2019.05.24에 할꺼
프로그래밍

=

지팡이
=
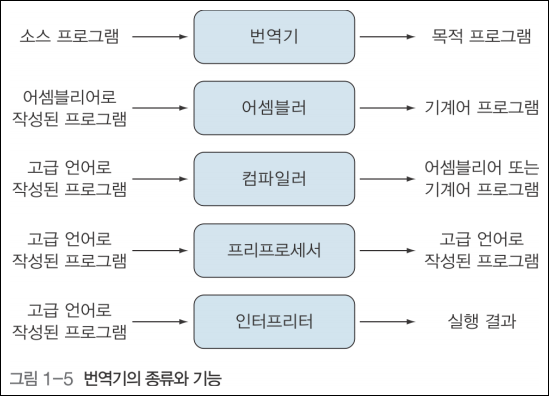
컴파일러
주문
=
프로그래밍 언어
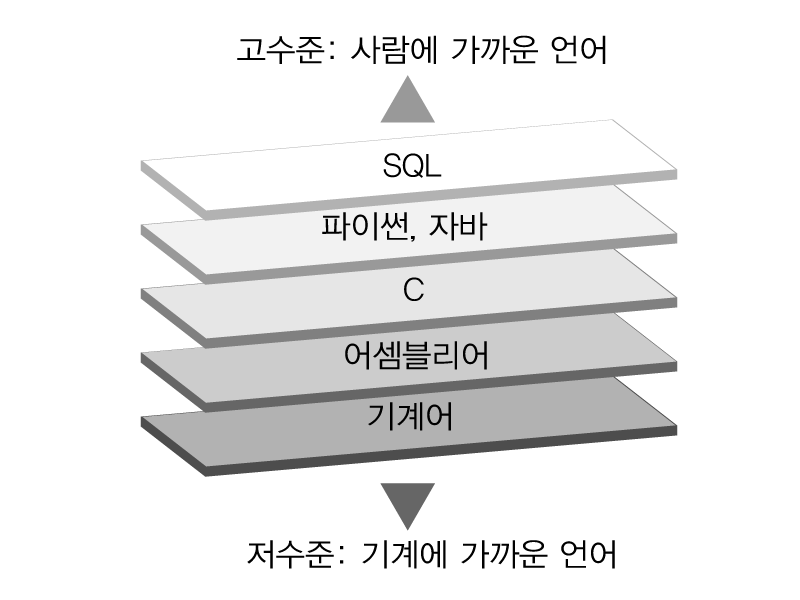
c# ≈ 고수준
컴파일러
=
번역기
(언어 => 기계어)

변수
변수
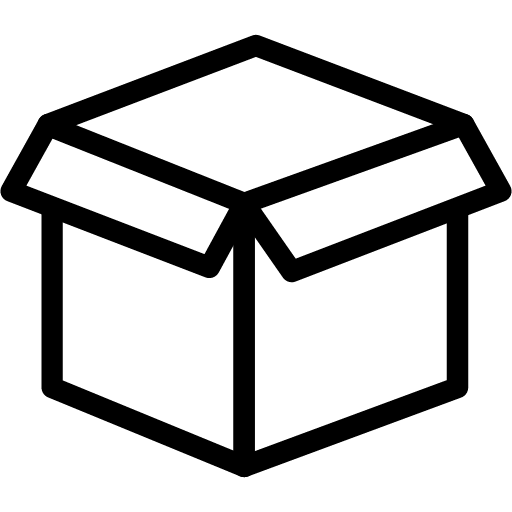
값
어떤 값을 이름 붙인 상자에 넣는다
어떤 값에 이름을 붙인다

숫자
(정수;int)

숫자
(실수;float)

문자
(char)

문자열
(string)
변수
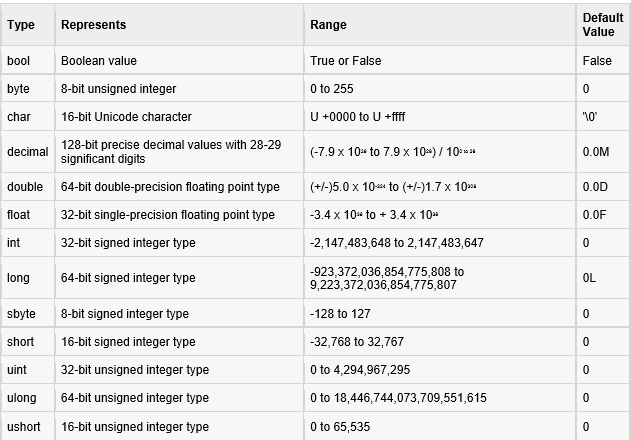
+ string
입출력
Console.WriteLine(string str)
값
(값 or 변수)
using system;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] arg)
{
//바로 값을 사용
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
//변수 사용
string str = "Hello World";
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
}Console.ReadLine(string str)

값

변수
using system;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] arg)
{
//변수 선언 부를 따로 분리
string str1;
str = Console.ReadLine();
// 변수 선언과 입력을 동시에,
// 단 동시에 작동하는 건 아니고
//표기를 동시에 한 것뿐!
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
}
}변환

문자열
(string)

숫자
(int, float, double)
값
Parse; 변환, 분석
변환(분석)된 값
int.Parse(int input)
float.Parse(int input)
double.Parse(int input)

숫자
(int, float, double)
값(문자열)
변환
using system;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] arg)
{
//"15"라는 문자열 값을 변수 value1에 넣음
int value1 = int.Parse("15");
//string 배열 속 값을 int값으로 바꾸어
//변수 value2에 넣음
string input = "15";
int value2 = int.Parse(input);
}
}
숫자
(A타입)

숫자
(B타입)
값
변환
변환
명시적 변환
(변환될 타입명;int, float...)변수명
암묵적 변환(큰 범위의 변수로 변환할 때)
(변환될 타입명;int, float...)변수명

숫자
(int, float, double)
값(숫자)
변환
using system;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] arg)
{
// 명시적 변환
int valueInt1 = 12;
float valueFloat1 = (float)valueInt1;
// 암묵적 변환
float valueFloat2 = 12f;
int valueInt2 = valueFloat2;
// == int valueInt2 = (int)valueFloat2;
}
}연산자
수식 : +, -, *, /, %
할당 : +=, -=, *=, /=, %=
증감 : 변수++, 변수--, ++변수, --변수
관계 : !=, ==, >, <, >=, <=
논리 : ||, &&, !
논리
추론과 같은 의미이며 틀린 추론을 하지 않기 위해 기호로 나타낸 것을 논리 기호라 함
true와 false를 나타내는(다루는) 것
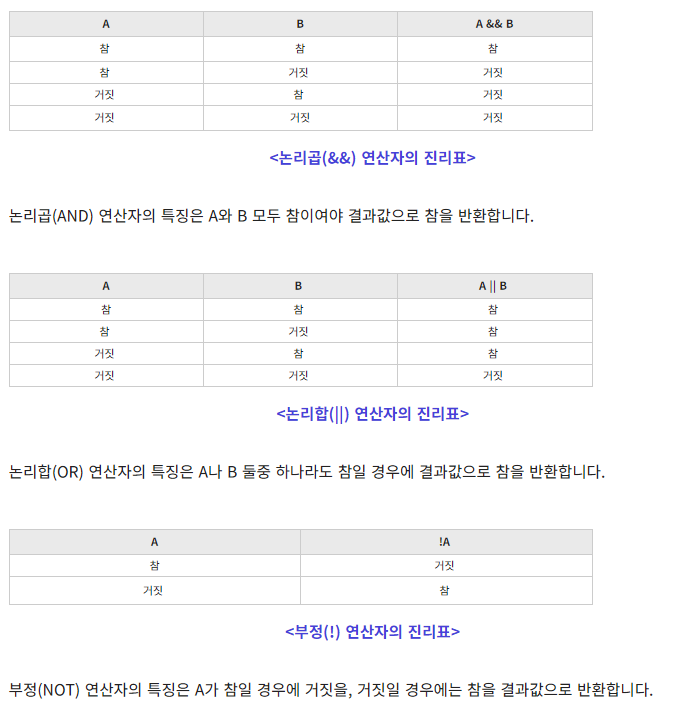
&& : 논리 곱, || : 논리 합, ! : 부정
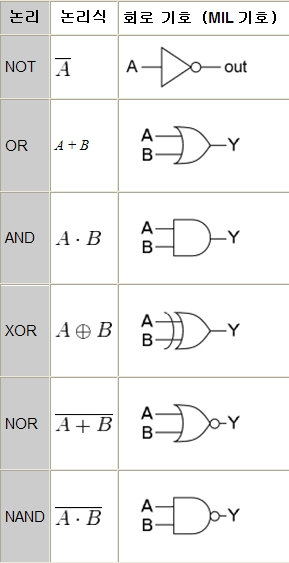
||(bool), |(bit)
&&(bool), &(bit)
!(bool), ~(bit)
!(A;bool || B;bool)
조건(문)
if; 만약~하다면
if(조건)
{
//명령
}
조건: bool(true, false), 논리 연산자, 관계연산자
명령 : 프로그래밍 언어(, 평소에 치던거)
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//bool 값을 조건으로
if (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
//관계연산자를 조건으로
string str = "name";
if(str == "name")
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
//논리연산자를 조건으로
bool condition1 = true;
bool condition2 = false;
if(condition1 || condition2)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}
}
조건이 맞으면
(조건 == true)
명령을 진행
if, else
;(이미 언급된 것에 덧붙여) 또 다른
if(조건)
{
//명령
}
else
{
//명령
}
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "name";
if(str == "name")
{
Console.WriteLine("str은 name이다.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("str은 name이 아니다.");
}
}
}
조건이 맞으면
(조건 == true)
if 블럭 안 명령을 진행
조건이 틀리면
(조건 == false)
else 블록 안 명령을 진행
if, else if, else
if(조건1)
{
//명령
}
else if(조건2)
{
//명령
}
else
{
//명령
}
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "name";
if(str == "name1")
{
Console.WriteLine("str은 name이다.");
}
else if(str == "name2")
{
Console.WriteLine("str은 name2이다.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("str은 name1도 name2도 아니다");
}
}
}
조건1이 맞으면
(조건1 == true)
if 블럭 안 명령을 진행
조건1이 틀리고
조건 2가 맞으면
(조건1 == false && 조건 2 == true)
else if 블록 안 명령을 진행
위 모든 조건이 틀리면
(조건1 == false && 조건 2 == false)
else 블록 안 명령을 진행
switch; 스위치
switch(변수)
{
case 값1:
//명령
break;
case 값2:
//명령
break;
...
default:
//명령
break;
}
using System;
namespace SwitchStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int number = 0;
switch (number)
{
case 0:
Console.WriteLine("0");
break;
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("1");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("변수의 값은 0이나 1이 아닙니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
변수의 값이 값1일때
(변수 == 값1)
값1 case의 명령 시행 후 break
변수의 값이 값2일때
(변수 == 값2)
값2 case의 명령 시행 후 break
변수의 값이 case에 없을 때
(변수 != 값1 && ...)
default의 명령 시행 후 break
switch; 스위치
switch(변수)
{
case 값1:
// 여기에 명령 X
case 값2:
//명령
break;
...
default:
//명령
break;
}
using System;
namespace SwitchStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int number = 0;
switch (number)
{
case 0:
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("0, 1");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("변수의 값은 0이나 1이 아닙니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
변수의 값이 값1이거나 값2 일때
(변수 == 값1 || 변수 == 값2)
값1,2 case의 명령 시행 후 break
변수의 값이 case에 없을 때
(변수 != 값1 && ...)
default의 명령 시행 후 break
if
switch
관계연산자 사용 O
관계연산자 사용 X
다중조건 O
다중조건 O
조건이 많을 경우 느림
조건이 많아도 속도 같음
반복문
while; ~하는 동안
while(조건)
{
//명령
}
조건이 맞는 경우(조건 == true)
명령을 계속 반복
조건 : bool, 관계 연산자, 논리 연산자
using System;
namespace WhileStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World");
}
}
}
}
while 탈출
using System;
namespace WhileStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 조건 바꾸기
int a = 0;
while(a < 5)
{
a++;
Console.WriteLine(a);
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
}
}
}
1. 조건을 false로 바꾼다.
2. break를 쓴다.
int a = 0;
조건 : a < 5 일때
a++를 명령에 넣으면
5번의 반복 후 탈출
while(조건)
{
break;
}
using System;
namespace WhileStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// break 1
while (true)
{
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
// break 2
int b = 0;
while (true)
{
if (b == 1)
{
break;
}
b++;
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
}
}
}
for; ~동안
while문에서 구간을 중요시한 반복문
int a = 0;
while(a < 5)
{
//명령
a++;
}
=
for(int a = 0; a < 5; a++)
{
//명령
}
for
for(초기식; 조건식; 증감식)
{
//명령
}
초기식 : 변수를 초기화 하는 식
('=' 사용)
증감식 : 변수를 증가 혹은 감소 하는 식
(대입 연산자나 증감 연산자 사용)
조건식 : 루프를 계속 진행할 건지 조건 검사하는 식
(관계연산자나 논리연산자 사용)
using System;
namespace ForStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//선언하고 for문의 초기식에서 변수 초기화
int i;
for (i = 0; i > 3; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
//변수 선언과 초기화를 for문의 초기식에서 진행
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
Console.WriteLine(j);
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
}
}
}
for 탈출
using System;
namespace ForStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//조건 바꾸기
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
}
}
}
1. 조건을 false로 바꾼다.
2. break를 쓴다.
조건식이랑 증감식만 제대로 써주면 됨.
for(초기식; 조건식; 증감식)
{
break;
}
using System;
namespace ForStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//break 1
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
//break 2
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
if (i == 1)
{
break;
}
}
Console.WriteLine("탈출");
}
}
}
for == while ?
for(;조건식;)
{
//명령
}
while(조건)
{
//명령
}
=
for(;;)
{
//명령
}
while(true)
{
//명령
}
=
using System;
namespace ForStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//for == while
int i = 0;
for(;i < 3;)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
while(i < 3)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
}
}
for 특징
어떤 범위를 반복하기 쉽다.
배열에서 편하게 쓰인다.
복잡하게 생겼다.
Q. 내 이름인지 검사하는 프로그램을 만들자.
입력 : 임의의 문자열이 끊임없이 주어진다.
출력 :
N번째 만에 이름이 주어졌습니다.
(단, 이때 N은 자신의 이름이 주어진 순서이며 0을 포함한 양의 정수이다.)
문제 : 입력된 문자열을 검사하여 만약 자신의 이름이라면 반복문을 멈추고 "출력"과 같이 출력하고 아닌 경우에는 처음부터 반복한다.
Q. for문으로 구구단 1단 만들기
입력 : 없음.
출력 :
1 * 1 = 1
1 * 2 = 2
...
1 * 9 = 9
Q. for문으로 구구단 만들기
입력 : 없음.
출력 :
1 * 1 = 1
1 * 2 = 2
...
1 * 9 = 9
2 * 1 = 2
...
9 * 9 = 81
continue; 계속되다
whlie(조건)
{
if(조건1)
{
continue;
}
//명령
}
for(초기식;조건식;증감식)
{
if(조건1)
{
continue;
}
//명령
}
using System;
namespace ForStatement
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//continue
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if (i == 4)
{
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
int j = 0;
while (j < 5)
{
if(j == 3)
{
continue;
}
Console.WriteLine(j);
}
}
}
}
}