Phase-Type Models in
Life Insurance

Dr Patrick J. Laub
Université Lyon 1




Work
Work
Coffee
Coffee
Lunch
Home
Chat
A typical work day
Work
Work
Coffee
Coffee
Lunch
Home
Bisous
Pause Café
Paperwork
Déjeuner
Il y a un pot
Une petite pinte
Paperwork
Sieste
(Talk)
A typical French work day
Work
Work
Coffee
Coffee
Lunch
Home
Chat
1/3
1/3
1/3
1
1
1
1
1
2
5
1
4
3
7
6
1/3
1/3
1/3
1
1
1
1
1
From Markov chains to Markov processes
- Coffee
- Work
- Lunch
- Coffee
- Work
- Chat
- Work
- Home
| State | Time in State |
|---|---|
| Coffee | 5 mins |
| Work | 2 hours 3 mins |
| Lunch | 26 mins |
| Coffee | 11 mins |
| Work | 1 hour 37 mins |
| Chat | 45 mins |
| Work | 2 hours 1 mins |
Chain
Discrete Time
Process
Continuous Time




Example Markov process
The Markov property
Markov chain State space
Markov process at times
Sojourn times
Sojourn times are the random lengths of time spent in each state

Transition rate matrices
2
5
1
4
3
7
6
1/3
1/3
1/3
1
1
1
1
1
Phase-type definition
Markov process State space
- Initial distribution
- Sub-transition matrix
- Exit rates
Example
Markov process State space
Phase-type distributions
Markov chain State space
Phase-type quiz...
Phase-type generalises...
- Exponential distribution
- Sums of exponentials (Erlang distribution)
- Mixtures of exponentials (hyperexponential distribution)
When to use phase-type?
When your problem has "flow chart" Markov structure.
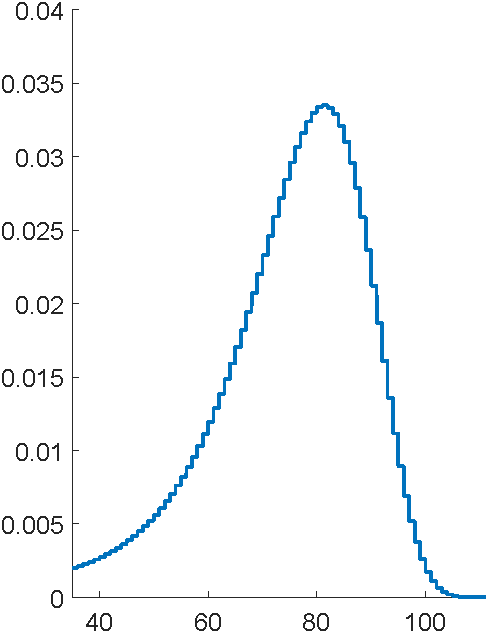
E.g. mortality. Age is a deterministic process, but imagine that the human body goes from physical age \(0, 1, 2, \dots\) at random speed.
("Coxian distribution")
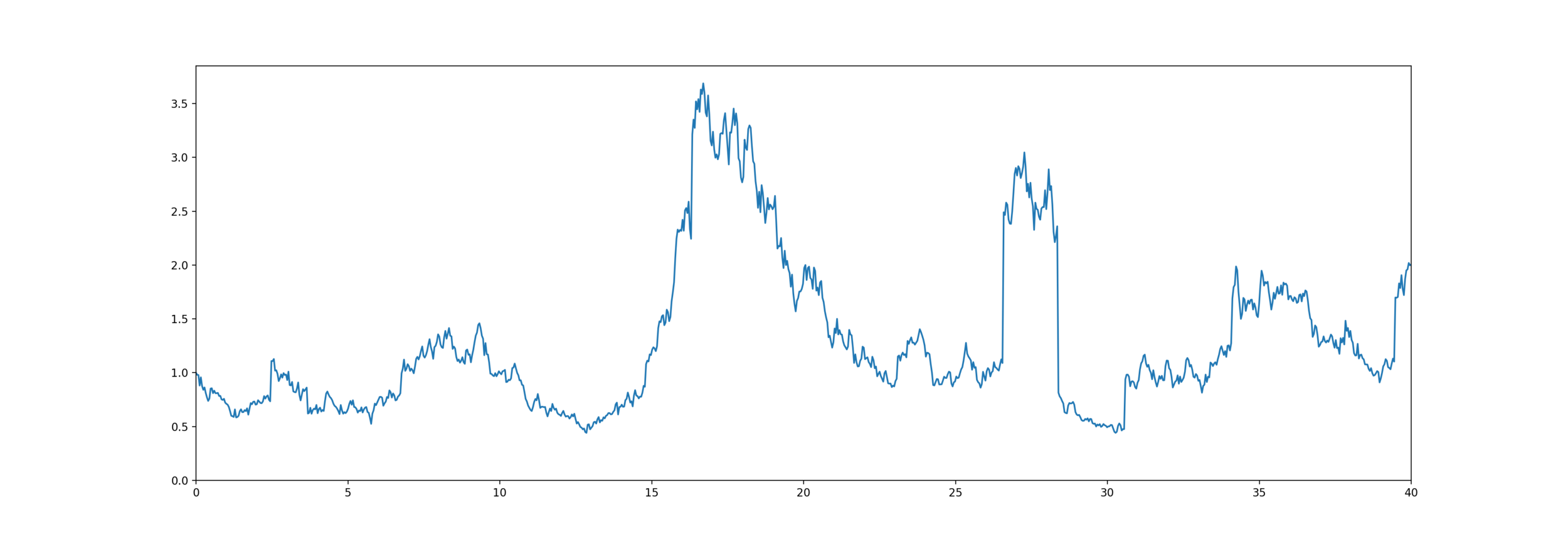
Class of phase-types is dense
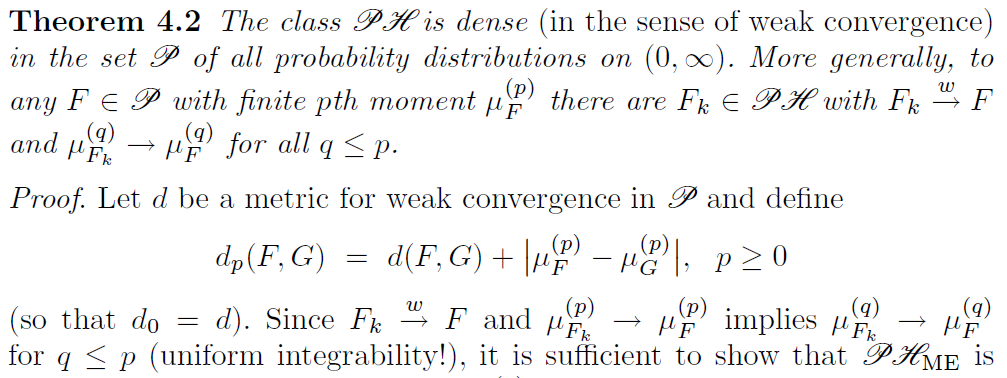
S. Asmussen (2003), Applied Probability and Queues, 2nd Edition, Springer
Class of phase-types is dense










Why does that work?
Can make a phase-type look like a constant value


More cool properties
Closure under addition, minimum, maximum
... and under conditioning
Phase-type properties
Matrix exponential
Density and tail
Moments
Laplace transform
Guaranteed Minimum Death Benefit
Application
Equity-linked life insurance
High Water Death Benefit
Equity-linked life insurance
Model for mortality and equity
The customer lives for years,
Equity is an exponential jump diffusion,
Exponential PH-Jump Diffusion
Problem: to model mortality via phase-type
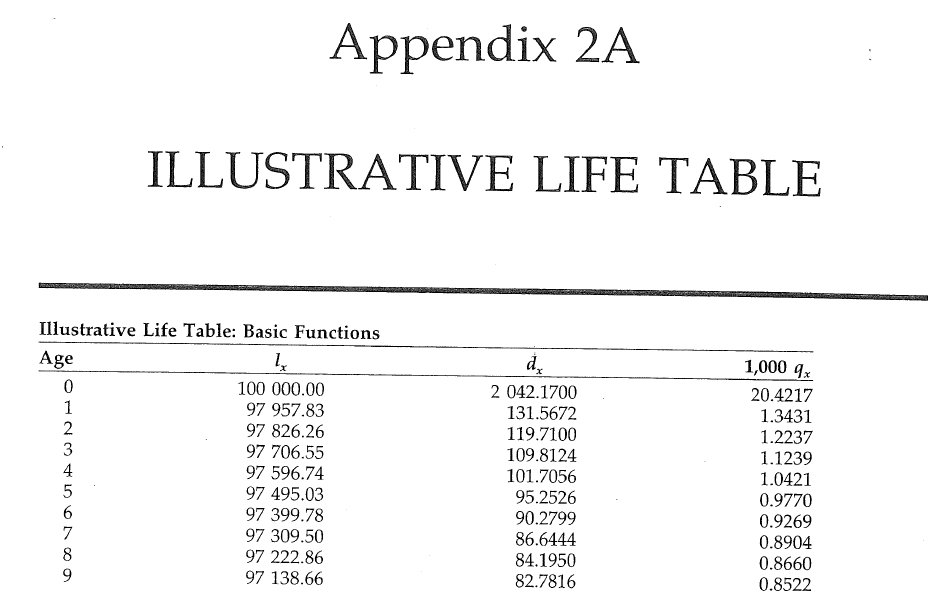
Bowers et al (1997), Actuarial Mathematics, 2nd Edition
Fit General Phase-type

Representation is not unique
Also, not easy to tell if any parameters produce a valid distribution
Lots of parameters to fit
- General
- Coxian distribution
Fit Coxian distributions

General vs Coxian

Rewrite in Julia
void rungekutta(int p, double *avector, double *gvector, double *bvector,
double **cmatrix, double dt, double h, double **T, double *t,
double **ka, double **kg, double **kb, double ***kc)
{
int i, j, k, m;
double eps, h2, sum;
i = dt/h;
h2 = dt/(i+1);
init_matrix(ka, 4, p);
init_matrix(kb, 4, p);
init_3dimmatrix(kc, 4, p, p);
if (kg != NULL)
init_matrix(kg, 4, p);
...
for (i=0; i < p; i++) {
avector[i] += (ka[0][i]+2*ka[1][i]+2*ka[2][i]+ka[3][i])/6;
bvector[i] += (kb[0][i]+2*kb[1][i]+2*kb[2][i]+kb[3][i])/6;
for (j=0; j < p; j++)
cmatrix[i][j] +=(kc[0][i][j]+2*kc[1][i][j]+2*kc[2][i][j]+kc[3][i][j])/6;
}
}
}
This function: 116 lines of C, built-in to Julia
Whole program: 1700 lines of C, 300 lines of Julia
# Run the ODE solver.
u0 = zeros(p*p)
pf = ParameterizedFunction(ode_observations!, fit)
prob = ODEProblem(pf, u0, (0.0, maximum(s.obs)))
sol = solve(prob, OwrenZen5())https://github.com/Pat-Laub/EMpht.jl
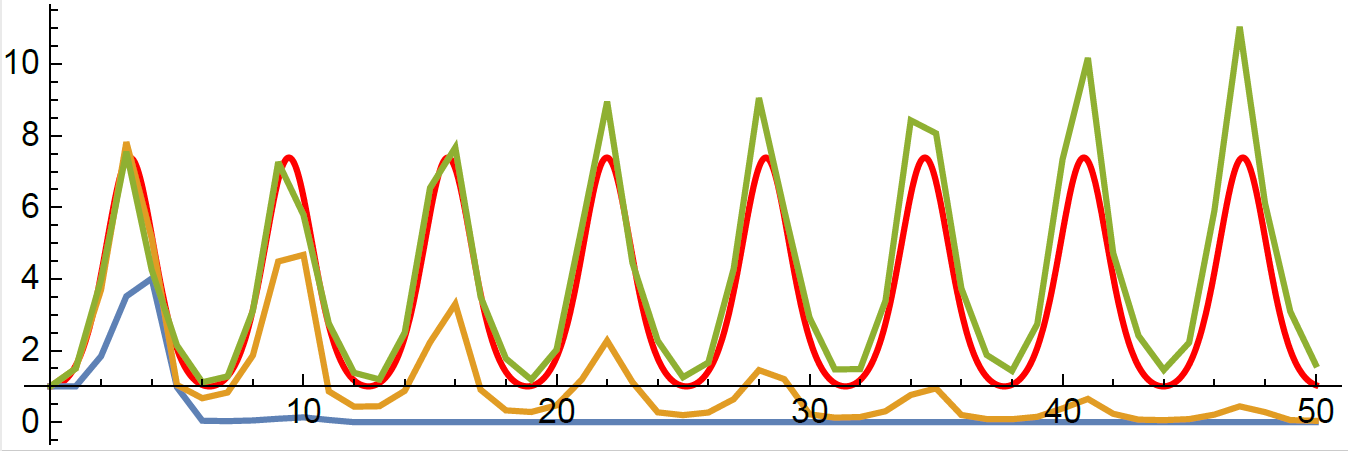

DE solver going negative
Coxian with uniformization

A twist on the Coxian form
Canonical form 1
Et voilà

using Pkg; Pkg.add("EMpht")
using EMpht
lt = EMpht.parse_settings("life_table.json")[1]
phCF200 = empht(lt, p=200, ph_structure="CanonicalForm1")How to fit them?
Observations:
Derivatives??
How to fit them?
Hidden values:
\(B_i\) number of MC's starting in state \(i\)
\(Z_i\) total time spend in state \(i\)
\(N_{ij}\) number of transitions from state \(i\) to \(j\)
Fitting with hidden data
EM algorithm
Latent values:
\(B_i\) number of MC's starting in state \(i\)
\(Z_i\) total time spend in state \(i\)
\(N_{ij}\) number of transitions from state \(i\) to \(j\)
- Guess \( (\boldsymbol{\alpha}^{(0)}, \boldsymbol{T}^{(0)} )\)
- Iterate \(t = 0,\dots\)
- E-step
- M-step
EM algorithm:

Questions?
https://slides.com/plaub/phase-type-lecture
