

Kumar Ratnam Pandey
Software Engineer at
GeekyAnts

@ratnam99
Why
State Management?
- State Synchronization
- Re-rendering

- The persistent state and the server state store the same information. So do the client state and the URL. Because of this we have to synchronize them.
State Synchronization
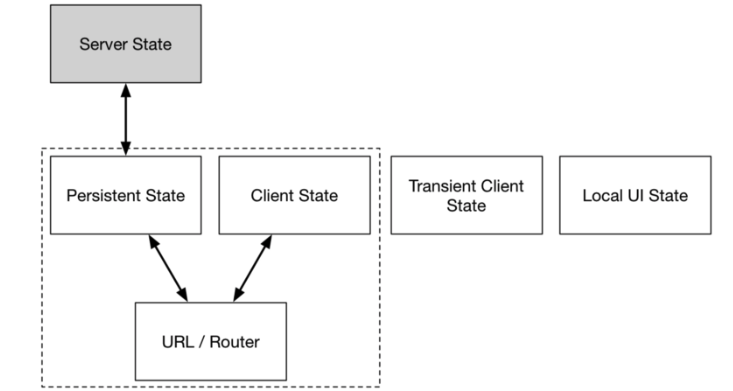
Re-rendering
Data Layer
UI
Changes
Changes
Example
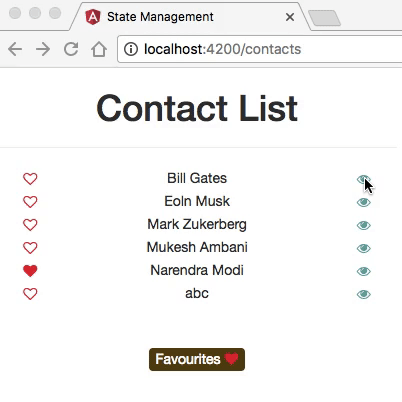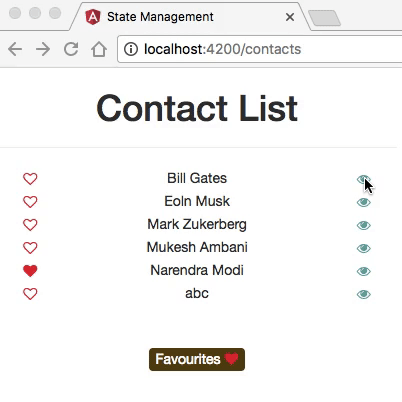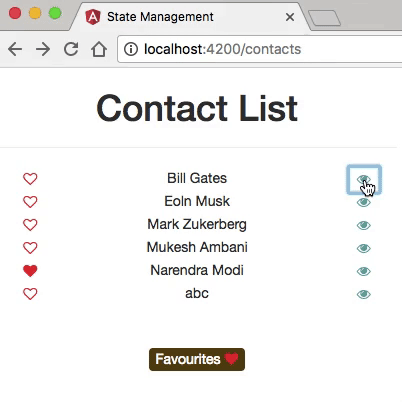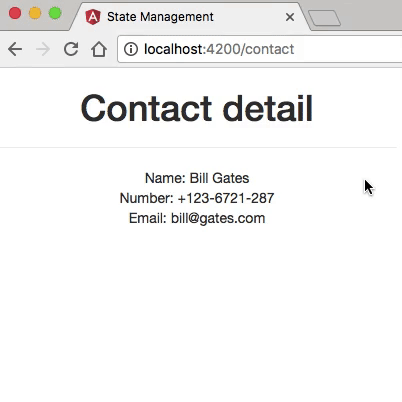
- The application has two main routes: one that displays a list of contacts, and the other one showing detailed information about each contact.
Server
Backend
Url / Router
WatchService
ContactsAndFiltersCmp
ContactsDetailsCmp
FiltersCmp
ContactsCmp
ContactCmp
FavBtnCmp
WatchBtnCmp
Server State
Persistent, Client, Transient Client and URL/ Router State
Local UI State
export interface Contact {
id: number;
name: string;
number: string;
email: string;
isFav: boolean;
}
export interface Filters {
name: string;
fav: boolean;
}Application Model
@Component({
selector: 'contact-details-cmp',
templateUrl: './contact-details.html',
styleUrls: ['./contact-details.css']
})
export class ContactDetailsCmp {
contact: Contact;
constructor(private backend: Backend,
public watchService: WatchService,
private route: ActivatedRoute) {
route.params.mergeMap(p => this.backend.findContact(+p['id']))
.subscribe(t => this.contact = t);
}
handleFav(fav:boolean): void {
this.backend.makeFav(this.contact.id, fav);
}
handleWatch(): void {
this.watchService.watch(this.contact);
}@Component({
selector: 'app-cmp',
templateUrl: './contacts-and-filters.html',
styleUrls: ['./contacts-and-filters.css']
})
export class ContactsAndFiltersCmp {
constructor(public backend: Backend) {}
handleFiltersChange(filters: Filters): void {
this.backend.changeFilters(filters);
}
}contacts-filters.ts
contacts-details.ts
@Injectable()
export class Backend {
_contacts: {[id:number]: Contact} = {};
_list: number[] = [];
filters: Filters = {name: null, fav: false};
constructor(private http: Http) {}
get contacts(): Contact[] {
return this._list.map(n => this._contacts[n]);
}
findContact(id: number): Observable<Talk> {
return of(this._contacts[id]);
}
makeFav(id: number, fav: number): void {
const contact = this._contacts[id];
contact.isFav = fav;
this.http.post(`/fav`, {id: contact.id, isFav: fav}).forEach(() => {});
}
changeFilters(filters: Filters): void {
this.filters = filters;
this.refetch();
}
private refetch(): void {
const params = new URLSearchParams();
params.set("name", this.filters.name);
params.set("fav", this.filters.fav);
this.http.get(`/contacts`, {search: params}).forEach((r) => {
const data = r.json();
this._contacts = data.contacts;
this._list = data.list;
});
}
}Backend
export class WatchService {
watched: {[k:number]:boolean} = {};
watch(contact: Contact): void {
console.log("watch", contact.id);
this.watched[contact.id] = true;
}
isWatched(contact: Contact): boolean {
return this.watched[contact.id];
}
}Watch Service
Everything looks fine?
Problems
-
Syncing Persistent and Server State.

Problems
- Syncing URL and Client State
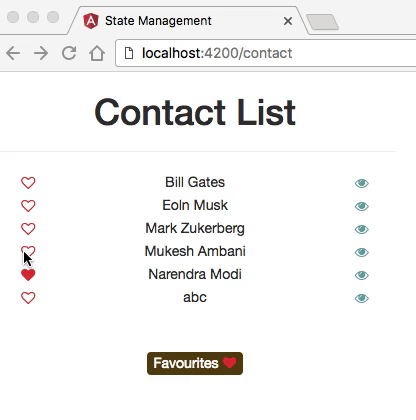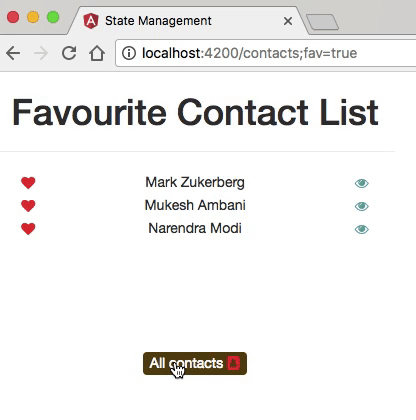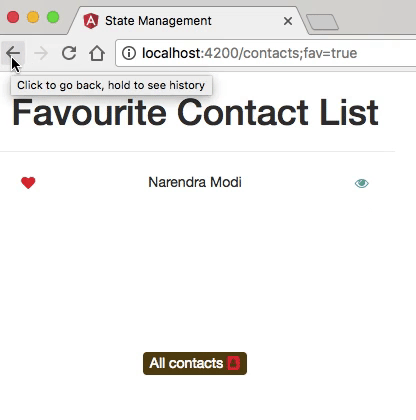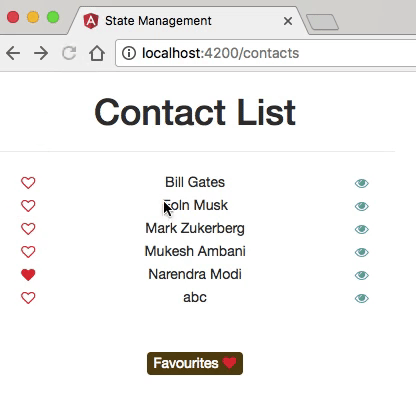
State Management?
Types
- Server state.
- Persistent state.
- The URL and router state.
- Client state.
- Transient client state.
- Local UI state.
Let's see what
manages each type
of state in this application.
Refactoring 1:
Separating State Management
Introducing

Architecture
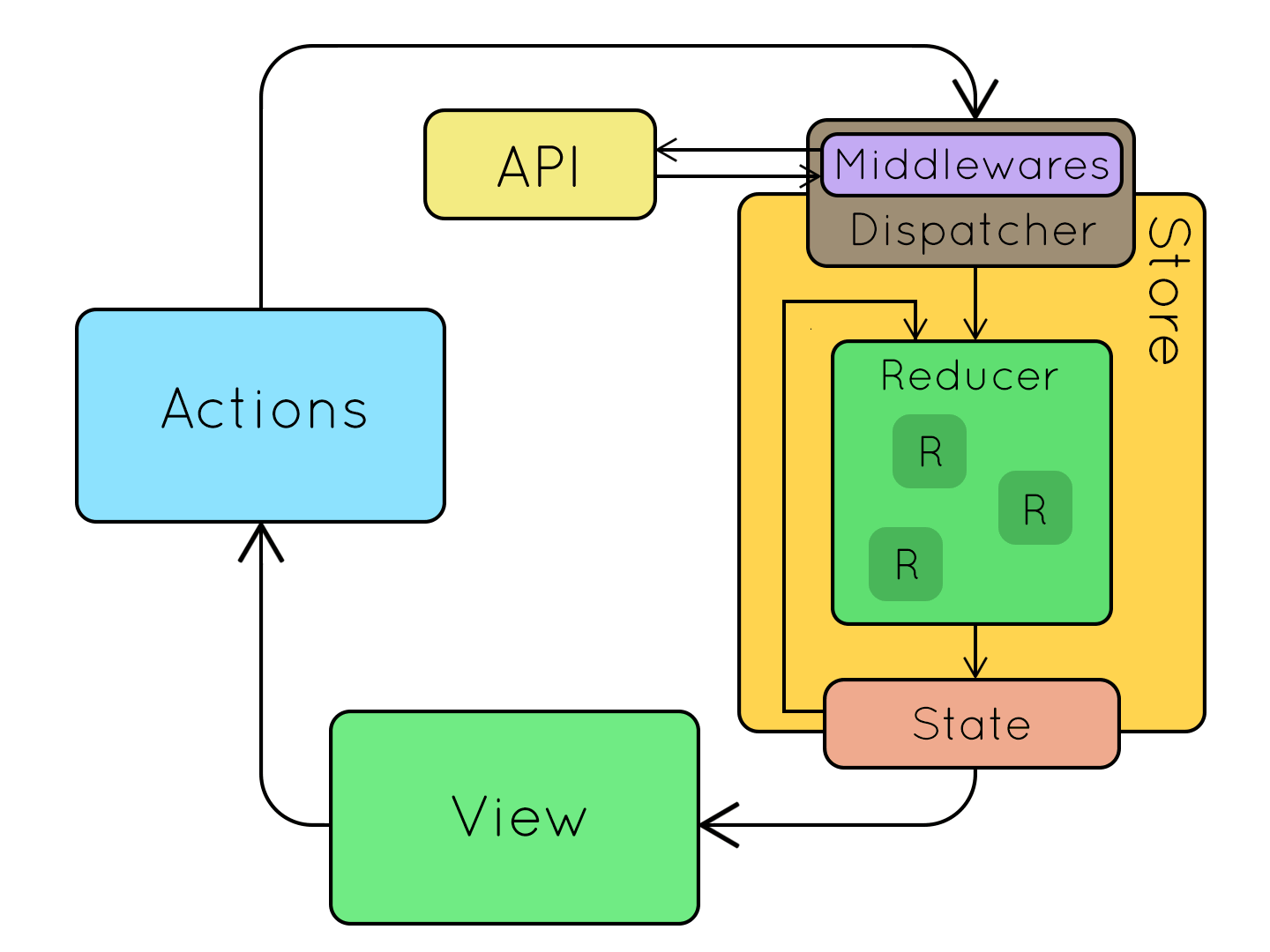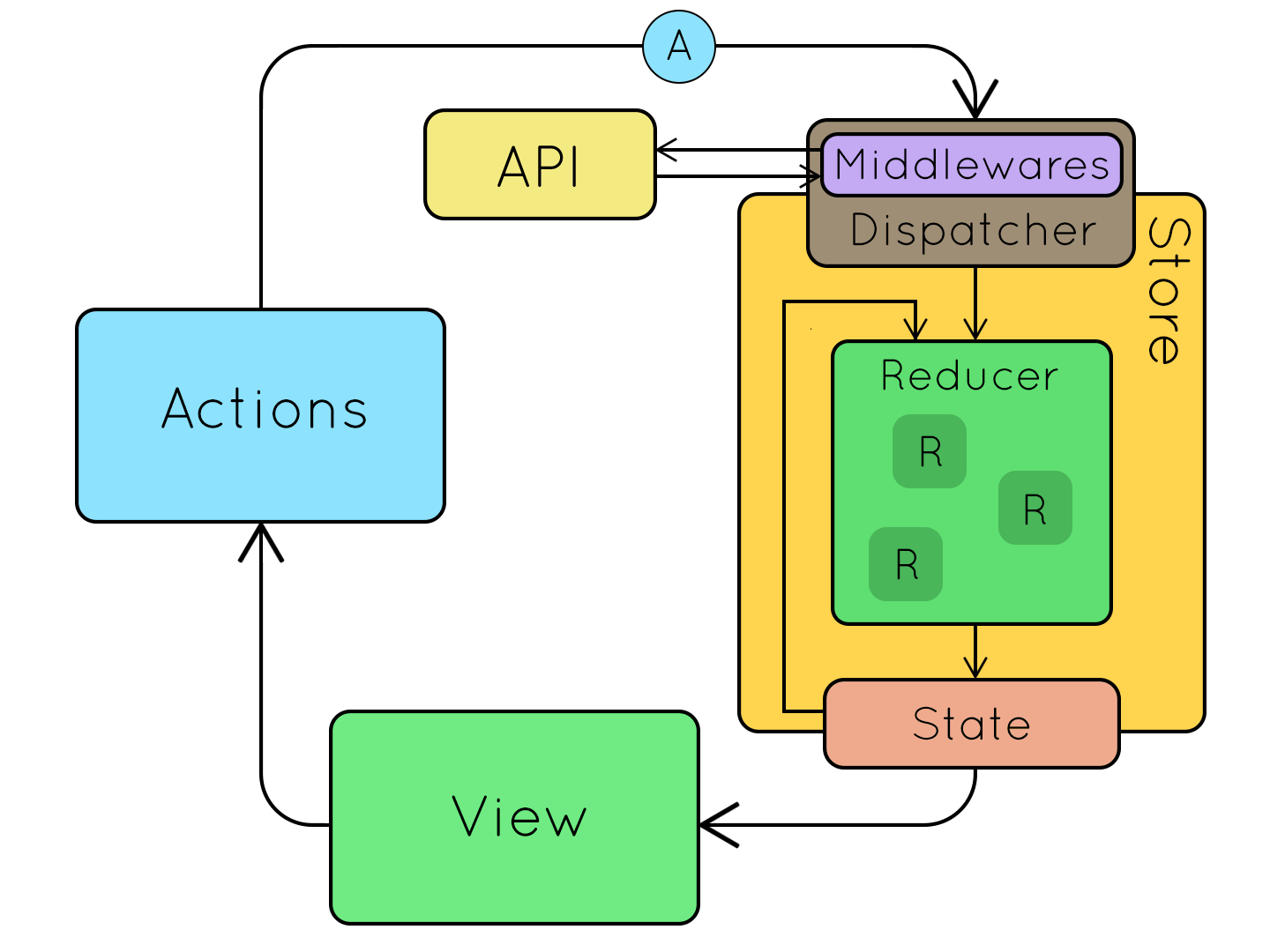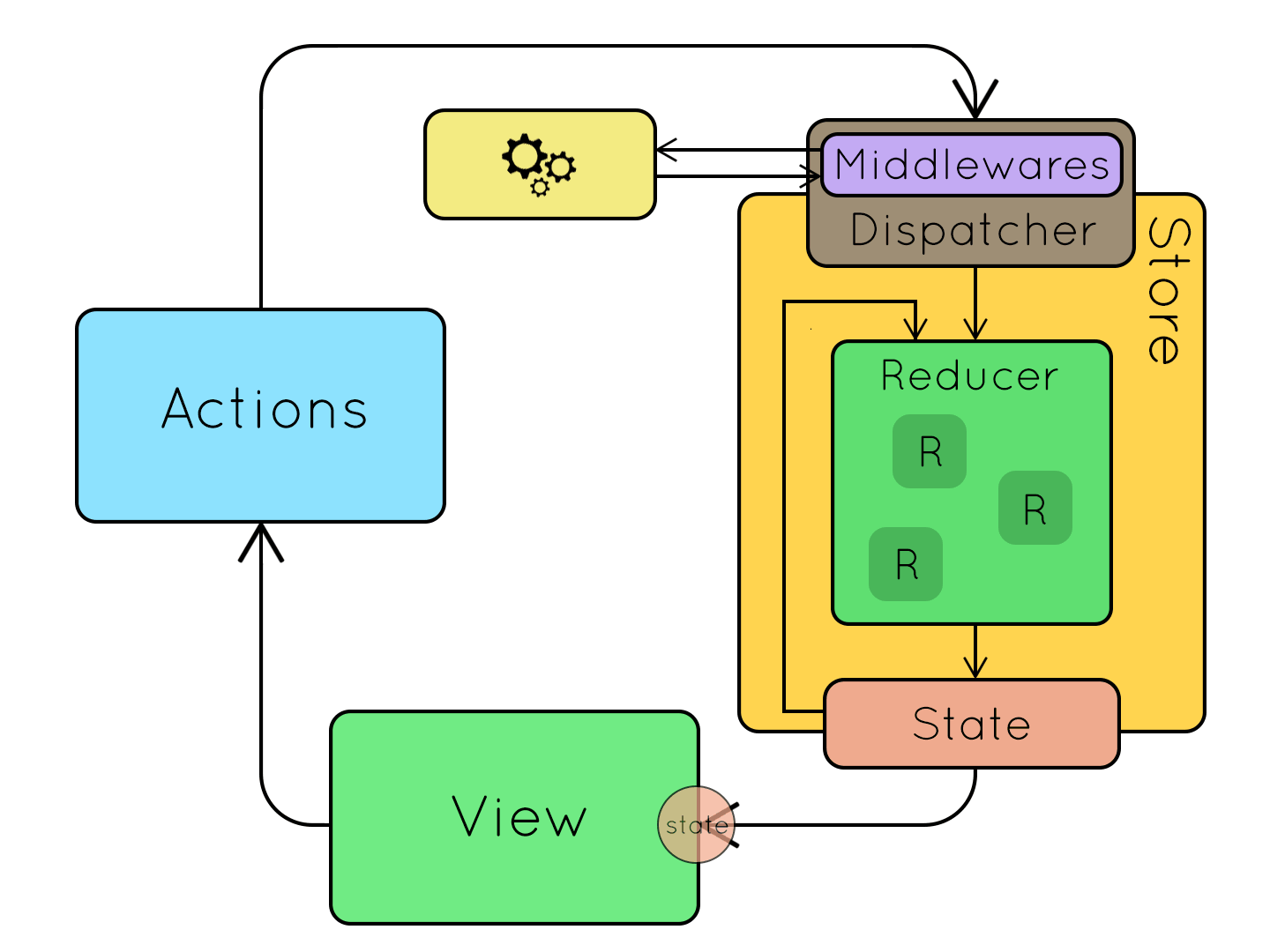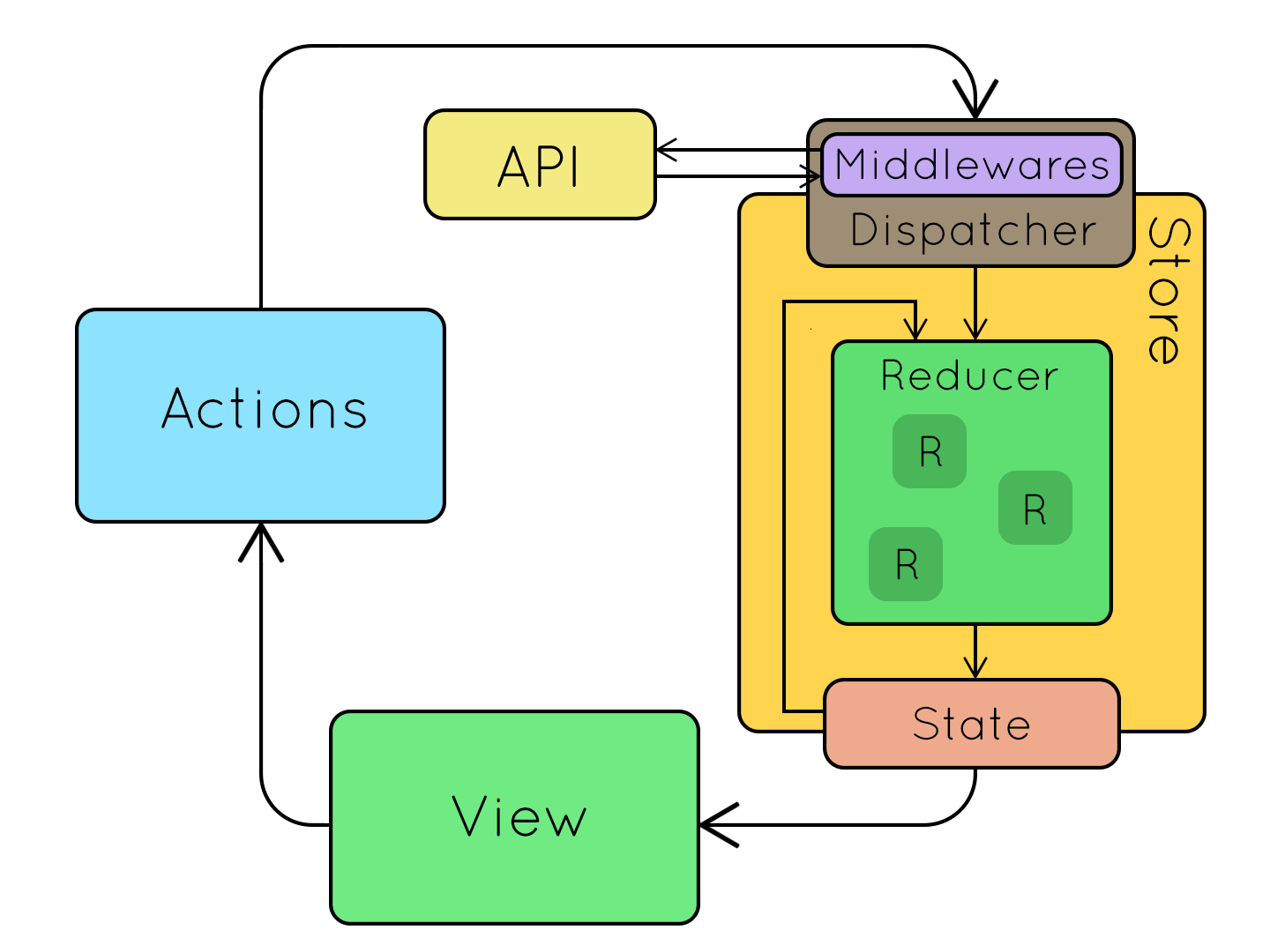
3 simple steps
- Defining all the actions our application can perform.
Eg-: export type Filter = {
type: 'FILTER',
filters: Filters
};2. Then the state.
// all non-local state of the application
export type State = {
contacts: { [id: number]: Contact },
filters: Filters,
};
// init state
export const initState: State = {
contacts: {},
filters: {fav: null}
};3. And, finally, the reducer.
// a factory to create reducer
export function reducer(backend: Backend, watch: WatchService) {
return (store: Store<State, Action>, state: State, action: Action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'FILTER':
return backend.findContacts(action.filters).
map(r => ({...state, ...r, filters: action.filters}));
case 'SHOW_DETAIL':
if (state.contacts[action.contactId]) return state;
return backend.findContact(action.contactId).
map(c => ({...state, contacts: {...state.contacts, [c.id]: c}));
default:
return state;
}
}
}-
State management and computation/services are separated. The reducer is the only place where we manipulate non-local state.
- We no longer use mutable objects for persistent and client state.
Analysis
Redux should be the means of achieving a goal, not the goal
Alternatives
Introducing
Mobx

2 simple steps
- Making the store observable
Eg: import {observable} from 'mobx';
.
.
.
export default filter observable=([
fav:boolean
]);2. Make the component as an observer.
import {observer} from 'mobx';
.
.
.
@observer
export class ContactsAndFiltersComponent implements OnInit {
contactList:Contact[]=[];
current:string="Contact";
filter:Filters={
name:'',
fav:false
};
constructor(public backend: Backend, private router: Router, private route: ActivatedRoute, private watchService:WatchService) {
}
viewContact(contact){
this.watchService.id=contact.id;
this.router.navigate(['contact']);
}
makeFav(contact:Contact){
console.log("make Fav", contact);
let newContactList=this.contactList.map((eachContact)=>{
if(eachContact.id===contact.id){
eachContact.isFav=!contact.isFav;
}
return eachContact;
})
this.contactList=newContactList;
this.backend.makeFav(this.contactList);
}
viewFavlist(){
let filters:Filters={
name: this.filter.name,
fav: true
}
this.router.navigate(['/contacts',this.createParams(filters)]);
}
viewAllContacts(){
let filters:Filters={
name: this.filter.name,
fav: false
}
this.router.navigate(['/contacts',this.createParams(filters)]);
}
private createParams(filters: Filters): Params {
const r:any = {};
if (filters.name) r.name = filters.name;
if (filters.fav) r.fav = filters.fav;
return r;
}
}- Less and clean code.
-
It's easier to make Async calls and handle side-effects.
-
With the flexibility of observers architecture can easily be spoilt.
- A lot goes behind the scene
Analysis
Introducing

NgRx

1. Defining the state of our application.
Eg-: export const initState: State = {
contacts: {},
filters: {fav: null}
};2. Defining all the actions our application can perform.
Eg-: export type Filter = {
type: 'FILTER',
filters: Filters
};3. Next, the effects class.
class TalksEffects {
// @Effect() navigateToContacts = ...
// @Effect() navigateToContact = ...
// @Effect() favContact = ...
constructor(
private actions: Actions,
private store: Store<State>,
private backend: Backend,
private watch: WatchService) {
}
}4. Then, the reducer.
function appReducer(state: AppState, action: Action): AppState {
switch (action.type) {
case 'CONTACTS': // ...
case 'CONTACT_UPDATED': // ...
case 'FAV': // ...
case 'UNFAV': // ...
default: return state;
}
}Remaining Problems
- If the router needs some information from Backend, it cannot reliably get it.
- if Backend needs something from the router or the URL, it cannot reliably get it.
- The reducer cannot stop the navigation.
- The synchronization is ad-hoc. If we add a new route, we will have to reimplement the synchronization code there as well.
Refactoring 2:
Store and Router.
Make navigation part of updating the store.
And finally we can make updating the store part of navigation.
imports: [
//...
RouterConnectedtoStore.forRoot(
"reducer",
[
{ path: '', pathMatch: 'full', redirectTo: 'talks' },
{ path: 'contacts', component: ContactsAndFiltersCmp },
{ path: 'contact/:id', component: ContactDetailsCmp }
]
)
],RouterConnectedToStoreModule will set up the router in such a way that right after the URL gets parsed and the future router state gets created, the router will dispatch the an appropriate action (say STORE_ROUTE_NAVIGATION).
// a factory to create reducer
export function reducer(backend: Backend, watch: WatchService) {
return (store: Store<State, Action>, state: State, action: Action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'STORE_ROUTE_NAVIGATION':
// Logic for proper navigation
case 'SHOW_DETAIL':
if (state.contacts[action.contactId]) return state;
return backend.findContact(action.contactId).
map(c => ({...state, contacts: {...state.contacts, [c.id]: c}));
default:
return state;
}
}
}Then we define the case for STORE_ROUTE_NAVIGATION action inside the reducer function.
- This refactoring tied the client state to the URL. The router navigation invokes the reducer, and then once the reducer is done, the navigation proceeds using the new state.
Analysis
-
The main takeaway is you should be deliberate about how you manage state. It is a hard problem, and hence it requires careful thinking. Do not trust anyone saying they have “one simple pattern/library” fixing it — that’s never the case.
-
Decide on the types of state, how to manage them, and how to make sure the state is consistent. Be intentional about your design.
Takeaway