Amazon
Web Service
Agenda
- Amazon S3
- Amazon Cloudfront
- EBS
- SQS
- SNS
- Security @ AWS
Amazon S3
S3 stands for simple storage service
Provided by a Web service interface (REST & SOAP )
Based on the same infrastructure amazon uses for its global network of websites
- Optimized for WORM (Write once Read many )
- Eventually Consistent
How much data can i store ?
Write, read, and delete objects containing from 1 byte to 5 terabytes of data each. The number of objects you can store is unlimited.
Common S3 Terms
S3 Namespace 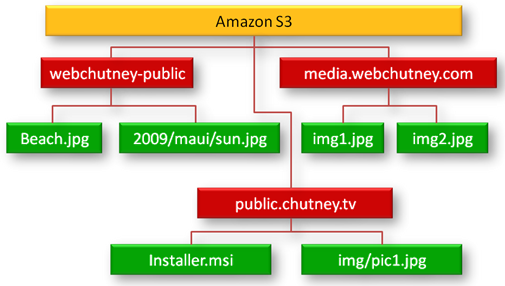

Function & Concept S3
- Objects consist of the raw object data and metadata .
- Object are stored and retrieved using a developer -assigned key .
- Data is kept secured from unauthorised access through authentication .
- Object can be made available to public by HTTP or BitTorrent protocol.
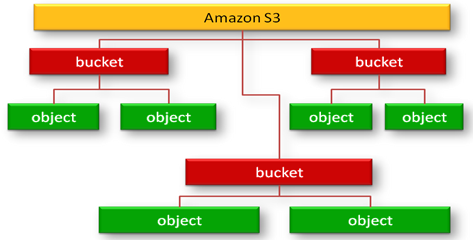
- All object are stored in buckets.
- A bucket is simply a container for objects . it is used to partition the namespace of objects at the highest level .
Continue..
-
A key is the unique identifier for an object within a bucket
- Buckets are similar to internet domain name accessed via [bucketname.s3.amazonaws.com]
-
A bucket and a key together uniquely identify each object in S3 . Every object can be addressed through bucket and key combination
-
The AWS Auth Mechanism allows the bucket owner to create an authenticated URL with a time time -bounded validity that means we can create a URL , that can be handed off to 3rd party for access for a period such as the next 30 min or the next 48 Hour.
Example
S3 - Access Control List
- Control access to bucket or to Object
- No inheritance from bucket to object
- Set at Create ,Write or anytime
- Permission :
- READ - Object or Bucket and it's Metadata
- WRITE - Create , Overwrite , Delete objects in Bucket Not applied on object.
- READ_ACP - Read ACL for bucket or object
- WRITE_ACP - Overwrite ACL for bucket or object.
- FULL_CONTROL - All of the above
S3 Use case



S3 Backed Instance Lifecycle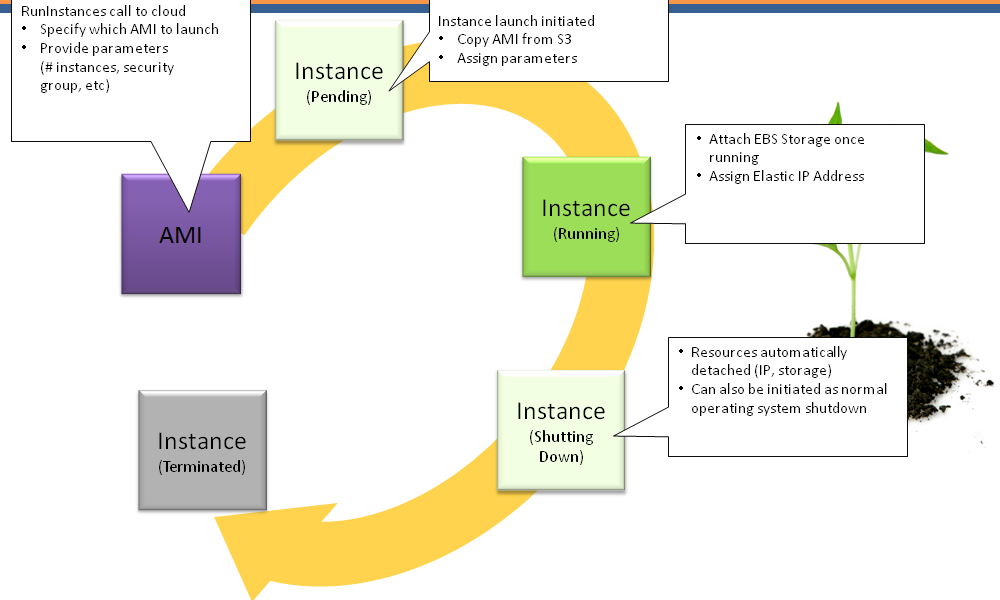
S3 Access
-
Code (S3 APIs)
-
Command Line
-
Browser (AWS Management Console, S3Fox [firefox extension]
- Free and commercial file transfer tools
-
Backup utilities
-
Cloud storage appliances (e.g. Bluejet)
Amazon S3 API
ListAllMyBuckets
PutObject PutObjectInline GetObject GetObjectExtended DeleteObject GetObjectAccessControlPolicy SetObjectAccessControlPolicy
CreateBucket DeleteBucket ListBucket GetBucketAccessControlPolicy SetBucketAccessControlPolicy GetBucketLoggingStatus SetBucketLoggingStatus

Cloudfront
Content Delivery using Amazon Cloudfront
A CDN (content delivery network) use a network of Geographically dispersed servers (Edge location or POP's ) to cache copies of content close to end user , Lowering Latency when they Download or stream objects .
A POP is a Point Of Presence, an access point to the Internet. It is a physical, strategically placed location that houses multiple CDN servers. Edge locations serve requests for CloudFront
Cloudfront in a Nutshell
Low Latency : Improves media load time
High Bandwidth : Enables High bit rate HD Video and other media application
Redundant : Eliminate Single point of failure
Cost Effective : Pay as you go model provide flexibility for you business CAPEX become OPEX
Scaleable : Ensure Great Experience as no. of End user grows
Global : Worldwide Network provides great experience regardless of geography
Cloudfront : non cached
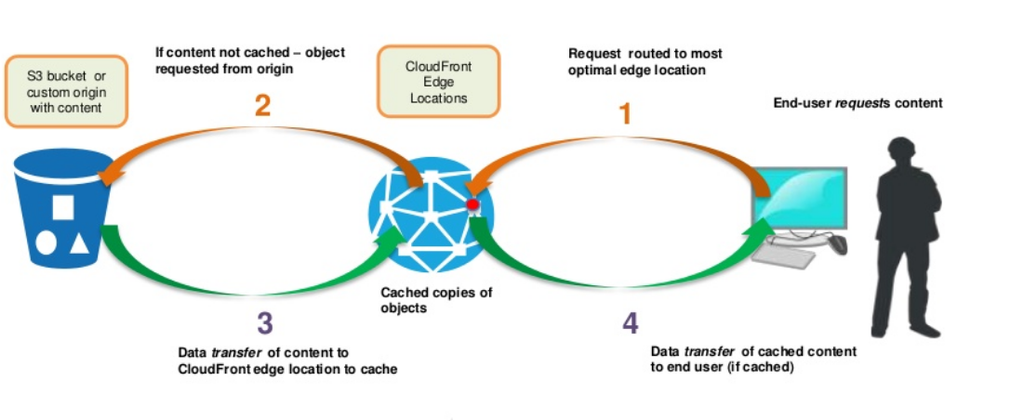
Cloudfront : cached
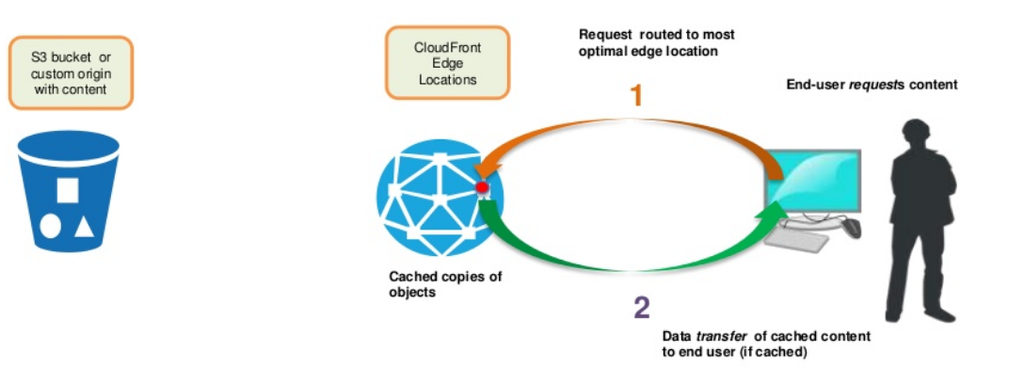
Key features of Cloudfront
For Ref.
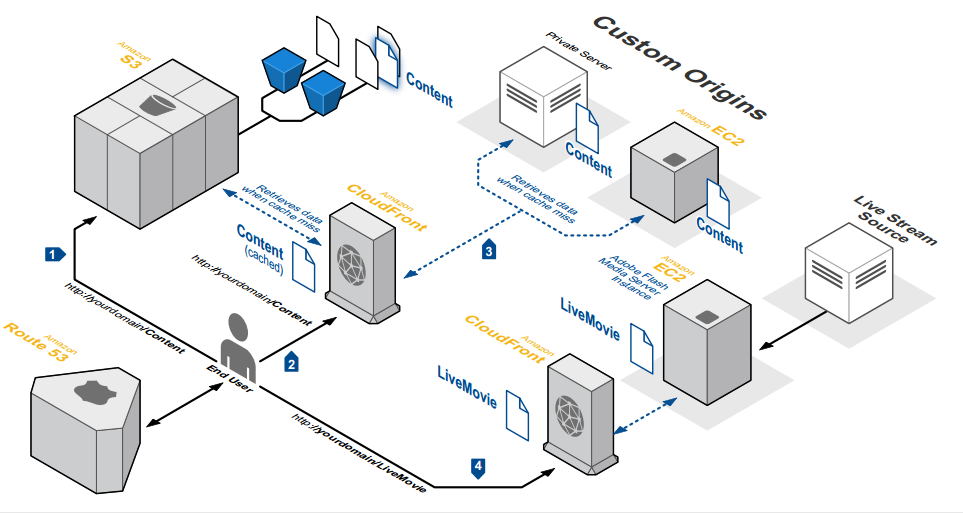
Cloudfront Use case
-
Static Content use case
- Media Delivery
- Software Download
- Web Assets (image , CSS , Js)
- Dynamic Content use case
- News
- Weather
- Social Media
- Advertising
-
Live Streaming
- Events
- Sports
Elastic Block Storage
-
Persistent Storage
- Volume lifetime is independent of any particular EC2 Instance
- General Purpose
- Raw ,unformatted ,block device. Use from Linux ,solaris or Window
- High Performance
- Equal to or better than local EC2 Drive
-
High Reliability
- Built in redundancy with in the availability zone AFR(Annual Failure rate ) is between 0.1% - 1%
- Scalable
- Volume Size ranging from 1GB to 1TB
- Easy
-
Easy to create , attach ,backup ,restore and delete volume
Elastic Block Storage
-
Standard EBS Volumes are the first generation EBS Volumes that are suitable for sequential IO workloads.
- PIOPS Volumes are more consistent and are targeted towards OLTP (Online Transaction processing ) workloads.
- EBS Volumes have redundancy built-in , which means that they will not fail if an individual drive fails. But there redundancy is limited to Availability Zone Scope.
- EBS does not replicate data automatically across multiple AZ's
Some Definitions
EBS volume Lifecycle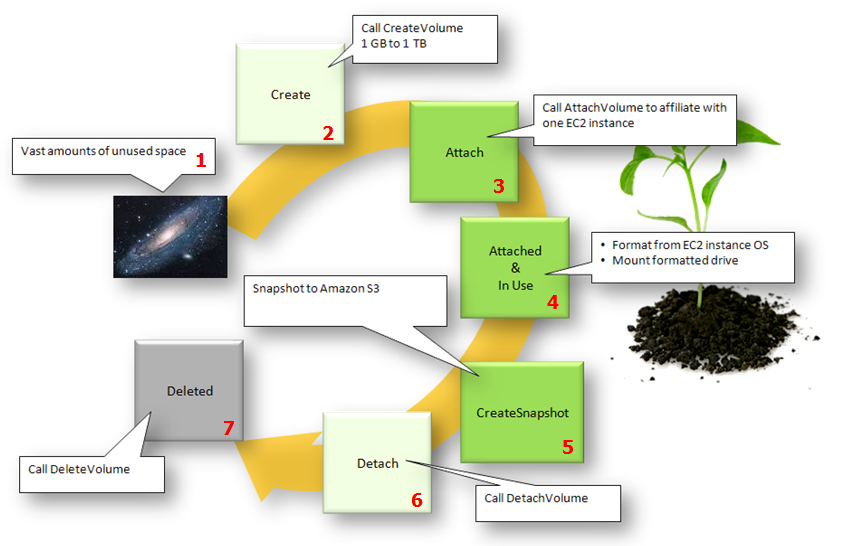
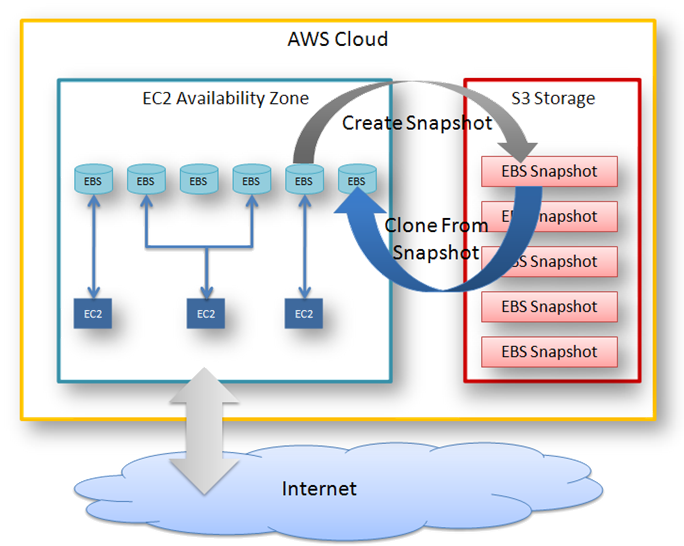
How EBS Interact with EC2 & S3
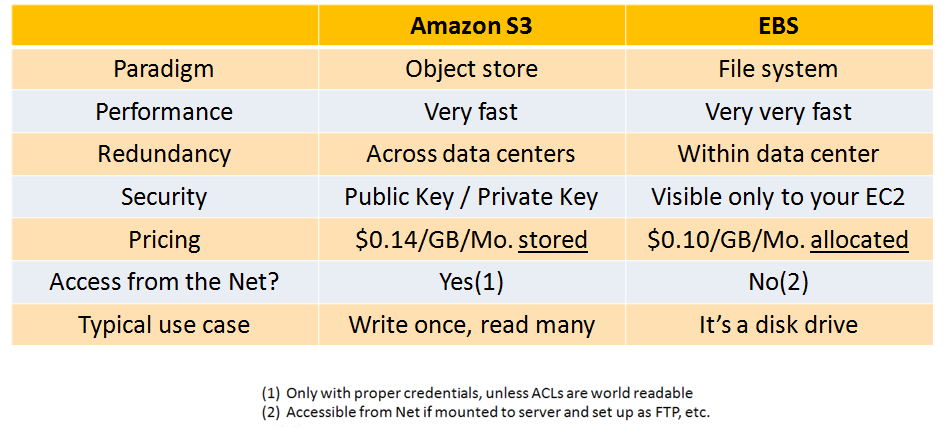
Diff Between EBS & S3
EBS 'Snapshot'
New generation Storage arrays have the ability to speed up dramatically the backup process by using a technique called as “Snapshot”
Amazon EBS snapshots are incremental backups, meaning that every snapshot only copies the blocks in the volume that were changed since the last snapshot.
If you have a volume with 10 GB of data, but only 2GB of data have changed since your last snapshot, only the 2 GB of modified data is written to Amazon S3 during the snapshot process.
Snapshot ...Explained
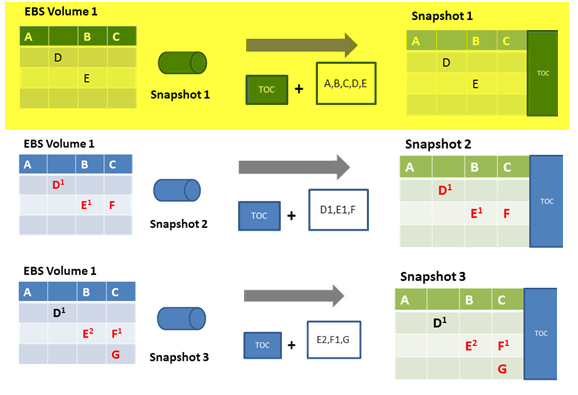
Step 1 : when you take snapshot of an EBS volume for the first time, it is a full snapshot, but it only copies the blocks in the EBS volume that contains data. During the first snapshot, the full TOC and all blocks containing data (A, B, C, D, and E) is moved asynchronously to S3.
Snapshot ...Explained 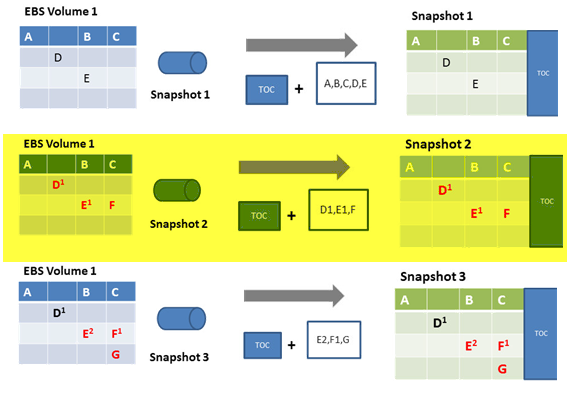
Step 2: Imagine in meantime, blocks D and E were changed and F is newly added from the snapshot 1. When you take snapshot 2, this time the TOC and only the changed blocks D1, E1 and F are moved to S3.
Snapshot ...Explained 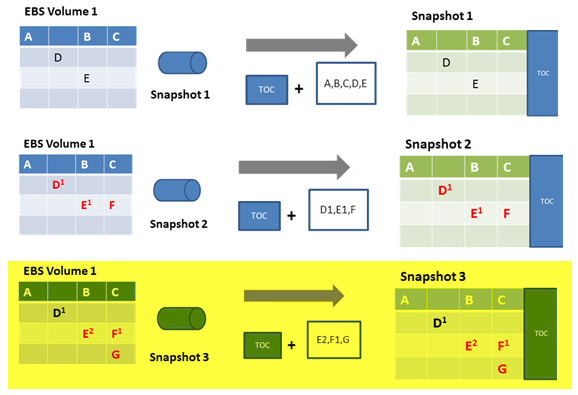
Step 3: when you take snapshot 3, blocks E and F are changed and G is newly added as per diagram. This time the TOC and only the changed blocks E2, F1 and G are moved to S3.
Snapshot..Explained
Step 4: since snapshot 3 is the recent and contains the latest data, you can go ahead and delete older snapshots like 1 and 2. The capacity occupied by blocks like D, E, F, E1 are no more relevant, and they are released and not charged by AWS. Amazon Simple Queue Service
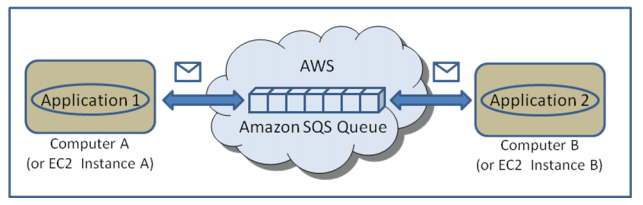
Two distributed applications communicating asynchronously by passing messages through an Amazon SQS queue. SQS.. Example
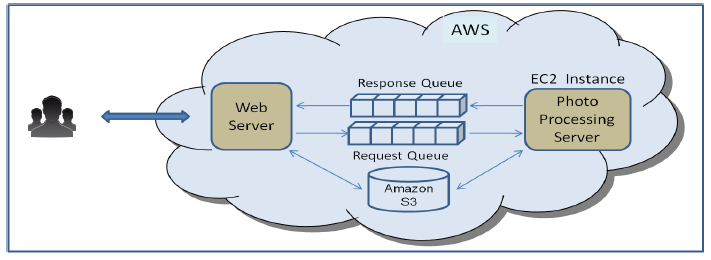
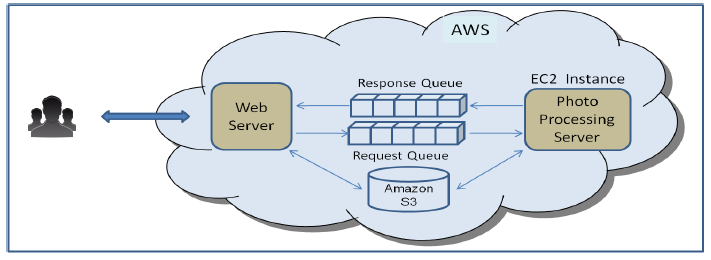
Assume you are running Online photo sharing & Filtering services for consumer. This service lets consumer specify operations they want to performed on their photos. Some of the Example for operation will be (red eye reduction , Cropping , re-coloring , teeth whitening, color filter). User can submit as few as one or as many as hundreds of photos in a single upload session . User can come back and check status of their photo. Once processing is done they can download the photos from the website.Let's assume different operations take different processing times ,ranging from few seconds to several minutes, Therefore the time to complete user's request depends on the number of photo , size of the photo and the processing operations to be performed.
End to End flow
-
Every user request results in a message being queued into the Amazon SQS “Request” queue.
- At the same time Application stores the photos in Amazon S3
- The message in the queue contains (among other things) the photo processing operation to be performed and a pointer to the location of the photos in Amazon S3.
- Photo processing server,running in EC2 instance >> Read the Message from "Request " Queue
- Process the request
- On Completion Post a status message to "Response" Queue
Case 1 : Due to bug or some other reason, the photo processing server crashes or become temporarily unavailable as shown below
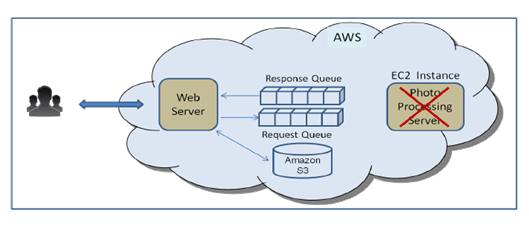
- Amazon SQS isolates failures of a component from the rest of the system
- The failure will be transparent to end user
- User operation will continue and in turn the web server can continue to send message to "Request" queue Message will remain in the queue until photo processing server is back online
- Photo Processing Server does not have to do anything extra to remember the last message it processed before the crash
-
Amazon SQS will ensure that the server will resume processing the message from where it left
Case 2 : let’s consider the case where the Photo Processing Server or the EC2 instance in which it is running cannot be restarted for an extended period of time. While the user will be able to post their photos to the site , they will not be able to get back their processed photos. Solution is to start another , identical , Photo processing server , in its own EC2 instance , to replace the failed server ,shown below.
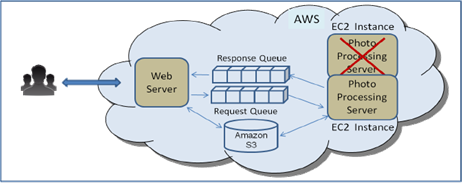
Amazon SQS makes it possible to just drop in a replacement server without impacting the rest of the system. All that is needed to implement this solution is to make sure that the replacement server is pointing to the same Amazon SQS Request/Response queue pair.
Case 3 : For the next scenario, consider the case where a single Photo Processing Server is not sufficient to meet user demand. With Amazon SQS, it is possible to introduce additional instances of the Photo Processing Server to meet increasing demand, as shown in the figure below.
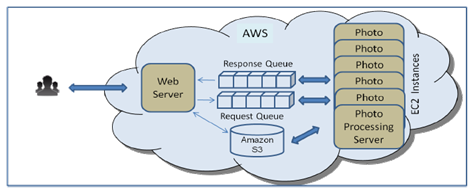
Two specific features of Amazon SQS make this possible
- A single Amazon SQS queue can be shared by multiple servers simultaneously.
- A server that is processing a message can prevent other servers from processing the same message at the same time by temporarily “locking” a message. The server can specify the amount of time the message is locked. When the server is done processing the message, it should delete the message. If the server fails while processing the message, another server can get the message after the lockout period.
Amazon SNS
N stands for Notification
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service ) is a distributed message delivery service roughly similar to AMQP or Java Message Service . It uses a publish-subscribe paradigm and supports push delivery of notification using HTTP and email. Mostly used in back-end application , such server sending notification to one another . You need to know following terms in order to understand its working .
Owners create topics and control all access to the topic. The owner can define the permissions for all of the topics that they own.
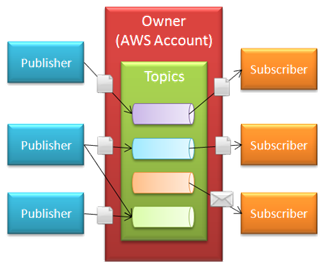
Subscribers are clients (applications, end-users, servers, or other devices) that want to receive notifications on specific topics of interest to them.
Publishers send messages to topics. SNS matches the topic with the list of subscribers interested in the topic, and delivers the message to each and every one of them. Here's how it all fits together:
Key Points
-
You can create topics and publish messages to these topics.
- Others can subscribe to the topics and they will get messages pushed to them.
- Messages can be pushed over HTTP or SMTP (email).
- Using access control policies one can control who is allowed to subscribe to a topic.
-
The SNS system is redundant and retries message delivery if necessary.
SNS example
- Application Monitoring
- Mobile Application
- Application Integration
Security @ AWS
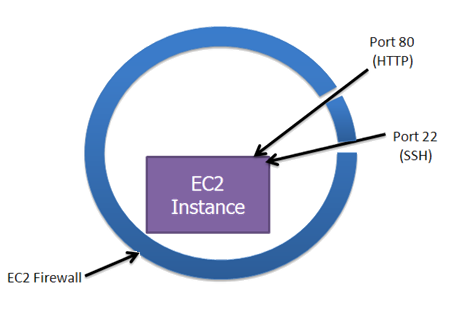
-
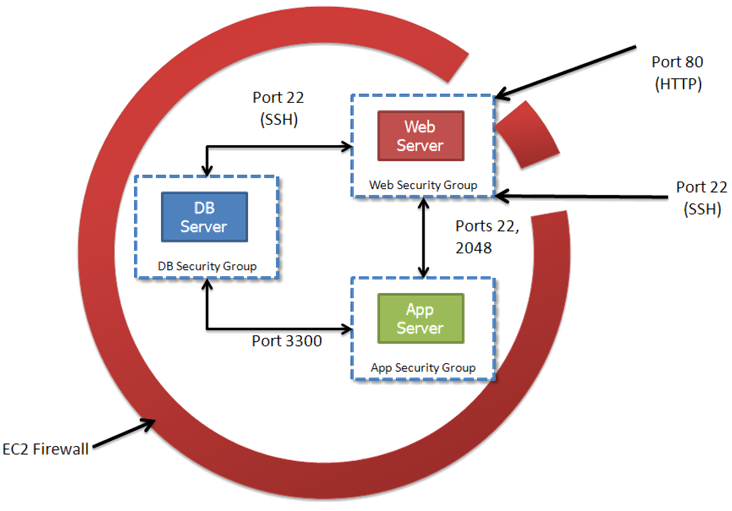
Each Account has a virtual Firewall
-
Secure by Default
-
Open Ports as needed
-
Default Group : Nothing is open
We can restrict traffic between Security groups in addition to blocking Internet Traffic
EC2 Network Sec Parameters
-
Inbound access control only
-
Security Group - is a collection of access rules
-
Assign group(s) on instance launch
-
Modify existing group on running Instance
- Access Rule
- Name
- Description
- Protocol
- Port range
- IP Address range