Microservices Caching Patterns with Spring Boot
Pulkit Pushkarna
What is caching ?
- Cache is a part of temporary memory (RAM). It lies between the application and the persistent database.
- Caching is a mechanism used to increase the performance of a system. It is a process to store and access data from the cache.
-
It stores the recently used data. This helps to reduces the number of database hits as much as possible.
Why should we use the cache ?
- It makes data access faster and less expensive.
- It improves the performance of the application.
- It gives response quickly.
- Data access from memory is always faster than fetching from database.
- It reduces the costly backend requests.
What data should be cached ?
- The data that do not change frequently.
- The frequently used read query in which the results does not change in each call at least for a period.
Types of Caching
- In-memory
- Distributed caching
- Client Server
Spring Boot Caching
Spring boot provides a Cache Abstraction API that allow us to use different cache providers to cache objects.
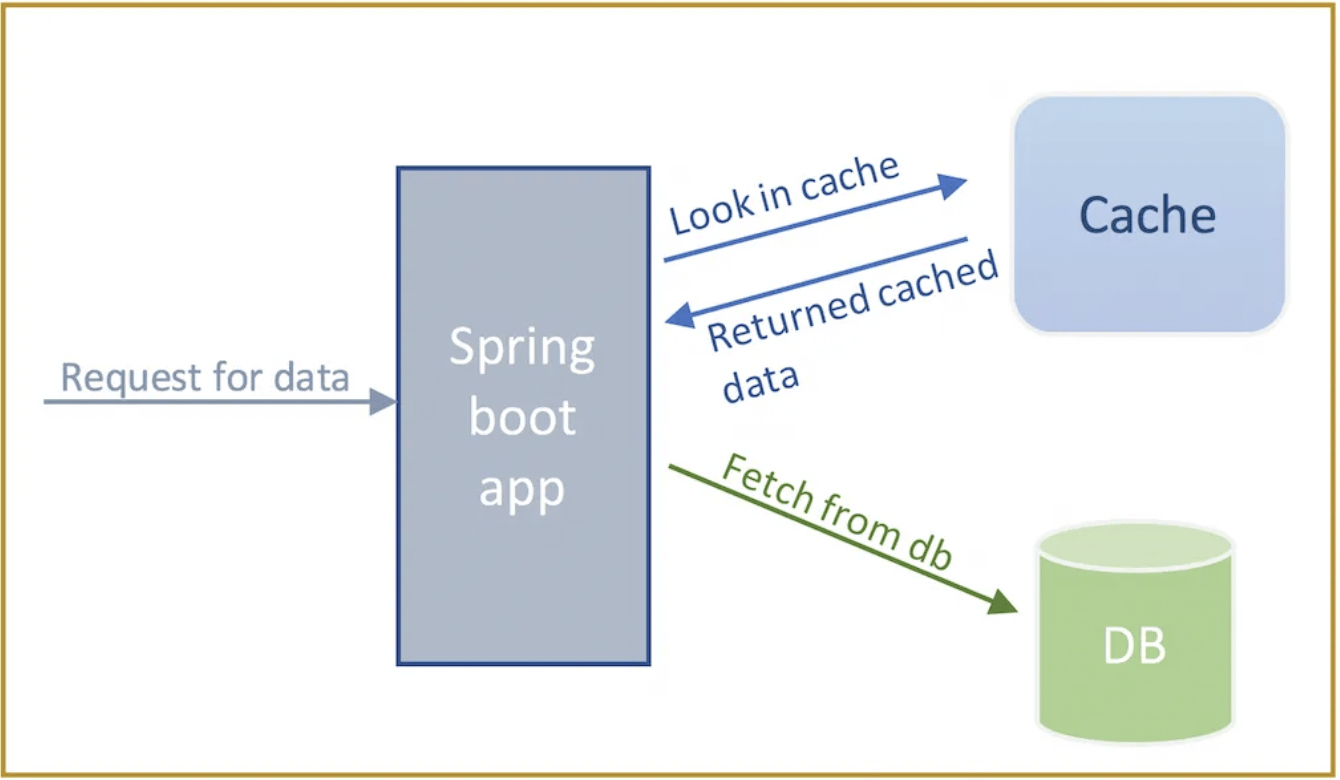
The below is the control flow of Spring Boot Caching.
When the caching is enabled then the application first looks for required object in the cache instead of fetching from database. If it does not find that object in cache then only it access from database.
Spring Boot Cache Providers
The following are the cache provider supported by Spring Boot framework :
- JCache (JSR-107)
- EhCache
- Hazelcast
- Infinispan
- Couchbase
- Redis
- Caffeine
- Simple
Spring Boot Cache Annotations
@EnableCaching
It is a class level annotation. It is used to enable caching in spring boot application. By default it setup a CacheManager and creates in-memory cache using one concurrent HashMap.
It is also applied over a Spring configuration class as below :
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringBootCachingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCachingApplication.class, args);
}
}@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
// some code
}@Cacheable
- It is a method level annotation.
- It is used in the method whose response is to be cached.
- The Spring boot manages the request and response of the method to the cache that is specified in the annotation attribute.
We can provide cache name to this annotation as follow :
@Cacheable(“employees”)
public Employee findById(int id) {
// some code
}This annotation has the following attributes :
-
cacheNames
- The cacheNames is used to specify the name of the cache
- key
- This is the key with which object will be cached. It uniquely identifies each entry in the cache.
@Cacheable(cachNames=”employees”)
public Employee findById(int id) {
// some code
}@Cacheable(value=”employees”, key="#id")
public Employee findById(int id) {
// some code
}@CachePut
- It is a method level annotation.
- It is used to update the cache before invoking the method.
- By doing this, the result is put in the cache and the method is executed.
- It has same attributes of @Cacheable annotation.
@CachePut(value=”employee”)
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee employee) {
// some code
}@CacheEvict
- It is a method level annotation.
- It is used to remove the data from the cache.
- When the method is annotated with this annotation then the method is executed and the cache will be removed / evicted.
- We can remove single entry of cache based on key attribute.
- It provides parameter called allEntries=true. It evicts all entries rather one entry based on the key.
@CacheEvict(value=”employee”, key="#id")
public void deleteEmployee(int id) {
// some code
}@CacheEvict(value=”employee”, allEntries=true)
public void deleteEmployee(int id) {
// some code
}Spring Boot in-memory cache
- In-memory caching is a technique which is widely used. In this type of caching, data is stored in RAM
- By default it setup a CacheManager and creates in-memory cache using one ConcurrentHashMap.
- Your frequently used data will be saved as key-value pairs.
- Therefore, you don’t need to fetch those data from the database frequently.
- Access data from this in-memory ConcurrentHashMap (cache) is always faster than fetching data from the actual database.
Let us create a student microservice
values for application properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=password
hibernate.dialect=mysql
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverpackage com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long studentId;
private String name;
private int age;
}
Create a student Entity class
package com.springcache.springcachedemo.repository;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> {
}
Create a Student repository
Create a Student Controller
package com.springcache.springcachedemo.controller;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity.Student;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
StudentRepository studentRepository;
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(StudentController.class.getName());
@GetMapping("/students")
public Iterable<Student> getStudents(){
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/students/{id}")
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable Long id){
logger.info("Fetching data for student id ::"+id);
Optional<Student> studentOptional = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(studentOptional.isPresent()){
return studentOptional.get();
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
@PostMapping("/students")
public Student postStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
return studentRepository.save(student);
}
@PutMapping("/students")
public Student putStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
logger.info("Updating student data for student id ::"+student.getId());
Optional<Student> studentOptional= studentRepository.findById(student.getId());
if(studentOptional.isPresent()){
return studentRepository.save(student);
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
@DeleteMapping("/students/{id}")
public Student deleteStudent(@PathVariable Long id){
logger.info("Deleting data for student id ::"+id);
Optional<Student> optionalStudent = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(optionalStudent.isPresent()){
studentRepository.delete(optionalStudent.get());
return optionalStudent.get();
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
}
Introducing caching
package com.springcache.springcachedemo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringCacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCacheDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
Introducing caching annotations in controller
package com.springcache.springcachedemo.controller;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity.Student;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
StudentRepository studentRepository;
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(StudentController.class.getName());
@GetMapping("/students")
public Iterable<Student> getStudents(){
return studentRepository.findAll();
}
@GetMapping("/students/{id}")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "student",key = "#id")
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable Long id){
logger.info("Fetching data for student id ::"+id);
Optional<Student> studentOptional = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(studentOptional.isPresent()){
return studentOptional.get();
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
@PostMapping("/students")
public Student postStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
return studentRepository.save(student);
}
@PutMapping("/students")
@CachePut(cacheNames = "student",key = "#student.id")
public Student putStudent(@RequestBody Student student){
logger.info("Updating student data for student id ::"+student.getId());
Optional<Student> studentOptional= studentRepository.findById(student.getId());
if(studentOptional.isPresent()){
return studentRepository.save(student);
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
@DeleteMapping("/students/{id}")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "student",key = "#id")
public Student deleteStudent(@PathVariable Long id){
logger.info("Deleting data for student id ::"+id);
Optional<Student> optionalStudent = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(optionalStudent.isPresent()){
studentRepository.delete(optionalStudent.get());
return optionalStudent.get();
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("Student Not found");
}
}
}
Distributed Cache in Spring Boot
- A distributed caching system aggregates the RAMs of numerous computers connected to a network.
- Distributed caches are very beneficial in high data volume and load scenarios.
- The distributed architecture enables gradual expansion/scaling by adding more computers to the cluster, allowing the cache to increase in pace with the data.
What is Hazelcast ?
- Hazelcast is a distributed In-Memory Data Grid platform for Java.
- The architecture supports high scalability and data distribution in a clustered environment.
-
It supports the auto-discovery of nodes and intelligent synchronization.
Let us create executable jar of our microservice
Run 2 seperate instances
java -jar spring-cache-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8082
java -jar spring-cache-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8081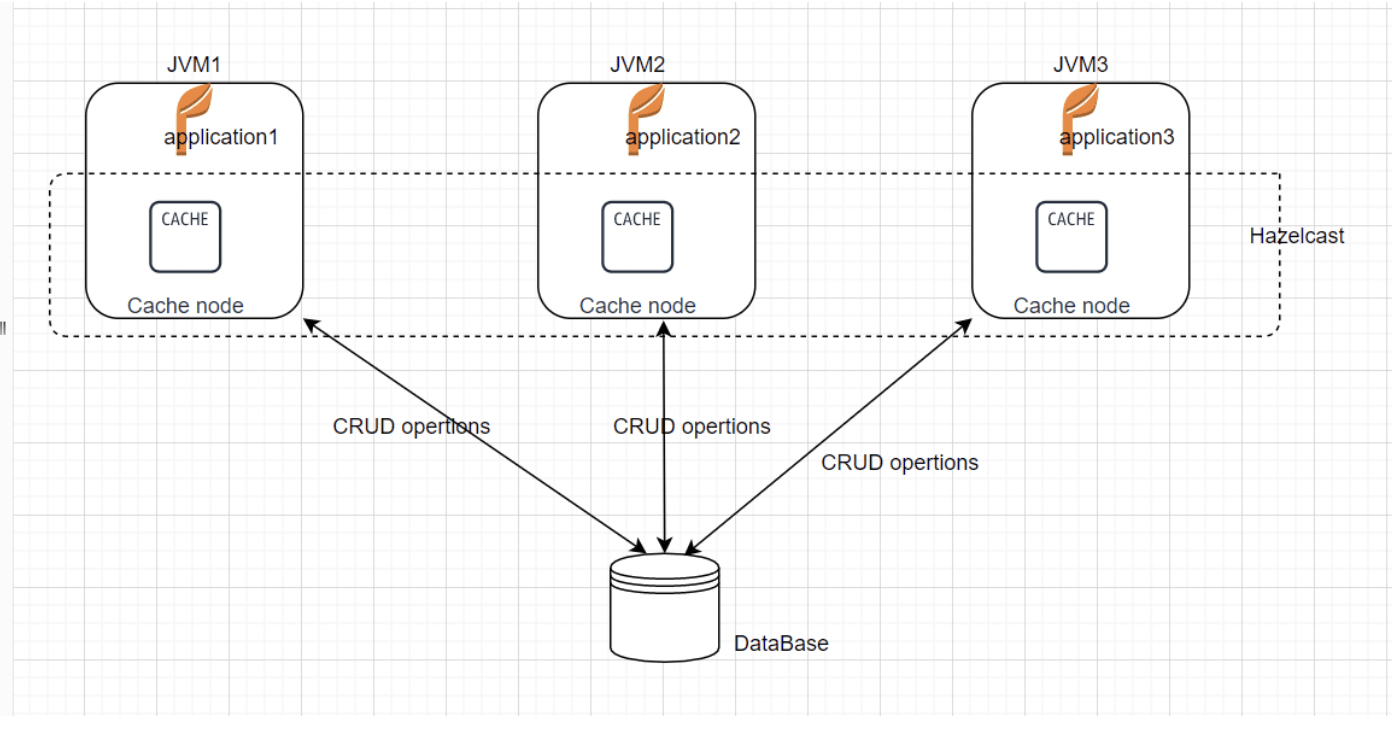
Add hazelcast dependency in build.gradle
implementation group: 'com.hazelcast', name: 'hazelcast-all', version: '4.2.7'Add configuration for Multicast Discovery – the way by which each embedded cache server can communicate with all other embedded cache servers in the network.
Add a file “hazelcast.yaml” in src/main/resources folder with following content.
hazelcast:
network:
join:
multicast:
multicast-group: 224.0.0.1
enabled: trueNow rebuild the boot jar and run 3 instances again to check the distributed cache
Implement Serializable interface in Student class
package com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class Student implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
}
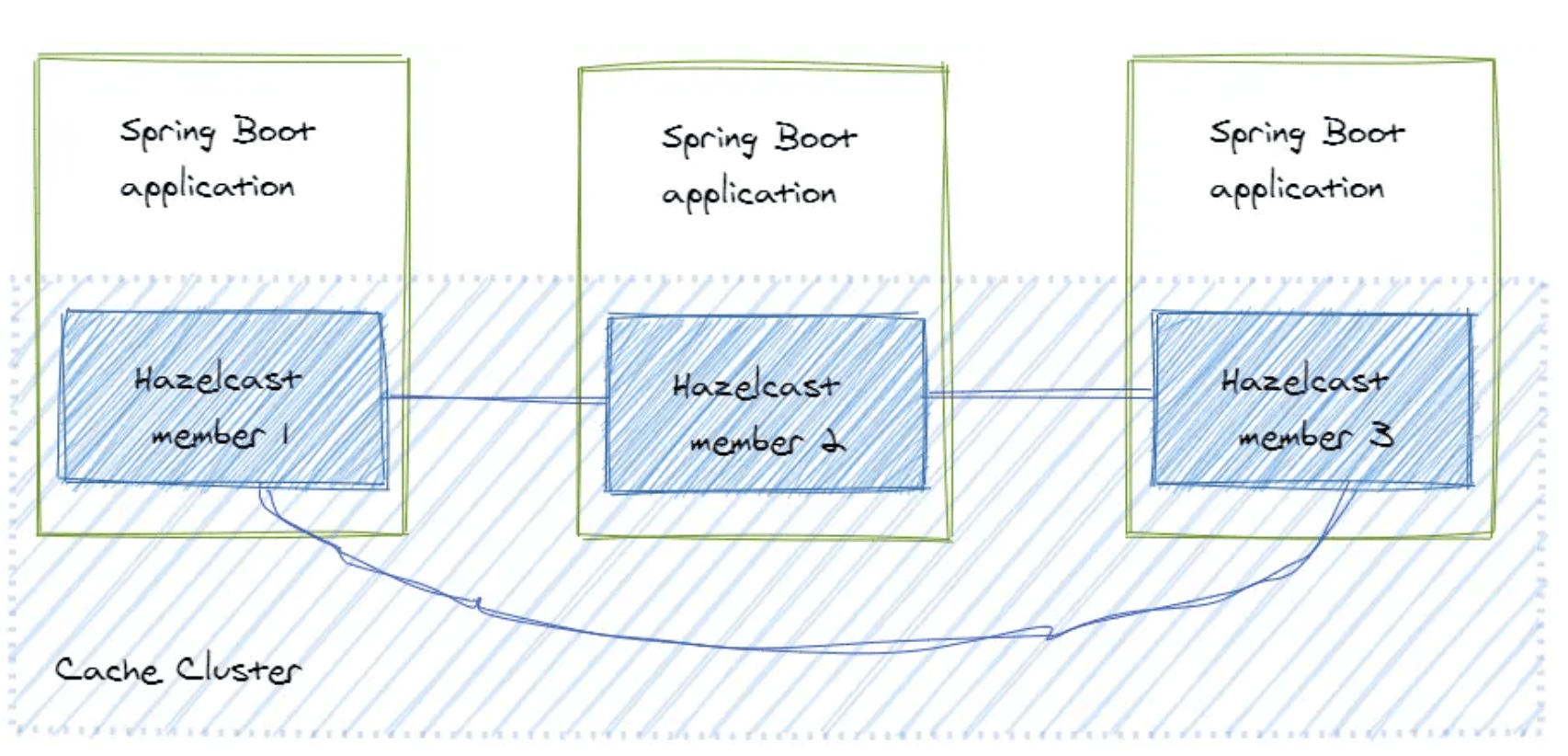
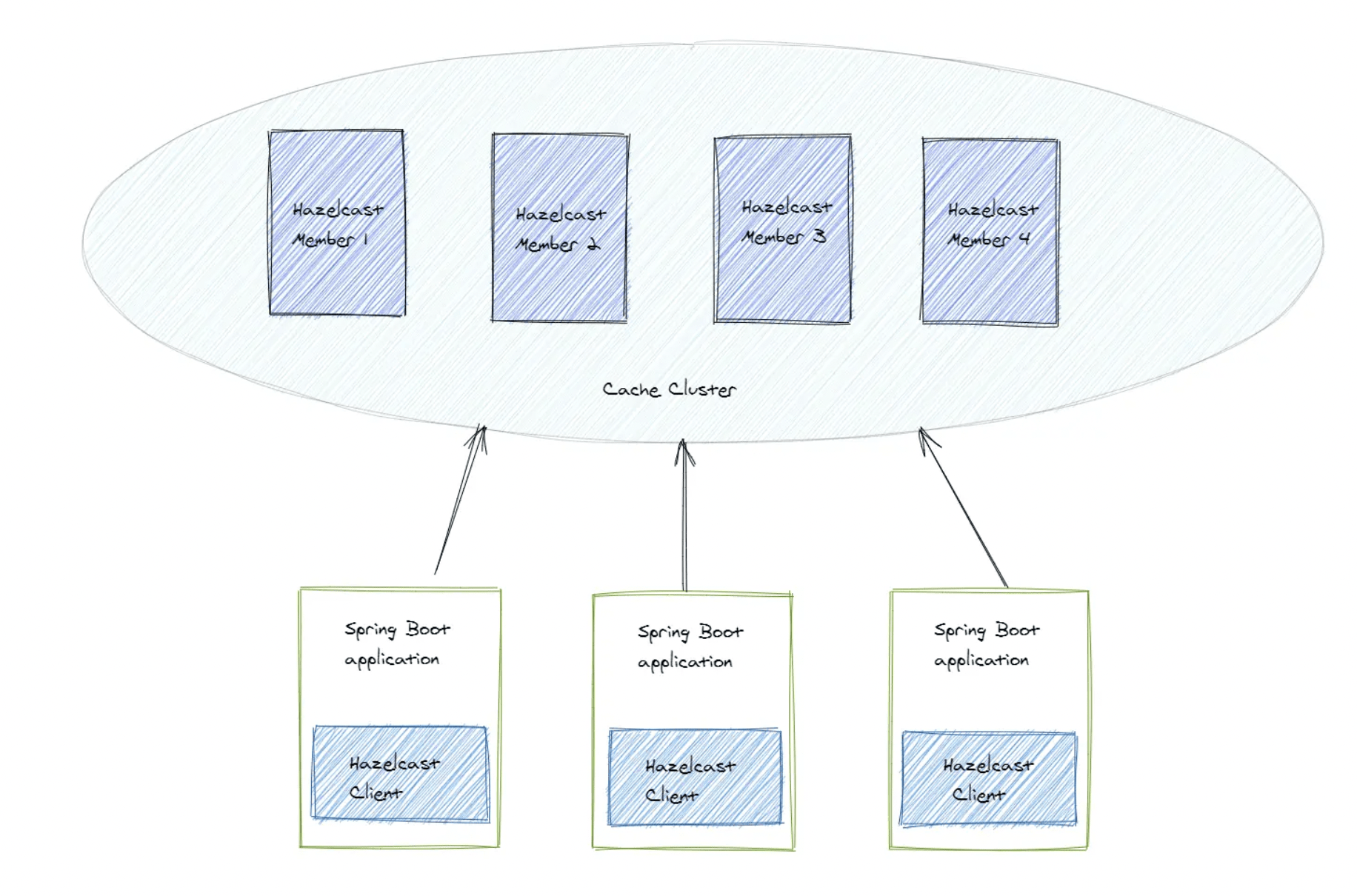
Client-Server Topology
- This topology means that we set up a separate cache cluster, and our application is a client of this cluster.
- The members form a separate cluster, and the clients access the cluster from outside.
- To build a cluster we could download the latest version of Hazelcast fromhttps://hazelcast.com/open-source-projects/downloads/
- Download the Zip file of lastest Hazelcast Platform
- Extract th file and go inside bin folder
- Now run the following command from 2 terminals to create 2 Hazlecast members.
./hz start Hazlecast Management Center
- Hazlecast Management Center helps to monitor the different members of a Hazlecast cluster.
- We can see the matrics of different members like the kind of data they store and the frequence of use etc.
- We can download the latest stable version of Hazlecast Management Center from https://hazelcast.com/open-source-projects/downloads/
- Download the Zip file under Hazlecast Management Center.
- Extract the zip file
- You will see the a jar file
- Execute the jar file using the command below :
java -Dhazelcast.mc.http.port=8083 -Dhazelcast.mc.contextPath='hazelcast-mc'
-jar
hazelcast-management-center-5.3.3.jar
- In order to open the Hazelcast Management Center hit the following url from the browser
- Set up the credentials and enter the username and password
Click on the Add button
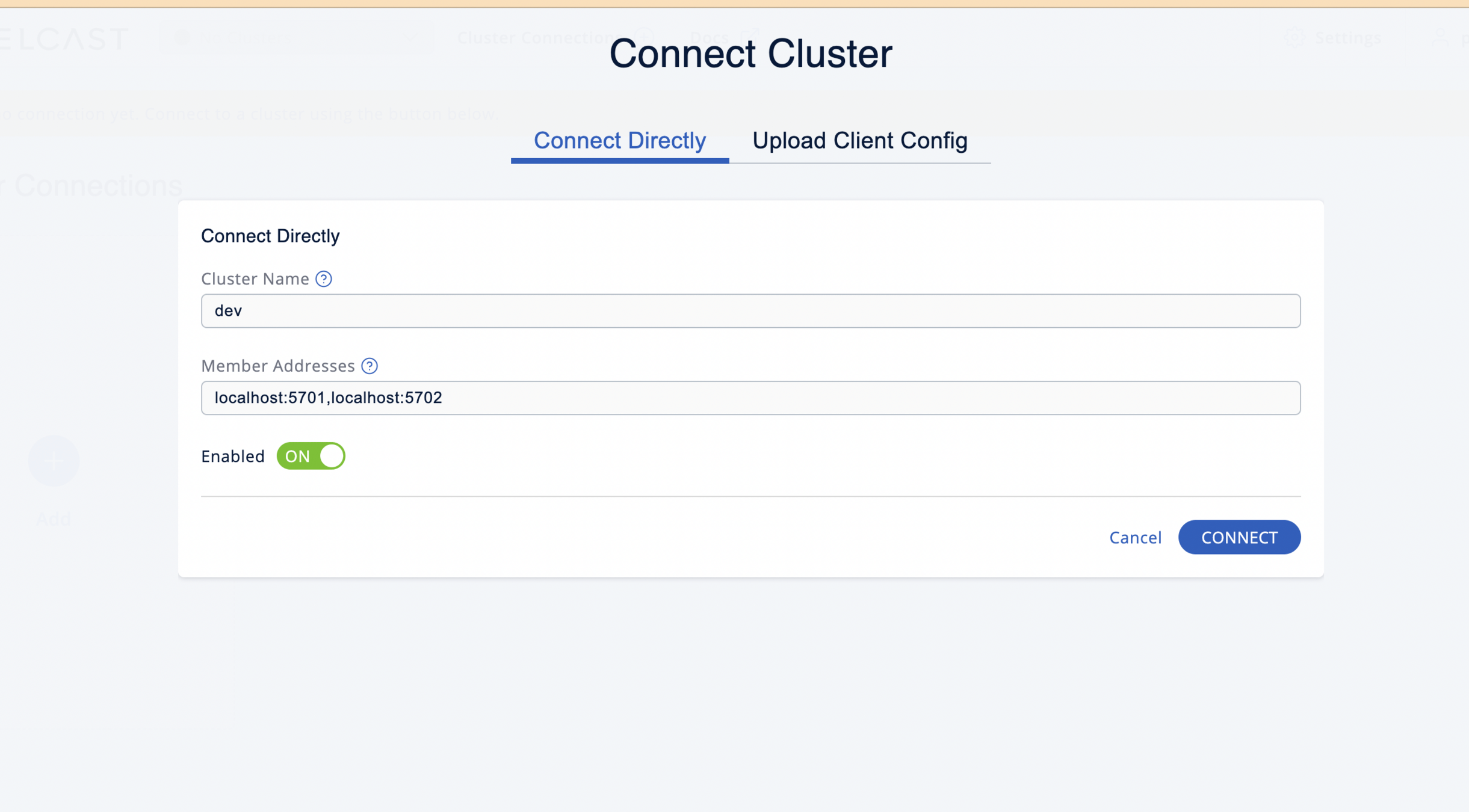
Enter the details of the cluster and press connect button
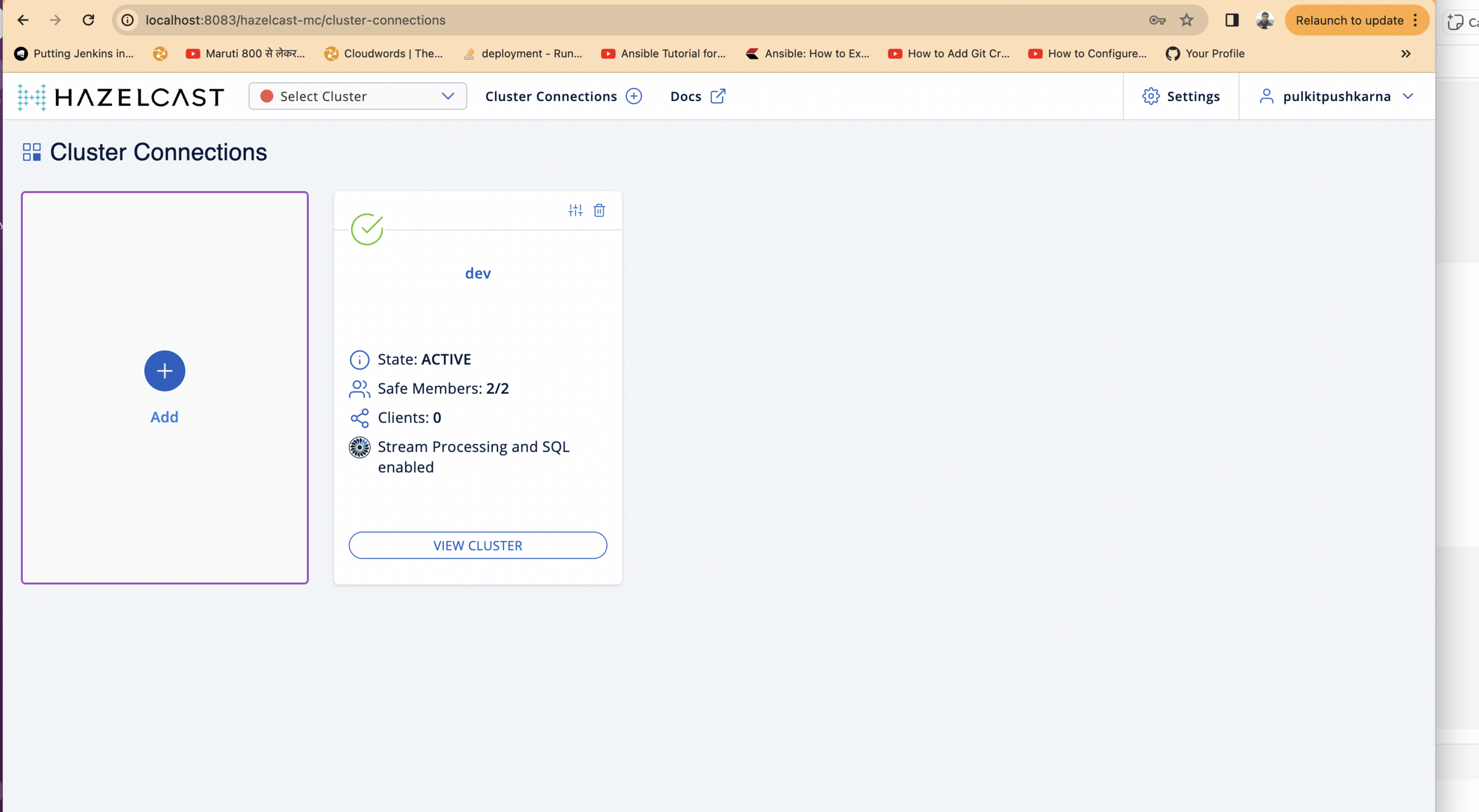
- Cluster should connect successfully after few seconds
- Click on the View Cluster button.
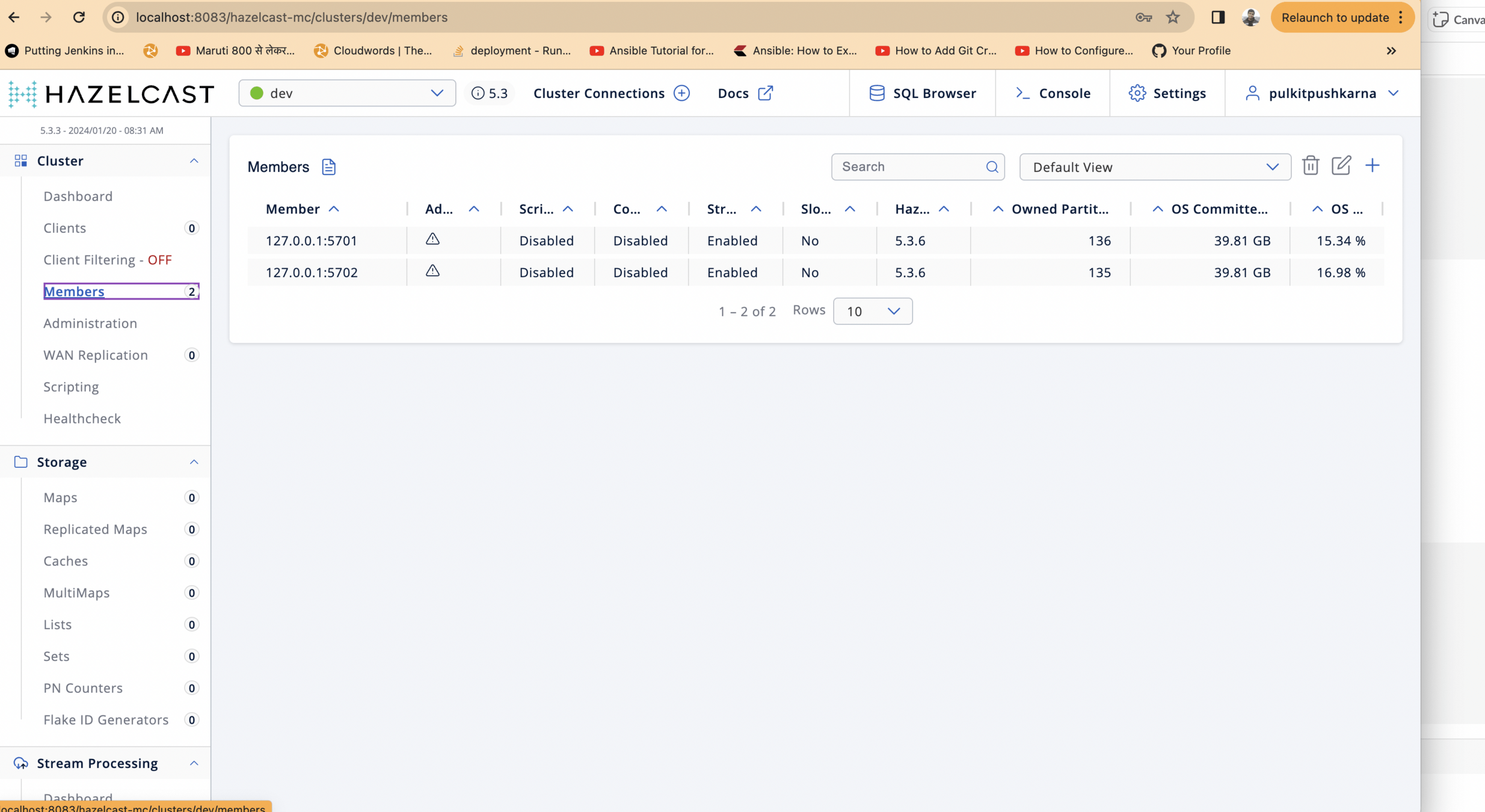
We can see 2 connected members from the cluster
Place hazelcast dependency in build.gradle
implementation group: 'com.hazelcast', name: 'hazelcast', version: '5.3.2'Create Hazelcast Client Instance
@Bean
public ClientConfig clientConfig() {
ClientConfig clientConfig = new ClientConfig();
clientConfig.setClusterName("dev");
clientConfig.getNetworkConfig().addAddress("127.0.0.1:5701", "127.0.0.1:5702");
return clientConfig;
}
@Bean
public HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance(ClientConfig clientConfig) {
return HazelcastClient.newHazelcastClient(clientConfig);
}
Create a controller which fetch Student from Hazelcast Client
package com.springcache.springcachedemo.controller;
import com.hazelcast.core.HazelcastInstance;
import com.hazelcast.map.IMap;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.entity.Student;
import com.springcache.springcachedemo.repository.StudentRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
@RestController
public class StudentClientCacheController {
@Autowired
HazelcastInstance hazelcastInstance;
@Autowired
StudentRepository studentRepository;
Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(StudentClientCacheController.class.getName());
@GetMapping("/studentClient/{id}")
Student getStudent(@PathVariable Long id){
IMap<Long, Student> studentMap = hazelcastInstance.getMap("student");
Student student = studentMap.get(id);
if(Objects.nonNull(student)){
return student;
}else{
logger.info("Fetching data for student id ::"+id);
Optional<Student> studentOptional = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(studentOptional.isPresent()){
Student student1 = studentOptional.get();
studentMap.put(id,student1);
return student1;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("No Student Found");
}
}
}
}
Create a boot jar and create run 2 instances of your microservice using the command below
java -jar spring-cache-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8082
java -jar spring-cache-demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8084Now check for the distributed caching you will observe that
the caching will persist even if the both the intances go down