DESIGN PATTERNS
Que vamos a Aprender
- Que son los Design Patterns
- Patterns y Anti-Patterns
- Patterns Comunes
- Constructor
- Prototype
- Observer and Pub/Sub
- Command Pattern
The Gang of four

QuÉ Son?
Soluciones a problemas que pueden ser reutilizadas fácilmente, como plantillas o recetas para problemas.
No son soluciones exactas.
Nos ayudan a crear un plan para construir nuestra solución.
Por Qué usarlas?
- Evitan problemas comunes
- Proveen soluciones generalizadas
- Disminuyen el tamaño total de nuestro código
- Añaden al vocabulario de un developer
- Evolucionan y mejoran
Pattern vs Anti-pattern
Patterns:
Prácticas standard
Anti-Patterns:
Lecciones aprendidas
Anti-Patterns
Un mal diseño que merece la pena documentar

design patterns
Constructor
Construyendo en JS
var newObject = {};
var newObject = Object.create(Object.prototype);
var newObject = new Object();
Constructor Básico
function Coche (modelo, año, km) {
this.modelo = modelo;
this.año = año;
this.km = km;
this.toString = function () {
return this.modelo + " tiene " + this.km + " km";
};
}
// Uso:
// Podemos crear nuevas instancias de 'Coche'
var civic = new Coche("Honda Civic", 2009, 20000);
var mondeo = new Coche("Ford Mondeo", 2010, 5000);
civic.toString(); // -> "Honda Civic tiene 20000 km"
mondeo.toString(); // -> "Ford Mondeo tiene 5000 km"Usando Prototype
function Coche (modelo, año, km) {
this.modelo = modelo;
this.año = año;
this.km = km;
}
Coche.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.modelo + ' tiene ' + this.km + ' km';
}
var miCoche = new Coche("Ford Escort", 1993, 150000);
console.log(miCoche) // --> "Ford Escort tiene 150000 km"PROTOTYPE
Object.create
var miCoche = {
nombre: "Ford Escort",
conducir: function() {
console.log("conduciendo!");
},
frenar: function() {
console.log("stop!");
},
}
// usa Object.create para instanciar un nuevo coche
var tuCoche = Object.create(miCoche);HEREDANDO
var vehiculo = {
getModelo: function() {
console.log("Modelo del vehículo", this.modelo);
}
};
var coche = Object.create(vehiculo, {
id: {
value: MY_GLOBAL.nextId(),
// writable: false, configurable: false <-- false by default
enumerable: true
},
modelo: {
value: "Ford Escort",
enumerable: true
}
});PROTOTYPE OVERRIDE
var vehiculoPrototipo = {
init: function(modelo) {
this.modelo = modelo;
},
getModelo: function() {
console.log("Modelo del vehículo: " + this.model);
}
};
function vehiculo(modelo) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = vehiculoPrototipo;
var f = new F();
f.init(modelo);
return f;
}
// lo usamos asi:
var coche = vehiculo("Ford Escort");
coche.getModelo();Usando Prototype
function Coche (modelo, año, km) {
this.modelo = modelo;
this.año = año;
this.km = km;
}
Coche.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.modelo + ' tiene ' + this.km + ' km';
}
var miCoche = new Coche("Ford Escort", 1993, 150000);
console.log(miCoche) // --> "Ford Escort tiene 150000 km"MODULE
Scope como Privacidad
var myNamespace = (function() {
// esta variable es privada
var myPrivateVar = 0;
// este método también
var myPrivateMethod = function(foo) {
console.log(foo);
};
return {
// Una variable pública:
myPublicVar: 'foo',
// un método publico que usa cosas privadas
myPublicFunction: function(bar) {
// Incrementa el contador privado
myPrivateVar++;
// llama a nuestro método privado usando bar
myPrivateMethod(bar);
}
};
})(); //<-- Invocamos la función directamenteVentajas de MOdule
- Facilita la transición a JS para programadores de otros lenguajes Orientados a objetos que echan de menos las Classes.
- Provee soporte a datos privados
DESVentajas de MOdule
- Los miembros privados y públicos se acceden de manera distinta, por tanto si queremos cambiar la visibilidad de un campo, necesitamos cambiar todas las referencias en las que éste se use.
- No podemos acceder a los miembros privados en métodos añadidos a nuestro módulo despés de su creación.
- No es posible escribir unit tests para miembros privados.
- Los miembros privados no pueden ser parcheados, así que si hay que reparar un bug, debemos modificar todos los miembros públicos.
Singleton
var mySingleton = (function () {
var instance;
function init() {
function privateMethod() {
console.log("soy Privado");
}
var privateVariable = "yo también soy privada";
var privateRandom = Math.random();
return {
publicMethod: function () {
console.log( "el público me puede ver!");
},
publicProperty: "y a mi también",
getRandomNumber: function() {
return privateRandomNumber;
}
};
};
return {
getInstance: function() {
if (!instance) {
instance = init();
}
return instance;
}
};
})();Observer
Coponentes
-
ObserverList: Una lista de Observadores que nos permite añadir, quitar y moverlos
-
Subject: Mantiene una lista de Observadores, y los añade o quita.
- Observer: Nuestro objeto tiene que implementar una interfaz para recibir notificaciones de cambio de estado en un Sujeto, por ejemplo, un callback
observer list
function ObserverList() {
this.observerList = [];
}
ObserverList.prototype.add = function(obj) {
return this.observerList.push(obj);
}
ObserverList.prototype.count = function() {
return this.observerList.length;
}
ObserverList.prototype.get = function(index) {
if (index > -1 && index < this.observerList.length) {
return this.observerList[index]:
}
}
ObserverList.prototype.indexOf = function(obj, startIndex) {
var i = startIndex;
while (i < this.observerList.length) {
if (this.observerList[i] === obj) {
return i;
}
i++;
}
return -1;
};
ObserverList.prototype.removeAt = function(index) {
this.observerList.splice(index, 1);
};Subject
function Subject() {
this.observers = new ObserverList();
}
Subject.prototype.addObserver = function(observer) {
this.observers.add(observer);
};
Subject.prototype.removeObserver = function(observer) {
this.observers.removeAt(this.observers.indexOf(observer, 0));
};
Subject.prototype.notify = function(context) {
var observerCount = this.observers.count();
for (var i = 0; i < observercount; i++) {
this.observers.get(i).update(context);
}
};Observer
function Observer() {
this.update = function() {
// ...
}
}PUB/SUB
var noLeidos = 0;
// podemos tener un subscriptor atento a cuando lleguen nuevos mensajes
// y que se encargue de renderizarlos en la pantalla:
var subs1 = subscribe("inbox/mensajeNuevo", function(sujeto, datos) {
// ** haz algo con el mensaje
renderizaMensaje(datos);
});
// y otro subscriptor que se encargue de actualizar el contador de
// mensajes no leidos
var subs2 = subscribe("inbox/mensajeNuevo", function(sujeto, datos) {
// actualiza el contador
actualizarContador(++unreadCount);
});
// y luego en otra parte de nuestro código:
publish("inbox/mensajeNuevo", [
{
sender: 'hello@google.com',
body: 'hola! que tal?'
}
]);VENTAjas
- Es uno de los patrones más importantes en Javascript
- Nos ayuda a pensar en las relaciones entre las diferentes partes de nuestro app
- Nos ayuda a identificar qué partes de nuestro sistema que contienen relaciones directas entre objetos pueden ser reemplazadas con sujetos + observadores
- Nos ayuda a dividir nuestro sistema en partes más pequeñas, testables y no co-dependientes.
Desventajas
- Es más dificil garantizar que partes del sistema funcionen de manera correcta si las hacemos demasiado independientes.
- Los subscriptores no saben si los publicadores estan funcionando correctamente
COMMAND
Comandos en los juegos
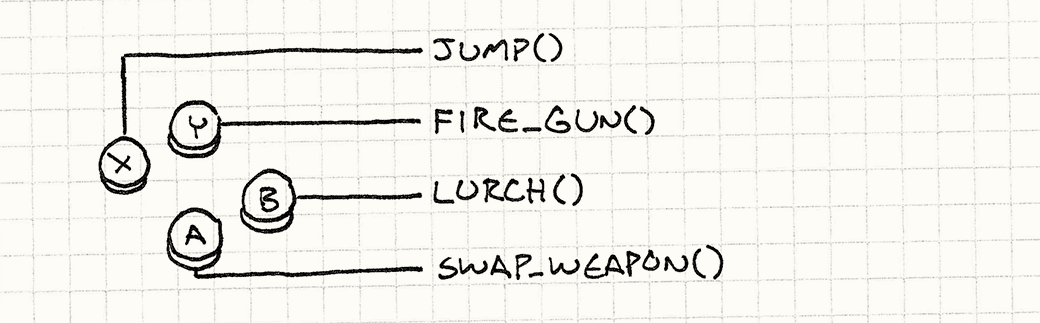
(from Game Programming Patterns)
Input Handler
handleInput() {
if (isPressed(BUTTON_X)) jump();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_Y)) fireGun();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_A)) swapWeapon();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_B)) crouch();
}
COMMAND INTERFACE
var Command = function() {
this.execute = function() {};
}Commando Acción
function JumpCommand() {
this.execute = function() {
jump();
}
}
function FireCommand() {
this.execute = function() {
fireGun();
}
}
function InputHandler () {
var botones = {
X : new Command(),
Y : new Command(),
A : new Command(),
B : new Command()
};
return {
handleInput() {
if (isPressed(BUTTON_X)) botones.X.execute();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_Y)) botones.Y.execute();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_A)) botones.A.execute();
else if (isPressed(BUTTON_B)) botones.B.execute();
},
setButton(boton, comando) {
// nos aseguramos de que `comando` implementa la interfaz
// de Command
if (!comando.hasOwnProperty('execute')) return null
botones[boton] = comando;
}
}
}Desaciendo
function Command () {
this.execute = function() {};
this.undo = function() {};
}function CommandHistory() {
this.undoHistory = [];
this.redoHistory = [];
this.performCommand = function(command) {
undoHistory.push(command);
command.execute();
}
this.undo = function() {
var lastCommand = undoHistory.pop();
if (!lastCommand) return null;
lastCommand.undo();
redoHistory.push(lastCommand);
}
this.redo = function() {
var lastCommand = redoHistory.pop();
if (!lastCommand) return null;
lastCommand.execute();
undoHistory.push(lastCommand);
}
}