I N T E R N A L a n d EXTERNAL ANALYSIS
THE BUSINESS AND ITS MARKETING ENVIRONMENT
S E S S I O N F O U R
Use Down Arrow to Scroll through the Slides
Mostafa Purmehdi
SWOT
STRATEGIC ANALYSIS
O B J E C T I V E S

SWOT
I N T E R N A L A N A L Y S I S O F
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES
S T R A T E G I C A N A L Y S I S O F
OPPORTUNITIES AND THREATS
Boat
No, yes
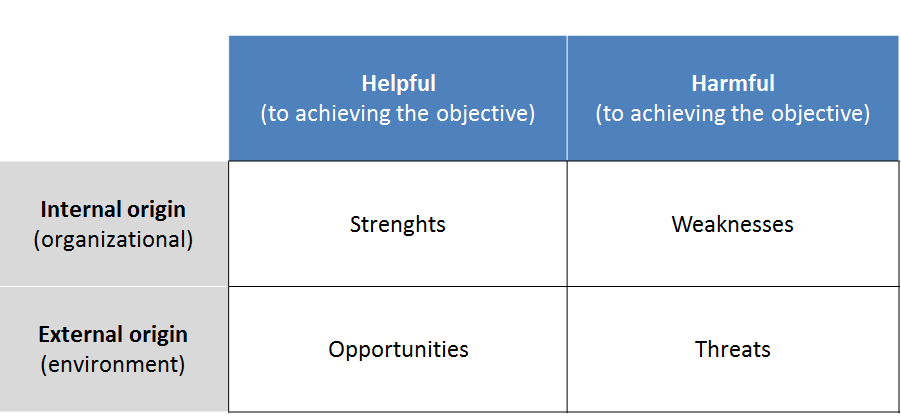
SWOT ANALYSIS MODEL
Internal Analysis
O B J E C T I V E S


Internal Analysis
V A L U E
C H A I N
A N A L Y S I S
B E N C H
M A R K
K I N G


The steps an organization follows to develop, produce and deliver its products, goods or services
Each step represents an opportunity to gain a Competitive advantage
An ongoing process of research, comparative analysis, adaptation and implementation of best practices to improve the performance of various business processes and functions
VALUE
PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
SUPPORT ACTIVITIES
CHAIN
ANALY
-SIS
-
Supply chain logistics: reception of raw materials and inventory management
-
Manufacturing: processing of raw materials into finished products or services
-
Marketing logistics: order intake, preparation and shipping, and inventory management
-
Marketing communication and sales: the most skilled companies in marketing and sales usually have considerable competitive advantages
-
Peripheral services: installation, repairs and technical support
internal analysis > value chain analysis > PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
Core competency: Supply chain logistics
Core competency:
Peripheral services





Logistics
Manufacturing
Communication and Sales
Peripheral Services
internal analysis > value chain analysis > PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
-
Company infrastructure: services required for the organization to function, such as administration, financial management, strategic planning, and quality control
-
Human resource management: capability to attract and retain talent
-
Research and development (R&D): company’s ability to innovate quickly implement product development
-
Purchasing: decrease procurement costs, from raw materials to other products and services
internal analysis > value chain analysis > SUPPORT ACTIVITIES
Core competency: Research and development

What products came out of R&D?
BENCHMARKING
Samsung


Microsoft
B E N C H M A R K I N G
Apple
B E N C H M A R K I N G
developed "benchmarking"
in the 1980s
B E N C H M A R K I N G
IS MARKETING A
CORE COMPETENCY
?
H O W
Core Competencies to Make Marketing a Strength
-
Product development capability
-
Customer satisfaction capability
– Basic factors
– “Wow” factors
– Performance factors
-
Brand
-
Distribution networks
-
Strategic partnerships
-
Information
External Analysis
O B J E C T I V E S

Micro Analysis
Macro Analysis
MICRO vs. MACRO
* for a complete list of items please refer to your textbook.
External analysis
Examination of different dimensions of the business environment and their management consequences
Micro-environment vs Macro-environment
MICRO
d i r e c t
MACRO
i n d i r e c t
E F F E C T O N B U S I N E S S
M i CRO
ENVIRO
N MENT
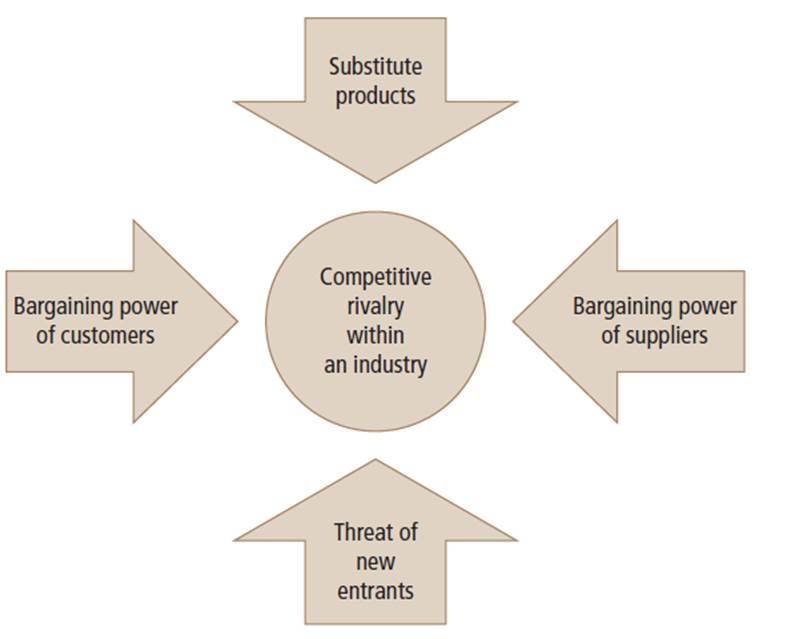
PORTER'S FIVE FORCES
M I C R O E N V I R O N M E N T

MR. PORTER
B A T N A
BEST ALTERNATIVE TO A NEGOTIATED AGREEMENT
[ READ: WORST THAT CAN HAPPEN IF NEGOTIATIONS FAIL ]
B a r g a i n i n g P o w e r o f C u s t o m e r s
PATENTS
B a r r i e r s f o r N e w E n t r a n t s
POWERFUL BRAND
DISTRIBUTION
LOYALTY
ECONOMY OF SCALE
VARIETY
PRICE ADVANTAGE
T h r e a t o f S u b s t i t u t e P r o d u c t s
NO TRANSFER COSTS
NO DIFFERENTIATION




Substitute Products
Complementary Products
MACRO
ENVIRO
N MENT
M A C R O E N V I R O N M E N T
ECONOMYGOVERNMENTDEMOGRAPHYSOCIOCULTURALASPECTS
ECONOMY
- Economic performance (indicator: GDP)
- Consumers’ purchasing power (indicator: GDP/capita)
- Economic distribution (indicator: Gini index)
- Important factors:
- Technological development
- Education
- Regulation
- Globalization
GDP
Quebec vs. Canada
G D P P E R C A P I T A
$81000
Alberta
$63000
Saskatchewan
$62000
NFL & LBD
$39000
Quebec
Gini index
0
1
perfect distribution of wealth or income
one person holds 100% of the wealth
I N C O M E I N E Q U A L I T Y
M A C R O E N V I R O N M E N T
ECONOMYGOVERNMENTDEMOGRAPHYSOCIOCULTURALASPECTS
GOVERNMENT
-
Type of government > Stability
- Power of legislation > Attractiveness

M A C R O E N V I R O N M E N T
ECONOMYGOVERNMENTDEMOGRAPHYSOCIOCULTURALASPECTS
DEMOGRAPHY
- Population size and distribution
- Age distribution
- Level of education and income
- Ethnic origin
- Religious faith
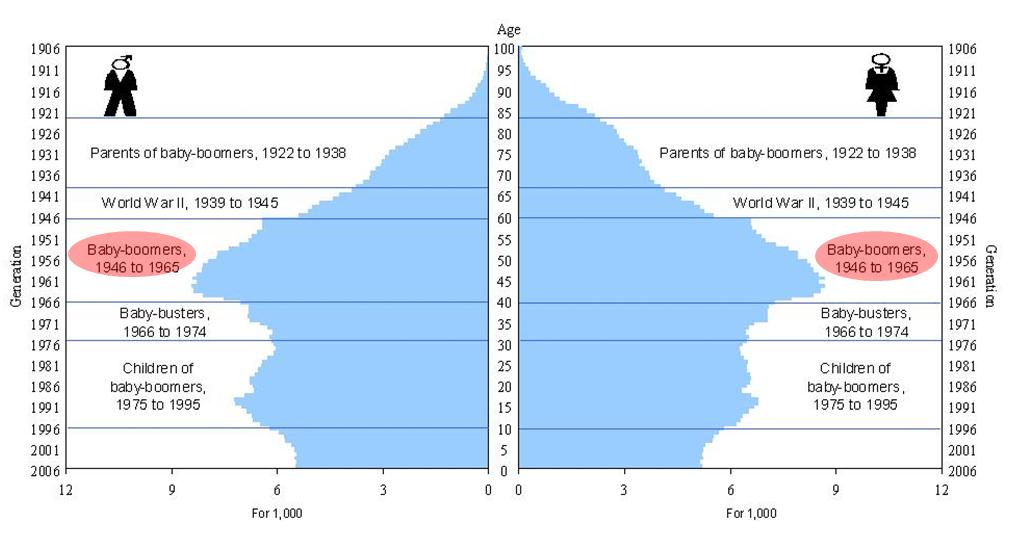
A G E D I S T R I B U T I O N I N C A N A D A
M A C R O E N V I R O N M E N T
ECONOMYGOVERNMENTDEMOGRAPHYSOCIOCULTURALASPECTS
SOCIOCULTURAL
- Culture
-
Generational cohorts
- Baby boomers
- Generation X
- Millennial generation
SILENT GENERATION, BABY BOOMERS, GENERATION X, MILLENNIALS
BABY BOOMERS VS. MILLENNIALS
Baby boomers
(born 1946 – 1964)
Live to work, Picky on products and services that precisely meet their need.
Generation X
(born 1965– 1980)
First to have both parents in the workforce, Work to live, Own ways of doing things, Clearly defined goals and values
Millennial generation
(born 1981– 2000)
Generation D (Digital), C (Connected), Access to information, Curious and confident, focusing on breath but neglect the depth.
HOW TO CONNECT WITH GENERATIONS
T H E B U S I N E S S
ECOSYSTEM
a network of interdependent elements
[ C O O P E T I T O R S ]
Information System
O B J E C T I V E S

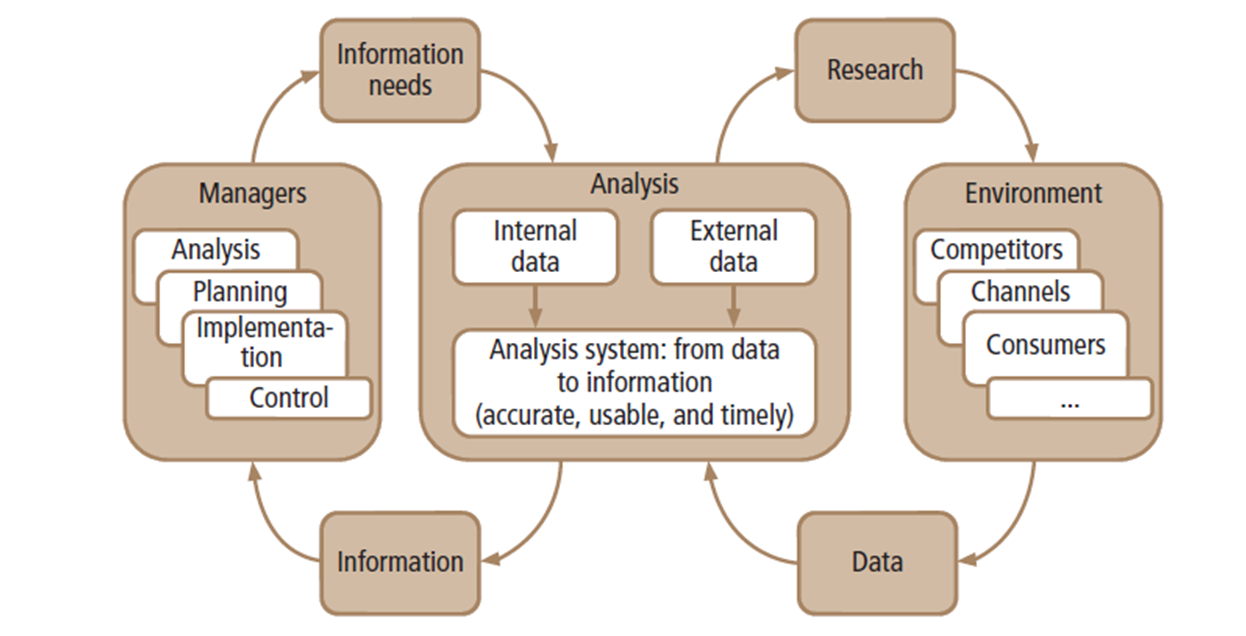
M A R K E T I N G I N F O R M A T I O N S Y S T E M
Internal Data
- Accounting system
- CRM or Customer Relationship Management
- Data related to contacts
- Details of sales activities
- Problems raised and the progress of the sales process

External Data
Secondary
Primary
Gathered by other organizations:
- Market studies
- Reports by industrial associations and companies
Qualitative research
Exploratory research
Ethnography
Netnography
Quantitative research
Confirmatory research
Survey or other methods

study of people and cultures

study of free behaviour of individuals on the Internet
ETHNOGRAPHY
NETHNOGRAPHY
SWOT Examples
O B J E C T I V E S

P O W E R E D B Y
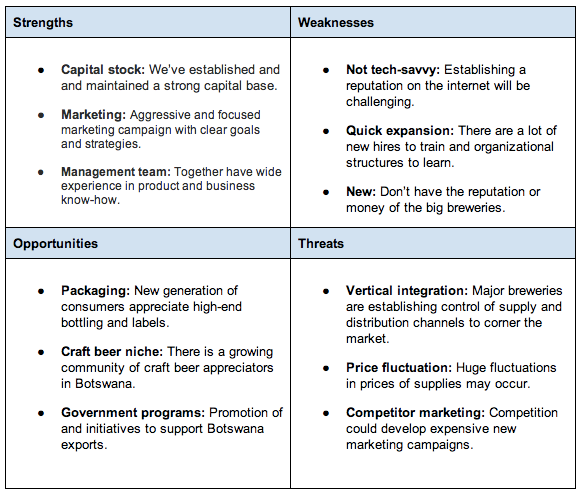
Sedibeng Breweries
a medium-scale brewery in Botswana. Sedibeng’s primary market advantages are their company culture, consistent “quality” branding, traditional brew recipes, and commitment to rural distribution.
Sedibeng Breweries
Potential Strategies for Growth
Two important things to focus on in the “Weaknesses” column:
- building an informational website, and
- developing an efficient employee training program.
Ignoring these weaknesses for too long could have disastrous consequences.
A potential opportunity is a government-subsidized export operation, ideally to target markets in neighboring countries
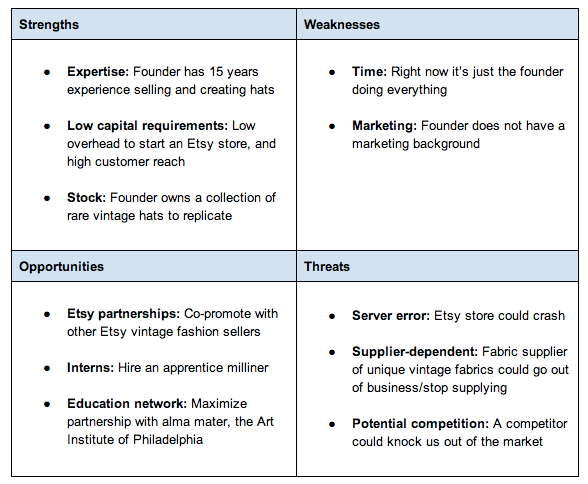
Haley’s Vintage Hats
an online-only business that sells affordable replicas of vintage designer hats. Owner Haley Truit operates Haley’s Vintage Hats through an Etsy storefront and hopes that it will become successful enough that she can quit her other job and run her dream company full-time.
Haley’s Vintage Hats
Potential Strategies for Growth
- Take full advantage of the opportunities as an Etsy seller.
- Partnering with other vintage fashion vendors on Etsy could help her lack of a marketing background (a major company weakness).
- with Haley’s expertise as a milliner, developing an apprenticeship program could help the company cheaply expand its production capacity and support the increase in sales that would come with its expanded marketing efforts.
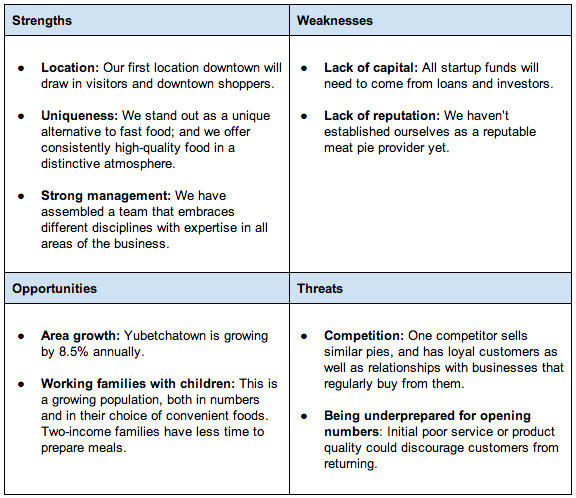
UPer Crust Pies
a specialty meat and fruit pie cafe in Michigan’s Upper Peninsula that sells hot, ready-to-go pies, frozen take-home options, fresh salads, and beverages.
The company is planning to open its first location in downtown Yubetchatown, and is very focused on developing a business model that will make it easy to expand quickly and that opens up the possibility of franchising.
UPer Crust Pies
Potential Strategies for Growth
- investigate its options for obtaining capital. Funding a new business can take time, and the sooner UPer Crust Pies gets started on this process, the better.
- Because they are targeting working families, a key piece of that marketing plan will be the store’s grand opening, and the promotional strategies necessary to get UPer Crust Pies’ target market in the door.
THANK YOU
For Your Attention
s e e y o u n e x t w e e k


