CMS
Week 6
Working with Drupal 8
Part 2
Field trip!
Kantoorbezoek Intracto
Getting started with module development
+ Rondleiding
18/12
2 Groepen: Voormiddag/Namiddag, gedeelde lunch
Carpooling - To be arranged
Aanwezigheid verplicht!
More info TBA.
Slides
Download
Summary
-
Content modelling
- Content types
- Fields
- Views
- Relationships
- Exercises: CT Course & View
- User management
- What
- How to
- Exercise: Webmaster role
- Reverse engineering a concept
- New Thomas More website
Content modelling
Content types
In Drupal, a Content Type is a pre-defined collection of data types (Fields) which relate to each other by an informational context.
In this sense, "context" means "parts that should be considered as a correlated whole."
Some simple examples
-
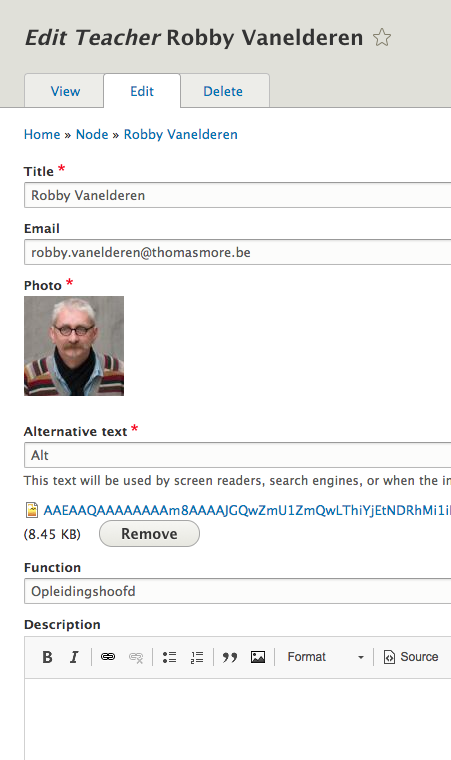
Teacher
- Has a name, a function, an email address, a photo, ...
-
Course
- Has a name, course information, files such as documents & courses, is given on a certain campus, ...
-
Campus
- Has a name, an address, ...
But there are many others
All sources of information can be grouped like this.
Like a contractor who has a website showing projects that he has built. The project itself could be a content type containing fields for the name, address, a teaser description, longer text describing the build or materials used, an image album, references to used materials, ...
Then the used materials can be turned into a content type itself. It could support fields like: name, retail identification number, a reference to a retailer, ...
How to use
Content type parts
Drupal has 4 distinct parts to a content type:
-
Edit page
- same as add page
- Manage settings
-
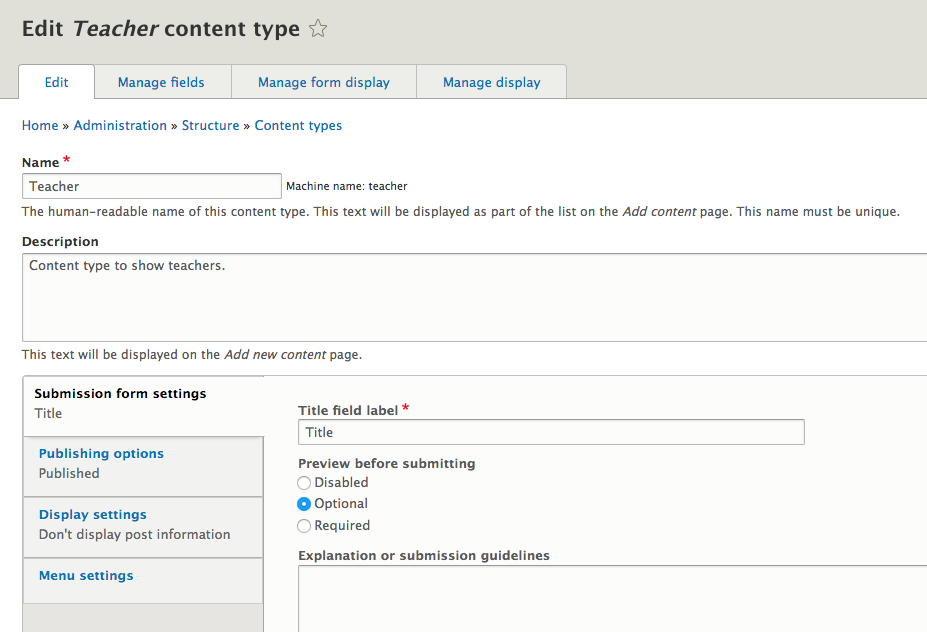
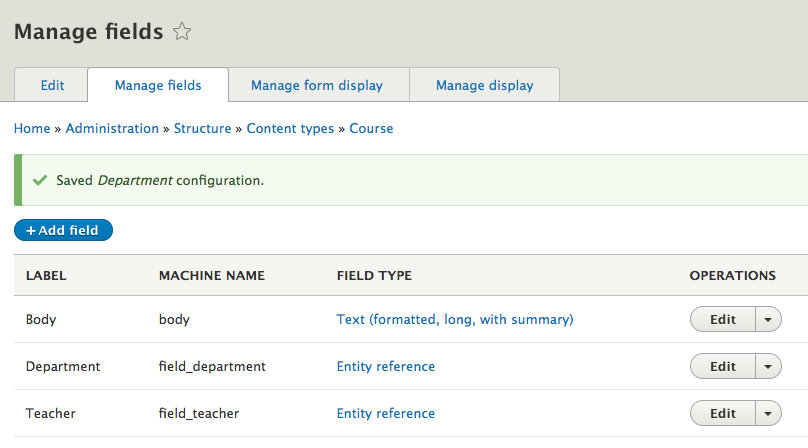
Manage fields
- Add & edit fields
-
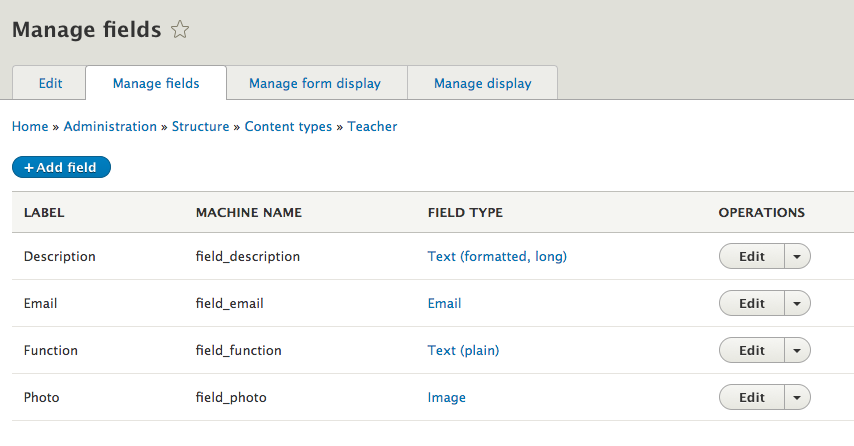
Manage form display
- Change how you add/edit content of this type
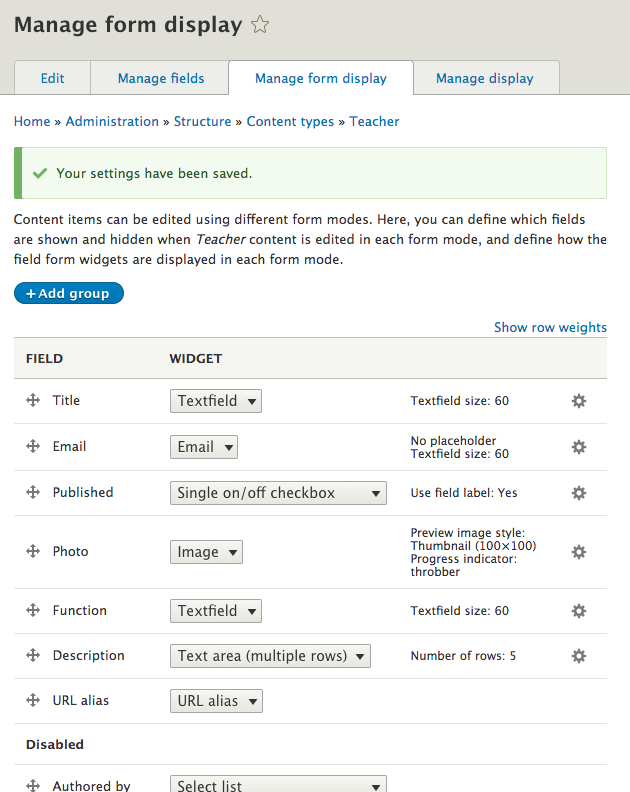
- Manage display
- Manage the way the fields are displayed
Add/Edit Page
Manage fields
Manage form display
Manage display
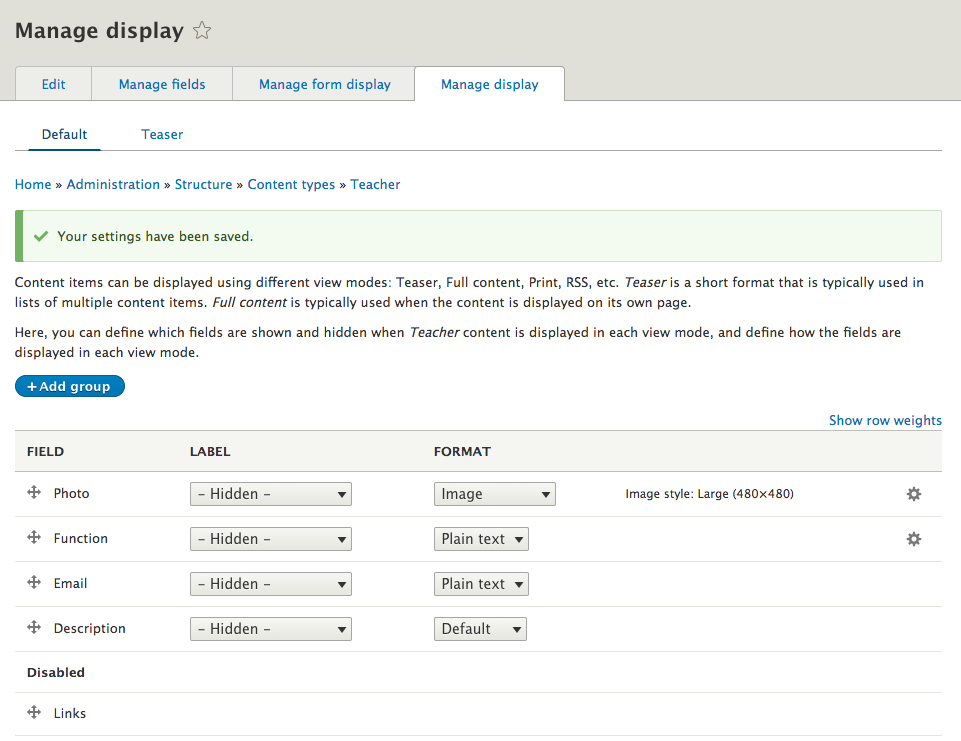

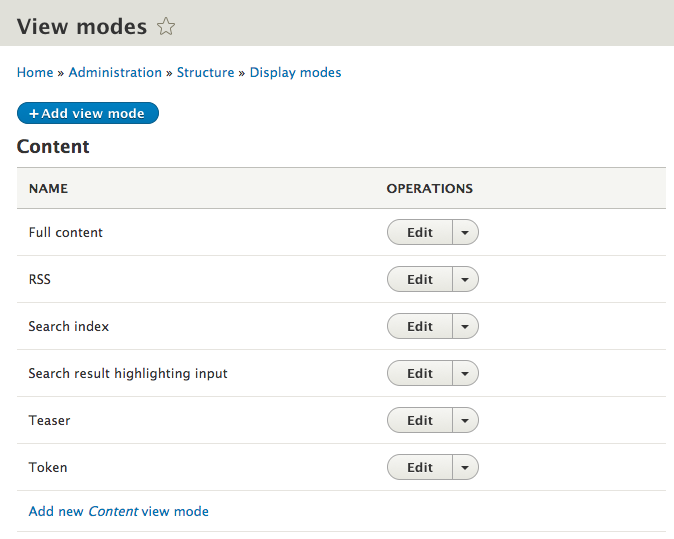
View modes
How a node is displayed depends on the context in which it is viewed, such as the difference between full nodes and teasers.
View modes: default
- For a full page or detail page
- Fields:
- Displays all fields
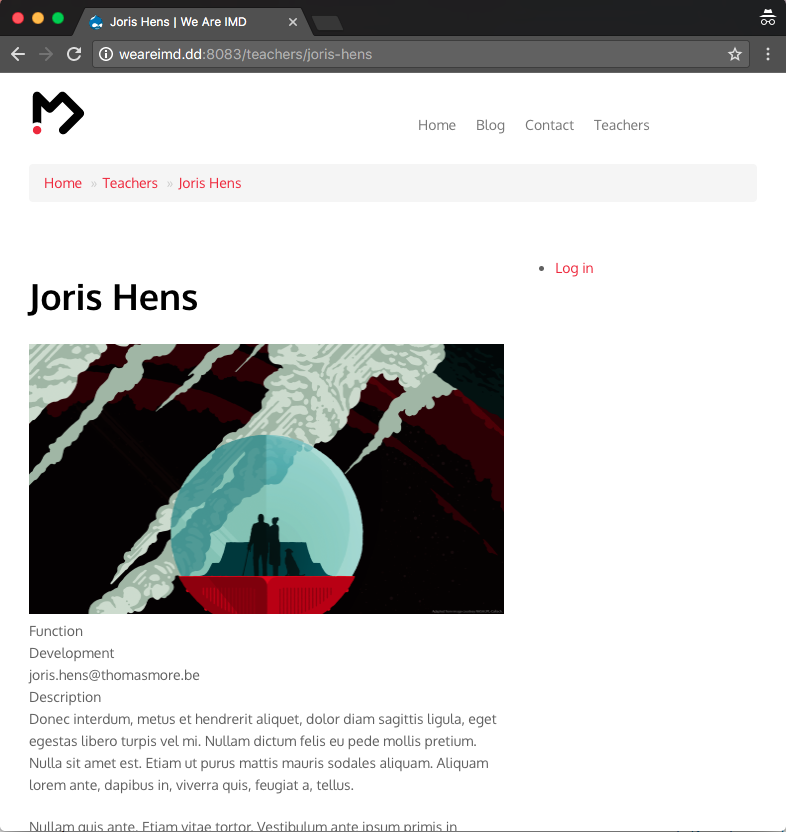
View modes: teaser
- Used in
- overviews
- lists
- Fields:
- Title (default)
- Photo
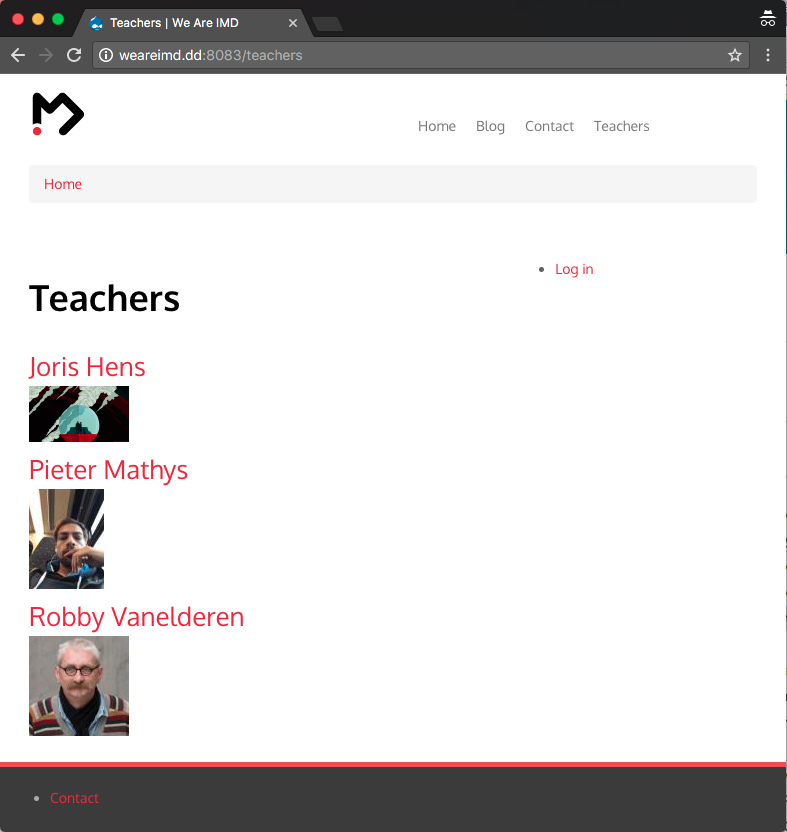
View modes: other?
You can enable more view modes or add custom ones
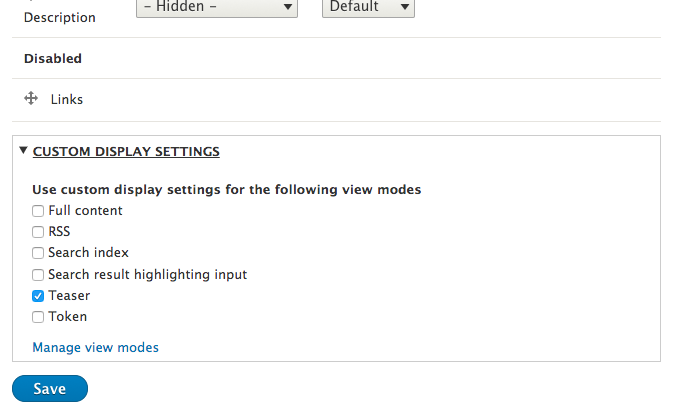
View modes: manage
Fields
Field terminology
-
Field.
- A category of data that can be added to an element, for example, Title, Body, Comment body, Tags, Image.
-
Field type.
- The data type of a field, for example, text, integer, image.
-
Field instance.
- A field added to an element
Field UI
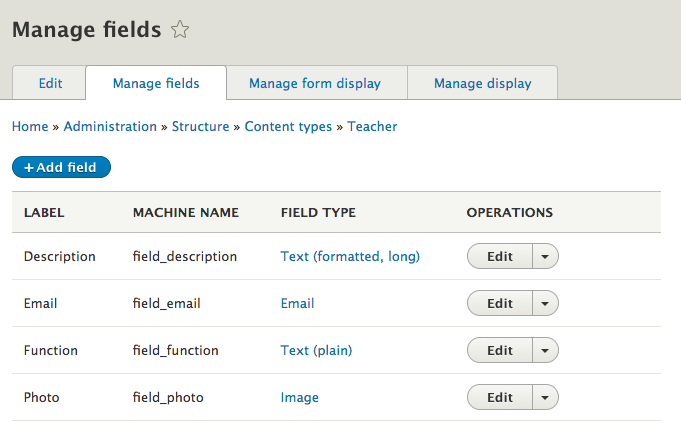
Field UI: add field
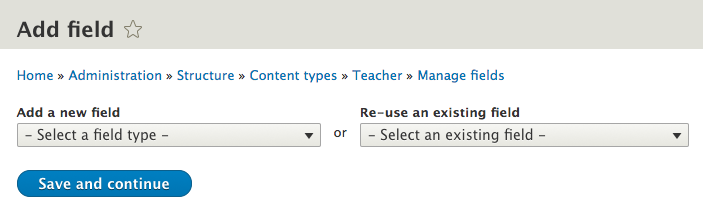
Field UI: default types
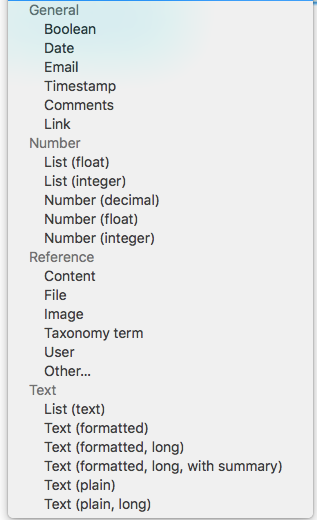
What type of data the field will store
Each field can store one type of data (text, number, file, etc.).
When you define a field, you choose a particular field type, which corresponds to the type of data you want to store.
The field type cannot be changed after you have created the field.
Field UI: add

Machine name is the unique name of the field, all Drupal entities have a machine name. This process is automatic, but can be manually altered.
Can't be changed later.
Field UI: add - settings
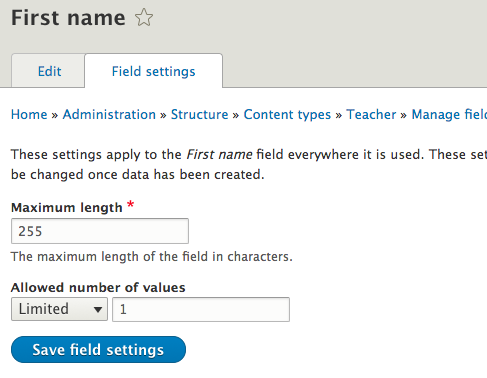
Depends on the type.
F.e.: Image has a lot more settings.
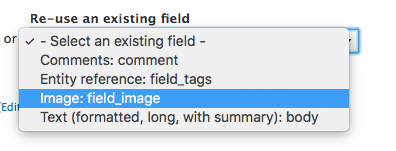
Field UI: re-use
Sometimes different content types will use very similar fields. If you are sure that the field and its use will be the same for both content-types, than you can re-use existing fields.
This is a very good practise for maintainability.
For example you can use the same Description field on a few content-types and then have a single template in your theme to change the output.
Field UI: re-use
Views
What is a view?
The views module allows administrators and site designers to create, manage, and display lists of content.
Each list managed by the views module is known as a "view", and the output of a view is known as a "display".
Displays are provided in either block or page form, and a single view may have multiple displays.
Managing views
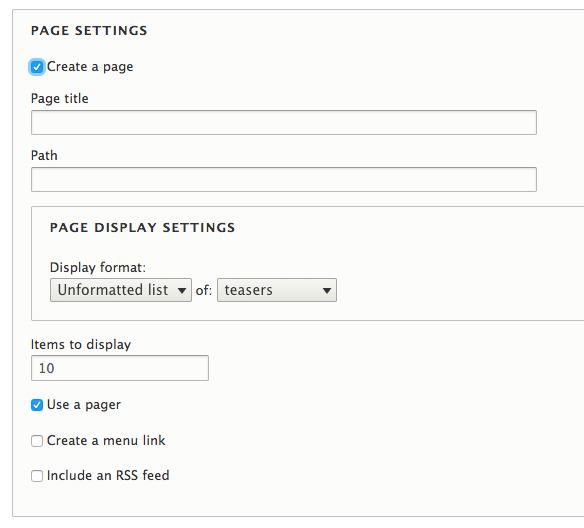
Adding a view
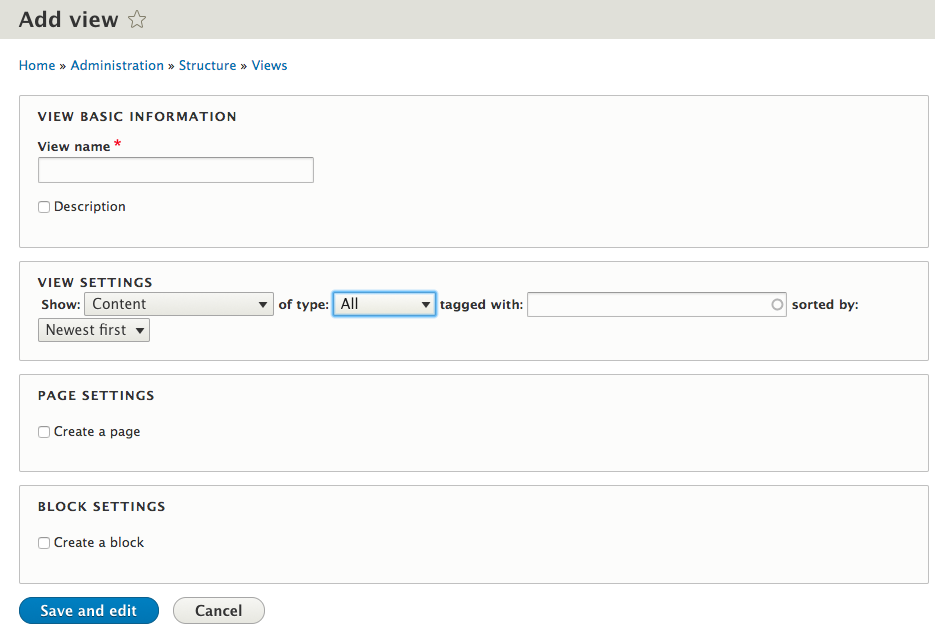
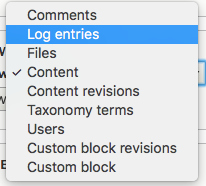
Adding a view
When you add a view, consider this screen a quick setup wizard.
By making some basic choices, you can easily create a simple view.
Later on you can customise this completely.
Adding a view: block/page
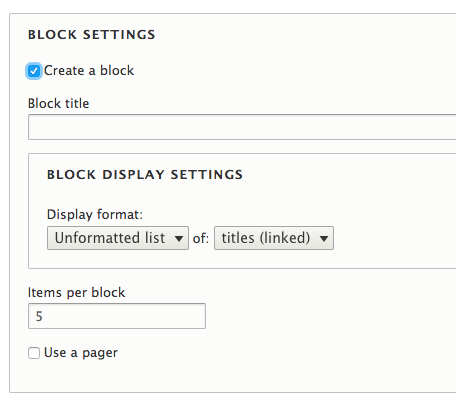
Adding a view: formats
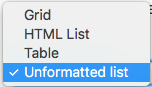
default drupal html grid, rather basic
<ul><li>node</li><ul>
<table><tr><td>
<div class="views-row">
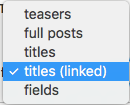
view mode teaser
view mode default
field: title
field: title w/ link
fields: all fields
All of these can be changed & customized later
Editing a view
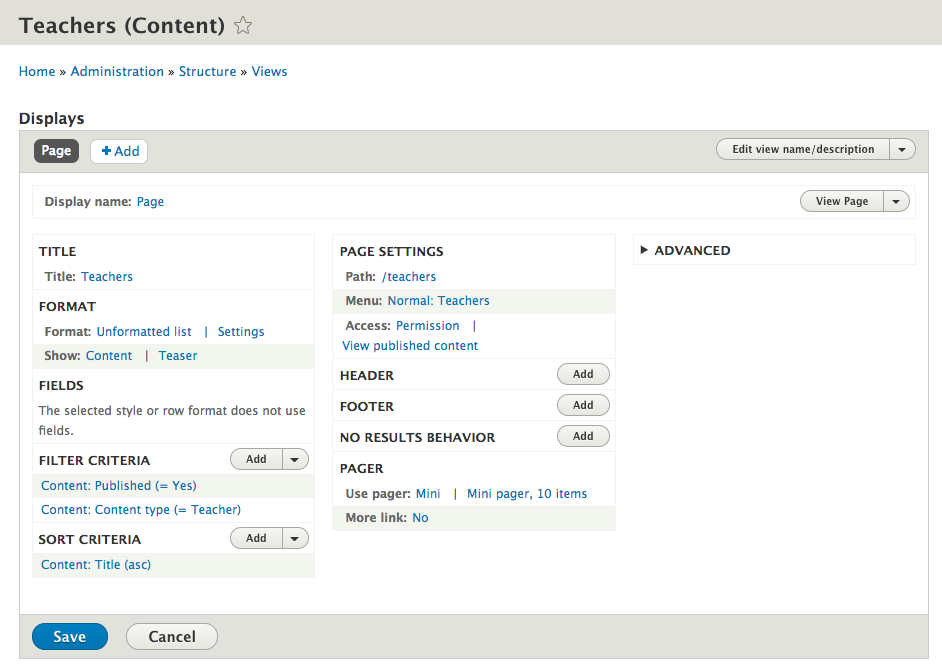
Editing a view: preview
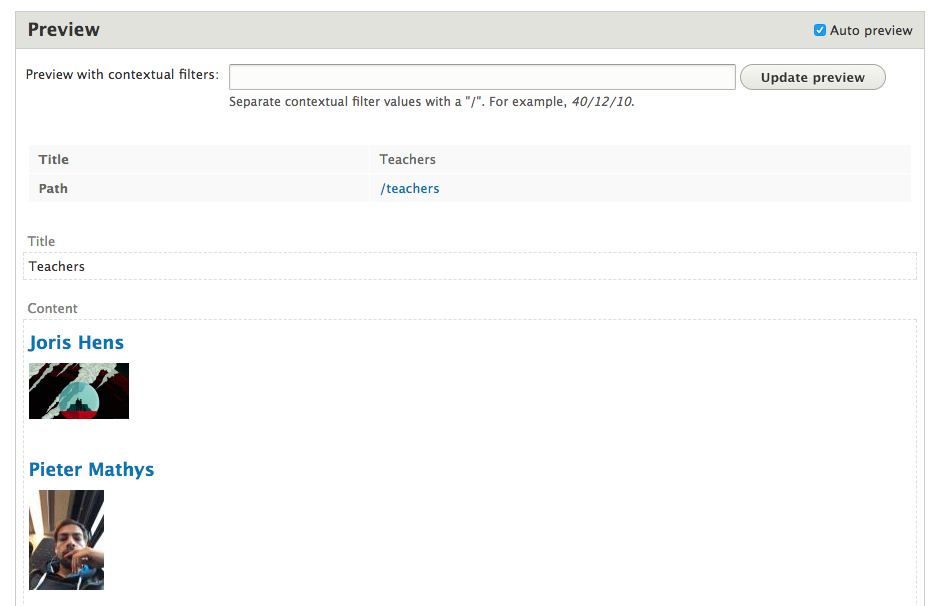
This does not use your front-ends css/js! Go to the view page for that.
Relationships
Use cases & setting up
Use case: CT Course
We want to add a new content type called Course. Each Course contains field to describe a school course. It has a Name (title) and a Description (body).
We want to link our Teachers to a Course, so that we can see which Teacher gives what Course.
Meet the reference field.
First: create the CT
Create a new Content type called Course.
For settings:
- Publishing options -> leave only published on
- Display settings -> dont display
- Menu settings -> none
This content type has (by default) a title, and a body field.
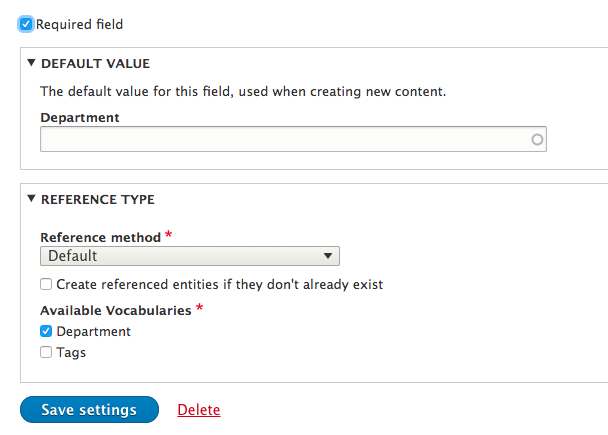
Add a reference field
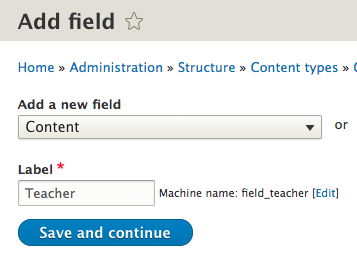
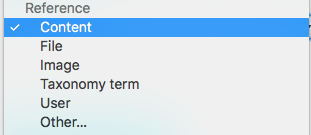
Add a reference field
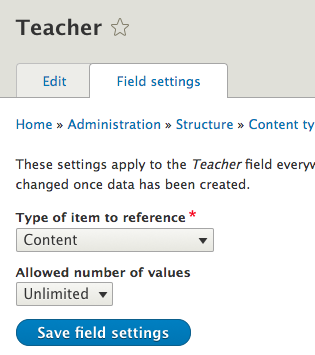
Create some courses
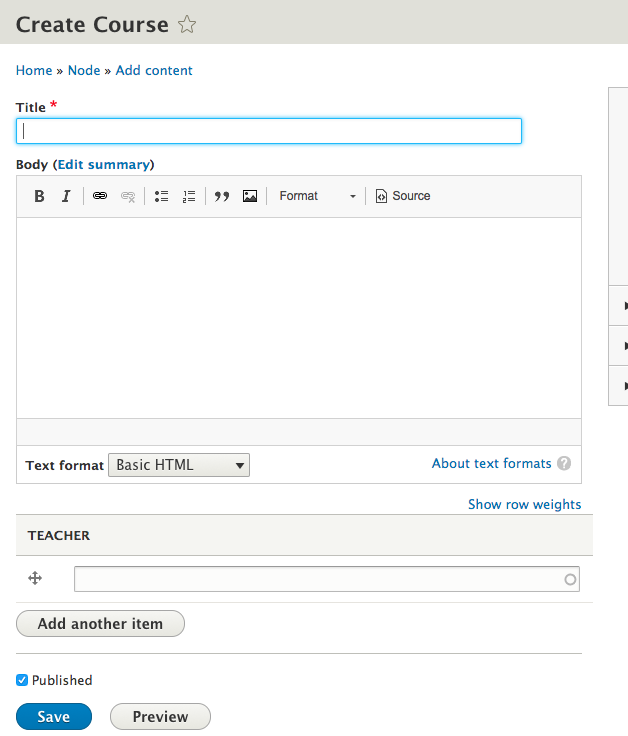
Teacher field in action
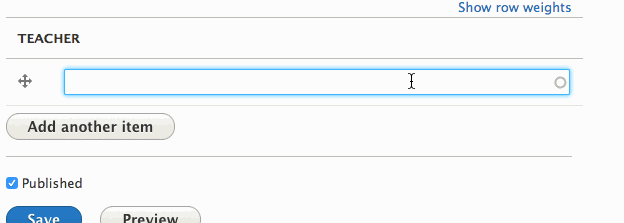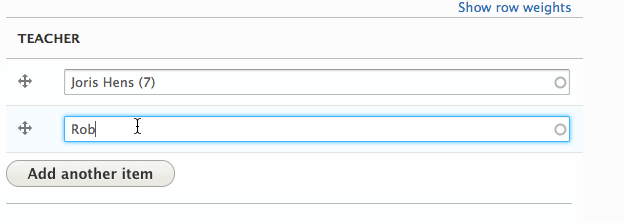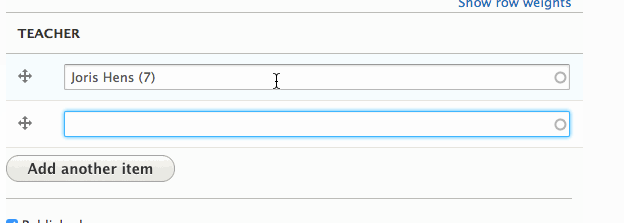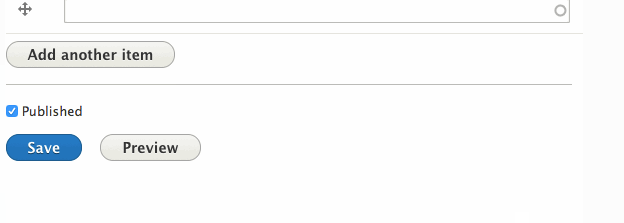
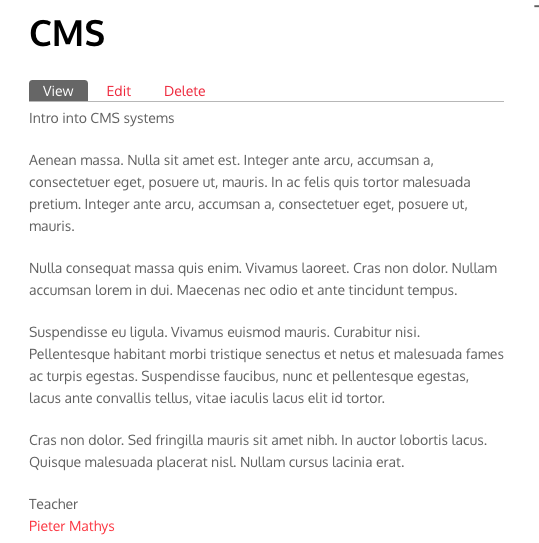
Result
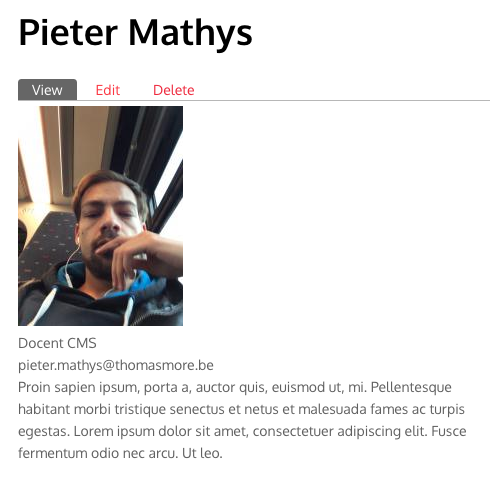
Reference field: taxonomy
Works the same way as a Reference field: content, except that it links to a specific/multiple taxonomies.
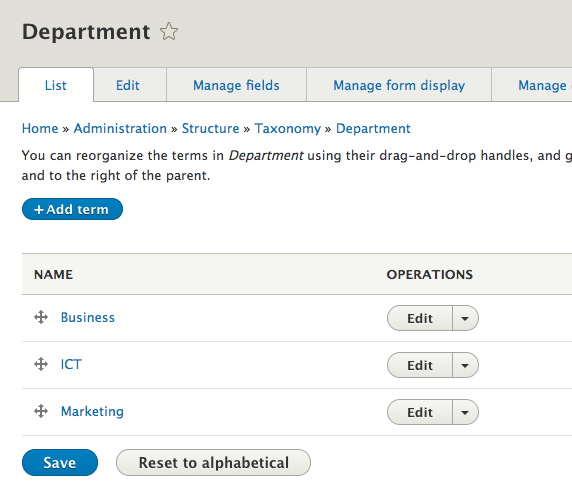
Taxonomies are managed under structure/taxonomy
Taxonomies (aka vocabulary) are basically lists of items, usually used for categorisation, tagging, etc
There are cases where the administrator manages them, but these can be also be setup to be freely added by users
Taxonomy: add/edit
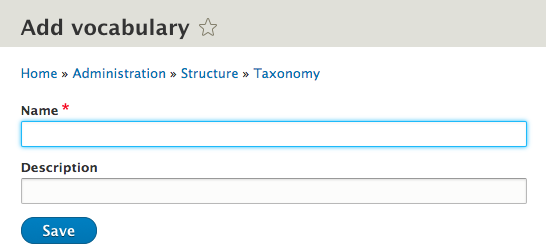
Add field
Edit field settings
Exercises
- Add CT Course like the example
- Add a page view showing all Courses
- Add some Content
- Think of other things you can add
- Add Department taxonomy to Courses
- CT Campus
- add a view with a list
- link Courses to a Campus
- ...
User management
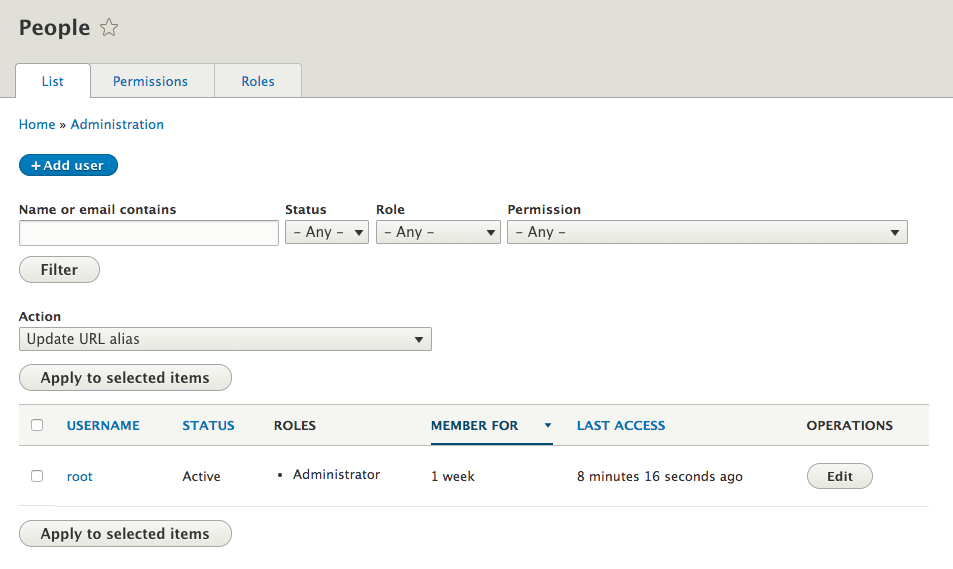
User management
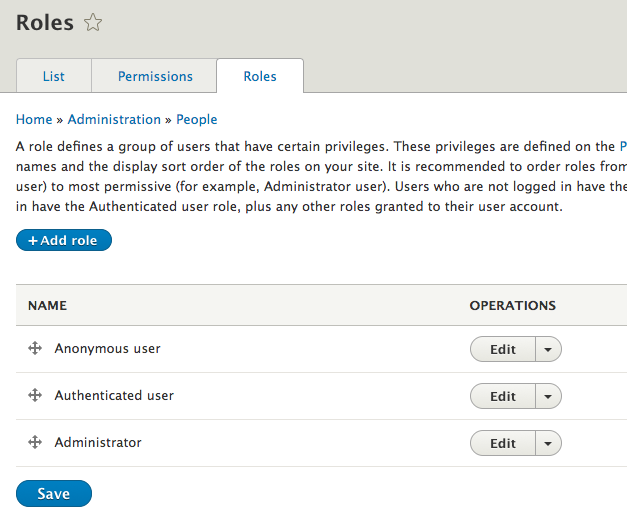
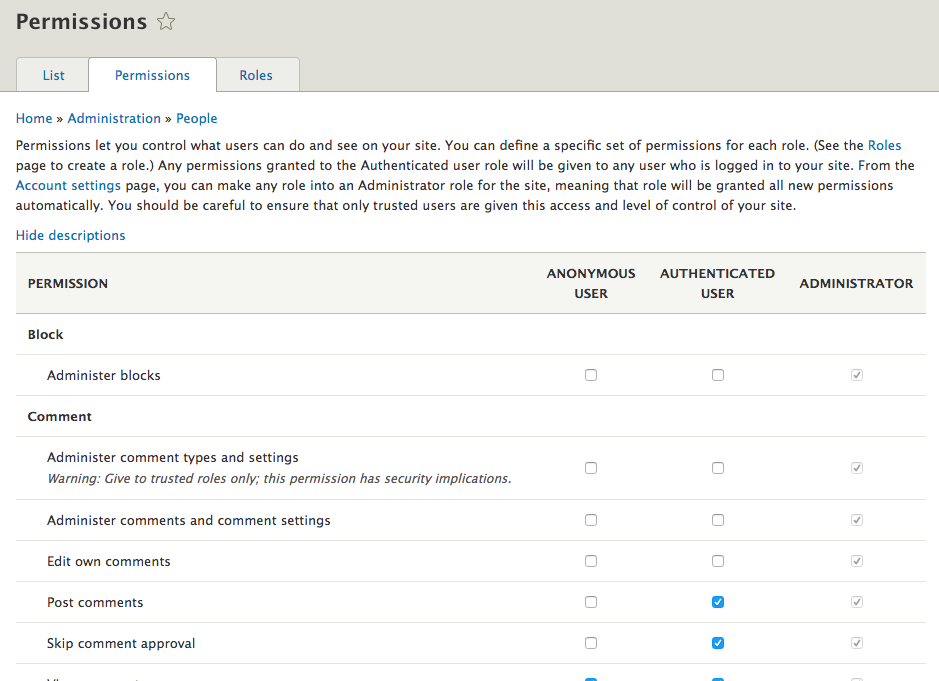
One of the great features of Drupal is the ability to control how and what people can access on your site.
You can set permissions for these "users" to define who can do what for Drupal core features and contributed modules.
For example, you probably won't want casual visitors to edit your homepage. However, the site owner or trusted user should be able to do so.
Users: how to
Users: Roles
Users: Permissions
Exercise
Add user role: Webmaster
Add user role: Webmaster
Add a new role Webmaster & set permissions.
This user needs to be able to:
- Use the Admin interface
- Access files
- Add/Edit/Remove content
- Use Basic/Full html
- Create/Edit URL aliases
- Use/Change shortcuts
- Change menus & items
- Use the toolbar
Add user role: Webmaster
Test this user!
Make sure you can do all of the actions listed before!
Protip: use a second browser or incognito window