Git
a free and open source distributed version control system

Index
- What is Git and why Git?
- Git WorkFlow
- Basic Introduction
- Gitk - a graphical history viewer
- Merge vs Rebase ? when to use what?
- Merge Squashing
- Cherry-pick patch to branches
-
Git Cli
- Basc commands (init/clone, add, commit, push, stash)
- Destructive commands (rebase, reset, force update)
- Update Comment message (--amend vs rebase -i)
- Reverting a merge Commit (revert Vs reset)
cont...
- Git Cli Scenario which may not be handle with IDE's
- SVN to Git Migration
- Remove Secrets from git commits
- Repository itself moved
- Push Old code where many jira's in commits are closed
- Moving a file from one project to other project
- Pro ductivity hacks
- Alias which i use daily
- Configure Default Editor
- Git ssh
- Reverting a merge Commit (Revert Vs reset)
- Get full file history of moved file
What is Git and why Git?
Git is an Open Source Distributed Version Control System.
There are two types of VCS:
- Centralized Version Control System (CVCS)
- Distributed Version Control System (DVCS)
Centralized Version Control System (CVCS)
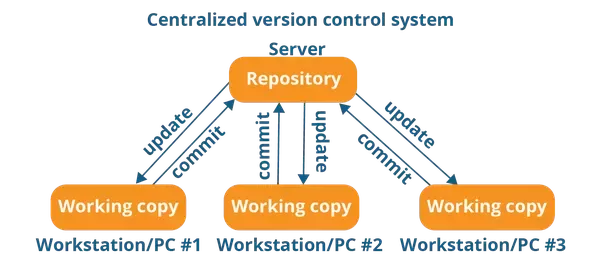
Distributed Version Control System (DVCS)

Git WorkFlow
- Working Tree
- Staging Area
- Local Branch
- Remote
- Stashing Area
Each layer hold the Complete snapshot reference of code at that given moment
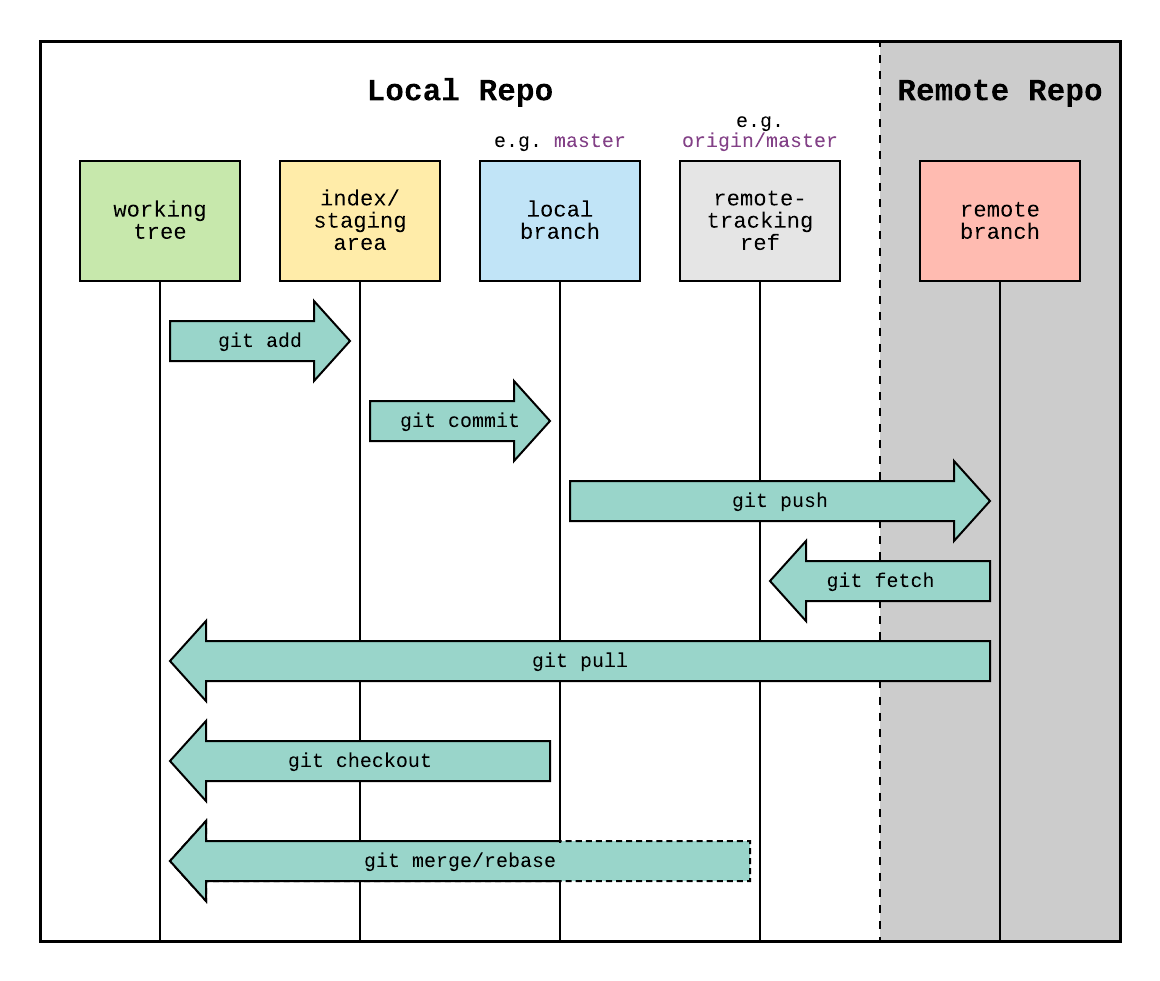
Git WorkFlow
Working Tree

The Currnet working folder
Git WorkFlow
Staging Area

Place where we select files which can be add to commit
Git WorkFlow
Local Branch

Local Repo where our changes are saved
Git WorkFlow
Remote Repo

Git server Repo where our changes are stored
Git WorkFlow
Stashing Area
A Place to park our current change

Stash Area
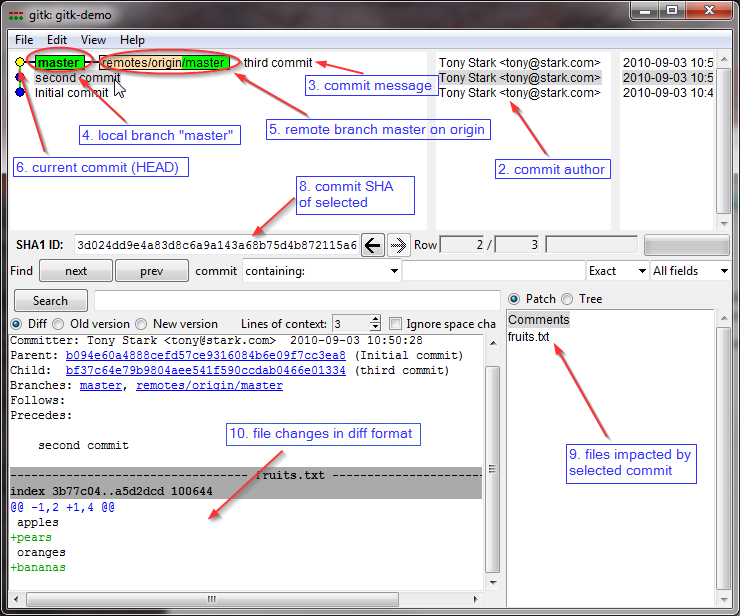
Gitk is a graphical history viewer
Basic Introduction
Rebasing and merging are both designed to integrate changes from one branch into another branch but in different ways.
(Rebasing is better to streamline a complex history,)
Merge vs Rebase ? when to use what?

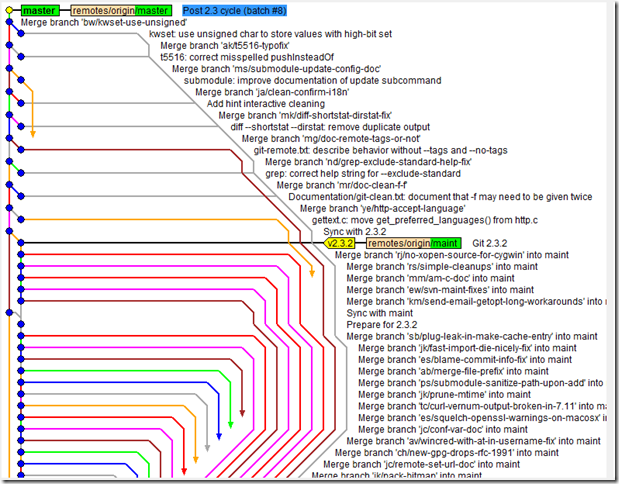
Merge vs Rebase ? when to use what?
Result of unnecessary local merges
To know more link
To avoid his use rebase while pulling you Change in local
-> git pull origin <branchName> --rebase
Squashing these commits can make the log more readable and understandable, both for ourselves and others.
git merge --squash FeatureBranc
Squash the on merge

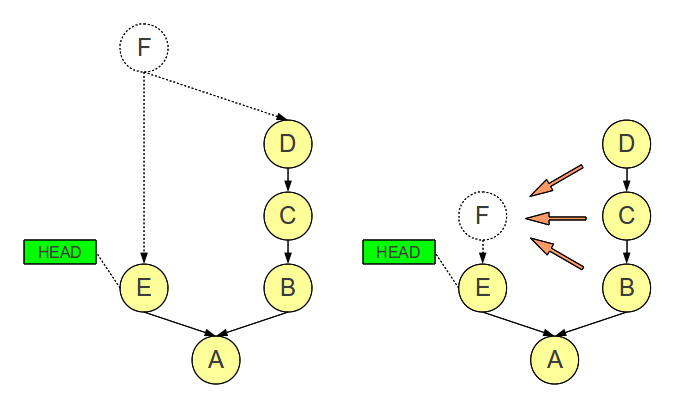
Squash
git cherry-pick is a powerful command that enables arbitrary Git commits to be picked by reference and appended to the current working HEAD.
git cherry-pick <commit-hash>
Cherry-pick patch to branches
Cherry-Pick
Git Cli - Basic
Baisc commands
-> git init or git clone
-> git add sample.txt
-> git commit -m "Jira No:XYZ Added new File"
-> git remote add origin "git@git.bnymellon.net:XBBNNMH/git-demo.git" // Optional for git clone
-> git push origin master
Get Update From Remote
-> git pull origin <branch> or
-> git pull origin master --rebase
Amend Last Commit
-> git commit --amend
-> git commit --amend -m "an updated commit message"
->git commit --amend --no-edit
- (init/clone, add, commit, push, stash)
- Destructive commands (rebase, reset, force update)
- Update Comment message (--amend vs rebase -i)
- Get full file history of moved file
- Reverting a merge Commit (Revert Vs reset)
Git Cli - Basic
Safely Revert Pushed commits
-> git revert <Commit-id>
Park Current Changes
-> git stash save "Message"
-> git checkout master && git pull --rebase
...
-> git checkout featureBranch
-> git stash pop
Git Cli - Destructive
Git Destructive cmd are rewrite the git history or that will altered the file changes in old commits pushed to remote
Permanently Remove Pushed commits
-> git reset <Commit-id> --hard
Amend Pushed commits
-> git rebase HEAD~5 -i
Force Push
-> git push origin branchName --force
- Destructive commands (rebase, reset, force update)
- Get full file history of moved file
- Reverting a merge Commit (Revert Vs reset)
Scenario's
1. Remove Secrets from git commits
if you commit sensitive data, such as a password or SSH key into a Git repository, you can remove it from the history, we can use either the git filter-branch command or the BFG Repo-Cleaner open source tool.
1. Loop through each commit and remove file
-> git filter-branch --force --index-filter \
"git rm --cached --ignore-unmatch ./password.properties"
2. Add .gitignore File to avoide pushing secure files in repo
3. Force push all branch and tags
-> git push origin --force --all
1 -> git push origin --force --tags
2. Repository itself moved
1. add a new remote in cmd
-> git remote add target <New git repo url>
2. Force push all branch and tags
-> git push target --force --all
-> git push target --force --tags
3. Push old Commits by appending new jira in all previous commits
1. Loop through each commit and update the matched commit
-> git filter-branch -f --msg-filter 'sed "s/OldText/NewText /g"' HEAD...HEAD~1 -- --all
2. Loop through each commit and update the matched commit
-> git filter-branch --msg-filter 'printf "NewJiraNumber: " && cat' master.. -- --all
3. Force push all branch and tags
-> git push target --force --all
-> git push target --force --tags
4. SVN to Git Migration
Steps
- Get svn auther's list
-> svn.exe log --quiet | ? { $_ -notlike '-*' } | % { "{0} = {0} <{0}>" -f ($_ -split ' \| ')[1] } | Select-Object -Unique
2. Clone svn repo
-> git svn clone ["SVN repo URL"] --prefix=svn/ --no-metadata --authors-file "authors-transform.txt" --stdlayout c:\mytempdir
3. Add .gitignore File
4. Add git remote and push it to git remote server
-> git remote add origin "git repo url"
-> git push
5. Moving a file from one project to other project
Steps
- Make Changes in soruce branch
git clone <git repository A url>
cd <git repository A directory>
git remote rm origin
git filter-branch --subdirectory-filter <directory 1> -- --all
mkdir <directory 1>
mv * <directory 1>
git add .
git commit
2. Merge files into new repository:
git clone <git repository B url>
cd <git repository B directory>
git remote add repo-A-branch <git repository A directory>
git pull repo-A-branch master --allow-unrelated-histories
git remote rm repo-A-branch
Productivity hacks
- Alias - Git Alias creation is a common pattern found in other popular utilities like `bash` shell.
- we can create a git alias to update the multiple repos in a single shot
- Configure Default Editor
-> git config --global core.editor
- Git SSH : Using the SSH protocol, you can connect and authenticate to remote servers and services. With SSH keys, you can connect to GitHub without supplying your username or password at each visit.
- Reverting a merge Commit: Give Jira number in all mergec request comments.
- Get full file history of moved file
-> git log -p --follow [file-path] -> git checkout -