VEhicle to CLoud Latency
Safety-related Connected vehicle Applications
Silicon Valley Automotive Open Source - Sept 12, 2016
About me
@rdematos
rdematos @ MIT
rdematos @ AWS
rdematos @ Alexa
Motivation
Safety
Text
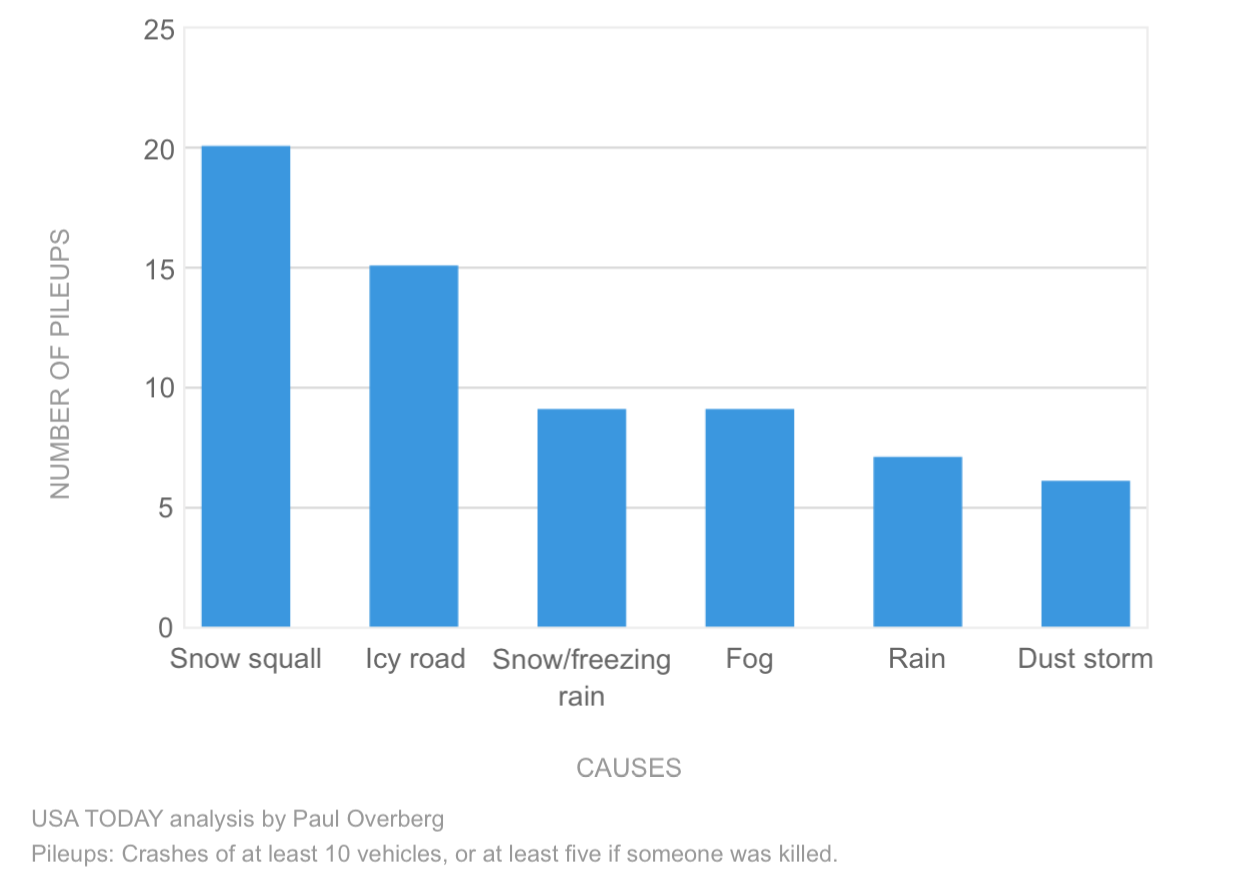
Avg 2 Pileups / Week in 2013
INSPIRATION
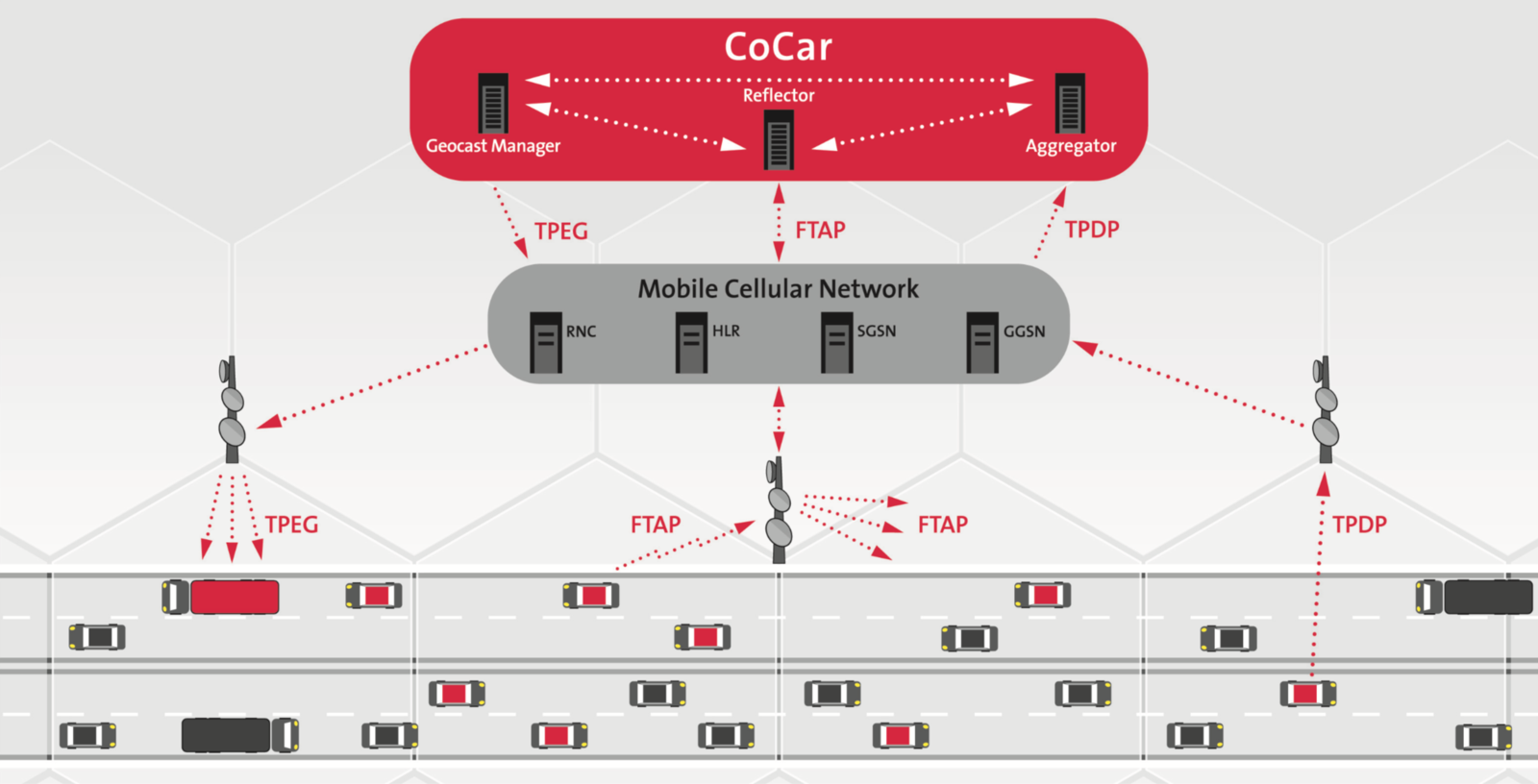
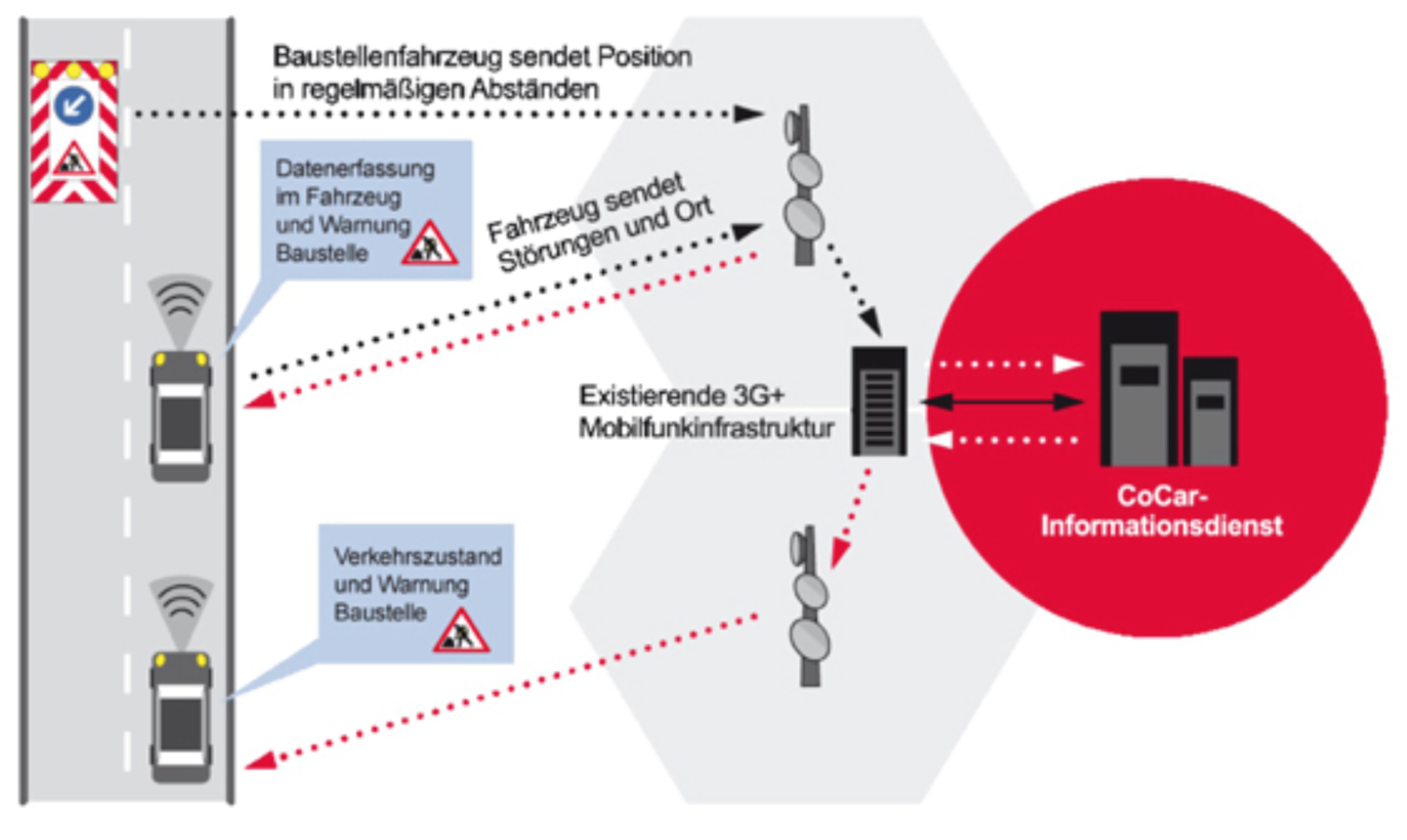
CoCar Feasibility Study
CoCAR Conclusions (2009)
-
Investigated CoCar focus applications are already feasible today from a technological and a commercial point of view
- The CoCar system provides safety gains for drivers. In the next step it should become complemented by short-range 802.11p-based vehicle communication
- LTE (Long Term Evolution) expected to be rolled out in 2010. LTE offers higher throughput and lower latency, allowing even more demanding automotive applications
Standards
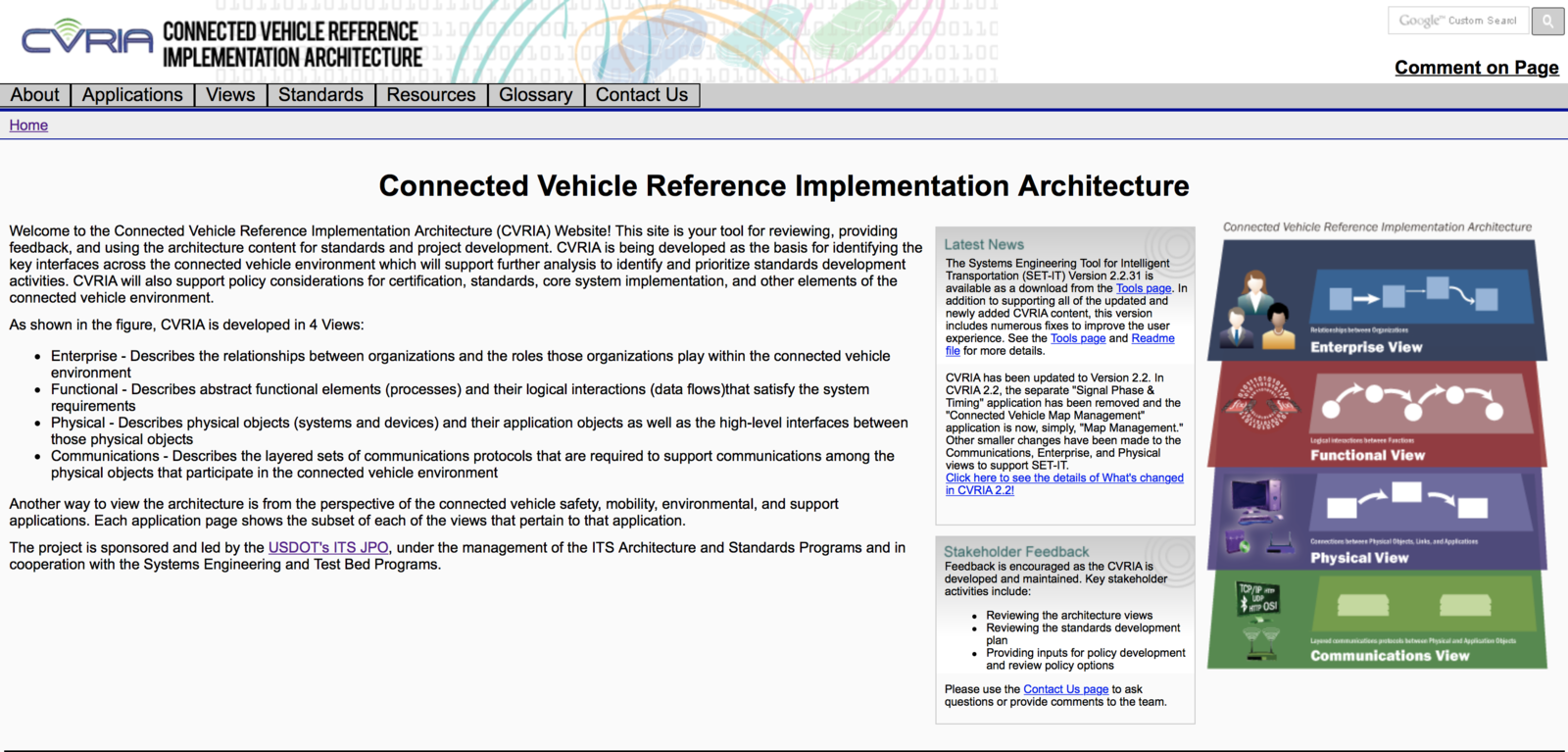
US DOT's Connected Vehicle program
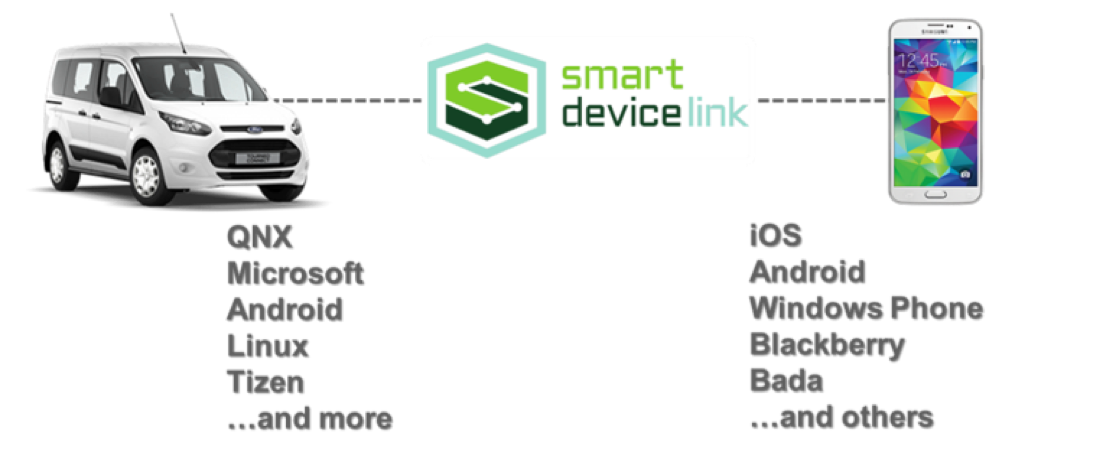
Open Source
SmartDeviceLink
HACK
First Attempt
syncbrake @ #TCDISRUPT 2015
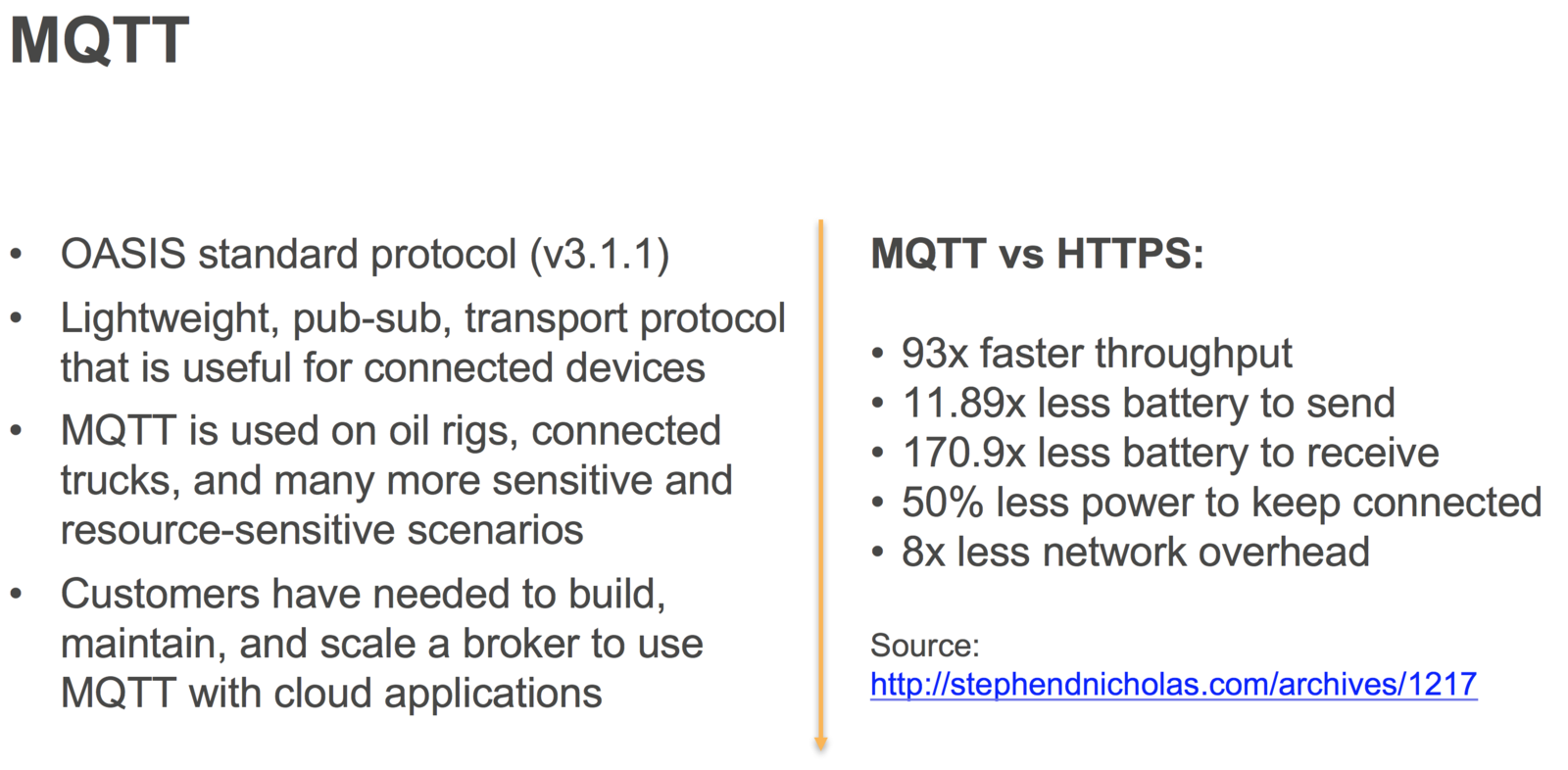
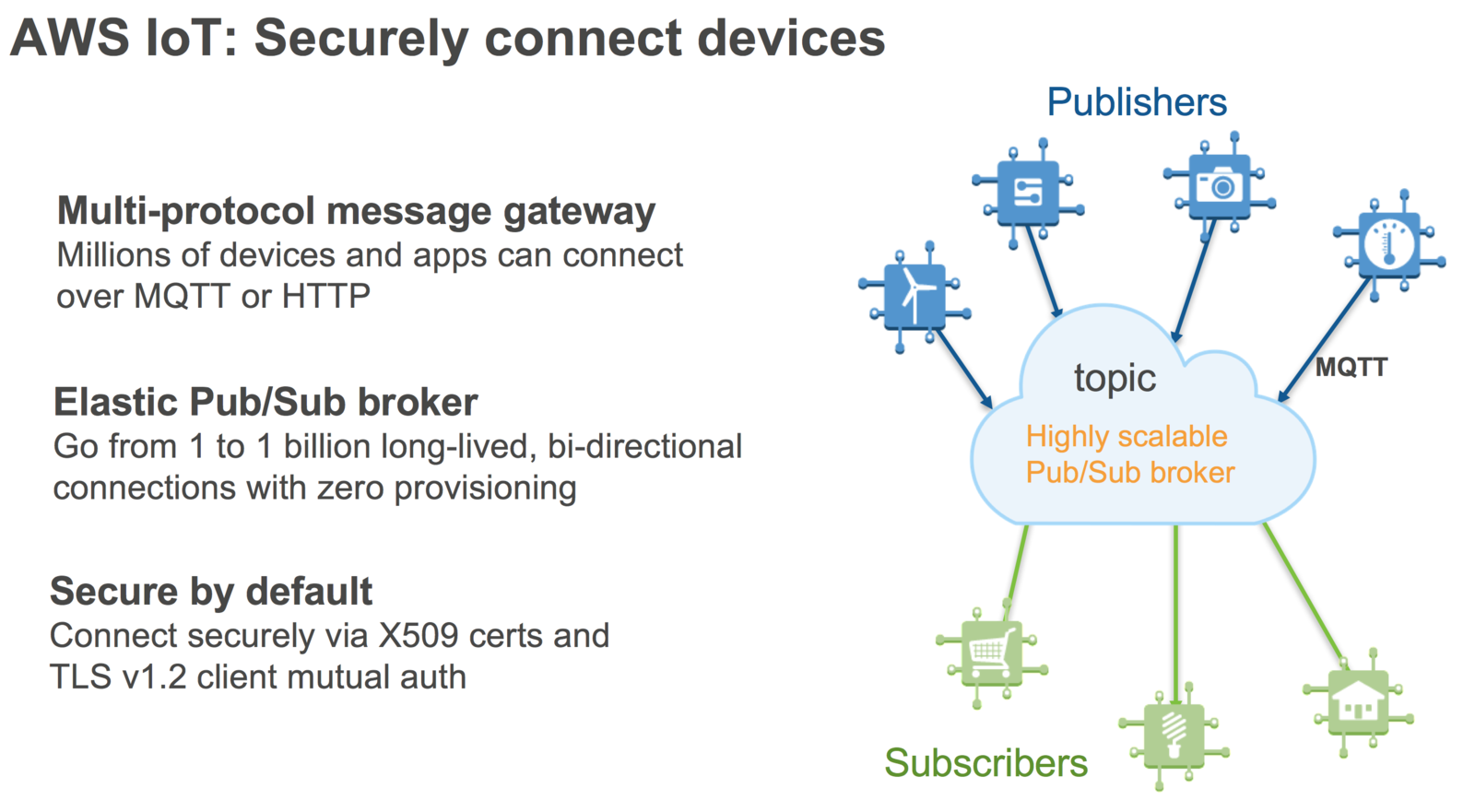
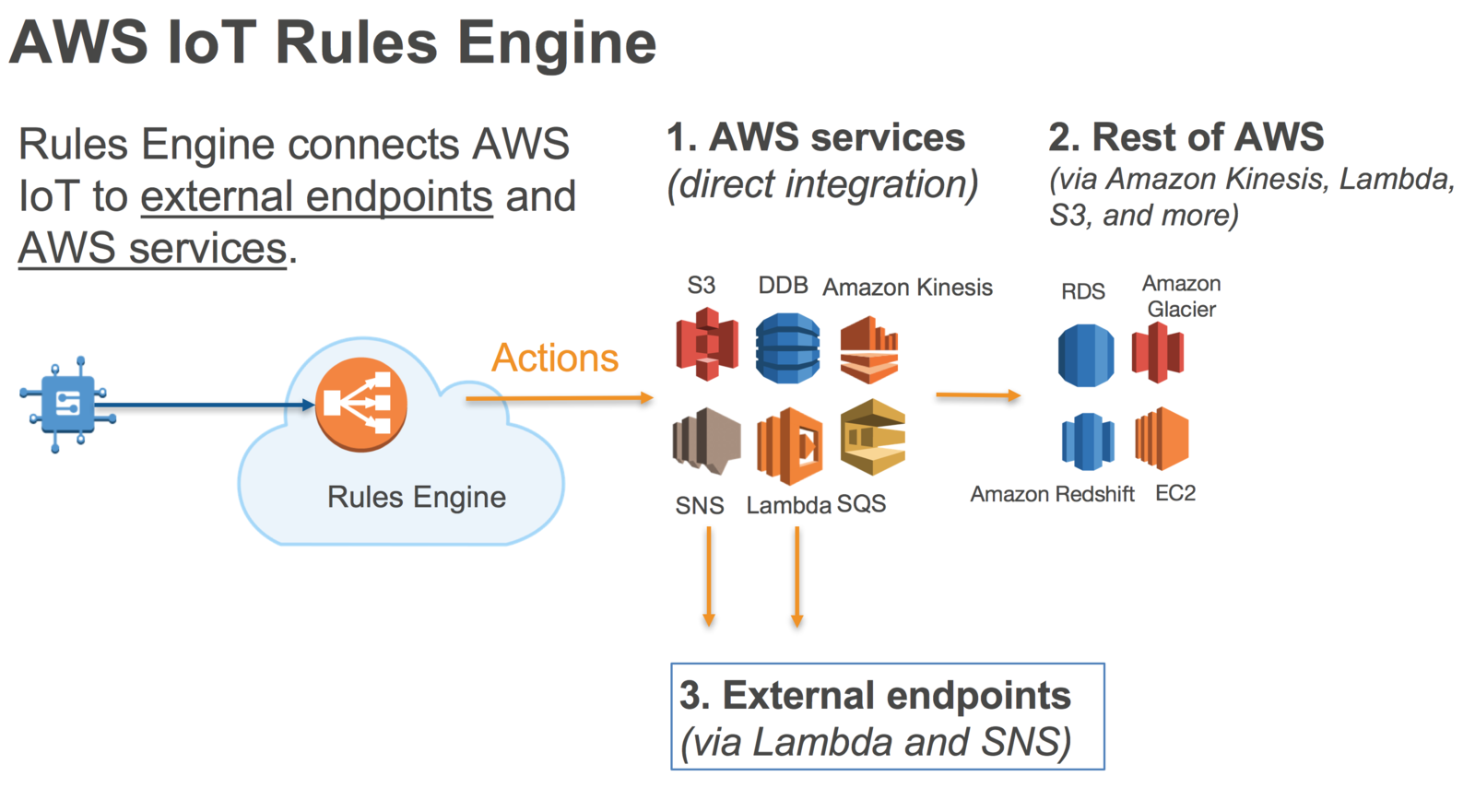
AWS IoT
re:Invent 2015 Proof Of Concept
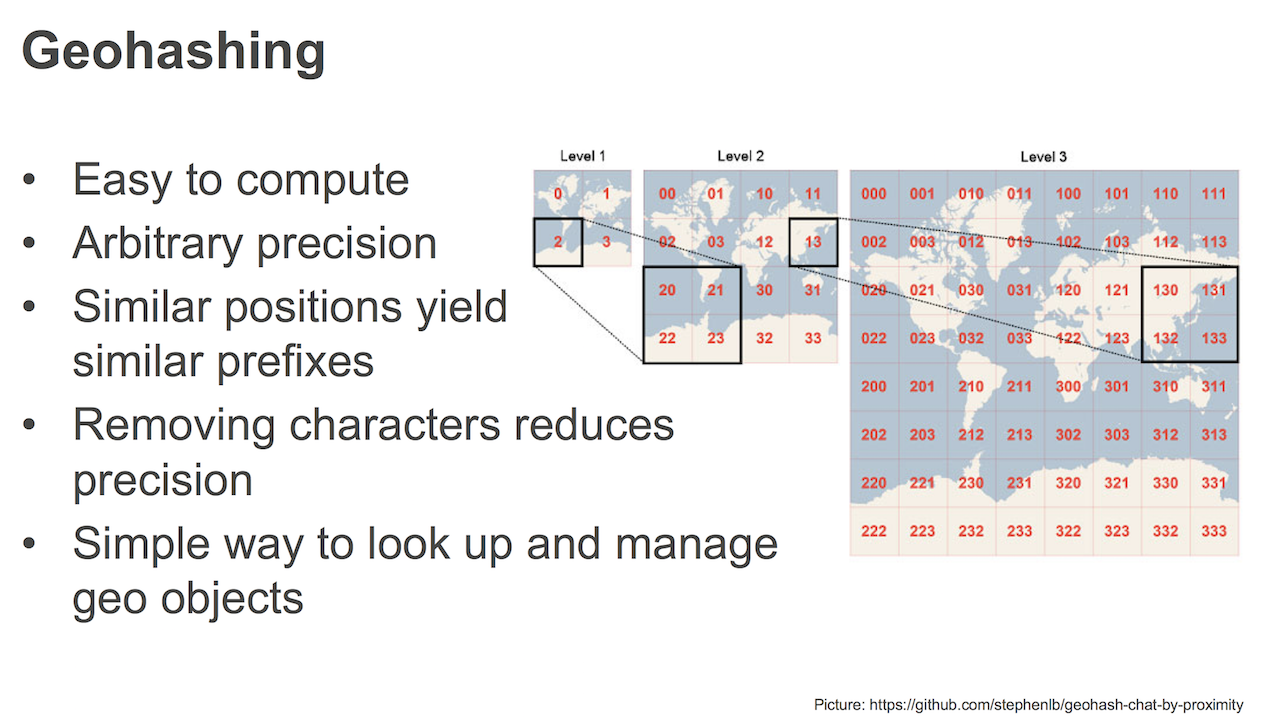
MQTT Topic Wildcards

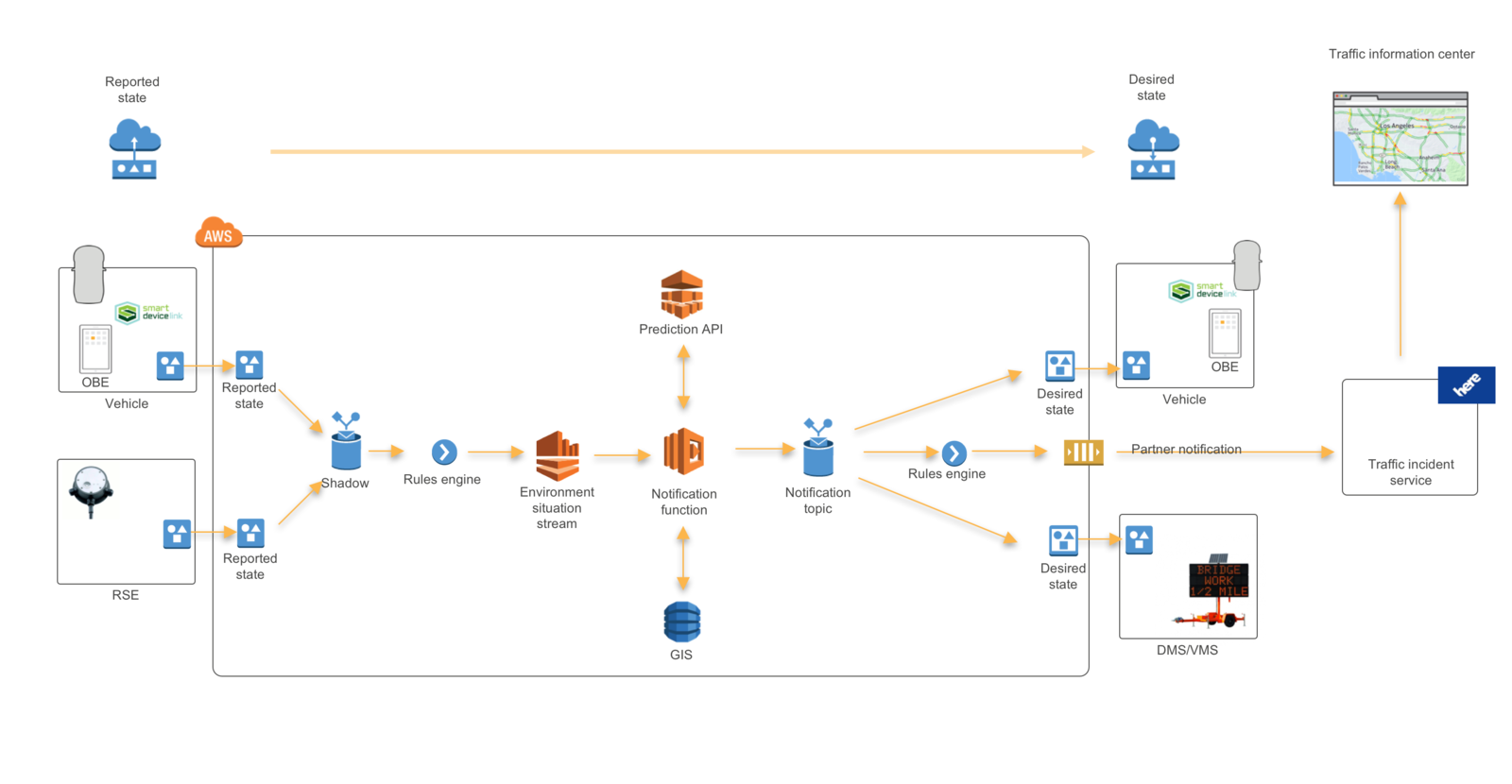
AWS Demo
re:Invent 2015
AWS Demo feedback
- privacy
- emulator
CES Demo
CES 2016
CES Demo FEEDback
- latency
Field Test
Testing Approach
- Open source tools
- Repeatable by anyone
- Route
- Open results
Tooling
Tests
UDP Latency and Packet Loss
- Measures the round trip time of small UDP packets between the application and a target test node.
- Each packet contains consists of an 8-byte sequence number and an 8-byte timestamp.
- If a packet is not received back within three seconds of sending, it is treated as lost.
- The test records the number of packets sent each hour, the average round trip time of these and the total number of packets lost.
- The test will use the 99th percentile when calculating the summarized minimum, maximum and average results.
Mobile HArdware/Operators
LG-H790 Nexus 5X on Android API 23 (Marshmallow)
- T-Mobile
- AT&T
- Google Project Fi (MVNO on Sprint, T-Mobile on June 2016)
- Verizon

Cloud Operators
All major US regions available on June 2016
- AWS: us-east-1, us-west-1, us-west-2
- Azure: us-east, us-north-central, us-central, us-south-central, us-west
- Google: us-east, us-central
Cloud INSTANCES
RHEL 6.7, smallest instance class
- Google: f1-micro, 1 Core, 0.60GB RAM, at ~ $0.066/hr
- AWS: t2.micro, 1 Core, 1.07GB at ~ $0.073/hr
- Azure: A0, 1 Core, 0.75 GB RAM ~ $0.078/hr
Route
Vehicle
Model S 70D with AutoPilot
Co-pilot 1: WEST LOOP
Co-pilot 2: EAST LOOP
Results
Test Coverage
Cloud REGION Differences
LOW LATENCY COrridors
Known issues
Verizon CDMA phone stability
AT&T device power
Timeout retries
GCE instance availability
Unknown Unknowns
Mobile network saturation level not known during tests
Mobile hardware stability
Results Summary
Analysis on June 2016
| Latency (rtt in ms) | Reach | Mobile | Cloud | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1000 | Regional | SIngle | Single Provider, Single Region | Project Fi on GCE |
| <1000 | National | Multiple | Single Provider, Single Region | AT&T or Verizon on aws-us-east-1 |
| <100 | National | Multiple | Single Provider, Multiple Regions | AT&T and Fi on Azure |
| <50 | National | Multiple | Multiple Providers, Multiple Regions | AT&T and Fi on AWS, GCE, and Azure |
What's Next
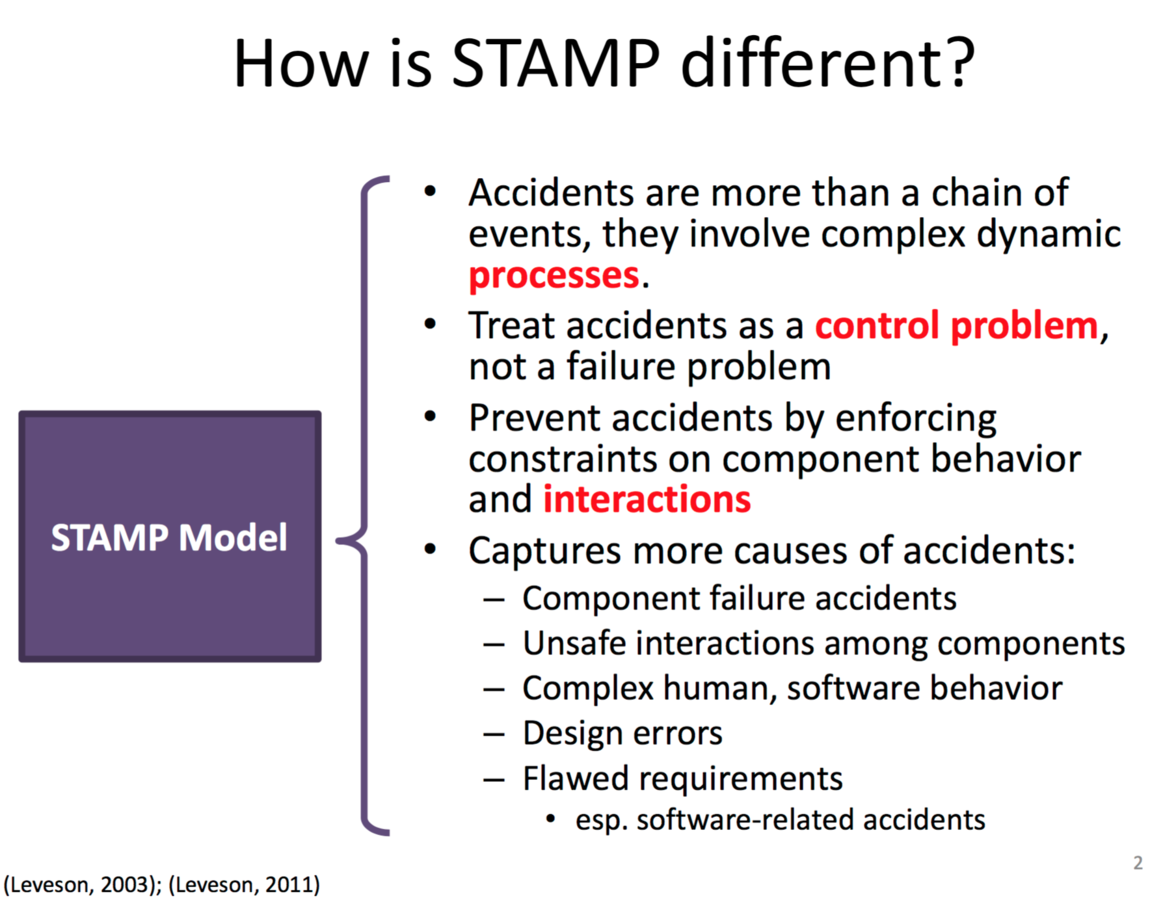
Systems Thinking Review
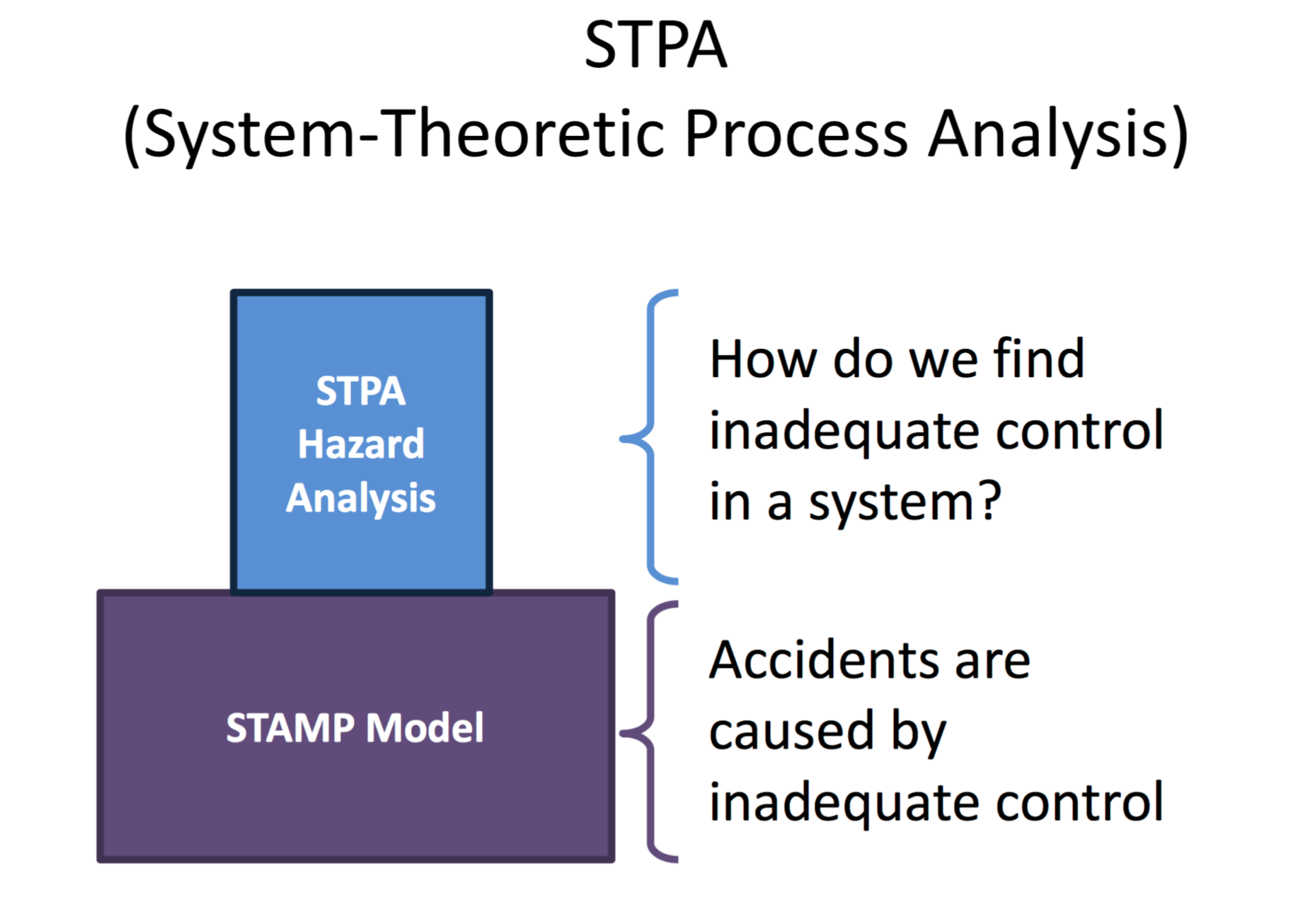
Systems Theoretic Analysis Model Process
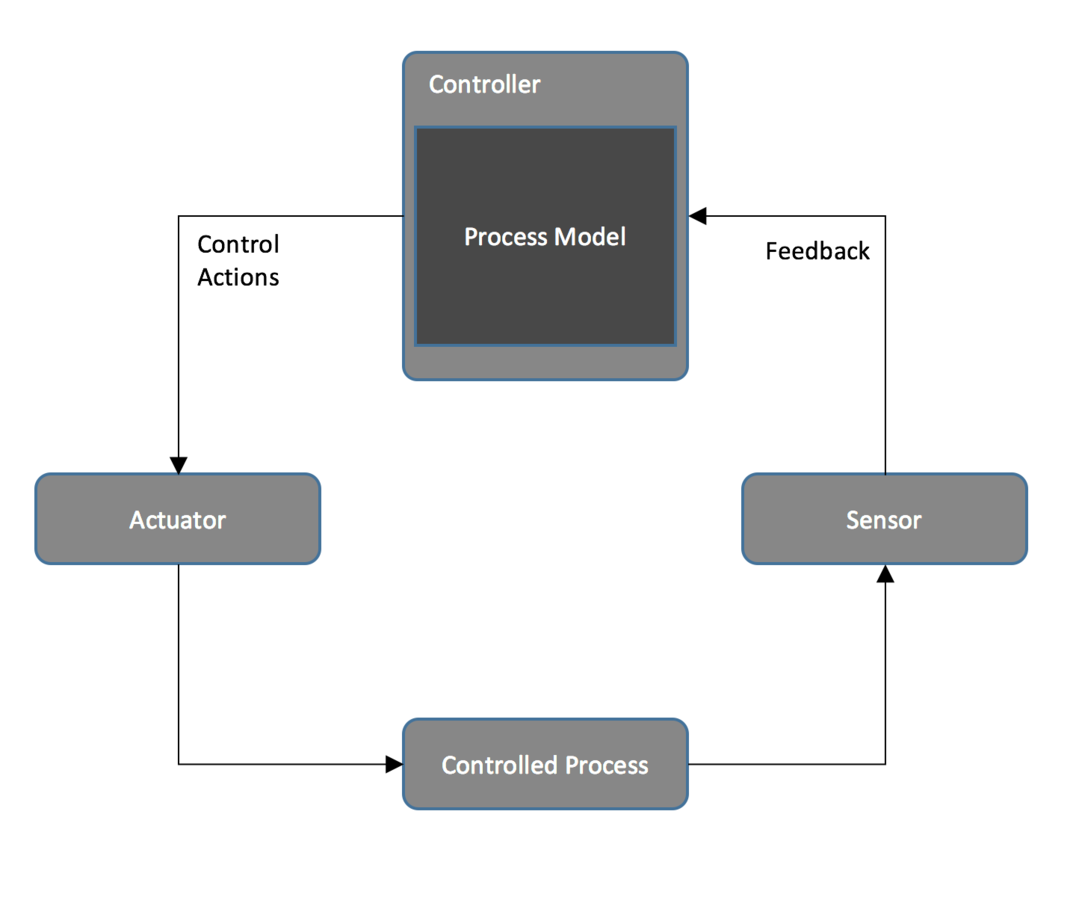
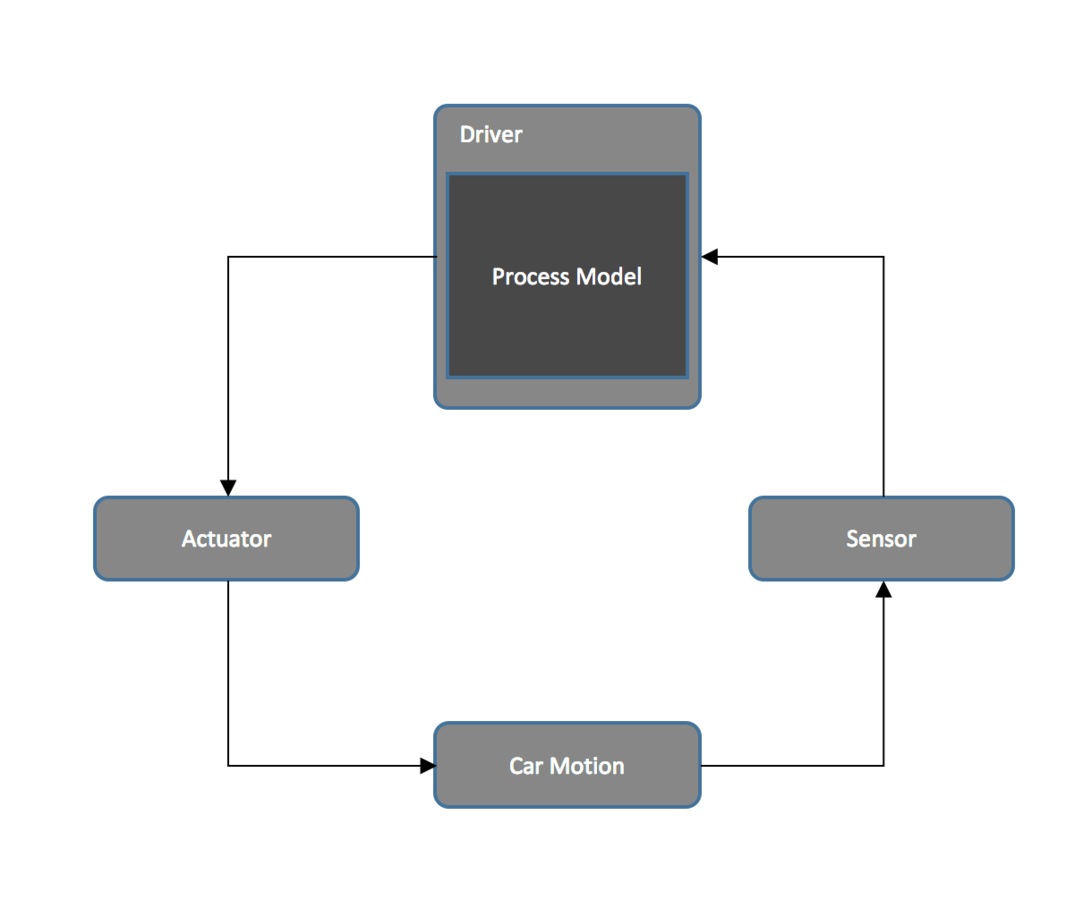
BAsic control loop
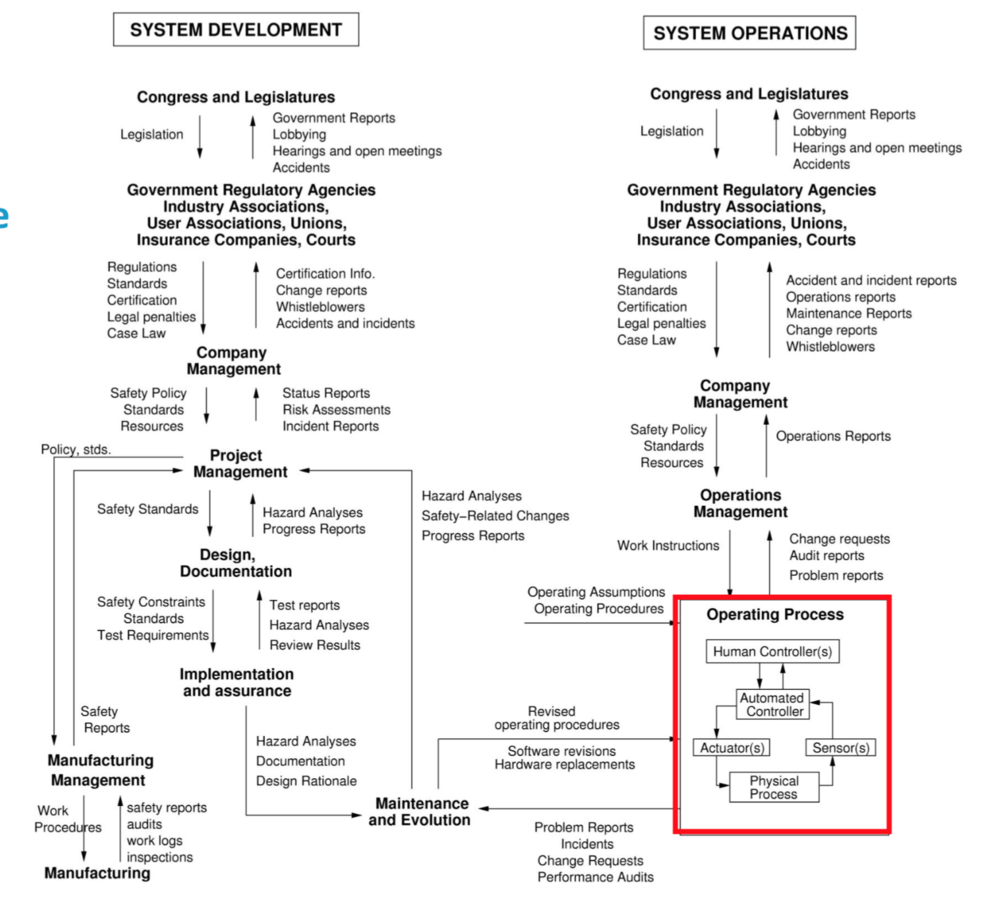
Generic control structure
Stamp
Controllers use a process model to determine control actions.
Accidents often occur when the process model is incorrect.

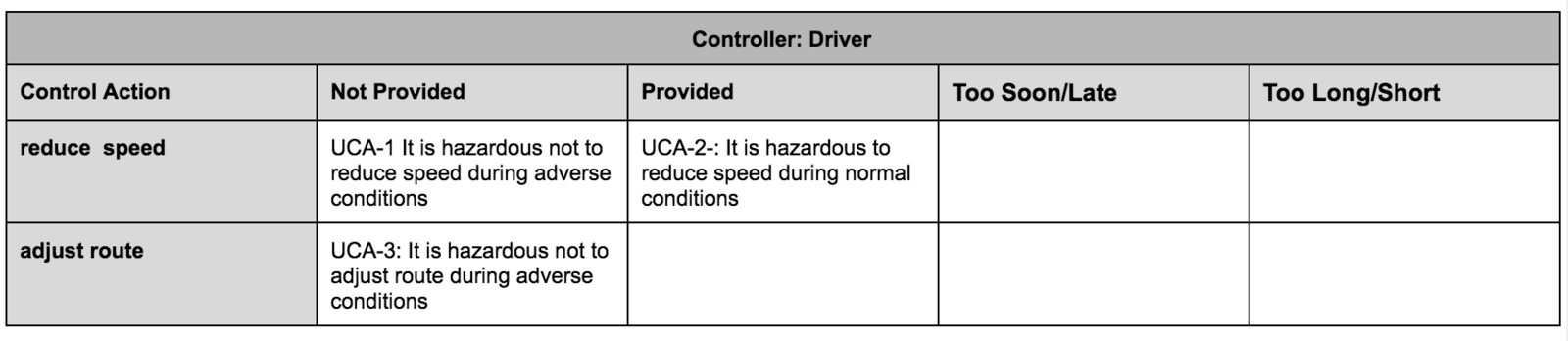
Four types of hazardous control actions:
1. Control commands required for safety are not given
2. Unsafe ones are given
3. Potentially safe commands but given too early, too late
4. Control action stops too soon or applied
Safety Engineering Tools

Want to Learn MORE?
STAMP/STPA Demo

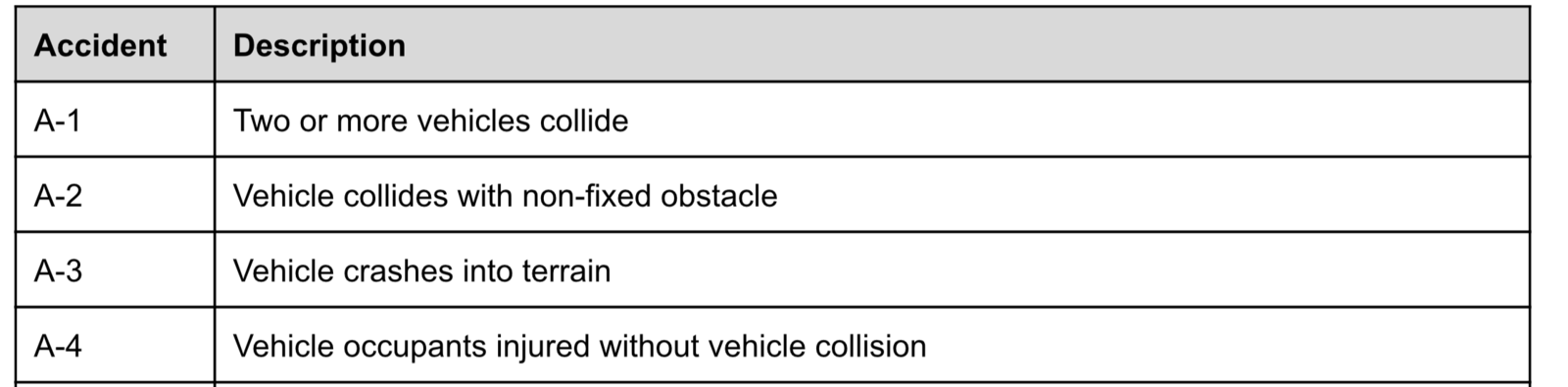
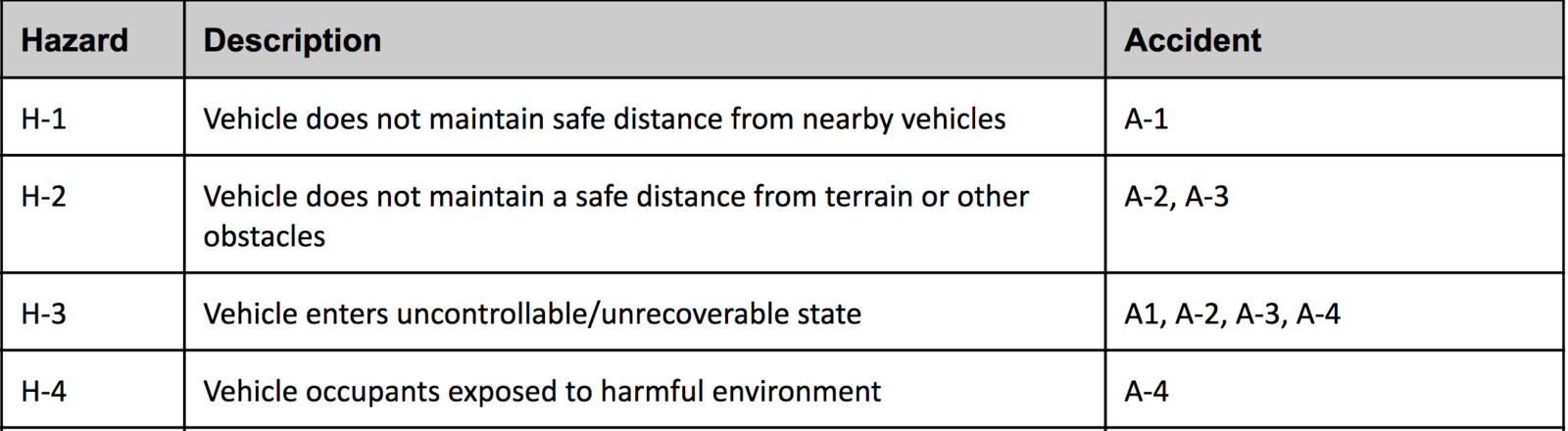
Example System
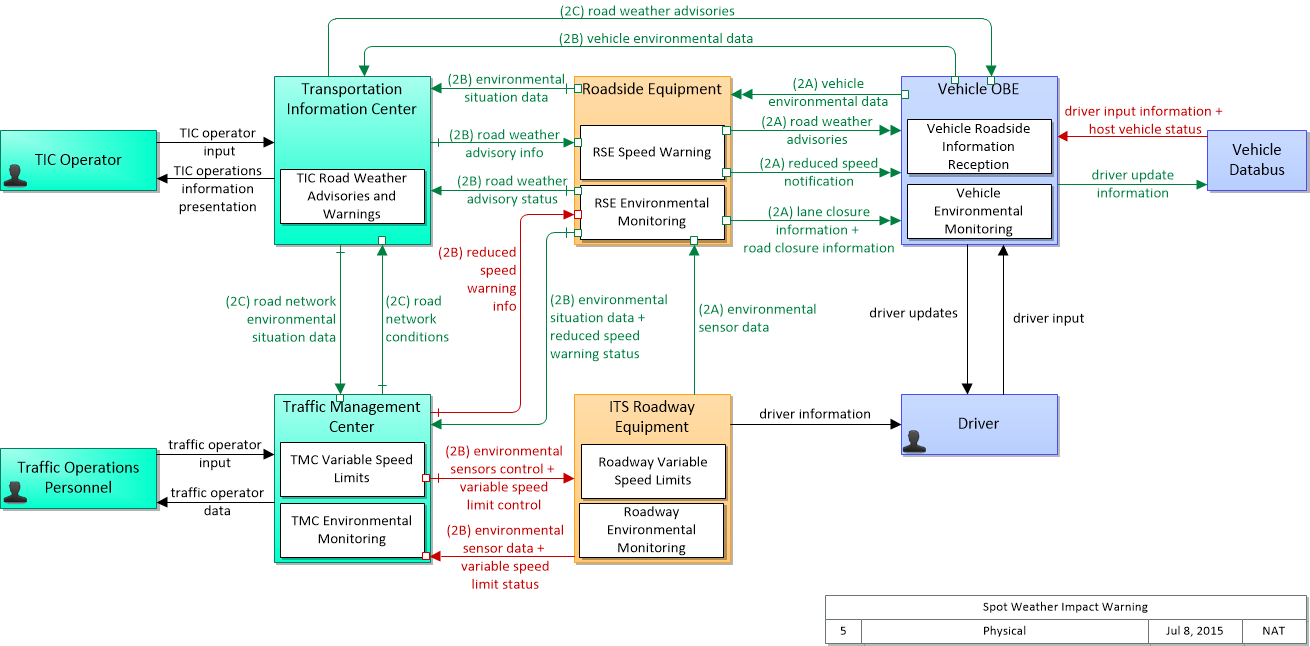
Road Hazard Warning System

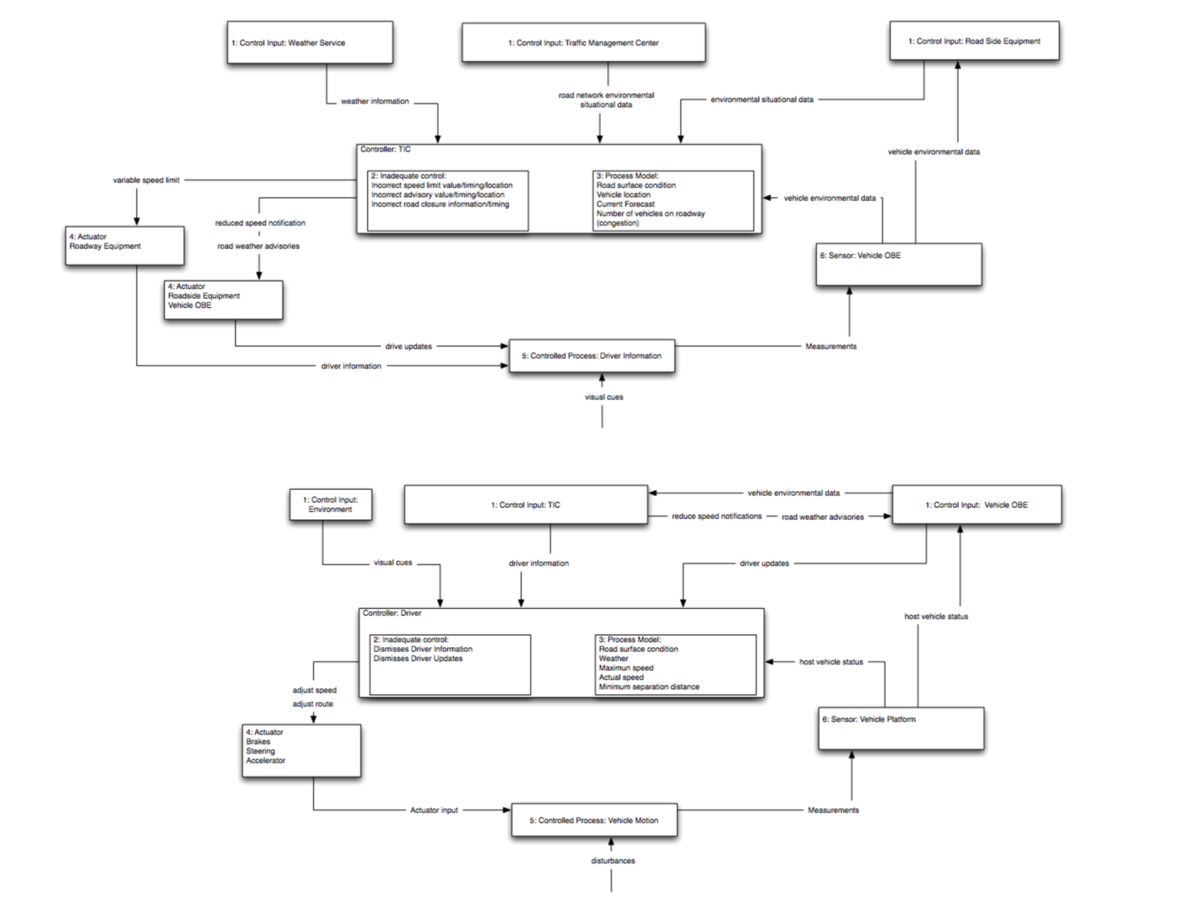
Control Structure
Components
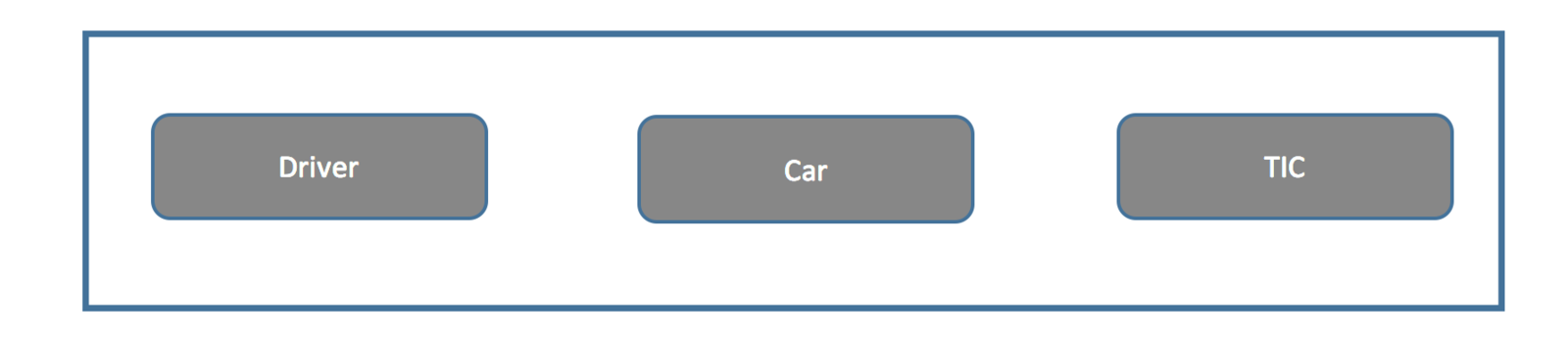
Control Structure
Loop
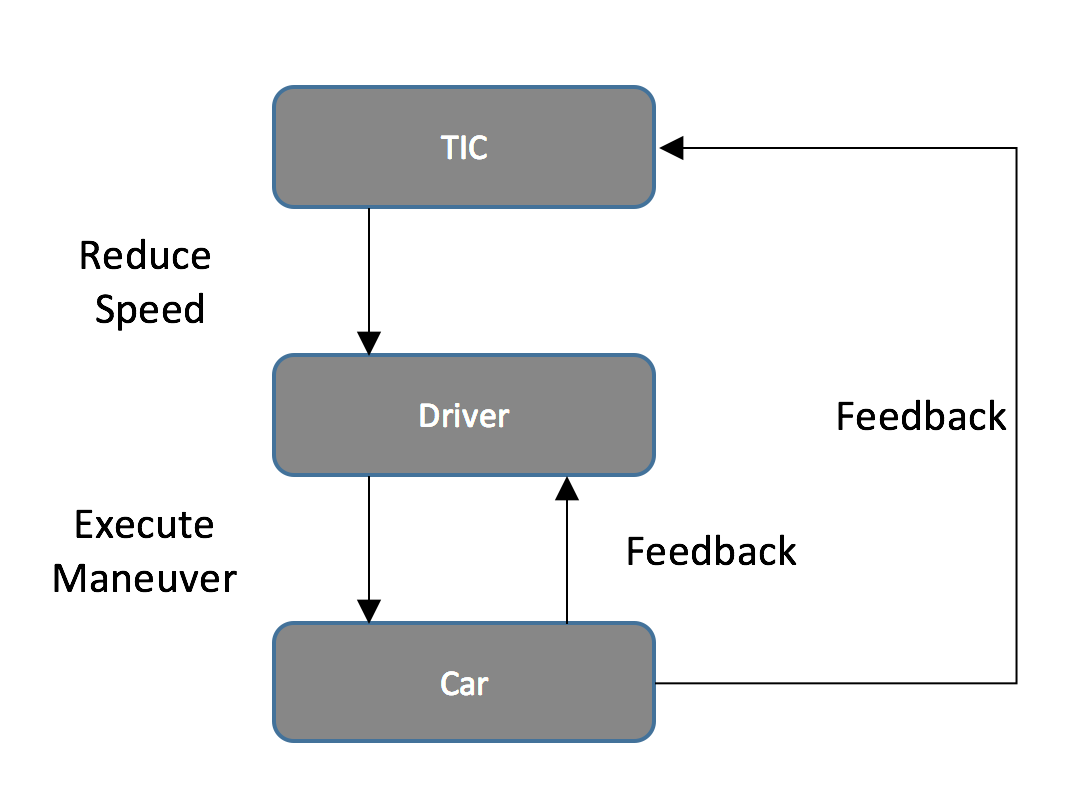
Control Structure
zoom in
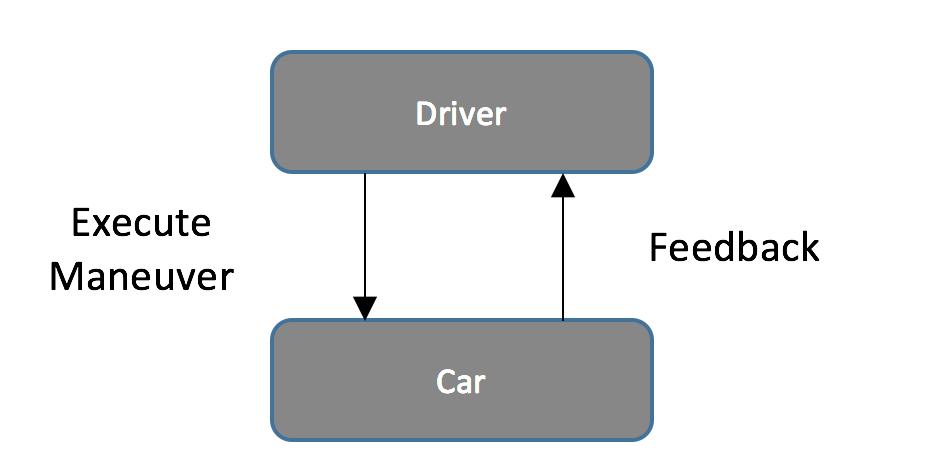
Control Structure
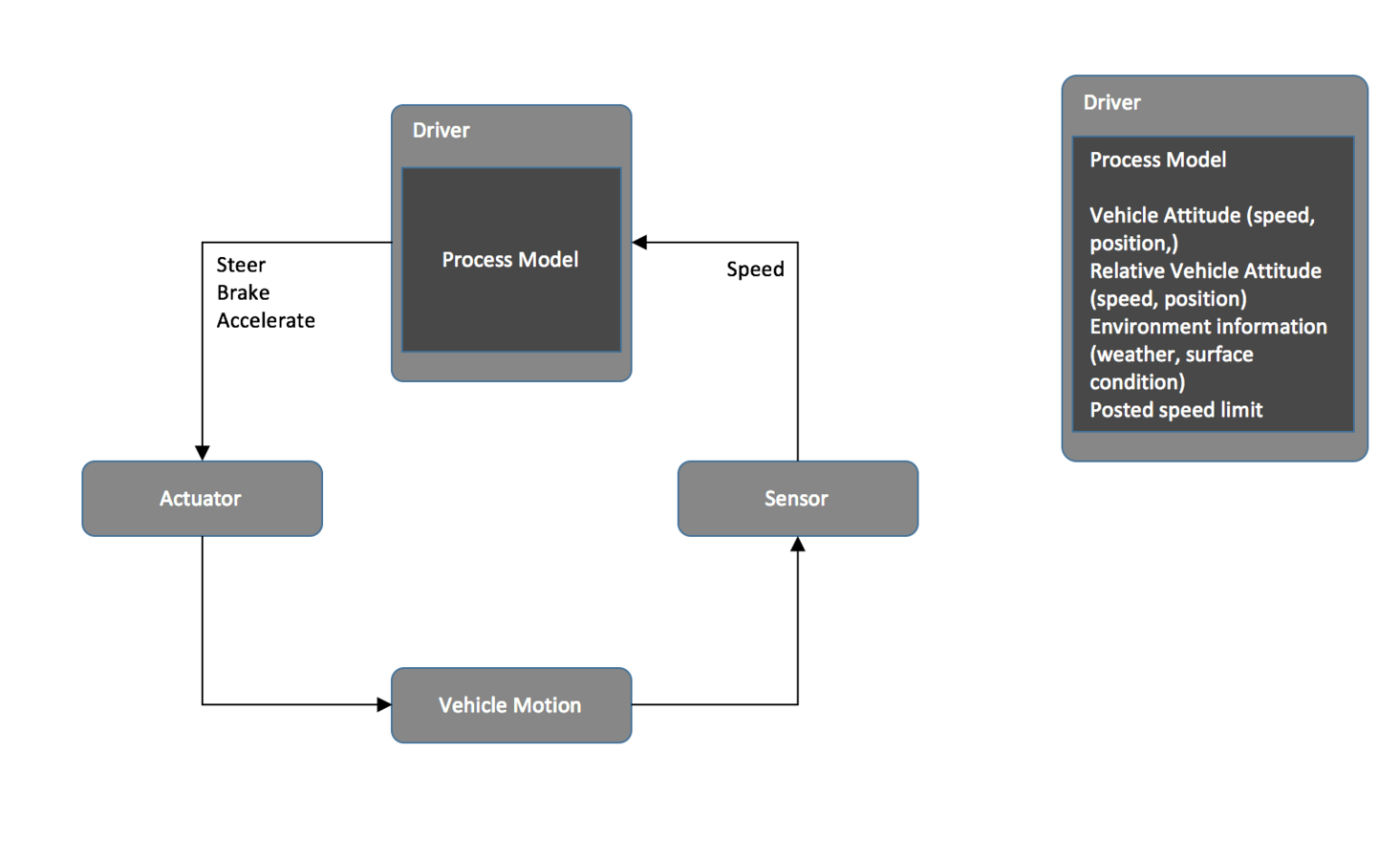
break out (decompose)
Control ACTIONS
brainstorm actions and process model
break out (decompose)
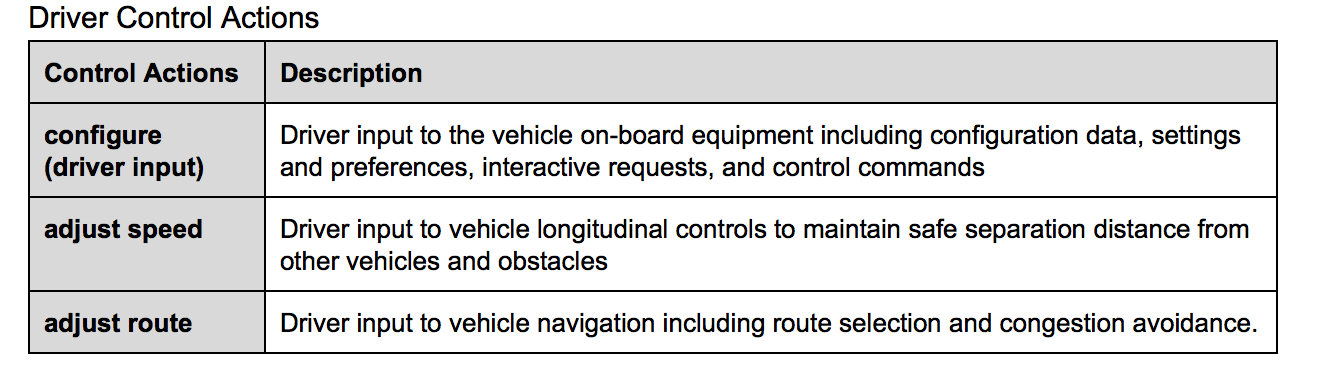
UNSAFE Control ACTIONS

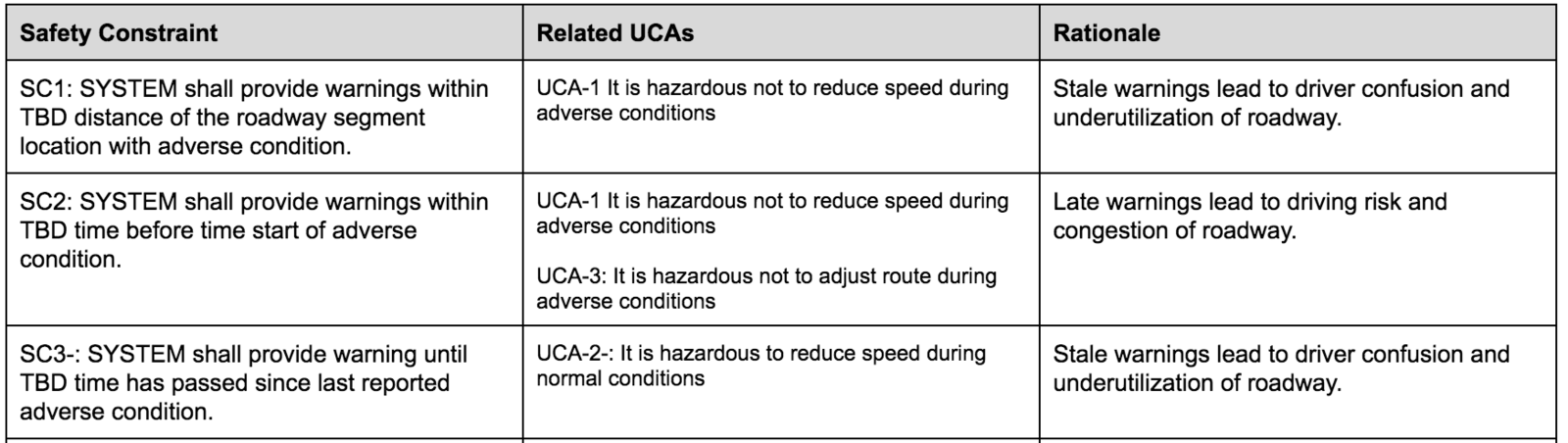
SaFETy CONSTRAINTs

Determine CAUSAL FACTORS
Some Hints
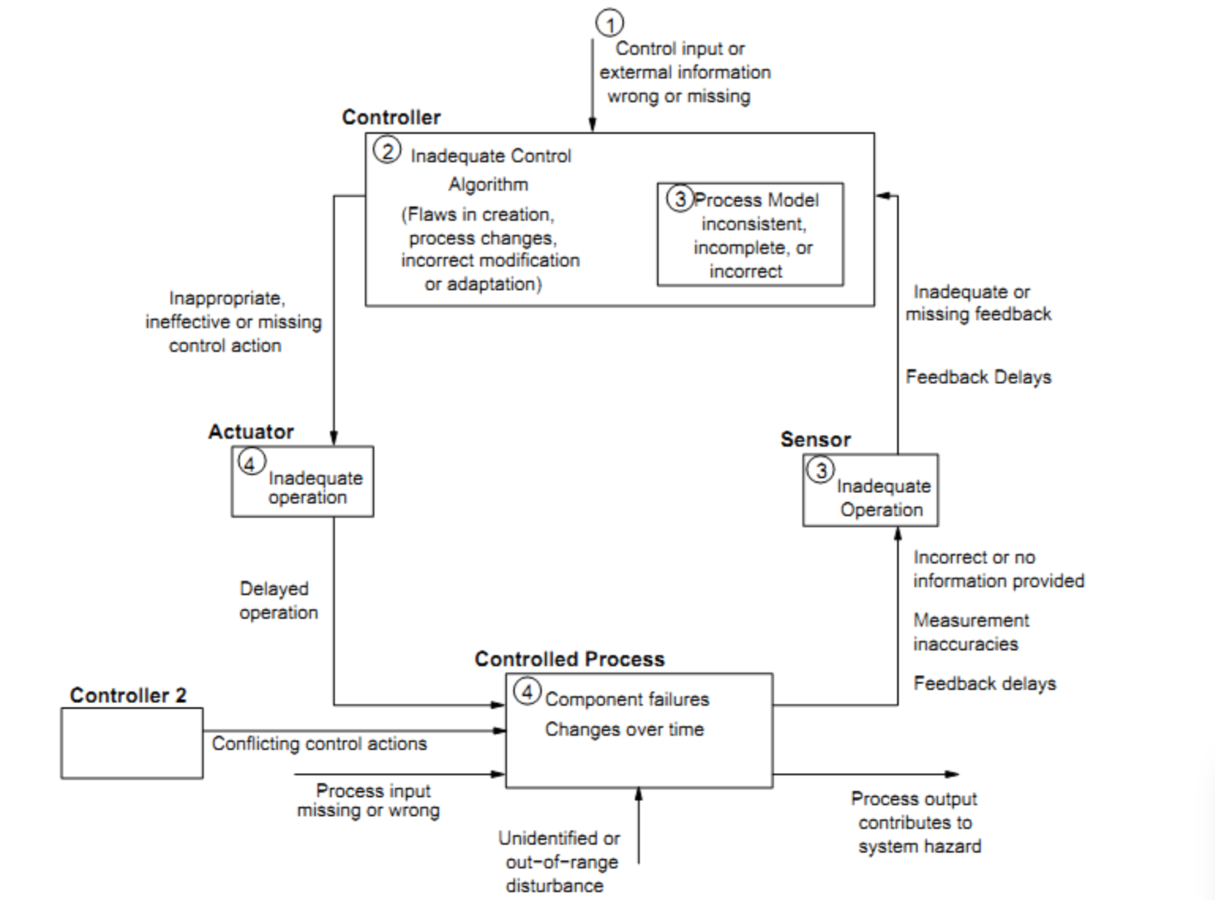
Determine CAUSAL FACTORs
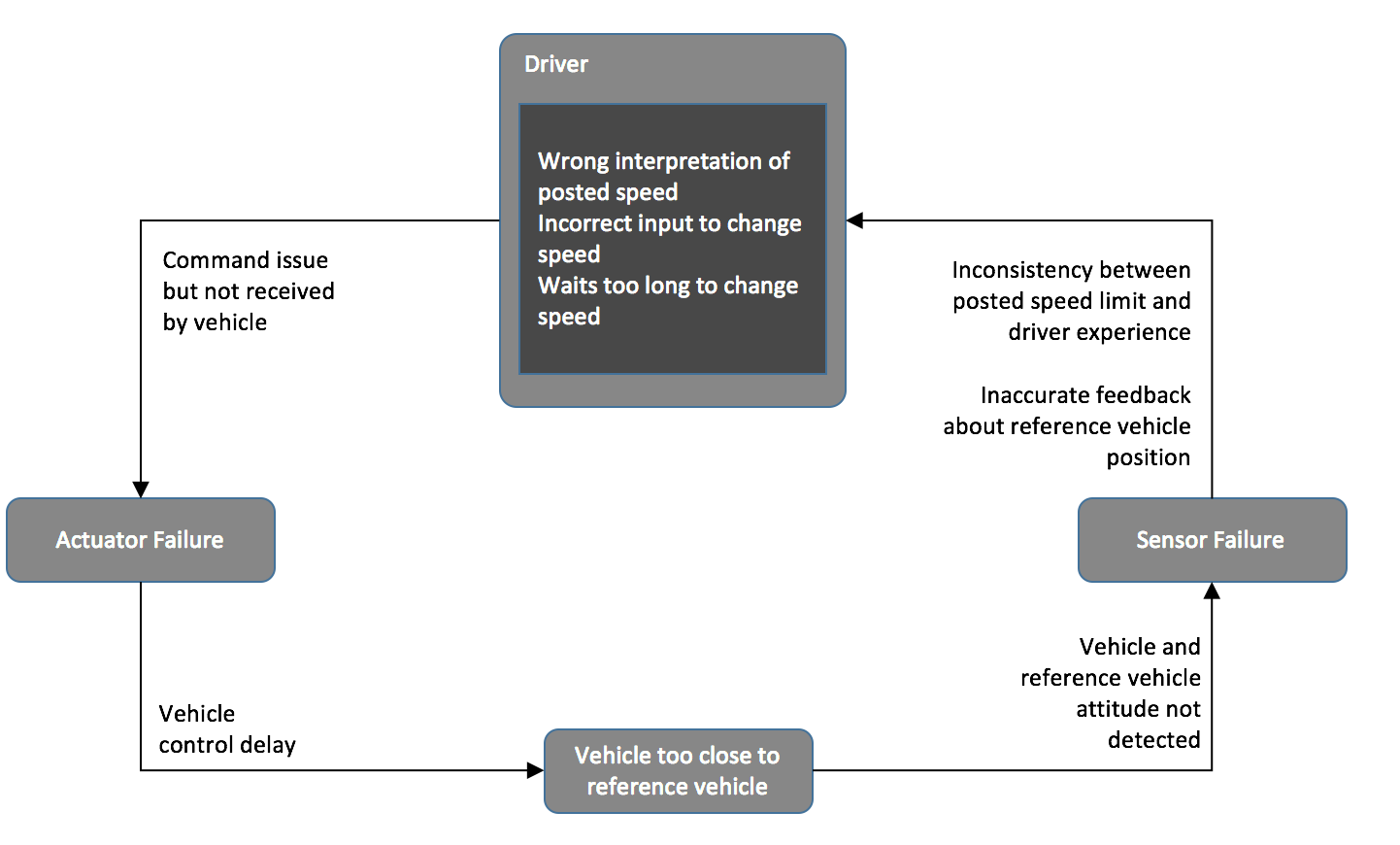
REvisit the control STRUCTURE
How could this action be caused by:
– Process model: anything missing?

REvisit the control STRUCTURE
How could this action be caused by:
– Feedback: missing feedback loops?
– Sensors: are additional sensors needed?
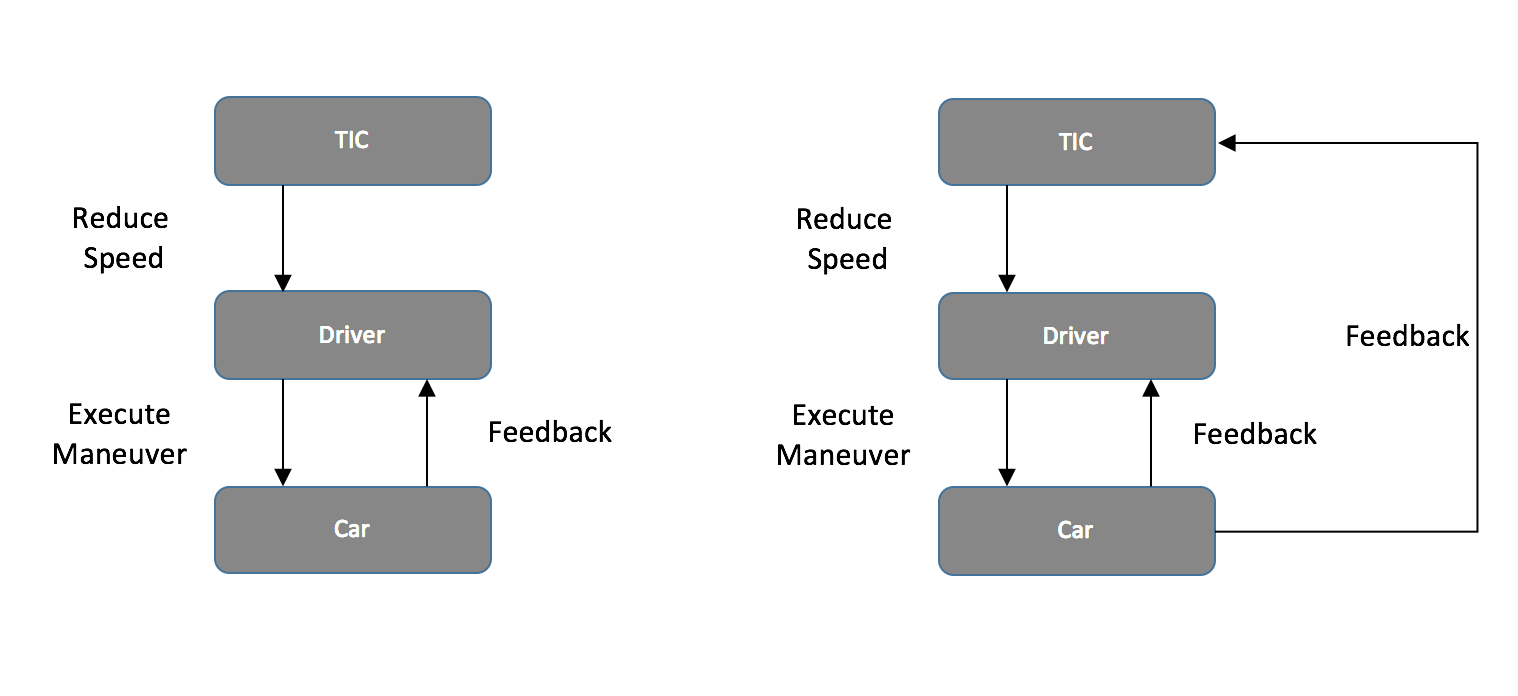
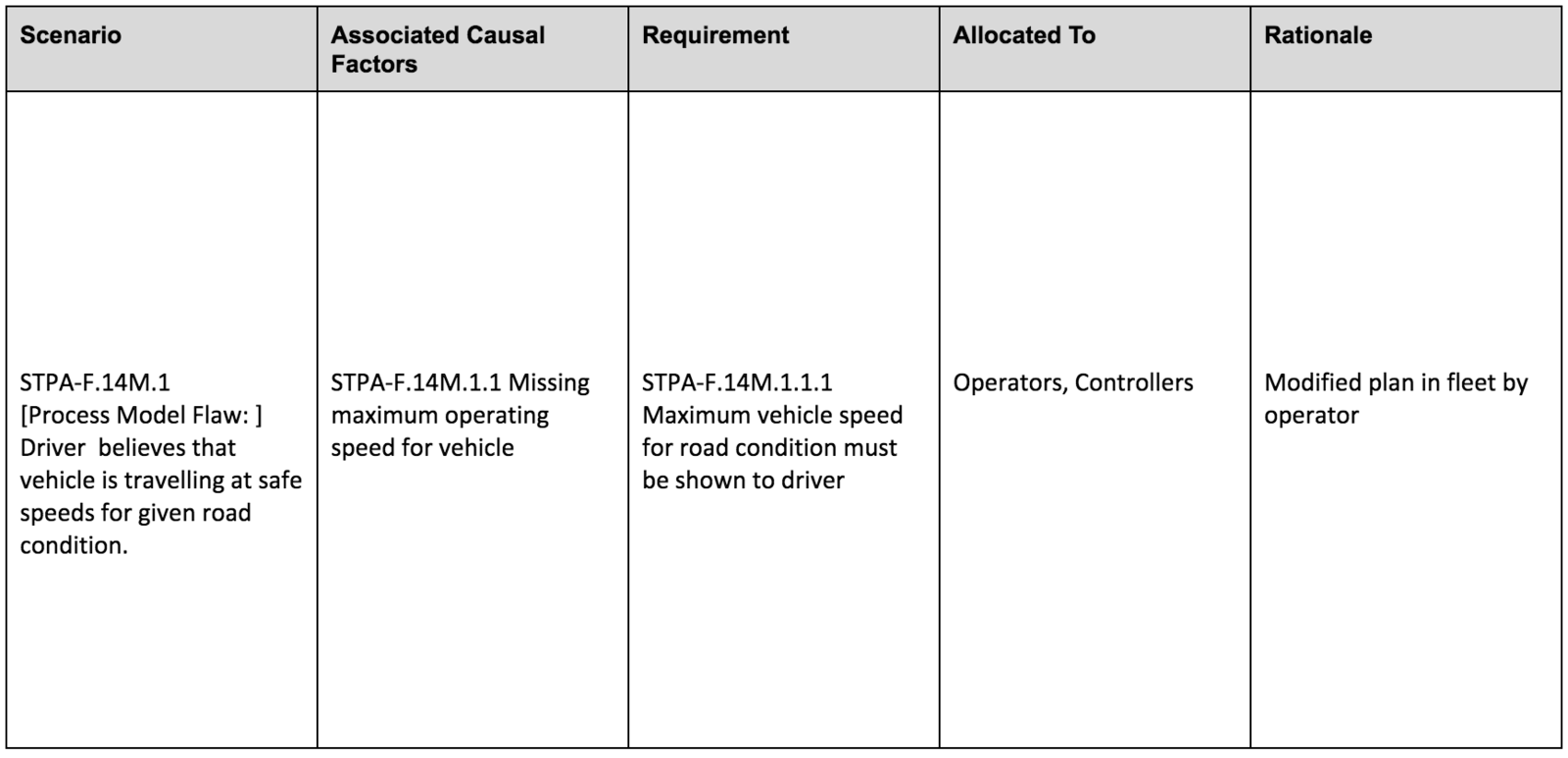
Create the Safety requirements
Exercise for the reader
See More EXAMPLES at
Summary
- Connected vehicle application use cases requiring low latency are feasible on today's mobile networks and public cloud providers.
- Low latency corridors have the potential to support even more demanding automotive applications but latency gaps still exist.
- Latency gaps may be mitigated through the use of multiple virtual mobile operators and regional cloud provider regions.
- Latency gaps add to the complexity of automotive control systems since the system interactions now include not only component interactions within the single automobile but also between automobiles and public cloud’s infrastructure.
- STPA/STAMP can be used to identify safety requirements of complex, multi-controler systems.
Questions?
rdematos@mit.edu
http://thesis.ricardodematos.com