Char Data Type, Character Arrays & C++ Strings


Agenda
- Char data type
- Functions on Char
- Char Array / C-Style Strings
- String Literals
- Functions on Char Array
- C++ Strings
- Functions on Strings

Character Datatype

- The char data type is used to store a single character.
- The character must be surrounded by single quotes, like 'A' or 'c':
LIVE DEMO
- ASCII was the first character set (encoding standard) used between computers on the Internet.
-
ASCII is a 7-bit character set containing 128 characters.
-
It contains the numbers from 0-9, the upper and lower case English letters from A to Z, and some special characters.
🚀 ASCII Character Set
LIVE DEMO
Character Functions - <cctype> library
isaplha(c)
isdigit(c)
islower(c)
isupper(c)
isspace(c)
. . .
Testing Functions
Character Functions - <cctype> library
toupper(c)
tolower(c)
Conversion Functions
LIVE DEMO
Reading a Char using cin.get() vs cin
- cin.get() reads all possible type of characters including whitespaces.
- Generally, cin with an extraction operator (>>) terminates when whitespace is found. However, cin.get() reads a string with the whitespace.

Shortest Path
Suppose you want to go to a location, located at (X,Y) starting from origin (0,0). Your friend tells you a long way by telling the steps you should walk in each direction (N,W,E or S). Find the shortest path. Input & Output is a string. Refer Example:
Input: NNNEEWS
Output: NNE


ABCD Pattern
Print a pattern of the following form.
AA
ABBA
ABCCBA
ABCDDCDA

Arrays of Characters /
C-Style Strings

- Sequence of characters stored in continguous memory (character array)
- Need to explicitly terminate by a null character.
- Character Arrays support read, write & update.
🚀 C-Style Strings / Char Array
- Sequence of characters written in double quotes.
- Stored in read only memory
- Terminated by a Null Character
String Literals
Understanding the term "null-terminated"
char name[ ] {"Prateek"}
- Problems
- Can't add more letters to an array
🚀 Creating String Variables (Char Array)
char name[10] {"Hello World"}
🚀 Creating String Variables (Char Array)
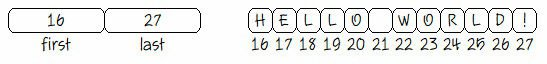
char name[10];
🚀 Creating C-style String Variables (Char Array)
name = "Prateek"; //Error array name and string literal are location in memory
strcpy(name, "Prateek") // Allowed
char name[10]; //no null initialisation by default
🚀 Functions for C-style String Variables
- Length
- Copy
- Concatenation
- Searching
- and more
char name[10];
- Input using "cin"
- Input using "cin.get()"
- Input using "getline()"
🚀 Input/Output
char name[10]; //no null initialisation by default
-
Printing name can possibly print garbage letters until a null is found in the memory.
- So either initialise the array, using a string literal or take input from the user.
🚀 Input/Output
🚀 Live Demo
//Include the Header file
#include<cstring>
char str[100];
strcpy(str, "Hello"); //Copy
strcat(str," world"); // Concatenatio
cout << strlen(str) <<endl; // length
strcmp(str, "anothe string"); //comparison
cstdlib
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout<<"Hello World!";
return 0;
}Recap
cstring proivides functions to operate on character arrays.
cctype provides us functions to operate on characters.
LIVE DEMO
C++ Strings

C++ Strings
string class available in C++ Standard Template Library.
- contiguous in memory
- dynamic size can grow & shrink during run time ⭐️
- better than character arrays, due to fixed size of char arrays
- support lot of useful member functions, no need to write functions from scratch
- support operators like (+, =, <, <=, ==, != , [] ...)
- safer, provide methods for bound checking
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s1;
string s2{"Hello"};
string s3{s2};
string s4{"Hello",3}; //Hel
string s6{s2, 0,2} // He
string s5(3,'X'); //XXXString Initialisation
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s1;
cin>>s1;
getline(cin,s1); //Reads and stores in s1
getline(cin,s1,'$'); //Reads and stores in s1String Input cin vs getline()
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s1;
s1 = "Hello World";
string s2 = "Hi";
s2 = s1; //Overwrite
String Assignment = Operator
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string firstname = "Prateek"
string lastname = "Narang"
string fullname = firstname + " " + lastname;
String Concatenation + Operator
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string firstname = "Prateek"
string lastname = "Narang"
firstname.at(0)
firstname[0]
String Accessing Characters
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string firstname = "Prateek"
string lastname = "Narang"
for(char c:firstname){
cout << c <<endl;
}
for(int c:firstname){
cout << c <<endl;
}
Range Based Loops
Comparison, Concatenation Operators
==
!=
>
>=
<
<=
+
+=
Substrings
string_object.substr( index, length);
Find
string_object.find(other_string);
Concatentation
+=
Next Step - Solve a Problem !

🚀 Average the Marks
Given marks of a student in 3 subjects - Physics, Chemistry and Maths - print their average.
Sample Input
Physics = 90
Maths = 75
Chemistry = 68
Sample Output
77.66
C++ Digger Deeper


Digging Deeper ...
- Preprocessor Directive
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- main()
- Namespaces
- The preprocessors are the directives, which give instructions to the compiler to preprocess some code before actual compilation starts.
- The directive begins with '#'
- The actual code is compiled by compiler only.
🚀 Preprocessor Directive
#include
directive tells the compiler to include the header file in the source code.
#include<iostream>
#incldue<algorithm>
#include<stack>
int main(){
....
}#define
directive tells the compiler to create symbolic constants. The symbolic constant is called a macro.
All subsequent occurrences of macro in that source code will be replaced by its replacement text before the program is compiled.
#define PI 3.14
int main(){
//Area of Circle
int r = 5;
float area = PI*r*r;
return 0;
}#define
directive tells the compiler to create symbolic constants. The symbolic constant is called a macro.
All subsequent occurrences of macro in that source code will be replaced by its replacement text before the program is compiled.
#define PI 3.14
#define AREA(l,b) (l*b)
int main(){
//Area of Rectangle
int area = AREA(10,5);
return 0;
}- Both an identifier and a variable are the names allotted by users to a particular entity in a program.
-
The identifier is only used to identify an entity uniquely in a program at the time of execution whereas, a variable is a name given to a memory location, that is used to hold a value.
🚀 Identifiers

float calculateMarks(int p,int c, int m){
float average = (p+c+m)/3;
return average;
}Identify the Identifiers
- Keywords are the word that have a special meaning for the compiler.
- These keywords can't be used as an identifier.
- C++ has about 95 reserved words.
🚀 Keywords
auto double int struct
break else long switch
case enum register typedef
char extern return union
const float short unsigned
continue for signed void
default goto sizeof volatile
do if static while
32 Keywords common in C++ and C
asm dynamic_cast namespace reinterpret_cast
bool explicit new static_cast
catch false operator template
class friend private this
const_cast inline public throw
delete mutable protected true
try typeid typename using
using virtual wchar_t
Some new Keywords in C++
int factorial(int n){
if(n<0){
cout << "Invalid Input";
return -1;
}
int ans = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ans = ans*i;
}
return ans;
}
Identify the Keywords
Main Function

- Every C/C++ Program stars executing with main.
- There is exactly 1 main function.
- return 0, indicates successful execution of main.
🚀 main() function
int main(){
//Execution stars from here
// Your Work
return 0;
}int main(){
//logic
return 0;
}Most common way
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
//logic
return 0;
}Command Line Apps
- main is not a keyword in C/C++.
- main is not predefined, but it is predeclared.
- In C++, your code is linked against a small runtime library that constitutes the true starting point of your program.
- It is this small library calls a function called main--it's hardcoded to do so.
- Your code runs because you supply the code inside main, also called function definition.
Main Recap
- Naming conflicts can arise if you use multiple 3rd party libraries in same program.
- Namespaces are used to resolve naming conflicts.
- std is the name for the standard C++ Namespace.
- Writing std::cout will tell the compiler to use "cout" from standard namespace.
🚀 Namespaces
Third party Namespace
using namespace cv;
To avoid data structure and function name conflicts with other libraries, OpenCV has its own namespace: cv.

#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
cout<<"Welcome to Image Editing App";
Mat image = imread("Bob.jpg");
return 0;
}Example of Third Party Namespace
- Comment is text that is normally used to annotate code for future reference.
- Comment is ignored by compiler but that is useful for programmers.
- You can use comments in testing to make certain lines of code inactive.
- We can write single line or multi-line comments in a C++ Program.
🚀 Comments
🚀 Summary
- Keywords have special meaning for the compiler.
- Identifiers are used to name an entity, variable name is also a type of identifier.
- Header files include some pre-written code required to execute our program.
- Program execution always starts with main()
- { } are used to enclose a block (function, if, while etc.}.
- C++ Compiler Ignores whitespace (space, carriage returns, linefeeds, tabs, vertical tabs, etc.)
- Output using cout
- Input using cin
- Comments (// & /*… */)
- Every statement must end with a semicolon ;
Variables & Constants

Variables
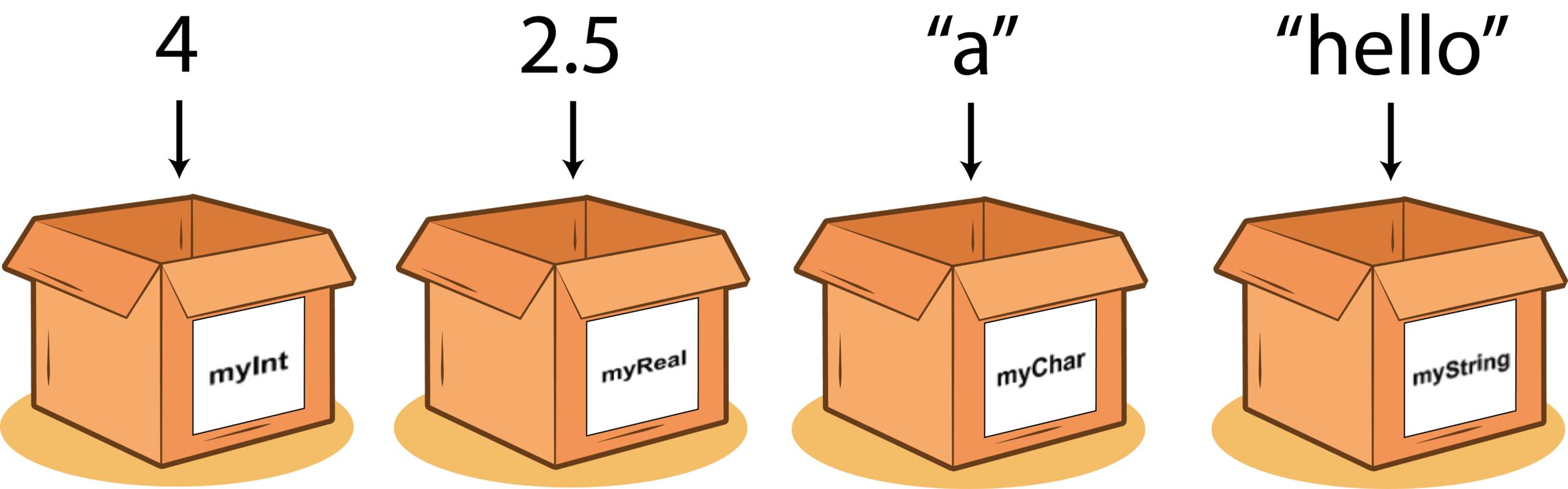
Variable name: A label for a memory location
Value: The something that would be
stored in a variable
Storage: A place where data can be stored
Declaration: Announcing a variable (usually) at the beginning of a program
Naming convention: A set of rules about the names of variables
Assignment: Giving (setting) a variable a value
🚀 Variables
🚀 Naming Variables
- For variable name we can use uppercase and lowercase letters, digits from 1 to 9 and underscore(_).
- First character must be underscore or letter.
- C++ is strongly typed language. So every variable needs to be declare before using it.
//Valid Names
double simple_interest;
int student_age;
float Student_percentile;
int prateek123;
//Invalid Names
int 123_age;
- Variables when just declared have garbage value until they are assigned a value for the first time.
- We can assign a specific value from the moment variable is declared, called as initialization of variable.
//Initialisation of Variable
float a = 10;
//Declaration
int b;
//Assignment
b = 20;Initialisation
🚀 Data-types
Boolean - boolean
Character - char
Integer – int
Floating Point – float
Double Floating Point – double
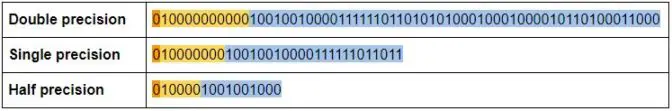
🚀 Binary Number System
🚀 Data-type Modifiers
Several of the basic types can be modified using one or more of these type modifiers
signed
unsigned
short
long
int marks;
unsigned int roll_number;
unsigned long long int large_factorial;
short int age;
How storage works?

Constants
Constants are variables or values in programming language which cannot be modified once they are defined.
const float pi = 3.14
const int loan_period = 10
//Don't do this, Initialisation is Must for constants
const int x;
x = 5;
// Assignment is not allowed here
Using a const keyword
Using preprocessor directive
#define PI 3.14
#define LOAN_PERIOD 10Operators, Statements & Expressions

Conditional Statements

Conditional Statements
// Single If
int marks = 90;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party!”;
}
Conditional Statements
If-else block
// If-Else Block
int marks = 70;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party”;
}
else{
cout<< “Work hard next time“;
}

Conditional Statements
If-else-if-else block
// If-Else Block
int marks = 70;
if (marks > 80) {
cout << “Let's Party”;
}
else if(marks>60){
cout<<"Good Job";
}
else{
cout<<"Work hard next time";
}
Challenge 🔥
Electricity Bill Calculator : Given total consumption of a
household in units, write a program to estimate the total bill amount as per the table.
| Units | Charges |
|---|---|
| 1 to 100 units | Free |
| 100 to 200 units | Rs. 5/unit |
| 200 to 300 units | Rs.10/unit |
| 300+ units | Rs.12/unit |

Ternary Operator
Switch Case

switch(expression) {
case x:
// code block
break;
case y:
// code block
break;
default:
// code block
}Loops

While Loop

While Loop

//Init
while(..condition is true ..){
//execute some stuff
//update
}Examples! 👨💻
For Loop

for(init;stopping_condition;update_statement){
//execute some stuff
}For Loop
for(int calories=0;calories<100;calories = calories+1){
//execute some stuff
cout<<"Run 1 step";
}Examples! 👨💻
Given N, Print following pattern (For Example N = 5)
*
***
*****
*******
🚀 Challenge - Star Pyramid
🚀 Challenge - ABCD Pattern
Given N, Print following pattern (For Example N = 5)
ABCDEEDCBA
ABCDDCBA
ABCCBA
ABBA
AA
🚀 Print All Prime
Given N, Print all Prime Numbers upto N.
For Example - N = 10
Output - [2,3,5,7]
Do While Loop

//init
do(){
//execute some stuff
}
while(condition);Do While Loop vs While

Do While Loop vs While
//init
do(){
//execute some stuff
}
while(condition);
//Exit Controlled Loop//init
//Entry Controlled Loop
while(condition){
//execute some stuff
}
Break and Continue
int calories = 0;
while(calories<20){
if(calories==15){
cout<<"Stop the Workout";
break;
}
cout<<calories<<" ";
calories = calories + 1;
}
cout<<"Complete";
int calories = 0;
while(calories<20){
if(calories==15){
cout<<"Stop the Workout";
calories = calories + 1;
continue;
}
cout<<calories<<" ";
calories = calories + 1;
}
cout<<"Complete";
Break Statement
int calories = 0;
while(calories<20){
if(calories==15){
cout<<"Stop the Workout";
break;
}
cout<<calories<<" ";
calories = calories + 1;
}
cout<<"Complete";
Stop the loop when executed.
Continue Statement
int calories = 0;
while(calories<20){
if(calories==15){
cout<<"Go to the next Step";
calories = calories + 1;
continue;
}
cout<<calories<<" ";
calories = calories + 1;
}
cout<<"Complete";
Control jumps to the beginning of the loop for next iteration
Practice Problems
- Print all Fibonacci number less than N
- Write code to print the following pattern
1
232
34543
4567654
567898765