https://slides.com/rachnerd/deck-1/live#/
npm i -g angular-cli
ng new ws-app --style=scss --prefix=ws
Rachèl Heimbach
Consultant @ Quintor





Hands-on
Angular 2
ChatApp
Content
- Components
- Services + RxJS
- Angular Material
- Angular Animations
- Routing
- Guards
- Change Detection
- View Encapsulation

Features
- const & let
- Arrow functions
- Class
- Value import/export
- Promises
const === final === readonly
const foo = 'bar';
foo = 'Something else'; // Error
const obj = {
foo: 'bar'
};
obj.foo = 'Something else'; // Ok let, how var should've worked
function varTest() {
var x = 1;
if (true) {
var x = 2; // same variable!
console.log(x); // 2
}
console.log(x); // 2
}function letTest() {
let x = 1;
if (true) {
let x = 2; // diff variable
console.log(x); // 2
}
console.log(x); // 1
}https://developer.mozilla.org/en/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/let
Stop using
var... Use const/let
Arrow functions
//http://es6-features.org/#ExpressionBodies
// ES5
odds = evens.map(function (v) { return v + 1; });
pairs = evens.map(function (v) { return { even: v, odd: v + 1 }; });
nums = evens.map(function (v, i) { return v + i; });
// ES6
odds = evens.map(v => v + 1)
pairs = evens.map(v => ({ even: v, odd: v + 1 }))
nums = evens.map((v, i) => v + i)
const plusOne = (v) => v + 1;
odds = evens.map(plusOne)Arrow function scope
this.foo = 'bar';
function logFoo() {
console.log(this.foo);
}
logFoo(); // undefinedthis.foo = 'bar';
const logFoo = () => {
console.log(this.foo);
}
logFoo(); // 'bar'this.foo = 'bar';
var self = this;
function logFoo() {
console.log(self.foo);
}
logFoo(); // barUse
Arrow =>
functions
class
class MyClass {
constructor() {
console.log('MyClass initialized');
}
foo() {
console.log('bar');
}
}
// Syntax sugar for
function MyClass() {
console.log('MyClass initialized');
}
MyClass.prototype.foo = function () {
console.log('bar');
}File scope
// a.js
const privateVariable = 'foo';
export const publicVariable = 'bar';
export default class Foo {
constructor() {
console.log('Foo bar');
}
}// b.js
import { privateVariable } from './a.js';
// Error
import { publicVariable } from './a.js';
// 'bar'
import anyName from './a.js';
// function Foo() {
// console.log('Foo bar');
// }
import * as everything from './a.js';
// {
// default: Foo(),
// publicVariable: "bar"
// }ES6
const + let are the new var.
Arrow functions can (almost) always replace the old function keyword.
class instead of prototype.
Many more features, mainly syntactic sugar.
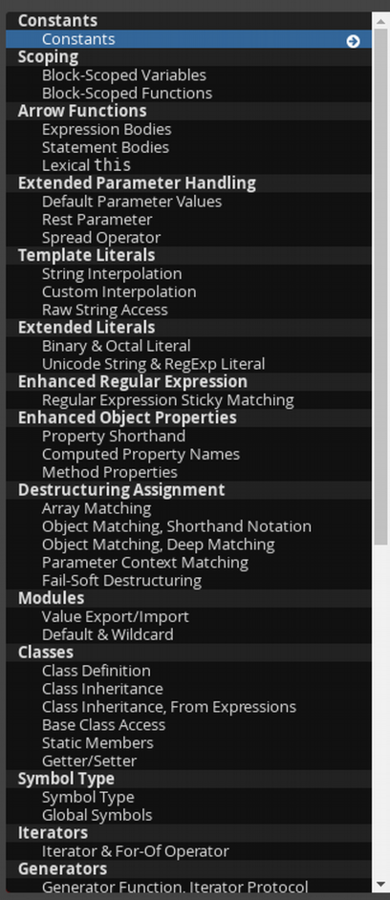

TypeScript
"JavaScript that scales."
TypeScript is a typed superset of JavaScript that compiles to plain JavaScript.
Any browser. Any host. Any OS. Open source.
TypeScript features
- Types
- Interfaces
- Decorators
- Access modifiers
Why types in JS?
- See errors at compile-time and not just at run-time.
- Using strong types prevent more bugs and side effects.
- Proper auto completion in smart IDE's.
const addNumbers = (n1: number, n2: number): number => {
return n1 + n2;
};
addNumbers(1, 2);
// 3
addNumbers('1', 2);
// Does not compile
const text: string = addNumbers(1, 2);
// Does not compile
addN
TS interfaces
- Help create data model
- Can be used by developers with an OOP approach
interface Person {
firstName: string;
lastName: string;
}
const person: Person = {
firstName: 'Foo'
}
// Does not compile
const person: Person = {
firstName: 'Foo',
lastName: 'Bar'
}
// Does compile
interface DoSomething {
doSomething(): void;
}
class Test implements DoSomething {
}
// Does not compile
class Test implements DoSomething {
doSomething(): void {}
}
// Does compileRuntime
===
JavaScript
Keep in mind...
Adding types is optional, but strongly recommended.
@Decorators
Ability to add metadata to variables/methods/classes
Ability to intercept functionality by applying logic before and after method execution.
Access modifiers
Control the visibility of your instance members/methods.
Create public API's in your classes.
class Foo {
private message: string = 'bar';
public constructor() {
}
public printMessage(): void {
console.log(this.message);
}
private someInternalProcess(): void {
// Do stuff
}
}
const foo = new Foo();
foo.Compiler
The TS compiler needs to be configured for the project.
TS compiler will scan the project and look for d.ts files.
(Most) JavaScript libraries have declaration files available so the TS compiler can understand them.
Tool: typings (on npm)
{
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "commonjs",
"target": "es5",
"outDir": "dist",
"rootDir": ".",
"sourceMap": true,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true,
"experimentalDecorators": true,
"moduleResolution": "node"
},
"exclude": [
"node_modules"
],
"awesomeTypescriptLoaderOptions": {
"useWebpackText": true
},
"compileOnSave": false,
"buildOnSave": false,
"atom": {
"rewriteTsconfig": false
}
}
Angular 2
- Components & Modules
- Dependency Injection
- Routing
- Directives/Pipes
- Angular 1
Webcomponents
- Custom html element.
- Isolated JS + HTML + CSS.
- API - Data in/Events out.
Everything
is a
Component
Subtitle

Chat
ChatForm
ChatList
ChatMessage
UserList
User
Component tree
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
ChatMessage

@Component
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-root',
template: `
<div>
Hello world
</div>
`
})
export class AppComponent {}<body>
<ws-root></ws-root>
</body>Hello world
Hello World App
/**
* A basic hello-world Angular 2 app
*/
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from '@angular/platform-browser-dynamic';
@NgModule({
declarations: [ RootComponent ],
imports: [ BrowserModule ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ],
})
class HelloWorldAppModule {}
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(HelloWorldAppModule);Angular
web-framework?

Angular 2

"For web, mobile web, native mobile and native desktop"
NativeScript + Angular 2
Cross platform (Android + iOS) native apps.



Back
to
Components!
@Component
Concepts
Smart
- Communicates with services and binds values to the template.
- Is the parent of one or multiple dumb components.
Dumb
- Has a public API of inputs and outputs.
- Contains no logic.
- Input by databinding.
- Output by event emitting.
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
Smart
Dumb
ChatMessage
Data binding
Event emitting
[Databinding] Input()
import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat-list',
template: `
<div *ngFor="let message of messages">
{{ message.content }}
</div>
`
})
export class ChatListComponent {
@Input()
messages: Array<ChatMessage>;
}<ws-chat-list [messages]="messages"></ws-chat-list>[ ]???
Template bindings
<input value="Some value" /> <!-- Literal bind -->
<input [value]="text" /> <!-- One way bind -->
<input (change)="handler($event)" /> <!-- Event handler -->
// Component config...
export class MyComponent {
text: string = 'Some value';
handler(event): void {
// do something
}
}Template references
<input #inputRef (change)="handler(inputRef)" />
// Component config...
export class MyComponent implements AfterViewInit {
@ViewChild('inputRef')
inputRef: ElementRef;
ngAfterViewInit() {
const input: HTMLInputElement = inputRef.nativeElement;
input.value = 'Initial value';
}
handler(input: HTMLInputElement): void {
input.value = '';
}
}(Event) @Output()
import { Component, Output,
EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat-form',
template: `
<form (ngSubmit)="send.emit(message.value)">
<input #message/>
</form>
`
})
export class ChatFormComponent {
@Output()
send: EventEmitter<string> = new EventEmitter();
}<ws-chat-form (send)="doSomething($event)"></ws-chat-form>Lifecycle
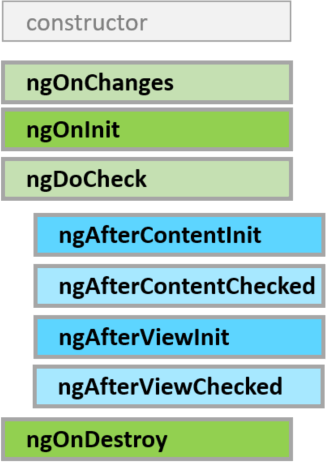
Angular 2 cheatsheet
Breathe...

Recap
- Component tree
- Databinding downwards
- Events upwards
- Smart components execute logic
- Dumb components receive [data] and emit (events)
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
Smart
Dumb
ChatMessage
DEMO/Break
import { Component, Output, EventEmitter } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat-form',
template: `
<form (ngSubmit)="send.emit(message.value)">
<input #message/>
</form>
`
})
export class ChatFormComponent {
@Output() send: EventEmitter<string>
= new EventEmitter<string>();
}import { Component, Input } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat-list',
template: `
<div *ngFor="let message of messages">
{{ message.content }}
</div>
`
})
export class ChatListComponent {
@Input() messages: Array<ChatMessage>;
}import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { ChatMessage } from './shared/chat.model';
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat',
template: `
<ws-chat-list [messages]="messages"></ws-chat-list>
<ws-chat-form (send)="onSend($event)"></ws-chat-form>
`
})
export class ChatComponent {
messages: Array<ChatMessage> = [];
onSend(content: string): void {
this.messages.push(new ChatMessage(content));
}
}Databind [messages]
Event (send)
Smart
Dumb
Dumb
Dependency Injection
Services
||
Values
Service
Instance containing reusable, grouped functionality.
Contains all logic of the application.
Only smart components call service methods that execute logic.
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { ChatMessage } from './chat-model';
@Injectable()
export class ChatService {
constructor() {}
getMessages():Array<ChatMessage> {
return [];
}
sendMessage(message: ChatMessage):void {
return;
}
}ng new class chat/shared/chat-service
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
ChatMessage
ChatService
+getMessages()
+sendMessage(message)
Providing
Creates an instance of the dependency.
Injecting
Injects the provided dependency into a component or service.
Provide B so A can inject B
Subtitle
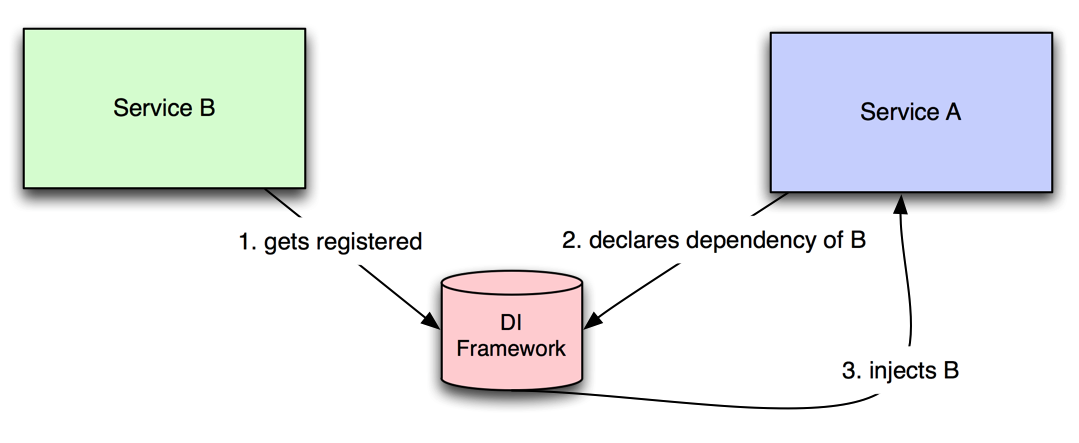
Services
!==
Singleton
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
ChatMessage
ChatService
+getMessages()
+sendMessage(message)
Inject
ChatService?
Nope (throws error)
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
ChatMessage
ChatService
+getMessages()
+sendMessage(message)
Inject
ChatService?
ChatService!
Provide
ChatService
Provide in module
Inject in any other dep.
@NgModule({
declarations: [
RootComponent,
ChatComponent
],
imports: [ BrowserModule ],
bootstrap: [ RootComponent ],
providers: [ ChatService ]
})
export class AppModule {}export class ChatComponent {
constructor(private chatService: ChatService) {
this.chatService.getMessages();
}
} App
Chat
ChatService
+getMessages()
+sendMessage(message)
App. Logic
in
Services
@Component({
//Config
})
export class ChatComponent {
messages: Array<ChatMessage> = [];
onSend(content: string): void {
this.messages.push({content});
}
}LOGIC!
@Component({
//Config
})
export class ChatComponent implements OnInit {
messages: Array<ChatMessage>;
constructor(private chatService: ChatService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.messages = this.chatService.getMessages();
}
onSend(content: string): void {
this.chatService.sendMessage(content);
}
}LOCAL STATE!
BETTER
HttpModule
export declare class Http {
//...
/**
* Performs a request with `get` http method.
*/
get(url: string, options?: RequestOptionsArgs): Observable<Response>;
/**
* Performs a request with `post` http method.
*/
post(url: string, body: any, options?: RequestOptionsArgs): Observable<Response>;
/**
* Performs a request with `put` http method.
*/
put(url: string, body: any, options?: RequestOptionsArgs): Observable<Response>;
/**
* Performs a request with `delete` http method.
*/
delete(url: string, options?: RequestOptionsArgs): Observable<Response>;
//...
}Observable<Response>?
ChatService
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import { ChatMessage } from './chat-model';
@Injectable()
export class ChatService {
constructor(private http: Http) {}
getMessages():Array<ChatMessage> {
return [];
}
sendMessage(message: ChatMessage):void {
return;
}
}error_handler.js:47ORIGINAL EXCEPTION: No provider for Http!
@NgModule({
declarations: [
RootComponent,
ChatComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpModule
],
bootstrap: [ RootComponent ],
providers: [ ChatService ]
})
export class AppModule {}ChatService
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import { ChatMessage } from './chat-model';
@Injectable()
export class ChatService {
constructor(private http: Http) {}
getMessages():Observable<Array<ChatMessage>> {
return this.http
.get(url)
.map((res: Response) => res.json());
}
sendMessage(message: ChatMessage):Observable<Response> {
return this.http
.post(url, {content: message});
}
}@Component({
//Config
})
export class ChatComponent implements OnInit {
messages: Array<ChatMessage>;
constructor(private chatService: ChatService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.chatService.getMessages()
.subscribe(
(messages: Array<ChatMessage>) => this.messages = messages,
(error: Response) => console.error(error),
() => console.log('Stream closed') //Completed
);
}
onSend(content: string): void {
this.chatService.sendMessage(content)
.subscribe(
(res: Response) => console.log('Sent'),
(error: Response) => console.error(error),
() => console.log('Stream closed') //Completed
)
}
}DEMO/Break
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import { ChatMessage } from './chat-message.model';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs/Rx';
@Injectable()
export class ChatService {
constructor(private http: Http) {}
getMessages():Observable<Array<ChatMessage>> {
return this.http
.get(url)
.map((res: Response) => res.json());
}
sendMessage(message: ChatMessage):Observable<Response> {
return this.http
.post(url, {content: message});
}
}import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ChatMessage } from './shared/chat-message.model';
import { ChatService } from './shared/chat-service.service';
import { Http, Response } from '@angular/http';
@Component({
//Config
})
export class ChatComponent implements OnInit {
messages: Array<ChatMessage>;
constructor(private chatService: ChatService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.chatService.getMessages()
.subscribe(
(messages: Array<ChatMessage>) => this.messages = messages,
(error: Response) => console.error(error),
() => console.log('Stream closed')
);
}
onSend(content: string): void {
this.chatService.sendMessage(content)
.subscribe(
(res: Response) => console.log('Sent'),
(error: Response) => console.error(error),
() => console.log('Stream closed')
)
}
}url = ....
Angular CLI
Styling?

Angular 2 Material
Google material design

Install Angular material 2
- Add MaterialModule.forRoot() to AppModule's imports
- Add to index.html:
- Add to styles.scss:
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/icon?family=Material+Icons" rel="stylesheet">@import '~@angular/material/core/theming/prebuilt/deeppurple-amber.css';
body {
margin: 0;
font-family: Roboto, sans-serif;
}
npm i --save @angular/materialAnimations

Animation syntax
@Component({
selector: 'ws-chat',
templateUrl: './chat.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./chat.component.scss'],
animations: [
trigger('fadeIn', [
transition('void => *', [
style({
opacity: 0
}),
animate('1s ease-in')
])
])
]
})<div [@fadeIn]><!--Content--></div>Animation state
@Component({
...
animations: [
trigger('heroState', [
state('inactive', style({
backgroundColor: '#eee',
transform: 'scale(1)'
})),
state('active', style({
backgroundColor: '#cfd8dc',
transform: 'scale(1.1)'
})),
transition('inactive => active', animate('100ms ease-in')),
transition('active => inactive', animate('100ms ease-out'))
])
]
})
export class ChatComponent {
state: string = 'inactive';
doSomething() {
this.state = 'active';
}
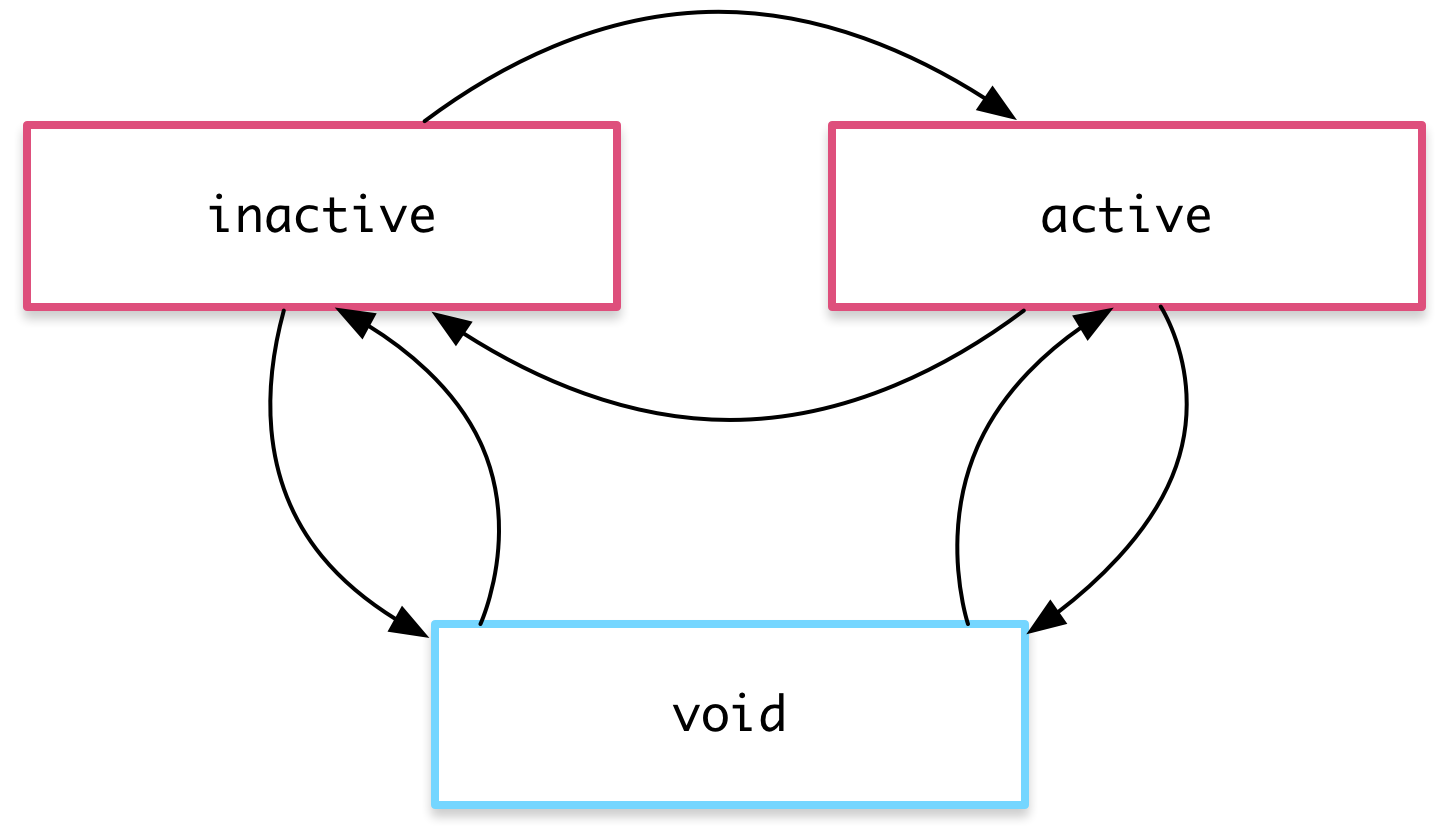
}<div [@heroState]="state"><!--Content--></div>Animations
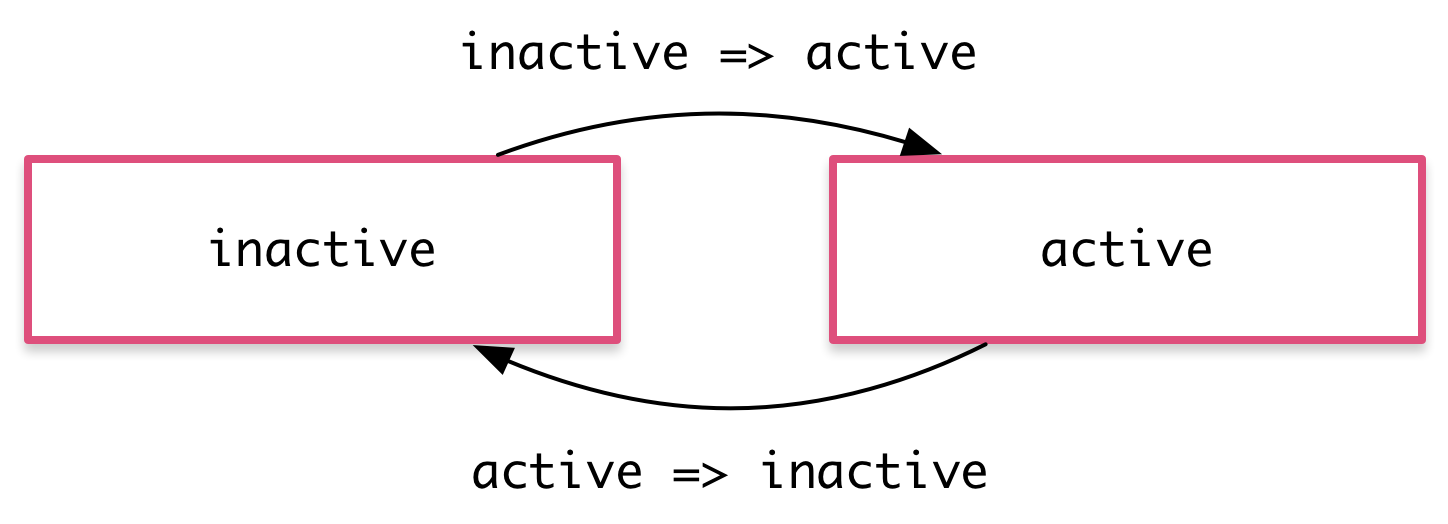
Complex animations
animations: [
trigger('heroState', [
state('inactive', style({transform: 'translateX(0) scale(1)'})),
state('active', style({transform: 'translateX(0) scale(1.1)'})),
transition('inactive => active', animate('100ms ease-in')),
transition('active => inactive', animate('100ms ease-out')),
transition('void => inactive', [
style({transform: 'translateX(-100%) scale(1)'}),
animate(100)
]),
transition('inactive => void', [
animate(100, style({transform: 'translateX(100%) scale(1)'}))
]),
transition('void => active', [
style({transform: 'translateX(0) scale(0)'}),
animate(200)
]),
transition('active => void', [
animate(200, style({transform: 'translateX(0) scale(0)'}))
])
])
]
Routing
App
Chat
ChatList
ChatForm
ChatMessage
const routes = [
{
path: '',
component: ChatComponent
}
];Routing module
const routes = [
{
path: '',
component: ChatComponent
}
];//imports
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
@NgModule({
declarations: [...],
imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot(routes),
...
]
...
})app-component.html
<example-toolbar></example-toolbar>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
<example-footer></example-footer><router-outlet></router-outlet>
<router-outlet name="sidebar"></router-outlet>
<router-outlet name="bottombar"></router-outlet>[
{
path: '',
component: GeneralChatComponent
},
{
path: 'team',
component: TeamChatComponent
},
{
path: 'friends',
component: FriendsComponent,
outlet: 'sidebar'
},
{
path: 'chat/:userId',
component: PrivateChatComponent,
outlet: 'bottombar'
}
]<router-outlet>
</router-outlet>
<router-outlet name="sidebar">
</router-outlet>
<router-outlet name="bottombar">
</router-outlet>:4200/
Main outlet
Bottombar outlet
Sidebar outlet
ChatComponent
Empty
Empty
:4200/team
Main outlet
Bottombar outlet
Sidebar outlet
TeamChatComponent
Empty
Empty
:4200/(sidebar:friends)
Main outlet
Bottombar outlet
Sidebar outlet
ChatComponent
FriendsComponent
Empty
:4200/
(sidebar:friends//bottombar:chat/123)
Main outlet
Bottombar outlet
Sidebar outlet
ChatComponent
FriendsComponent
PrivateChatComponent
(with user 123)
:4200/team
(sidebar:friends//bottombar:chat/123)
Main outlet
Bottombar outlet
Sidebar outlet
TeamChatComponent
FriendsComponent
PrivateChatComponent
(with user 123)
Lazy routes
- Code splitting.
- Load other chunks of the application when accessing certain routes.
- Less bandwidth usage (initial load).
- Fetch code run-time.
{
path: 'contacts',
loadChildren: 'contacts.bundle.js'
}Guards
Subtitle
Guards
- CanActivate - to prevent navigation to a route
- CanActivateChild - to prevent navigation to a child route
- CanDeactivate - to prevent navigation away from the current route
- Resolve - to pre-fetch data before activating
- CanLoad to prevent asynchronous routing
{
path: 'root',
canActivate: [],
canActivateChild: [],
canDeActivate: [],
resolve: {},
canLoad: [],
children: [
{
path: '',
component: Chat
}
]
}CanActivate
@Injectable()
export class CanActivateGuard implements CanActivate {
constructor(private chatService: ChatService) {
}
canActivate(
route: ActivatedRouteSnapshot,
state: RouterStateSnapshot
): Observable<boolean>|Promise<boolean>|boolean {
return true;
}
}Don't forget to provide guards to the module!
Break
Change detection
Subtitle
View encapsulation
Shadow DOM

RxJS
...is a set of libraries to compose asynchronous and event-based programs using observable collections and Array#extra style composition in JavaScript
RxJS
- Observables
- Angular 2
- Operators
- Subjects
Observables?
"Observables are functions that tie an observer to a producer."
Async data?
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if(condition) {
resolve('Done');
}else {
reject('Fail');
}
}, 1000);
})
.then(res => {})
.catch(err => {});Observable.create(observer => {
setTimeout(() => {
if(condition) {
observer.next('Done');
observer.complete(); //close
}else {
observer.error('Fail');
}
}, 1000);
})
.subscribe(
res => {},
err => {},
() => {}
);Start with the result
Angular Http requests
this.http.get('api/chat')
.subscribe(
(messages: Array<ChatMessage>) => {
console.log(messages)
},
(err: Response) => {
console.error(err)
}
);
// [Response Object]
// - status
// - statusText
// - text/json
// - etc...this.http.get('api/chat')
.map((res: Response) => res.json())
.subscribe(
(messages: Array<ChatMessage>) => {
console.log(messages)
},
(err: Response) => {
console.error(err)
}
);
// [Object, Object, Object]Messages?
Messages!
Issues while using map? Try:
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
rxmarbles
Cold
- 1 time usage, gets cleaned up after subscribe.
- Subscribe as many times as you want.
Hot
- Doesn't close after subscription.
- Subscriptions need to be manually unsubscribed
- Caution: memory leaks
State management
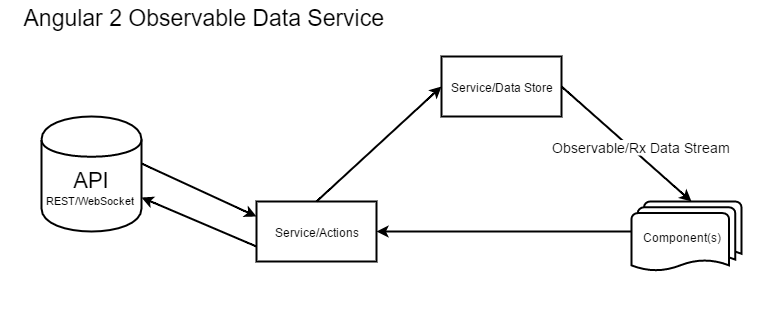
Subject
Observable
Subscription

Redux store
