Patch Clamping
Fan Jiang
A Practical Approach
South University of Science and Technology of China
Contents
- Intro to Membrane Potential and Its Measurement
- Intro to Patch Clamping, Basic Ideas
- Problems in the Technique, like...
- Different Requirements
- Const Voltage
- Const Current
- Minimal Disturbance etc.)
- Solutions, Advances, etc.
- Proper Grounding
- Differential Amplifiers
- High-Resistance Electrodes
What is Patch Clamping?
- A method to measure the membrane current/voltage in a very small area (e.g. around an ion gate)
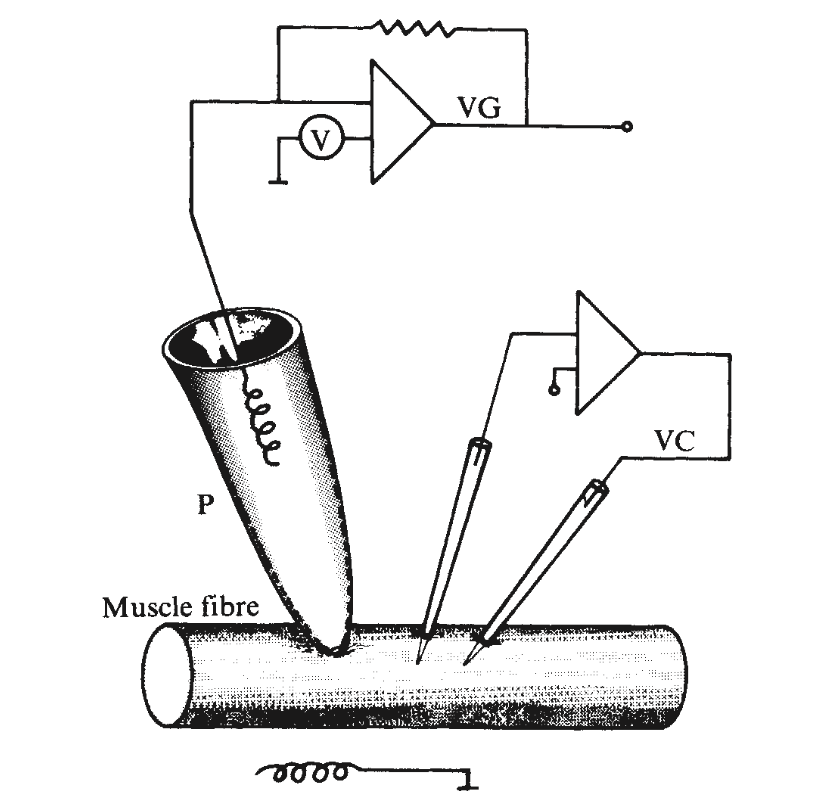
A Schematic of the First Patch Clamping
Sakmann, Neher (1976)
Single channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibers
- VG: Virtual Ground
- P: Patch
- VC: Voltage Clamp

Voltage Clamp
Sakmann, Neher (1976)
Single channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibers
The Voltage Clamp(VC) is used to keep the membrane voltage constant in a small area.
The VC uses the Patch as a reference, to compensate for the change in ion concentration

Patch Clamping
Sakmann, Neher (1976)
Single channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibers
The Current that flows through the Patch is amplified by the operational amplifier and recorded.
The recorded current reflects the flow of ions through the channel.
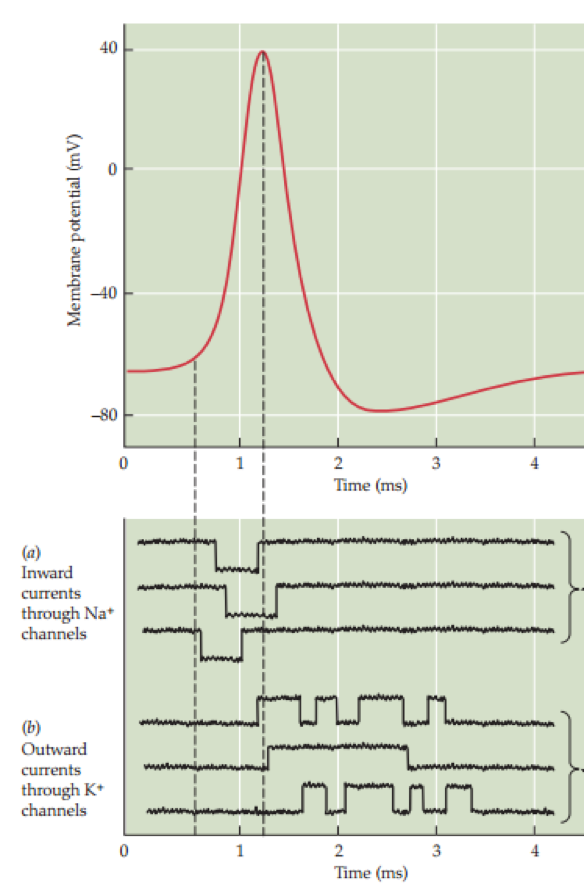
Example Patch Clamp Reading
- Current flows in "bursts" for each channel
- In fact there are so many channels that the process becomes continuous
- Can be seen as as an integration process:
Patch Clamping in General
General Patch Clamping
Ogden, D. & Stanfield P. (1994)
Patch clamp techniques for single channel and whole-cell recording. , Microelectrode techniques
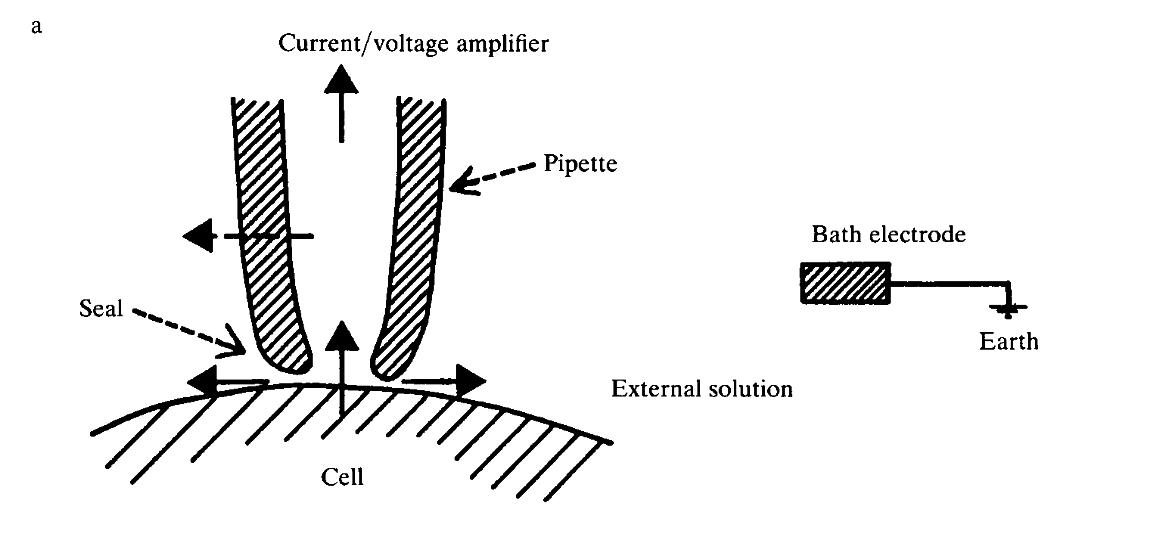
- No VCs used
- Bath electrode as Ground
General Patch Clamping
Ogden, D. & Stanfield P. (1994)
Patch clamp techniques for single channel and whole-cell recording. , Microelectrode techniques

- Generally, High is needed
- How?
General Patch Clamping
Ogden, D. & Stanfield P. (1994)
Patch clamp techniques for single channel and whole-cell recording. , Microelectrode techniques

Fact:
- The channel current is usually ~10pA
GigaSeal Patch Clamp
- A method to achieve a seal resistance of ~10GΩ
- Less background noise as
- Johnson noise due to resistance is proportional to 1/R
GigaSeal Cont. d
- Solution should be macromolecule-free
- Surface of membrane should be clean and free of extracellular matrix and connective tissue
- Pipette tip should be clean, which is usually achieved by burning
- An outflow of electrolyte is maintained at the tip before suction to keep the part clean

Image Quoted from Wikipedia, CC-BY-SA
Variations of Patch Clamping
Gigaseal Derivatives
Ogden, D. & Stanfield P. (1994)
Patch clamp techniques for single channel and whole-cell recording. , Microelectrode techniques
If you apply a suction that is too high, the membrane will be sucked in and create a pore. This can be used to make a whole-cell patch clamp.
Tearing up the membrane and you have either inside-out or outside-out patch.


Loose-patch Clamp
- In this case, the pipette is not tightly sealed to the membrane but is only loosely attached to it.
- Often used to record action potentials in neuronal cells
- Advantage: composition of the cytoplasm is not influenced
- However the intracellular environment cannot be controlled.
Hmm...

Maybe it's time for a wrap-up
Wrapping Up

A Schematic of the First Patch Clamping
Sakmann, Neher (1976)
Single channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibers
- VG: Virtual Ground
- P: Patch
- VC: Voltage Clamp