1.10 Vectors and Matrices
What are they and why to we care about them ?

Vectors
What are they ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Start with simple x1, x2 axis (not x, y).
- Show a point in this 2-d plane.
- Now show an arrow from the origin to this point
- Now repeat the above for a few more points (such that one of these vectors is shorter than the first and the other is longer)
- Now in pink bubble write two bullet points: "Magnitude of a vector" and "Direction of a vector"
- Show formula for L2 norm (magnitude of the vector) and compute the magnitude of these vectors
- Now show two points in the x1,x2, plane (1,1) and (-1,1) and compute the magnitude (you can delete the other points). Both these points will be
Guiding principle for this entire lecture:
Many students in the course may be hearing the word "vector" for the first time. So we have to be very slow and methodically compute everything (even something as simple as L2 norm)
Vectors
What are they ? (some jargon)
(c) One Fourth Labs

- On RHS, write the definition if Euclidean space in a pink bubble
- On LHS top show a 2D Euclidean space with some points and their co-ordinates written
- On LHS bottom first show a 3D Euclidean space with some points and their co-ordinates written
- Now in pink bubble add L2 norm is also called Euclidean norm
Euclidean space, In geometry, a two- or three-dimensionalspace in which the axioms and postulates of Euclideangeometry apply; also, a space in any finite number of dimensions, in which points are designated by coordinates (one for each dimension) and the distance between two points is given by a distance formula
Vectors
How do you add, subtract, multiply vectors ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Slide 1 (How do you add two vectors?)
- On LHS top show a 2D Euclidean space with two points and their co-ordinates written. On LHS write them as column vectors. Now add them and write the result. Now show the resulting vector on the Plot
- Repeat the above for 3d space
Slide 2 (How do you subtract one vector from another?)
- Repeat the above slide for subtraction
Slide 3 (How do you compute the dot product of two vectors?)
- LHS same as in the above two slides
- on RHS show the dot product formula for 2d and also show the column vectors
- Now show the formula in 3d and also show the column vectors
- For n-dimensions, show the formula
Slide 4 (How do you compute element-wise product of two vectors?)
- 2d, show formula \( \odot \), compute
- 3d, show formula \( \odot \), compute
- n-d, show formula
Vectors
How do you project a vector onto another ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Slide1:
- Same as this video upto 4:09 seconds (but change the vectors a bit
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fqPiDICPkj8
- Now take a numeric example in 2d and compute
- Now take a numeric example in 3d and compute
- Now give formula for n-dimensions
Vectors
How do you project a vector onto another ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

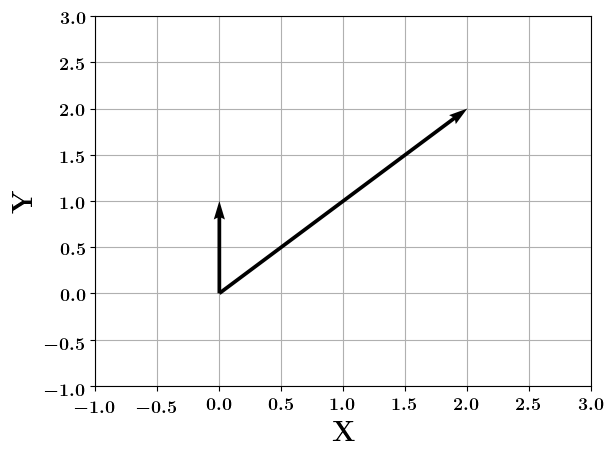
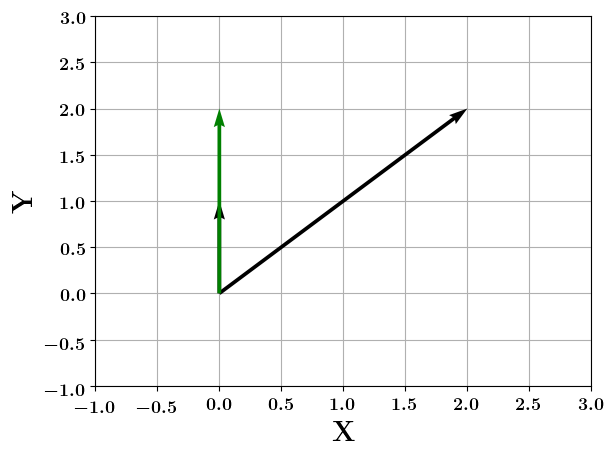
Vectors
How do you project a vector onto another ?
(c) One Fourth Labs



Vectors
What is a unit vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Slide1:
- Pink bubble "Any vector whose magnitude is 1?"
- Show the standard 0,1 and 1,0 vectors
- Show the 1/sqrt(2), 1/sqrt(2) vector
- Now show a non unit vector
- Now show how you get the unit vector in the direction of a vector
- repeat the same computation for one more vector (preferably with at least one -ve co-ordinate)
- Repeat the same for 3d space
Vectors
How do you compute the angle between two vectors ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- 2d vector on LHS, cos formula on RHS, computations
- 3d vector on LHS, cos formula on RHS, computations
Vectors
What are orthogonal vectors?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Show cos formula on RHS
- Orthogonal --> perpendicular --> \theta = 90 --> cos = 0 --> cosine_formula = 0 --> dot product = 0
- Show examples of 2d orthogonal vectors. First show column vectors, then compute dot product, show it is 0, then show the vectors on the plot to convey that they are indeed 0.
- Repeat point 2 with examples in 3d
- Now show one example in 5d (its okay if you need to spread this across more than 1 slide)
Vectors
Why do we care about them ?
(c) One Fourth Labs


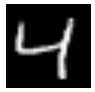
Matrices
What are they ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Start with a vector and stack more vectors to form a matrix
- Highlight one column and show that this is a column vector
- Highlight one row and show that this is a row vector
Matrices
How do you add two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show two matrices and show how the addition happens element-wise
Matrices
How do you add two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show a 2 x2 vector and multiply it with a 2x1 vector, show the formula for how you compute each element of the resulting vector. Show the corresponding animation also (highlight first row of the matrix and the vector, then the second row of the matrix and the vector)
- Now show the geometric interpretation of this (same as slide 3 lecture 6 from CS7015).
- Repeat the same for a 3 x3 matrix
- Now try multiplying a 3x3 matrix with a 2x1 vector. Show how this is not possible because there are 3 terms in the matrix and only two in the vector.
- Now try multiplying a 2x3 matrix with a 3x1 vector. This is possible. This results in the conclusion that the number of columns in the matrix should be the same as the number of rows in the vector.
For showing illegal use this icon
Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

?
illegal operation
Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

legal operation
Conclusion : Number of columns in the matrix should be the same as the number of rows in the vector.
Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply a matrix with a vector ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show two 3x3 matrices. Show the multiplication one column at a time (i.e., the matrix A first gets multiplied with the first column of matrix B, then next column and so on, similar animations as on the previous slide)
- Now try a 3x3 matrix with a 2x3 matrix. Show that you need to multiply the matrix A with the columns of B. Now this is not possible as we already saw on the previous slide.
- Try 3x2 with 2 x4 and show this is possible
- In general, m x k can be multiplied with kxn to get m x n output
Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Number of columns in the matrix is not equal to the number of rows in the vector.
Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Number of columns in the matrix is equal to the number of rows in the vector.
Matrices
How do you multiply two matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

Conclusion : Any m x n matrix can be multiplied with a n x k matrix to get a m x k output.
Matrices
Is there an alternate way of multiplying matrices ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show a 2x2 matrix with a 2 x1 vector say a11, a12, a21, a22 and b11, b21. Show the output as a11*b11 + a12* b21, a21*b11 + a22* b21. Now rewrite it as b11*[a11, a21] + b21*[a11, a21] (everything as column vectors not row vectors)
- Show a 2x2 matrix with a 2 x2 matrix. Repeat the same story as above where the first column of the output is the linear combination of the the columns if A and similar second column.....
Matrices
What is the common operation that you will see in this course ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show Wx + b in very big font
- Using an arrow point to W and write R^{mxn}
- [Now I will ask them the dimensions of x and b so pause]
- Now write the dimension of x
- Now write the dimension of b
Matrices
Why do we care about them ?
(c) One Fourth Labs

- Show an icon of a mobile phone. Now adjacent to this icons show one row containing specs of this phone
- Now below this show icons for multiple phones and there corresponding data so that we get a matrix
- Repeat the above by replacing phones by different MNIST digits.
Text

| Weight (g) | Screen Size(in.) | Dual SIM | Radio | Battery (mAh) | Price (INR) | Internal Memory (GB) |
|---|

| 151 | 5.8 | 1 | 1 | 3060 | 15000 | 64 |
| 180 | 6.18 | 1 | 0 | 3500 | 32000 | 64 |
| 160 | 5.84 | 0 | 0 | 3060 | 25000 | 64 |
| 205 | 6.2 | 0 | 1 | 5000 | 18000 | 64 |
| 162 | 5.9 | 0 | 1 | 3000 | 14000 | 64 |
| 182 | 6.26 | 1 | 1 | 4000 | 12000 | 64 |
| 138 | 4.7 | 0 | 0 | 1960 | 35000 | 64 |
| 185 | 6.41 | 1 | 0 | 3700 | 42000 | 64 |
| 170 | 5.5 | 0 | 0 | 3260 | 44000 | 64 |
Why do we care about them ?
(c) One Fourth Labs
Matrices
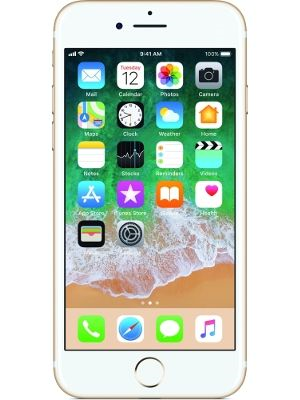



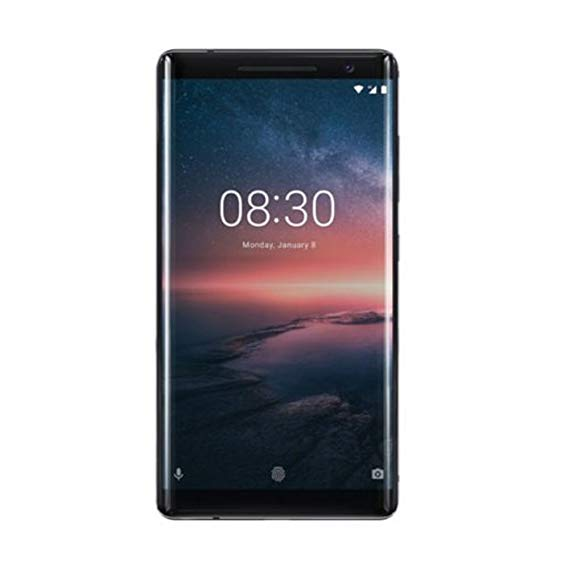





Why do we care about them ?
(c) One Fourth Labs
Matrices








| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | Fn |
|---|

Why do we care about them ?
(c) One Fourth Labs
Matrices
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | ... | Fn |
|---|