Virtualizzazione con Libvirt
la soluzione piu' comoda e open per Linux
Matteo Bernardini (matteo.bernardini _at_ gmail.com)
(nome di battaglia: ponce)

- usa Linux da piu' di quattro lustri
- esperienza lavorativa in diverse ditte ed enti pubblici italiani
- dal 2008 molto attivo su Slackware (virtualizzazione, ambienti grafici leggeri, desktop remoti)
- dal 2012 parte del gruppo di amministratori di SlackBuilds.org
- gestisce personalmente un fork di questo repository con script di terze parti per la versione di sviluppo di Slackware
Un breve riepilogo della virtualizzazione in ambiente x86
1999 - VMware Workstation (ESX Server solo dal 2001)
1999 - User Mode Linux
2000 - FreeBSD supporta le jail
2001 - Linux VServer
2003 - qemu
2003 - Xen
2004 - Solaris Containers
2004 - Linux cpusets
2004 - Innotek Virtualbox
2005 - OpenVZ (Open Virtuozzo)
2005 - libvirt
2006 - Linux cgroups
2006 - qemu-kvm
2008 - Proxmox
2008 - Linux user namespaces
2008 - LXC
2013 - docker
2013 - lmctfy (-> libcontainer -> runc)
2014 - rkt


Virtualizzazione
con Hypervisor
I container condividono il kernel dell'host e quindi sono molto meno pesanti della virtualizzazione dell'hardware. Volendo possono usare anche le librerie e i binari del sistema operativo ospitante per far girare applicazioni (ad esempio tramite bind mount).
VANTAGGI DEGLI HYPERVISOR
- si possono emulare sistemi operativi diversi da quello che gira sull'host virtualizzatore (Windows, i BSD, ecc.)
- in generale sono considerati più sicuri, essendo più diffusi e piu' "anziani" (anche se ogni tanto esce qualche grossa vulnerabilita')
VANTAGGI DEI CONTAINER
- le risorse occupate sono sensibilmente minori
- se ne possono installare molti di più su un determinato hardware
- sono molto più maneggevoli (tempi di avvio e spegnimento veloci, provisioning piu' semplice)
Cos'e' Libvirt?
E' una libreria scritta in C per gestire macchine virtuali
Gli hypervisor esistenti sono dinamici e spesso le interfacce da linea di comando cambiano o si evolvono: il vantaggio di libvirt e' che si puo' collegare a quasi tutti gli hypervisor esistenti offrendo un'interfaccia, una API e dei file di configurazione consistenti.
I file di configurazione sono scritti in xml.
A seconda dell'hypervisor sottostante non sono supportate tutte le funzionalita' ( tabella riassuntiva del supporto ).

demoni
libvirtd
fa tutto il lavoro
virtlogd
gestisce i log dei domini tramite socket dedicato: anche se e' accessibile solo tramite il demone principale e' stato deciso di usare un demone separato per evitare problemi derivanti dall'indisponibilita' dello stesso (riavvio, ecc.)
virtlockd
gestisce i lock sulle risorse assegnate ai domini tramite socket dedicato: anche se e' accessibile solo tramite il demone principale e' stato deciso di usare un demone separato per evitare problematiche analoghe a quelle di virtlogd.
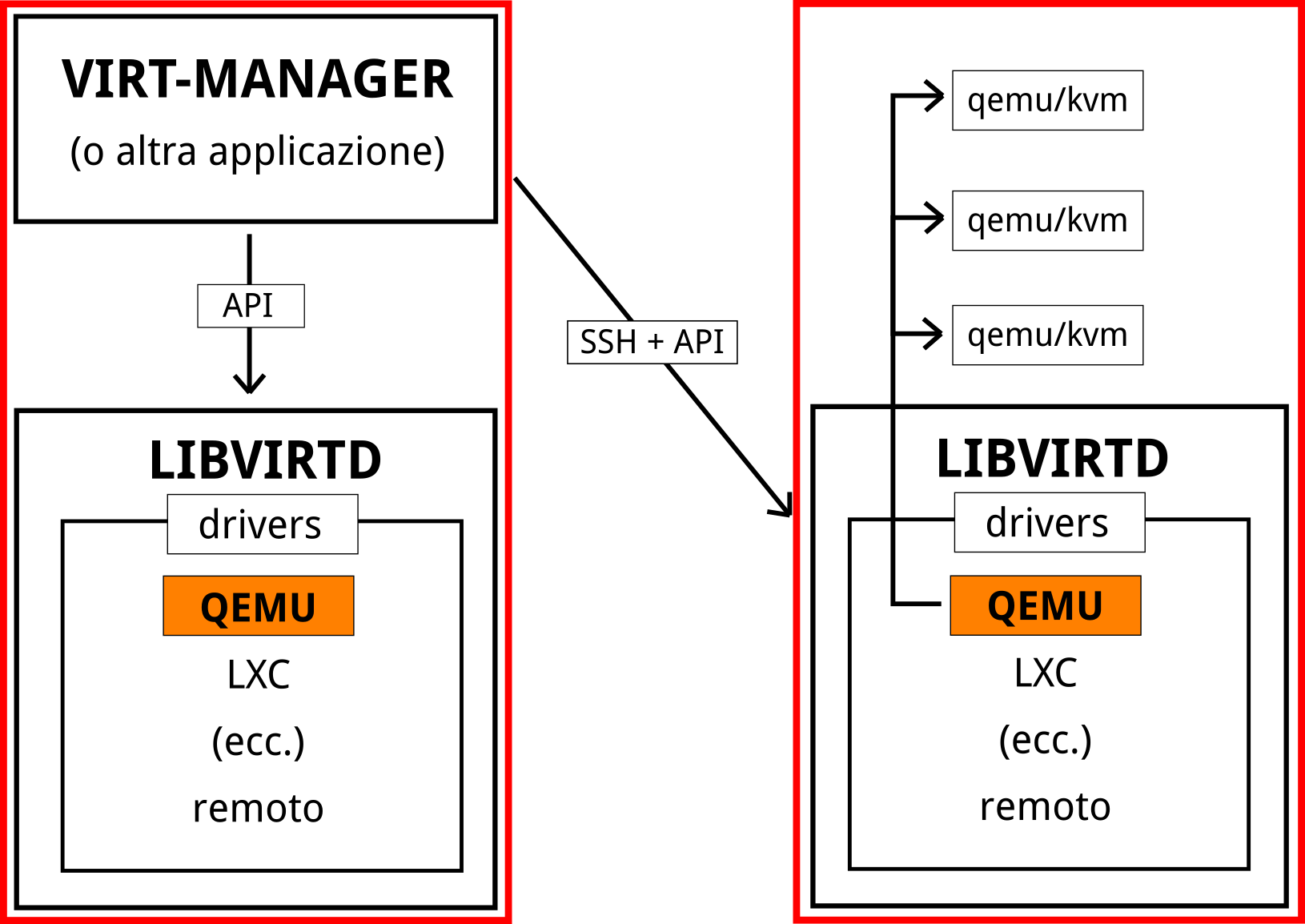
Come funziona libvirt?
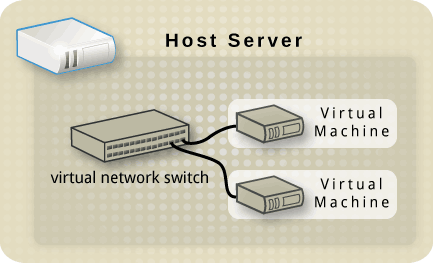
RETI VIRTUALI
Libvirt per default configura un network che usa NAT e le macchine virtuali sono in una rete privata 192.168.122.0/24.
In genere torna utile configurare le interfacce fisiche della macchina come bridge e far usare quelle alle macchine virtuali, che in questo modo possono utilizzare i network a cui sono collegate le interfacce (privato e pubblico, ad esempio).
Ovviamente con iptables (tramite gli nwfilters) si puo' implementare tutto quello che si vuole.
(per chi vuole approfondire e' disponibile il libvirt Networking Handbook)
Gestione da linea di comando: virsh
(nel gergo di libvirt l'host su cui gira e' indicato come "nodo"
e la macchina virtuale e' indicata come "dominio")
attivita' dei domini
start, shutdown, reboot, destroy, dumpxml
save, restore, suspend, resume, migrate
attach-device, attach-disk, attach-interface (e detach-*)
gestione dei dischi
(pool-*) list, info, dumpxml, define, edit, start, destroy,refresh
(vol-*) list, info, clone, create, delete, resize
gestione delle reti virtuali (net-*)
list, info, dumpxml, define, edit, start, destroy
monitoraggio dei domini (dom*)
informazioni sul nodo e l'hypervisor
interfacce di rete sull'host (iface-*)
filtri di rete (nwfilter-*)
periferiche dei nodi (nodedev-*)
gestione dei secret (secret-*)
snapshot (snapshot-*)
# virsh --help
virsh [options]... [<command_string>]
virsh [options]... <command> [args...]
options:
-c | --connect=URI hypervisor connection URI
-d | --debug=NUM debug level [0-4]
-e | --escape <char> set escape sequence for console
-h | --help this help
-k | --keepalive-interval=NUM
keepalive interval in seconds, 0 for disable
-K | --keepalive-count=NUM
number of possible missed keepalive messages
-l | --log=FILE output logging to file
-q | --quiet quiet mode
-r | --readonly connect readonly
-t | --timing print timing information
-v short version
-V long version
--version[=TYPE] version, TYPE is short or long (default short)
commands (non interactive mode):
Domain Management (help keyword 'domain')
attach-device attach device from an XML file
attach-disk attach disk device
attach-interface attach network interface
autostart autostart a domain
blkdeviotune Set or query a block device I/O tuning parameters.
blkiotune Get or set blkio parameters
blockcommit Start a block commit operation.
blockcopy Start a block copy operation.
blockjob Manage active block operations
blockpull Populate a disk from its backing image.
blockresize Resize block device of domain.
change-media Change media of CD or floppy drive
console connect to the guest console
cpu-stats show domain cpu statistics
create create a domain from an XML file
define define (but don't start) a domain from an XML file
desc show or set domain's description or title
destroy destroy (stop) a domain
detach-device detach device from an XML file
detach-device-alias detach device from an alias
detach-disk detach disk device
detach-interface detach network interface
domdisplay domain display connection URI
domfsfreeze Freeze domain's mounted filesystems.
domfsthaw Thaw domain's mounted filesystems.
domfsinfo Get information of domain's mounted filesystems.
domfstrim Invoke fstrim on domain's mounted filesystems.
domhostname print the domain's hostname
domid convert a domain name or UUID to domain id
domif-setlink set link state of a virtual interface
domiftune get/set parameters of a virtual interface
domjobabort abort active domain job
domjobinfo domain job information
domname convert a domain id or UUID to domain name
domrename rename a domain
dompmsuspend suspend a domain gracefully using power management functions
dompmwakeup wakeup a domain from pmsuspended state
domuuid convert a domain name or id to domain UUID
domxml-from-native Convert native config to domain XML
domxml-to-native Convert domain XML to native config
dump dump the core of a domain to a file for analysis
dumpxml domain information in XML
edit edit XML configuration for a domain
event Domain Events
inject-nmi Inject NMI to the guest
iothreadinfo view domain IOThreads
iothreadpin control domain IOThread affinity
iothreadadd add an IOThread to the guest domain
iothreadset modifies an existing IOThread of the guest domain
iothreaddel delete an IOThread from the guest domain
send-key Send keycodes to the guest
send-process-signal Send signals to processes
lxc-enter-namespace LXC Guest Enter Namespace
managedsave managed save of a domain state
managedsave-remove Remove managed save of a domain
managedsave-edit edit XML for a domain's managed save state file
managedsave-dumpxml Domain information of managed save state file in XML
managedsave-define redefine the XML for a domain's managed save state file
memtune Get or set memory parameters
perf Get or set perf event
metadata show or set domain's custom XML metadata
migrate migrate domain to another host
migrate-setmaxdowntime set maximum tolerable downtime
migrate-getmaxdowntime get maximum tolerable downtime
migrate-compcache get/set compression cache size
migrate-setspeed Set the maximum migration bandwidth
migrate-getspeed Get the maximum migration bandwidth
migrate-postcopy Switch running migration from pre-copy to post-copy
numatune Get or set numa parameters
qemu-attach QEMU Attach
qemu-monitor-command QEMU Monitor Command
qemu-monitor-event QEMU Monitor Events
qemu-agent-command QEMU Guest Agent Command
reboot reboot a domain
reset reset a domain
restore restore a domain from a saved state in a file
resume resume a domain
save save a domain state to a file
save-image-define redefine the XML for a domain's saved state file
save-image-dumpxml saved state domain information in XML
save-image-edit edit XML for a domain's saved state file
schedinfo show/set scheduler parameters
screenshot take a screenshot of a current domain console and store it into a file
set-lifecycle-action change lifecycle actions
set-user-password set the user password inside the domain
setmaxmem change maximum memory limit
setmem change memory allocation
setvcpus change number of virtual CPUs
shutdown gracefully shutdown a domain
start start a (previously defined) inactive domain
suspend suspend a domain
ttyconsole tty console
undefine undefine a domain
update-device update device from an XML file
vcpucount domain vcpu counts
vcpuinfo detailed domain vcpu information
vcpupin control or query domain vcpu affinity
emulatorpin control or query domain emulator affinity
vncdisplay vnc display
guestvcpus query or modify state of vcpu in the guest (via agent)
setvcpu attach/detach vcpu or groups of threads
domblkthreshold set the threshold for block-threshold event for a given block device or it's backing chain element
guestinfo query information about the guest (via agent)
Domain Monitoring (help keyword 'monitor')
domblkerror Show errors on block devices
domblkinfo domain block device size information
domblklist list all domain blocks
domblkstat get device block stats for a domain
domcontrol domain control interface state
domif-getlink get link state of a virtual interface
domifaddr Get network interfaces' addresses for a running domain
domiflist list all domain virtual interfaces
domifstat get network interface stats for a domain
dominfo domain information
dommemstat get memory statistics for a domain
domstate domain state
domstats get statistics about one or multiple domains
domtime domain time
list list domains
Host and Hypervisor (help keyword 'host')
allocpages Manipulate pages pool size
capabilities capabilities
cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU
cpu-compare compare host CPU with a CPU described by an XML file
cpu-models CPU models
domcapabilities domain capabilities
freecell NUMA free memory
freepages NUMA free pages
hostname print the hypervisor hostname
hypervisor-cpu-baseline compute baseline CPU usable by a specific hypervisor
hypervisor-cpu-compare compare a CPU with the CPU created by a hypervisor on the host
maxvcpus connection vcpu maximum
node-memory-tune Get or set node memory parameters
nodecpumap node cpu map
nodecpustats Prints cpu stats of the node.
nodeinfo node information
nodememstats Prints memory stats of the node.
nodesuspend suspend the host node for a given time duration
sysinfo print the hypervisor sysinfo
uri print the hypervisor canonical URI
version show version
Checkpoint (help keyword 'checkpoint')
checkpoint-create Create a checkpoint from XML
checkpoint-create-as Create a checkpoint from a set of args
checkpoint-delete Delete a domain checkpoint
checkpoint-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain checkpoint
checkpoint-edit edit XML for a checkpoint
checkpoint-info checkpoint information
checkpoint-list List checkpoints for a domain
checkpoint-parent Get the name of the parent of a checkpoint
Interface (help keyword 'interface')
iface-begin create a snapshot of current interfaces settings, which can be later committed (iface-commit) or restored (iface-rollback)
iface-bridge create a bridge device and attach an existing network device to it
iface-commit commit changes made since iface-begin and free restore point
iface-define define an inactive persistent physical host interface or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file
iface-destroy destroy a physical host interface (disable it / "if-down")
iface-dumpxml interface information in XML
iface-edit edit XML configuration for a physical host interface
iface-list list physical host interfaces
iface-mac convert an interface name to interface MAC address
iface-name convert an interface MAC address to interface name
iface-rollback rollback to previous saved configuration created via iface-begin
iface-start start a physical host interface (enable it / "if-up")
iface-unbridge undefine a bridge device after detaching its slave device
iface-undefine undefine a physical host interface (remove it from configuration)
Network Filter (help keyword 'filter')
nwfilter-define define or update a network filter from an XML file
nwfilter-dumpxml network filter information in XML
nwfilter-edit edit XML configuration for a network filter
nwfilter-list list network filters
nwfilter-undefine undefine a network filter
nwfilter-binding-create create a network filter binding from an XML file
nwfilter-binding-delete delete a network filter binding
nwfilter-binding-dumpxml network filter information in XML
nwfilter-binding-list list network filter bindings
Networking (help keyword 'network')
net-autostart autostart a network
net-create create a network from an XML file
net-define define an inactive persistent virtual network or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file
net-destroy destroy (stop) a network
net-dhcp-leases print lease info for a given network
net-dumpxml network information in XML
net-edit edit XML configuration for a network
net-event Network Events
net-info network information
net-name convert a network UUID to network name
net-start start a (previously defined) inactive network
net-undefine undefine a persistent network
net-update update parts of an existing network's configuration
net-uuid convert a network name to network UUID
net-port-list list network ports
net-port-create create a network port from an XML file
net-port-dumpxml network port information in XML
net-port-delete delete the specified network port
Node Device (help keyword 'nodedev')
nodedev-create create a device defined by an XML file on the node
nodedev-destroy destroy (stop) a device on the node
nodedev-detach detach node device from its device driver
nodedev-dumpxml node device details in XML
nodedev-list enumerate devices on this host
nodedev-reattach reattach node device to its device driver
nodedev-reset reset node device
nodedev-event Node Device Events
Secret (help keyword 'secret')
secret-define define or modify a secret from an XML file
secret-dumpxml secret attributes in XML
secret-event Secret Events
secret-get-value Output a secret value
secret-list list secrets
secret-set-value set a secret value
secret-undefine undefine a secret
Snapshot (help keyword 'snapshot')
snapshot-create Create a snapshot from XML
snapshot-create-as Create a snapshot from a set of args
snapshot-current Get or set the current snapshot
snapshot-delete Delete a domain snapshot
snapshot-dumpxml Dump XML for a domain snapshot
snapshot-edit edit XML for a snapshot
snapshot-info snapshot information
snapshot-list List snapshots for a domain
snapshot-parent Get the name of the parent of a snapshot
snapshot-revert Revert a domain to a snapshot
Storage Pool (help keyword 'pool')
find-storage-pool-sources-as find potential storage pool sources
find-storage-pool-sources discover potential storage pool sources
pool-autostart autostart a pool
pool-build build a pool
pool-create-as create a pool from a set of args
pool-create create a pool from an XML file
pool-define-as define a pool from a set of args
pool-define define an inactive persistent storage pool or modify an existing persistent one from an XML file
pool-delete delete a pool
pool-destroy destroy (stop) a pool
pool-dumpxml pool information in XML
pool-edit edit XML configuration for a storage pool
pool-info storage pool information
pool-list list pools
pool-name convert a pool UUID to pool name
pool-refresh refresh a pool
pool-start start a (previously defined) inactive pool
pool-undefine undefine an inactive pool
pool-uuid convert a pool name to pool UUID
pool-event Storage Pool Events
pool-capabilities storage pool capabilities
Storage Volume (help keyword 'volume')
vol-clone clone a volume.
vol-create-as create a volume from a set of args
vol-create create a vol from an XML file
vol-create-from create a vol, using another volume as input
vol-delete delete a vol
vol-download download volume contents to a file
vol-dumpxml vol information in XML
vol-info storage vol information
vol-key returns the volume key for a given volume name or path
vol-list list vols
vol-name returns the volume name for a given volume key or path
vol-path returns the volume path for a given volume name or key
vol-pool returns the storage pool for a given volume key or path
vol-resize resize a vol
vol-upload upload file contents to a volume
vol-wipe wipe a vol
Virsh itself (help keyword 'virsh')
cd change the current directory
echo echo arguments
exit quit this interactive terminal
help print help
pwd print the current directory
quit quit this interactive terminal
connect (re)connect to hypervisor
(specify help <group> for details about the commands in the group)
(specify help <command> for details about the command)
Di default l'interfaccia a linea di comando si collega a
software che implementa un particolare sistema di emulazione che permette di ottenere un'architettura informatica nuova e disgiunta in un'altra che si occuperà di ospitarla.
E' stato scritto da Fabrice Bellard, creatore, tra le altre mille cose, anche di ffmpeg.
Dalla sua integrazione col progetto KVM puo' anche operare in modo da utilizzare le estensioni della CPU, se disponibili, attraverso un modulo del kernel al posto dell'emulazione: in questo modo le macchine virtuali sono parecchio piu' reattive ed efficienti.
virsh opera collegato agli hypervisor e vi si connette tramite il suo URI (conformi alle specifiche dell'RFC 2396)
qemu:///system
lxc:///system
xen:///system
vbox:///session
vmware://{vpx,esx,gsx}
hyperv://
si possono definire degli alias nei file di configurazione
uri_aliases = [
"hail=qemu+ssh://root@hail.cloud.example.com/system",
"sleet=qemu+ssh://root@sleet.cloud.example.com/system",
]
ci si puo' collegare a libvirtd tramite socket locale accessibile al gruppo con cui abbiamo deciso di far girare il demone (/var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock e /var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock), ma si puo', in alternativa usare anche un'autentica tramite SASL (utente/password o kerberos).
il vettore di collegamento remoto e' principalmente ssh, ma si puo' usare anche tls o varianti implementative di ssh, come libssh/libssh2, o un collegamento tcp in chiaro (ovviamente sconsigliato se non su reti dedicate).
tramite policykit si puo' restringere l'accesso in modo granulare usando access list
Offre un'interfaccia di programmazione per molti linguaggi:
C
Python
Go
Perl
Objective Caml
Ruby
Java
Php
C#
Dbus
ecc.
CONVERTIRE / MANIPOLARE IMMAGINI DISCO
libguestfs
libreria per accedere e interagire con immagini disco: supporta moltissimi formati.
puo' agire tramite una shell scriptabile, guestfish o una rescue shell interattiva, virt-rescue.
per avere un'idea di quello che puo' fare date un'occhiata alle ricette.
qemu-img convert
supporta diversi formati:
QCOW2 (KVM, Xen), raw, VDI (VirtualBox), VHD (Hyper-V), VMDK (VMware)
qemu-img convert -f raw -O qcow2 image.img image.qcow2
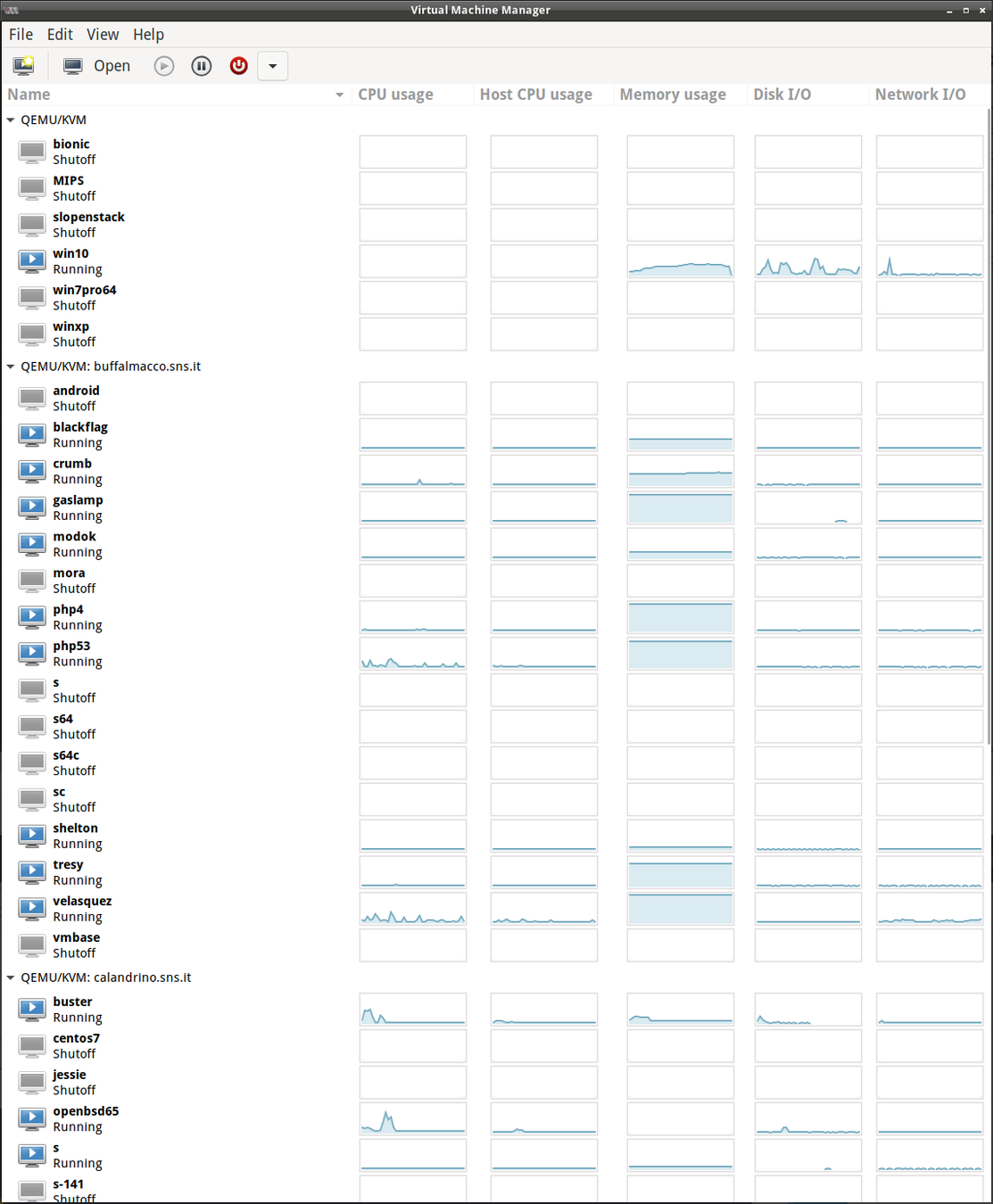
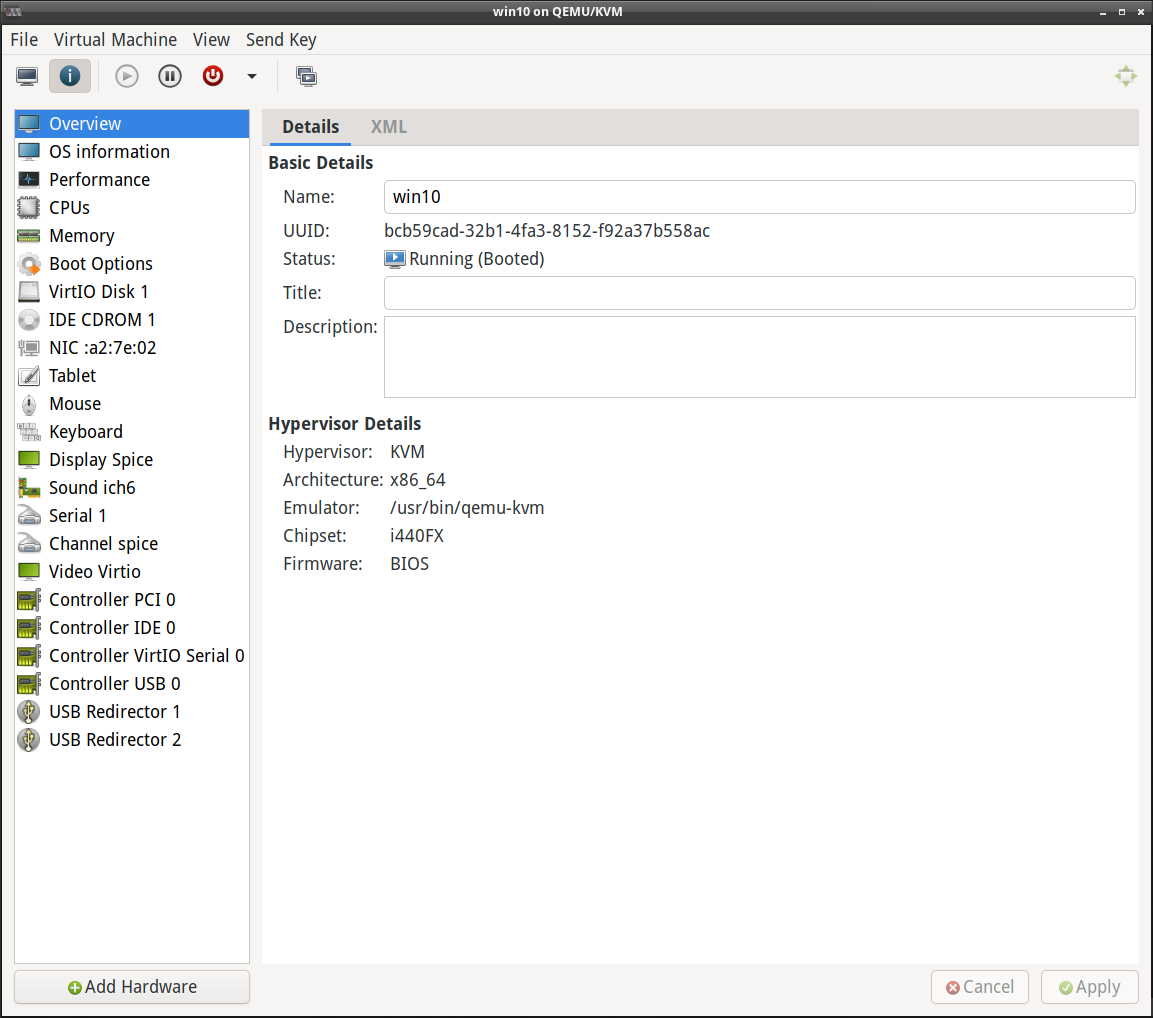
VIRT-MANAGER
GUI principale per l'amministrazione da remoto.
E' pensata principalmente per macchine virtuali che utilizzano KVM, ma funziona anche con container LXC e domini Xen.
Mostra una visione d'insieme dei domini in esecuzione, delle loro prestazioni in tempo reale e delle statistiche sull'utilizzo delle risorse.
Offre procedure guidate per la creazione dei domini e per l'allocazione a quest'ultimi di risorse e di hardware virtuale.
Sono disponibili dei visualizzatori delle console grafiche remote delle macchine virtuali sia tramite il protocollo VNC che quello SPICE.
Riferimenti
Libvirt: https://libvirt.org ( docs )
virt-manager: https://virt-manager.org
qemu: https://www.qemu.org
kvm: https://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page
applicazioni che usano libvirt: https://libvirt.org/apps.html
x ubuntu: https://help.ubuntu.com/community/KVM/Installation
x debian: https://wiki.debian.org/KVM
- SESSIONE PRATICA -
DOMANDE?