Actividades:
La crema en el pastel.

Acerca de mi
- Ramon Raya
- Software Engineer

Actividades
Según Android Developers:
An Activity is an application component that provides a screen with which users can interact in order to do something, such as dial the phone, take a photo, send an email, or view a map. Each activity is given a window in which to draw its user interface. The window typically fills the screen but may be smaller than the screen and float on top of other windows.
Más simple: La series de ventanas donde interactuas con tu app :D

Actividad!!

Pero, cómo lo hago?
Creando una actividad
- Convertirla en una subclase de Activity
- Los métodos más importantes a considerar:
- onCreate() -> setContentView(R.id.ViewGroup)
- onPause() -> por si el usuario regresa.
- onStop() -> qué pasa si todo explota?
- (estos no son los únicos)
Declarando existencia
El manifest -> w00t.jpeg
<manifest ... >
<application ... >
<activity android:name=".ExampleActivity" />
...
</application ... >
...
</manifest >Intent Filters
Proveen el super poder de inicializar una actividad no solo basandose en una petición explicita, sino también en una implícita (KHE?)
<activity android:name=".ExampleActivity" android:icon="@drawable/app_icon">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:mimeType="text/plain" />
</intent-filter>
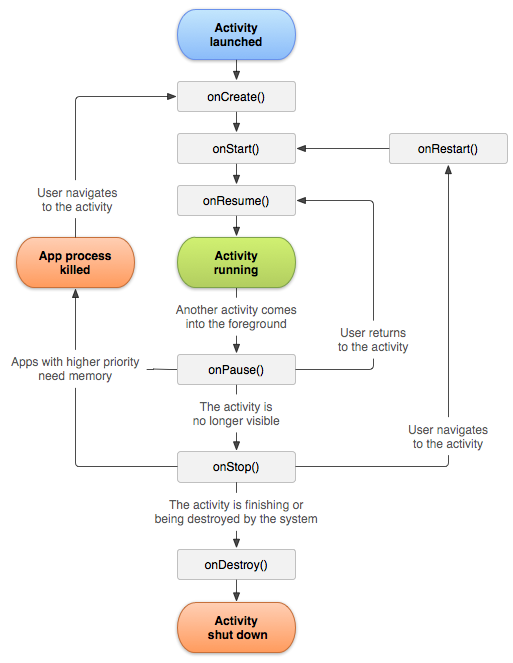
<activity>El ciclo de vida

Fragmentos

Que es un fragmento?
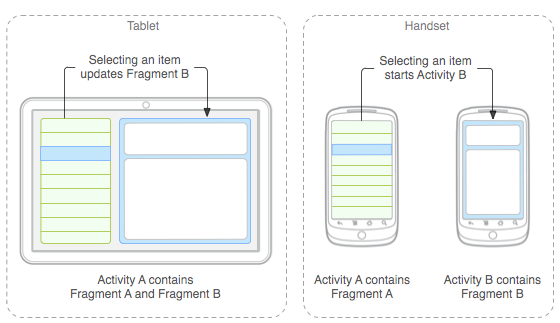

Cómo agrego uno?
El camino del layout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<fragment android:name="com.example.news.ArticleListFragment"
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<fragment android:name="com.example.news.ArticleReaderFragment"
android:id="@+id/viewer"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>El camino programático
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
ExampleFragment fragment = new ExampleFragment();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.fragment_container, fragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
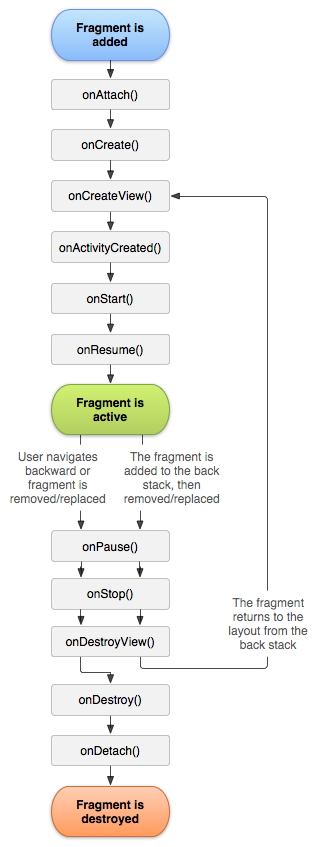
Ciclo de vida
Preguntas?

Muchas Gracias!

KHE ES UN INTENT?!?!

Según la literatura:
An Intent provides a facility for performing late runtime binding between the code in different applications. Its most significant use is in the launching of activities, where it can be thought of as the glue between activities. It is basically a passive data structure holding an abstract description of an action to be performed.

Intents para nuevos.
Un intent es básicamente una petición, un favor bonito al OS, el pegamento de la aplicación

Tipos de intent
Implicitos
// Create the text message with a string
Intent sendIntent = new Intent();
sendIntent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_SEND);
sendIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT, textMessage);
sendIntent.setType("text/plain");
// Verify that the intent will resolve to an activity
if (sendIntent.resolveActivity(getPackageManager()) != null) {
startActivity(sendIntent);
}Tipos de intent
Explicitos
// Executed in an Activity, so 'this' is the Context
// The fileUrl is a string URL, such as "http://www.example.com/image.png"
Intent downloadIntent = new Intent(this, DownloadService.class);
downloadIntent.setData(Uri.parse(fileUrl));
startService(downloadIntent);Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
El nombre del componente a inicializar.
Esto, a pesar de ser opcional, es importante para hacer el intent explícito.
Si lo marcas como implícito el sistema decide que hacer con él.
Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
El objeto URI que referencia los datos sobre los que se actuará.
Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
Es un String que provee de la acción genérica a ejecutar.
Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
Un String que contiene información adicional acerca del tipo de componente que se hará cargo del intent.
Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
Pares de Key-Value que alojan información requerida para completar la acción requerida.
Función: putExtra() y sus variantes.
Creando un intent
- Component Name
- Action
- Data
- Category
- Extras
- Flag
Banderas que instruyen al sistema de Android el cómo lanzar una actividad.
