Bitcoin & Cryptocurrencies
David Stancel
10.9.2017
Content
- What it is
- History and Background
- How it works
- Consequences
- Challenges
- Q&A
Bitcoin as a ...
Currency/Commodity/Asset?
- Decentralized with no middleman
- Independent
- Open-source
- Deflationary
- Fast (?)
- Pseudoanonymous
History & Background
- Inception of Assymetric Cryptography & PKI
- (Failed) Attempts for digital cash
- Cypherpunks
- Satoshi Nakamoto


How it works?
- Blockchain
distributed ledger of ALL transactions ever made
each node in the network has a copy
- Transactions
are divided into blocks
each block contains hash of a previous block

How it works? II.
- Distributed Consensus
mechanism that makes all nodes agree on order of transactions
- Proof of Work
Miners have to perform difficult mathematical operations in order to guess a puzzle
The one who is first wins a block reward and has right to propose a block
- Hashrate
the more computing power the more often you get reward
more miners --> bigger hashrate --> more secure --> difficulty increase (adjusted each 2016 blocks)
Hash Function



How transactions work?
- New transactions are broadcast to all nodes
- Each node collects transactions into a block
- In each block a random node gets to transact its block
- Other nodes accept the block only if it contains valid transactions (unspent, valid sigs)
- Node express their acceptance of the block by including its hash to a next block they create

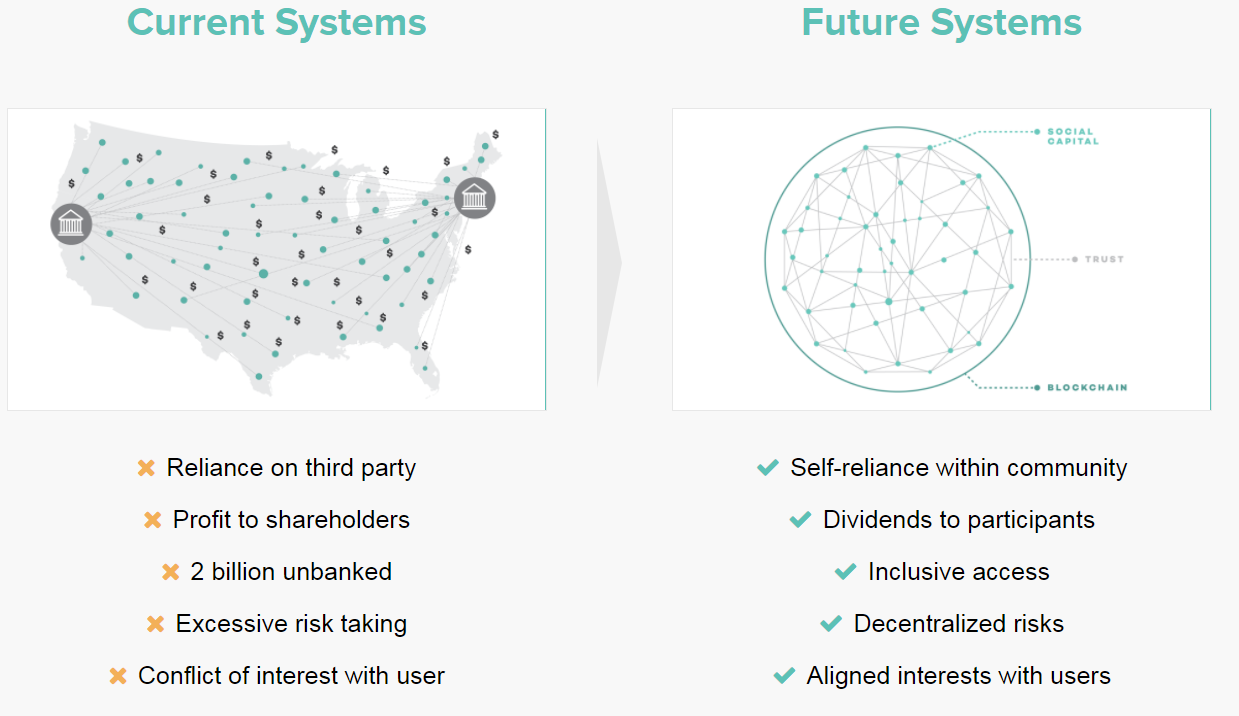
Consequences


Hashrate distribution

Bitcoin vs. Alts
ICOs

Consequences II

Challenges
- scaling
- mass adoption
- (de)centralization
- regulation
- security
- node incentivization
THANK YOU!
stancel@blockchainslovakia.sk