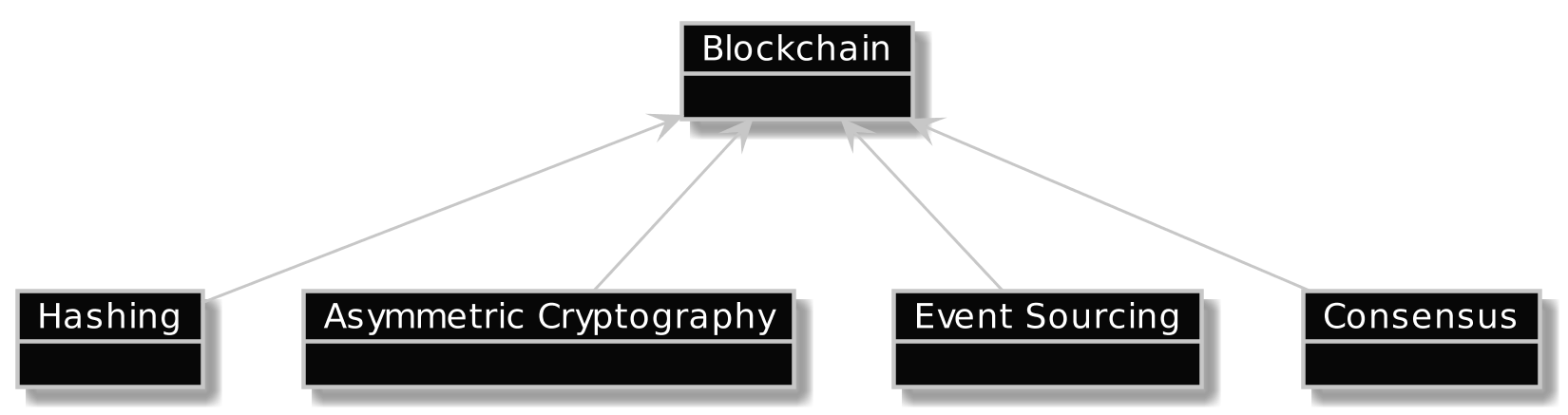
Granular Blockchain


About Me
Marten (Wiebe-Marten Wijnja)
- ~12 years of software development
- ~6 years of blockchains
- ~1.5 years of Resilia

Online: Qqwy

Contents
- Rationale
- Four major concepts
- short intro of 1 concept
- ~10-15 minutes of peer (to peer) discussion
- Closing Thoughts
- Non-Technical
- Not how it works
- but: what it does
- Properties: Good, Bad, Unimportant?
- Ask Questions!
Style
Recap: What is a Blockchain?
A Blockchain is a software system in which:
- All data is immutable
- Anyone can join and add data
- All members agree about the order of the data
Both large potential and large drawbacks!
- No Training Wheels
- 'Forgot Password'
- 'Forgot Password'
- Storing data is slow
- Can only store small bits of data at a time
Large potential, but large drawbacks:
Difficult to adapt current way of thinking

Solution:
Ease into it

Granular Blockchain
Hashing
- Making a unique colour or fingerprint based on your data chunk


Properties
- Small
- Reproducible
- Impossible to reverse
Example uses
- Password checking
- Integrity of files
- Making computers faster
- Authenticity (Plagiarism protection)
Hashing
Properties
- Small
- Reproducible
- Impossible to reverse
Example uses
- Password checking
- Integrity of files
- Making computers faster
- Authenticity (Plagiarism protection)
Hashing
Discuss!
Asymmetric Cryptography


Asymmetric Cryptography
- Encryption key separated from Decryption Key
- Public encryption key
- Private decryption key
- Private key can also be used to make signatures

Properties
- Send/receive encrypted messages
Signatures:
- data authenticity
- non-repudiation ('I did not write that' is impossible)
Example uses
- HTTPS
- PGP (Secure Email)
- WhatsApp etc.
- Storing private data in public places
Asymmetric Cryptography
Properties
- Send/receive encrypted messages
Signatures:
- data authenticity
- non-repudiation ('I did not write that' is impossible)
Example uses
- HTTPS
- PGP (Secure Email)
- WhatsApp etc.
Asymmetric Cryptography
Discuss!
Event Sourcing
- Store list of changes in system
- Audit Trail/Ledger
- Calculate 'current state' whenever desired
Properties
- History is kept
- Author of change known
- Reprocess/analyze as much as you like
Example uses
- Banking systems
- Other administrative systems
- Sensor data
- 'event-driven' architectures
Event Sourcing
Properties
- History is kept
- Author of change known
- Reprocess/analyze as much as you like
Example uses
- Banking systems
- Other administrative systems
- Sensor data
- 'event-driven' architectures
Event Sourcing
Discuss!
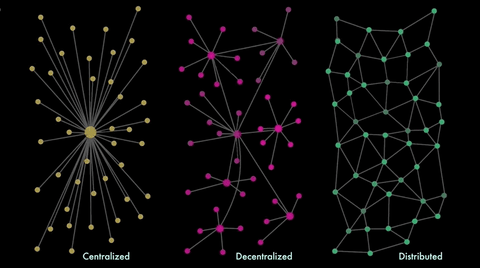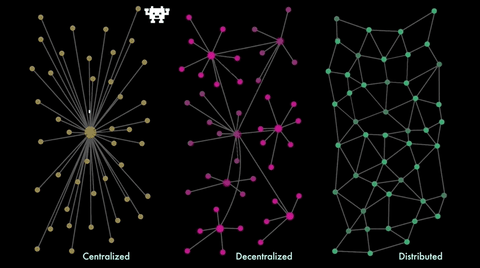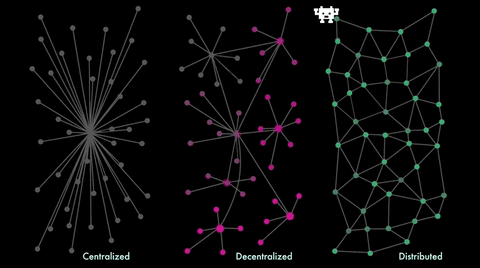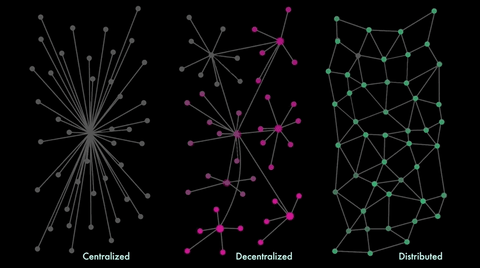
Consensus
- Distributed (and maybe decentralized) system
- Multiple parties in agreement about 'state'
- Potentially unreliable network
- Potentially some unreliable parties
A Blockchain is a software system in which:
- All data is immutable
- Anyone can join and add data
- All members agree about the order of the data
Recap:
Definition of a Public Blockchain:
Consensus: Proof-of-Work and variants
- Slow
- Expensive (electricity)
- Small amounts of data
A Blockchain is a software system in which:
- All data is immutable
- Anyone can join and add data
- All members agree about the order of the data
Consensus: (Delegated) Proof-of-Stake
- Relatively Slow
- Very difficult to implement in a fair way
- Small amounts of data
A Consortium/Private Blockchain is a software system in which:
- All data is immutable
Anyone can join and add data- All members agree about the order of the data
Consensus: 'Classical' Paxos, Raft, etc.
- Fast
- in use for 30+ years
- Small-ish amounts of data
a Decentralized Datastore is a software system in which:
- All data is immutable
- Anyone can join and add data
All members agree about the order of the data
Consensus: Not needed, because no ordering
(Data integrity is checked by hashing)
- Super fast!
- HUGE amounts of data
Consensus
| Name | Properties | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Public Blockchains | • Small amounts of data • Anyone can read/write • Ordered • Updates impossible • Slow |
Bitcoin, Ethereum |
| Consortium/Private Blockchains | • Medium amounts of data • Consortium/you decide(s) who can read • Consortium/only you can write • Ordered • Updates possible • Fast |
Hyperledger Fabric, Corda, MultiChain |
| Decentralized Datastores |
• Large amounts of data • Anyone can read/write • Unordered • Updates easy • Very Fast |
BitTorrent, IPFS |
Summary
- Starting to use a Blockchain is difficult
- Four Concepts:
- Hashing
- Asymmetric Cryptography
- Event Sourcing
- Consensus
- Easing in: It's not all-or-nothing!
- Use the right tool for the right job
