TDD in a nutshell and how to use it in Android

By Ramon Raya
rraya@nearsoft.com

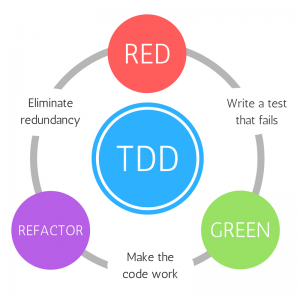
What is TDD?
Start from the top!

The lifecycle
of a failing project
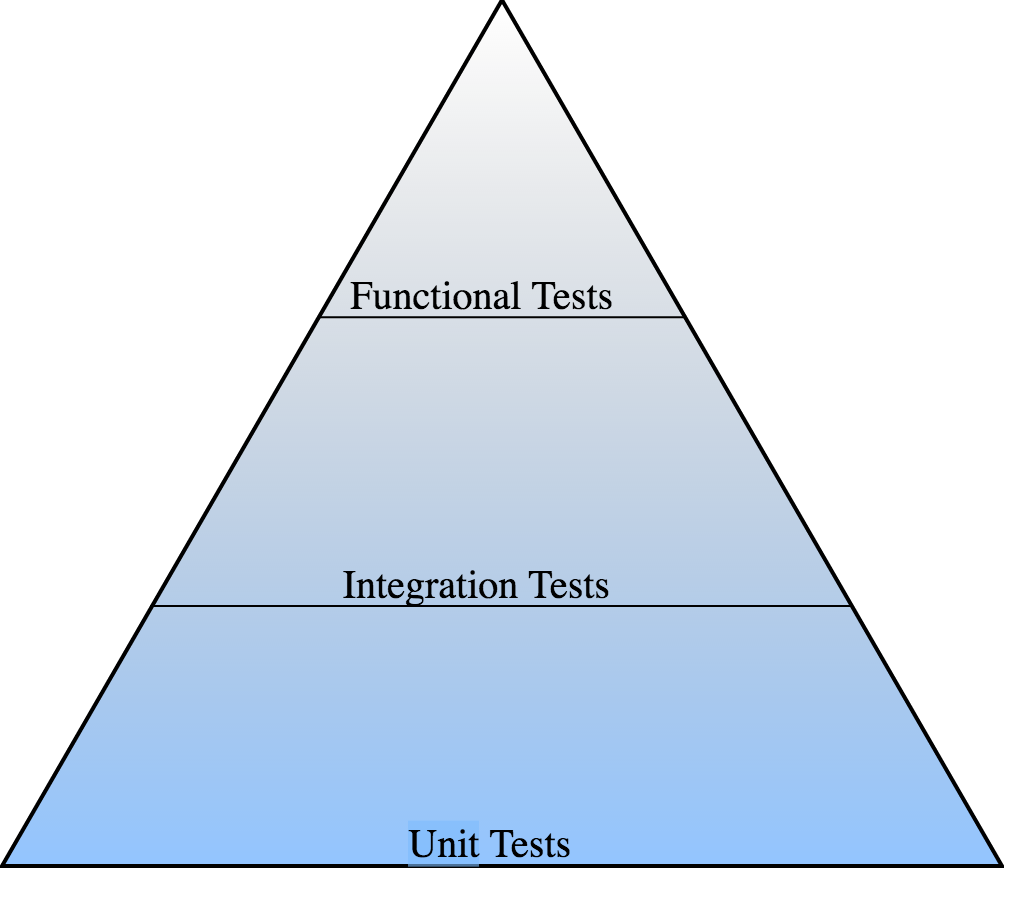
The testing pyramid
Unit testing in Android
JUnit and Robolectric


Simple example
@RunWith(RobolectricTestRunner.class)
public class WelcomeActivityTest {
@Test
public void 'Clicking login should start activity'() {
WelcomeActivity activity = Robolectric.setupActivity(WelcomeActivity.class);
activity.findViewById(R.id.login).performClick();
Intent expectedIntent = new Intent(activity, LoginActivity.class);
Intent actual = shadowOf(RuntimeEnvironment.application).getNextStartedActivity();
assertEquals(expectedIntent.getComponent(), actual.getComponent());
}
}Intrumentation tests in Android



Simple test with espresso
@Test
public void greeterSaysHello() {
onView(withId(R.id.name_field)).perform(typeText("Steve"));
onView(withId(R.id.greet_button)).perform(click());
onView(withText("Hello Steve!")).check(matches(isDisplayed()));
}Integration Tests
One test to rule them all

What is a mock?

Mockito example
// mock creation
List mockedList = mock(List.class);
// using mock object - it does not throw any "unexpected interaction" exception
mockedList.add("one");
mockedList.clear();
// selective, explicit, highly readable verification
verify(mockedList).add("one");
verify(mockedList).clear();
// you can mock concrete classes, not only interfaces
LinkedList mockedList = mock(LinkedList.class);
// stubbing appears before the actual execution
when(mockedList.get(0)).thenReturn("first");
// the following prints "first"
System.out.println(mockedList.get(0));
// the following prints "null" because get(999) was not stubbed
System.out.println(mockedList.get(999));Coverage?
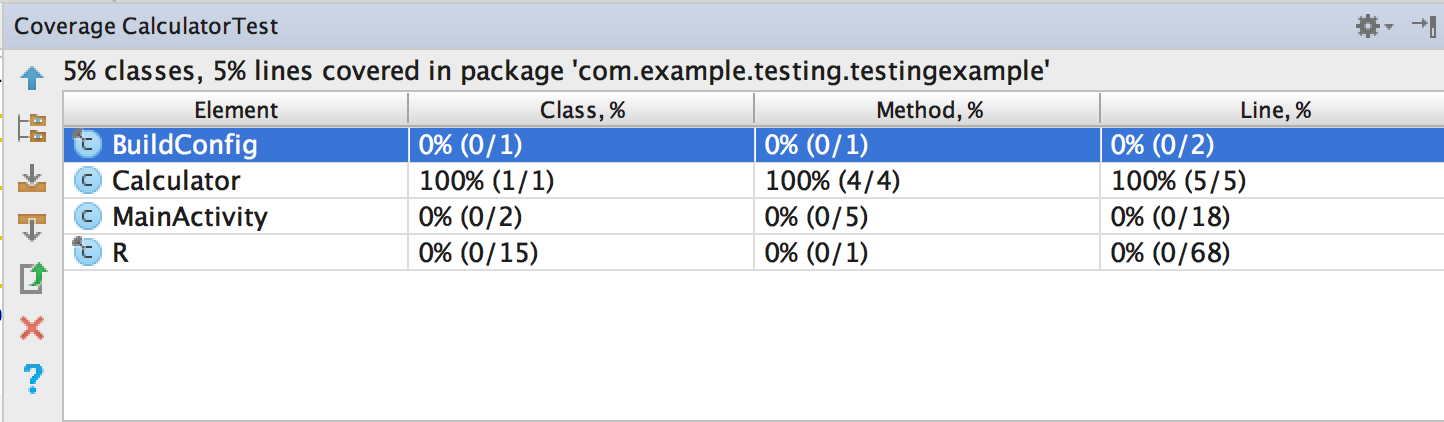

Why should I do this?
Well...

Don't be "that" guy
