Functions & Memory in Python 🐍
Lecture
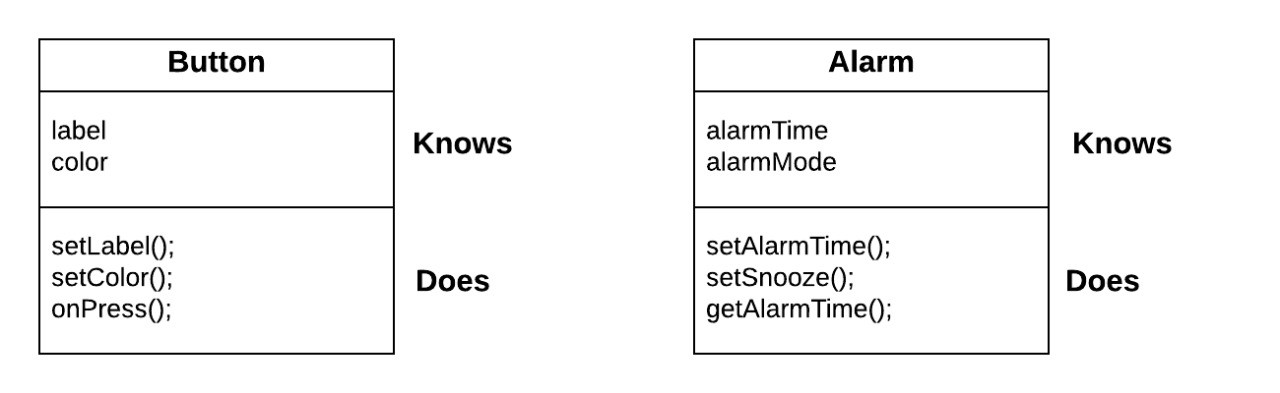
| Functions |
|
Objects in Python Life & Death on Heap |
| Call Stack |
| Stack vs Heap Memory |
| Functions |
| Garbage Collection |
| Problems |
id() function
What happens when you write?
Text
x = 10
y = 10
print(id(x))
print(id(y))Both 'x' and 'y' refer to same object.
Text
x = 10
y = 10
print(id(x))
print(id(y))- Python optimises memory utilisation by allocating the same object reference to a new variable if object has same value.
- A Python program accesses data values through references. A reference is a name that refers to the specific location in memory of a value (object). The object to which a reference is bound at a given time does have a type, however. Any given reference may be bound to objects of different types during the execution of a program.
Everything is a object in Python
Functions
Functions

A Function is a block of code which only runs when it is called.
You can pass data, known as parameters, into a function.
Example 👨💻
def sayHello():
print("hello world")
sayHello()Data can be passed to functions using one or more parameters. Parameters can have default values.
Functions can also return objects
Why Create Methods.
- Methods increase the reusability of code.
- Code looks more modular & organised.
Problems-I 🚀
Write a method to find absolute value of a number.
Problems-II 🚀
Write methods to convert
- decimal number to binary number.
- binary number to a decimal number
Stack & Heap Memory Models
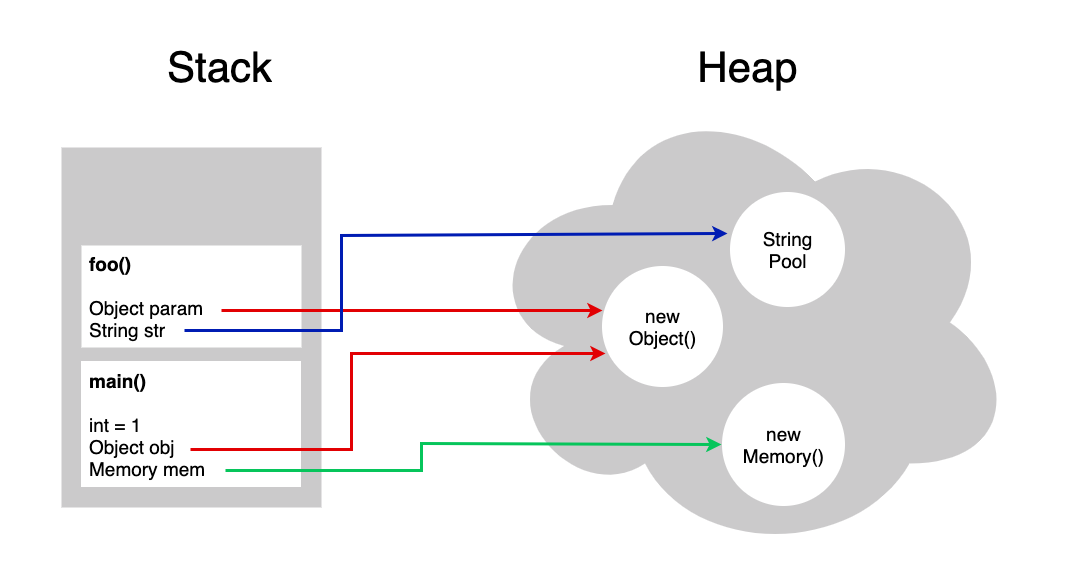
Objects live on the Heap!
Stack & Heap Memory
Garbage Collector!

Garbage Collection deals with finding and deleting the garbage from memory.
However, in reality, Garbage Collection tracks each and every object available in the heap space and removes unused ones.
In Java, GC works in two simple steps known as Mark and Sweep:
Mark – it is where the garbage collector identifies which pieces of memory are in use and which are not
Sweep – this step removes objects identified during the “mark” phase
In Python, GC works by reference counting algorithm. Memory is freed up when the reference count becomes zero for that object.
Advantages
- No manual memory allocation/deallocation handling because unused memory space is automatically handled by GC
- Automatic Memory Leak management (GC on its own can't guarantee the full proof solution to memory leaking, however, it takes care of a good portion of it)
Disadvantages
- Since GC has to keep track of object reference creation/deletion, this activity requires more CPU power than the original application. It may affect the performance of requests which required large memory
- Programmers have no control over the scheduling of CPU time dedicated to freeing objects that are no longer needed
- Automatised memory management will not be as efficient as the proper manual memory allocation/deallocation
Prime Number Print
