Variables & Datatypes

Prateek Narang

Topics

-
Variables
-
Input & Output
-
Airthmetic Operators
-
Datatypes
-
Datatype Modifiers
-
SizeOf Operator



Every program has set of instructions which work on some data.
Output

Input

Logic

"Ice Cream"

Cricket, 6 AM
9 PM,
"Meeting"
"Alia"

Variables!



Variables
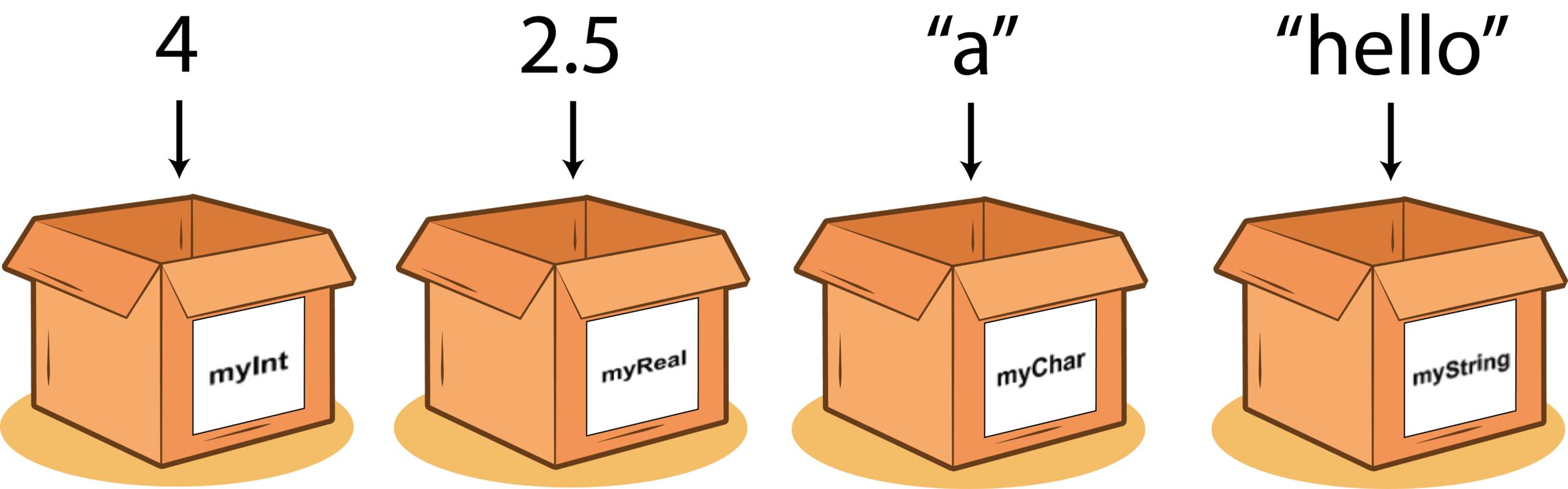
Variables are the buckets in the memory that hold some type of data.

Variable name: A label for a memory location
Value: The something that would be stored in a variable
Storage: A place where data can be stored
Declaration: Announcing a variable (usually) at the beginning of a program
Naming convention: A set of rules about the names of variables
Assignment: Giving (setting) a variable a value

Variables


// Valid names
int topics = 3
int marks = 20
int student_1 = 5
// Invalid Names
1_student = 8;Naming Convention
For variable name we can use uppercase and lowercase letters, digits from 1 to 9 and underscore(_).
First character must be underscore or letter.
C++ is strongly typed language. So every variable needs to be declare before using it


Variable Initialisation
Variables when just declared have garbage value until they are assigned a value for the first time.
We can assign a specific value from the moment variable is declared, called as initialisation of variable.
// Declare
int marks;
// Declare + Assign (Init)
int x = 10;

Variable Assignment
We can assign a specific value to the variable using '=' operator, called as assignment of a value to variable.
Variables by default contain a garbage value.
// Declare
int marks;
// Assignment
marks = 20;
// Assignment
marks = marks + 10;

Basic Airthmetic Operators
We can perform basic operations on variables using operators
+ Addition
- Subtraction
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Modulo
// Declare
int marks;
// Assignment
marks = 20 + 10;
// Assignment
marks = marks + 5;

Datatypes
Data comes in different types - such as integers, floats, string, boolean values etc. When you create the variable, you reserve some space in memory.
Memory is allocated based on the variable's data type. The amount of memory required depends on the data type.
// Here, int, char, bool are the datatypes
int marks = 80;
char letter = 'A';
bool isRainy = false;

Basic Data Types (Variables)
- int
- char
- bool
- float
- double
- void


sizeof()
The sizeof is a keyword, but it is a compile-time operator that determines the size, in bytes, of a variable or data type.
The sizeof operator can be used to get the size of variables, classes, structures like arrays, and any other user defined data type.
// Declare
int marks;
sizeof(marks);
sizeof(int);
sizeof(char);
sizeof(boolean);Data Type Modifiers




Data Type Modifiers
- long
- short
- signed
- unsigned


Challenge
