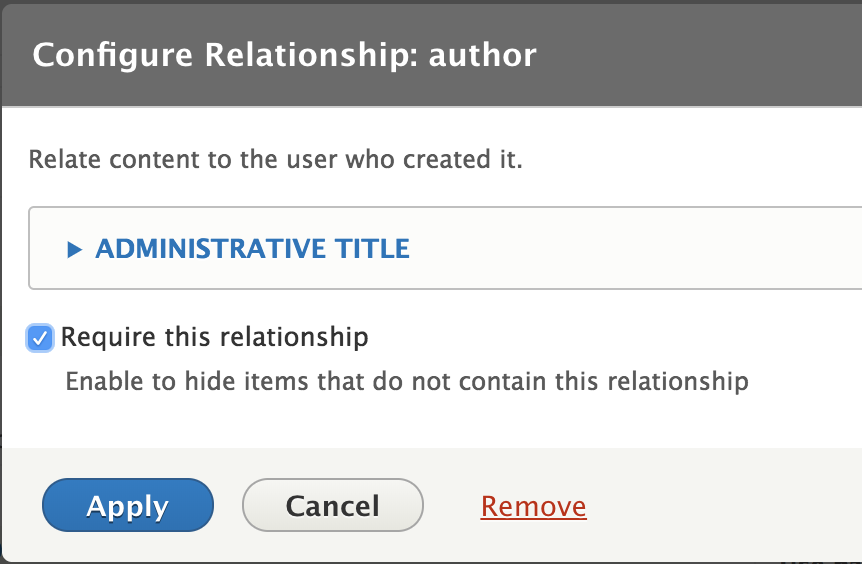
How to