Measuring cosmological parameters using Type Ia Supernovae
IDC 452: Seminar Delivery Course
Prajakta Mane
MS19054

- A supernova is a transient astronomical event that occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion.
- Is classified according to the light curves and the absorption lines of different chemical elements that appear in the spectra.
- Type Ia supernovae occur in binary systems in which one of the stars is a white dwarf.
- Have the light curves with a sharp maximum and gradual decline, producing a fairly consistent peak luminosity because of the fixed critical mass at which a white dwarf will explode.
Supernova Type Ia
Why study Type Ia Supernovae?
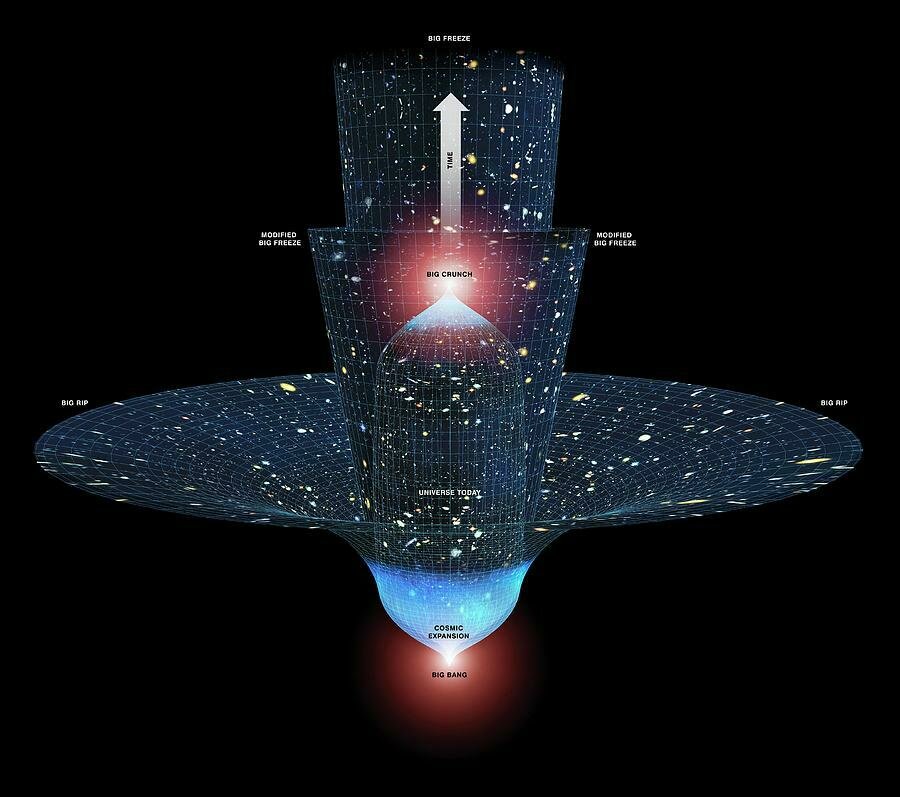
Cosmological parameters governing the evolution of the universe:
∵ First Friedmann Equation
Taylor expanding a(t):
∵ Independent of cosmological
models
∵ The Deceleration parameter
Parameters to be found observationally:
∵ Fluid Equation
- Standard Candles: Type Ia supernovae are the most useful, precise, and mature tools for determining astronomical distances and can provide constraints on value of the Hubble's constant.
The luminosity distance DL is defined as,
L: Standardized luminosity
f: Flux of the standard candle measured on earth
z: Redshift of the standard candle, found from (1+z) = 1/a(t) relation
Collaborations like High-z supernova Search Team, PI: Perlmutter;
Supernova Cosmology Project, PI: Schmidt and Riess
H0 measurement from low-z supernovae,
q0 measurement from high-z supernovae
- Dark Energy: Discovery and constraints
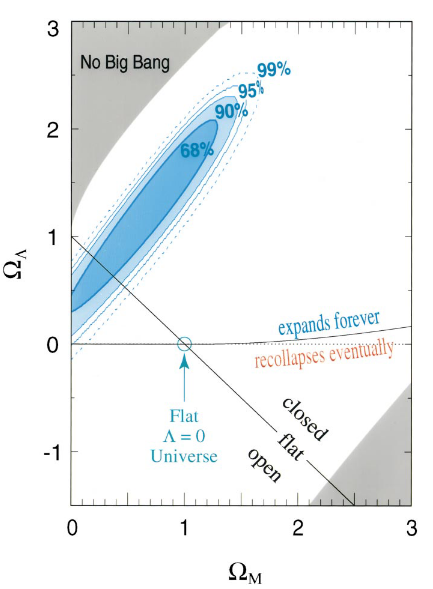
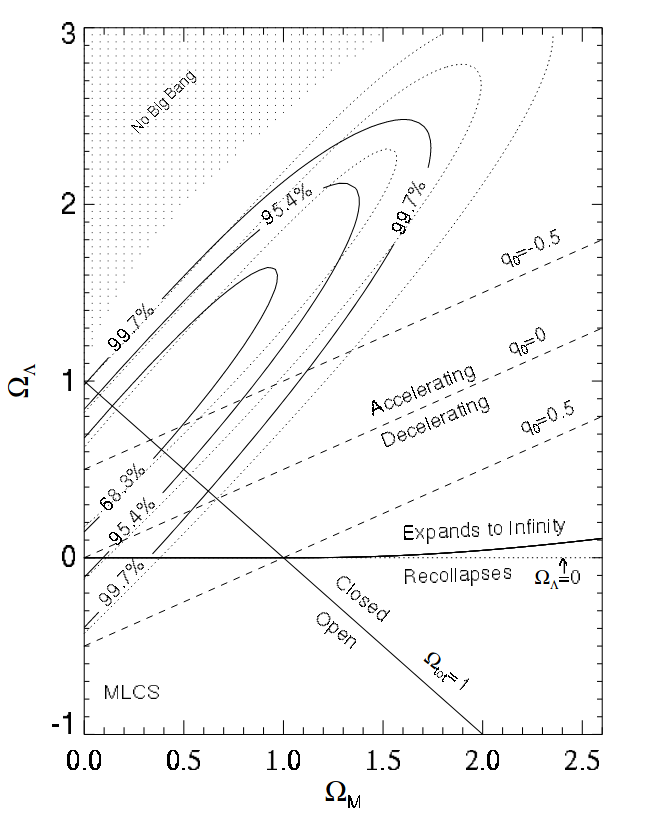
Riess et al, 1999
Permutter et al, 1999
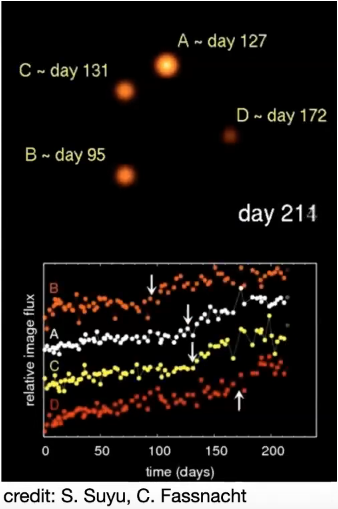
- Independent Method to Constrain the value of the Hubble's Constant: The time-delay measurements of the lensed, multiply imaged supernovae.
Collaborations like H0LiCoW, COSMOGRAIL, TDCOSMO
References:
1. Perlmutter, S. and Schmidt B., “Measuring Cosmology with Supernovae.” Lecture Notes in Physics 598 (2003): 195-217.
2. Barbara Ryden, "Introduction to Cosmology" (2003): Chapter 7.
3. Riess, A., et al, "Observational Evidence from Supernovae for an Accelerating Universe and a Cosmological Constant" (1998), Astrophys. J.
4. Perlmutter, S., et al., "Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 High-Redshift Supernovae", (1999), Astrophys. J.
5. Refsdal S., "On the Possibility of Determining Hubble's Parameter and the Masses of Galaxies from the Gravitational Lens Effect" (1964), MNRAS.
Thank You


Scan Me!

Want to know more about me?