COMP2511 Tute04
Agenda
- Admin Stuff
- Law of Demeter
- Our first design patterns!
- Composite Pattern
- Factory Pattern
Admin Stuff
-
Assignment 1 is due next Wednesday
- Get started if you haven't already
- You can run dryrun tests on GitLab by using the optional trigger pipelines (refer to spec)
- Get feedback on assignment UML,
- Feel free to come to me or the LA during the lab
Law of Demeter
"Principle of least knowledge"
Law of Demeter
What is it?
A method in an object should only call methods of:
- The object itself
- Attributes of the object
- Object passed in as a parameter to a method
- Objects instantiated within the method
Only talk to your immediate friends
Law of Demeter
Avoid doing method chaining! (You will lose marks)
o.get(name).get(thing).remove(node)Purpose?
Achieve loose coupling in code
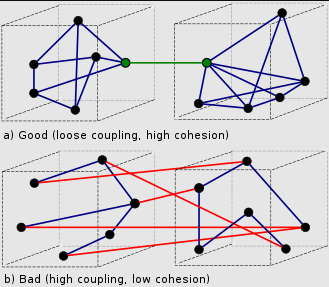
Coupling and Cohesion
Cohesion refers to what a class / module can do.
Low cohesion means class has a great variety of actions (broad, unfocused)
High cohesion means a class is focused on what it should be doing
Cohesion
Coupling
Coupling refers to how dependent classes are toward each other.
High coupling makes it difficult to change your code as classes are so knit together.
Good software design is
high cohesion
and
low coupling
Law of Demeter
In the unsw.training package there is some code for a training system.
- Every employee must attend a whole day training seminar run by a qualified trainer
- Each trainer is running multiple seminars with no more than 10 attendees per seminar
In the TrainingSystem class, there is a method to book a seminar for an employee given the dates on which they are available.
This method violates the principle of least knowledge (Law of Demeter).
Where and how is the Law of Demeter being violated?
TrainingSystem is getting instances of Seminar from instances of Trainer and calling its methods
Interacting with classes beyond its friends
public LocalDate bookTraining(String employee, List<LocalDate> availability) {
for (Trainer trainer : trainers) {
for (Seminar seminar : trainer.getSeminars()) {
for (LocalDate available : availability) {
if (seminar.getStart().equals(available) &&
seminar.getAttendees().size() < 10) {
seminar.getAttendees().add(employee);
return available;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}Law of Demeter
In violating this principle, what other properties of this design is not desirable?
Law of Demeter
-
TrainingSystemis needlessly tightly coupled withTrainerandSeminar -
TrainingSystemhas low cohesion as it relies on classes that are not its closest friends to achieve its purpose -
Seminarhas no control over the number of attendees. It relies onTrainingSystemto restrict number of attendees. This makesSeminarhard to re-use in the future (poor encapsulation)
In violating this principle, what other properties of this design is not desirable?
Law of Demeter
Let's refactor it together!
-
TrainingSystemis needlessly tightly coupled withTrainerandSeminar -
TrainingSystemhas low cohesion as it relies on classes that are not its closest friends to achieve its purpose -
Seminarhas no control over the number of attendees. It relies onTrainingSystemto restrict number of attendees. This makesSeminarhard to re-use in the future (poor encapsulation)
In violating this principle, what other properties of this design is not desirable?
Law of Demeter
- No longer tightly coupled.
TrainingSystemno longer has any knowledge ofSeminar. - Each class now has a clear purpose in booking a training seminar. Any behaviour that relates to them is now delegated to their classes.
- The
Seminarclass is responsible for ensuring number of attendees do no exceed 10.
In refactoring the principle is no longer violated, how has this affected other properties of the design?
Law of Demeter
Liskov Substitution Principle
How does OnlineSeminar violate LSP?
/**
* An online seminar is a video that can
* be viewed at any time by employees.
* A record is kept of which employees
* have watched the seminar.
*/
public class OnlineSeminar extends Seminar {
private String videoURL;
private List<String> watched;
}
Liskov Substitution Principle
How does OnlineSeminar violate LSP?
/**
* An online seminar is a video that can
* be viewed at any time by employees.
* A record is kept of which employees
* have watched the seminar.
*/
public class OnlineSeminar extends Seminar {
private String videoURL;
private List<String> watched;
}
Does not have a list of attendees, so clients won't be able to use it in the same way as Seminar.
i.e making a booking
Design Patterns
Design Patterns
Design patterns are blueprints for solving common design problems efficiently.
They help us make our code:
- Organised
- Reusable
- Easy to maintain
Design Patterns
We are going to learn many different design patterns from this week till the end of the course.
Design patterns are categorised into 3 main types:
- Behavioural: Focus on functionality / communication between objects
- Creational: Focus on object creation
- Structural: Focus on how classes are composed
Design Patterns
I recommend throughout this course noting down:
- The overall structure of the design pattern
-
What specific problem a design pattern is solving
- Common scenarios you might see a design pattern being used for
These will be useful for Assignment 2 where you have to choose which is the best design pattern to use and to implement them!
Composite Pattern
Composite Pattern
What is it?
Structural design pattern that allow objects to be composed into a tree structure such that individual objects and composites of such objects can be treated in the same way.
When to use?
Model a group of classes that forms a hierarchy
Composite Pattern
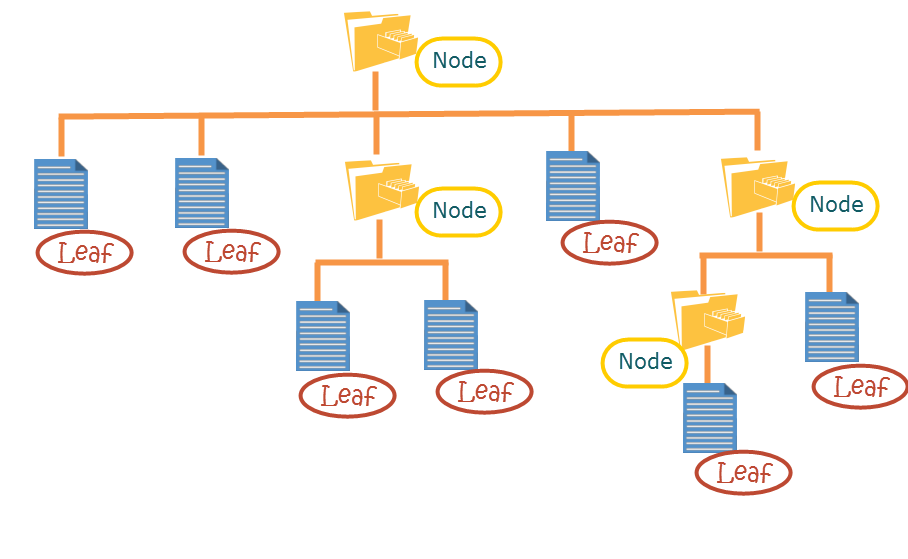
In Unix based operating systems, directories are just files that can contain other files
Composite Pattern
Leaf Nodes
Composite Nodes
- A composite stores a collection of children components (either Leaf and/or composite)
- Performs operations on its children
- Single part objects, are always located at the leaves of the tree
- Performs operations directly on the object
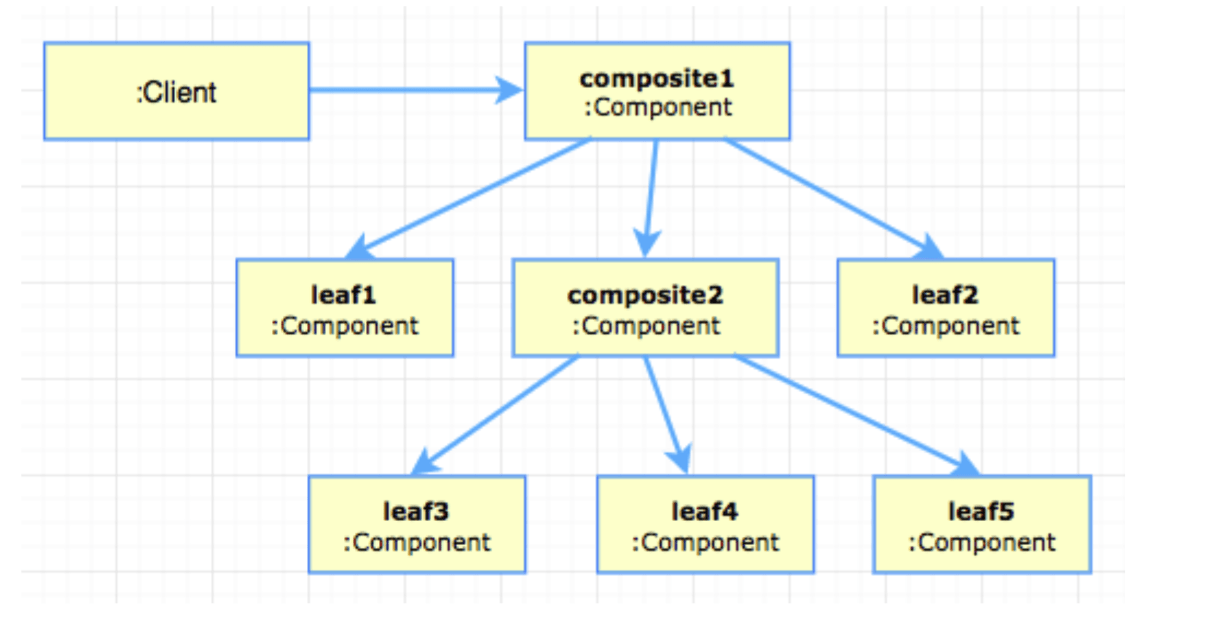
Composite Pattern
UML Diagram
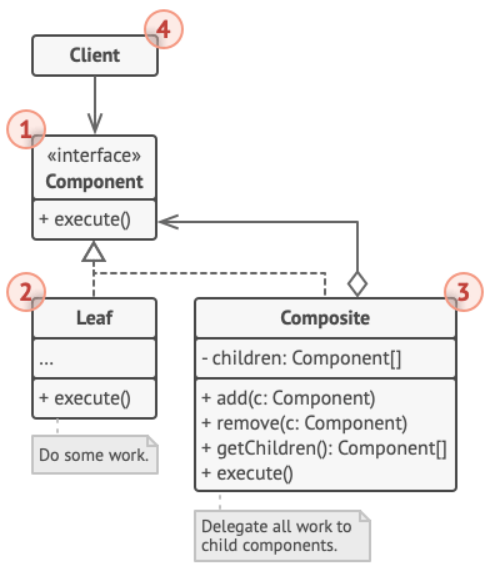
LeafandCompositeboth implement the same interface- Instances of
LeafandCompositecan be treated as the same - A
Compositecan hold more than oneLeaf -
Produces a tree-like structure that leans itself very well towards recursion
Composite Pattern
Use the composite pattern to design a simple calculator that can be used to evaluate an arithmetic expression.
Your calculator should be able to:
- Add two expressions
- Subtract two expressions
- Multiply two expressions
- Divide two expressions
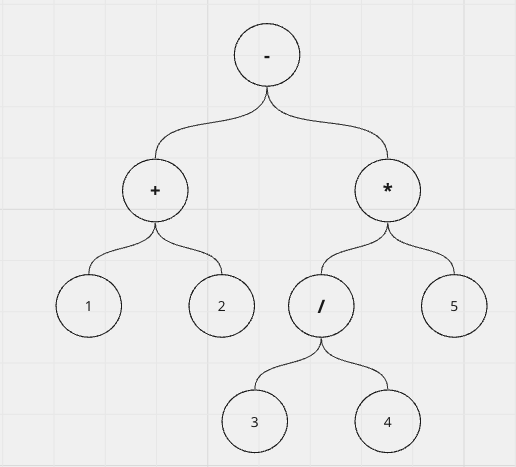
Composite Pattern
Tree representation
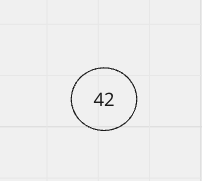
exp1 = 42
exp2 = ((1 + 2) - ((3 / 4) * (5))

















Composite Pattern
UML Diagram
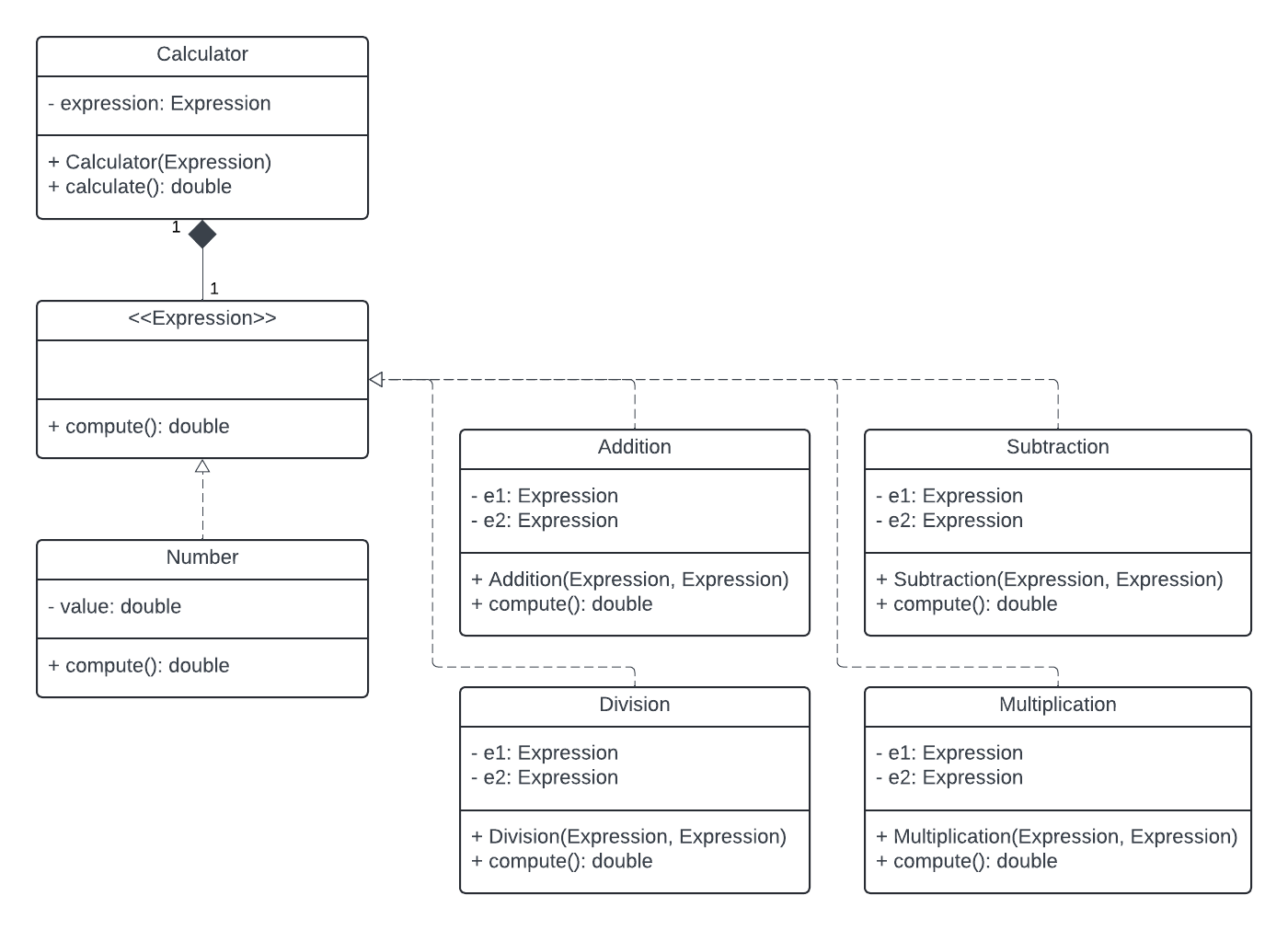
composite nodes
leaf node
Factory Pattern
Factory Pattern
Why use it?
- Reduce coupling between client code (creation logic) and the specific classes being instantiated
- Single responsibility principle: construction of every class in the family is handled at the same place
- Open-Closed principle: introducing new classes into the family simply requires a new factory subclass
What is it?
Creational design pattern that lets you define an interface for creating objects of a family in a superclass but allows subclasses to alter the type of object that will be created.
Factory Pattern
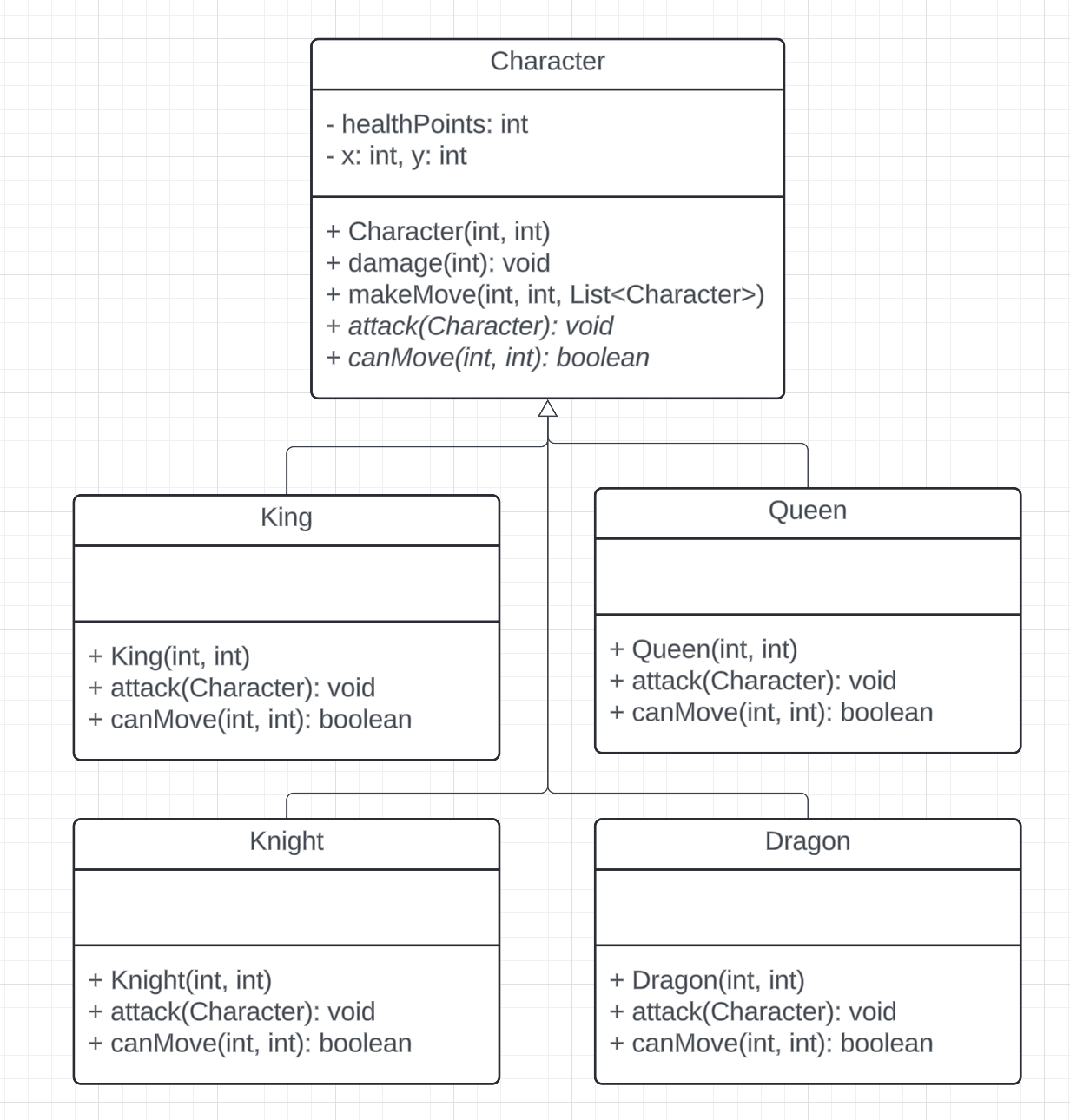
Imagine we are developing a game with different characters!
public class Game {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Game game = new Game();
game.addCharacter(new King(0, 0));
game.addCharacter(new Dragon(0, 1));
game.addCharacter(new Queen(2, 2));
game.play();
}
}



Factory Pattern

Factory Pattern
Refactor the code such that when the characters are created, they are put in a random location in a grid of length of length 5.
Here, because our number of characters that are needed to be created is relatively small, we can place all in a single CharactorFactory class.
Factory Pattern
- Abstract the construction of the character objects - this means we are not dealing directly with a constructor.
- Especially, we abstract the generating of random numbers to the factory and simply call
CharacterFactory.createKingetc, which makes our code more clean and less likely forGameto cause problems with creating the objects itself.
How does the Factory Pattern allow us to abstract construction of objects, and how will it improve our design with this new requirement?
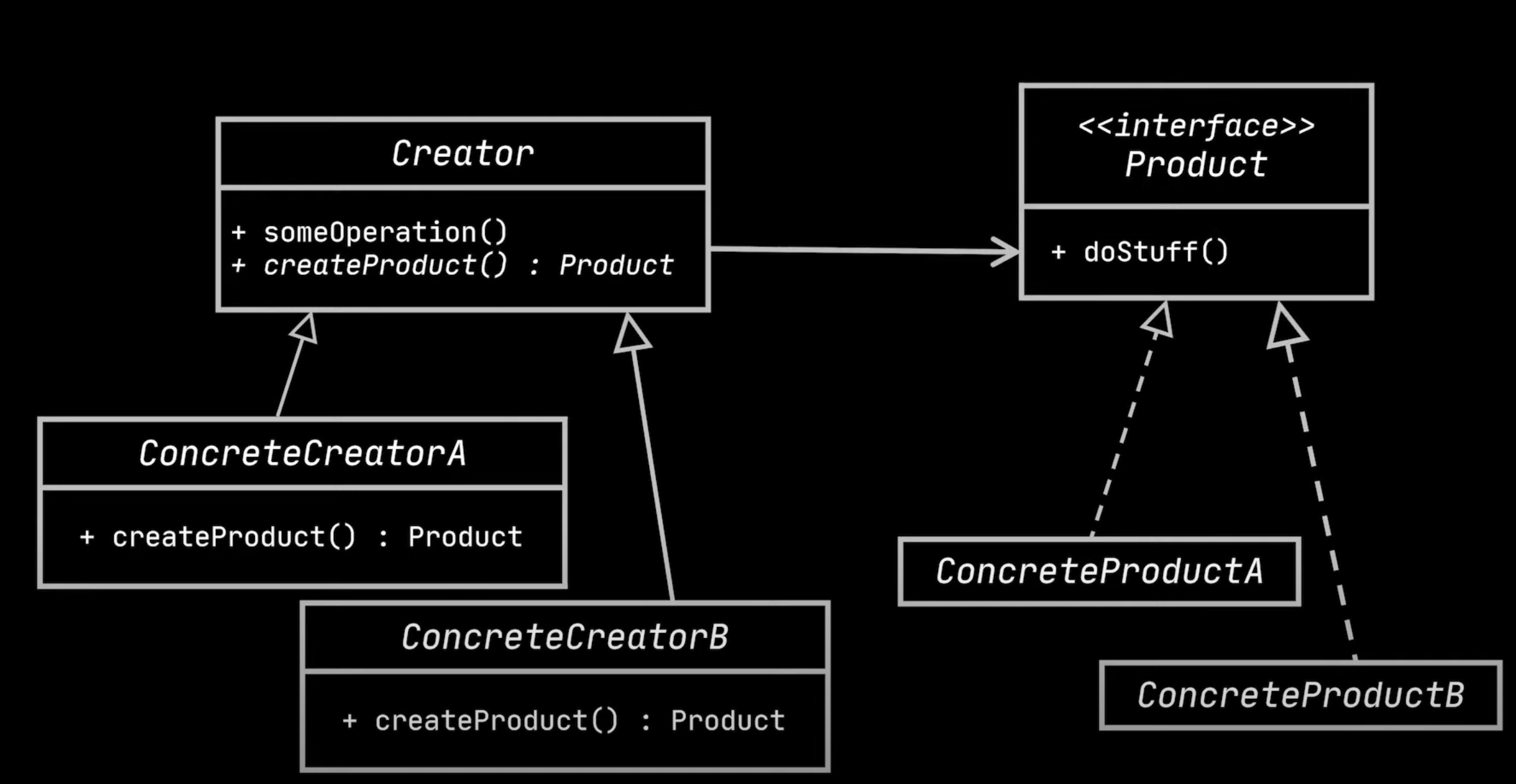
There is another version of the Factory pattern where we create a factory for each concrete product.
EntityFactory
KingFactory
QueenFactory
Character
King
Queen
- PRO: Avoids violation of Open-Closed principle
- CON: For many products, have to create many factories/files
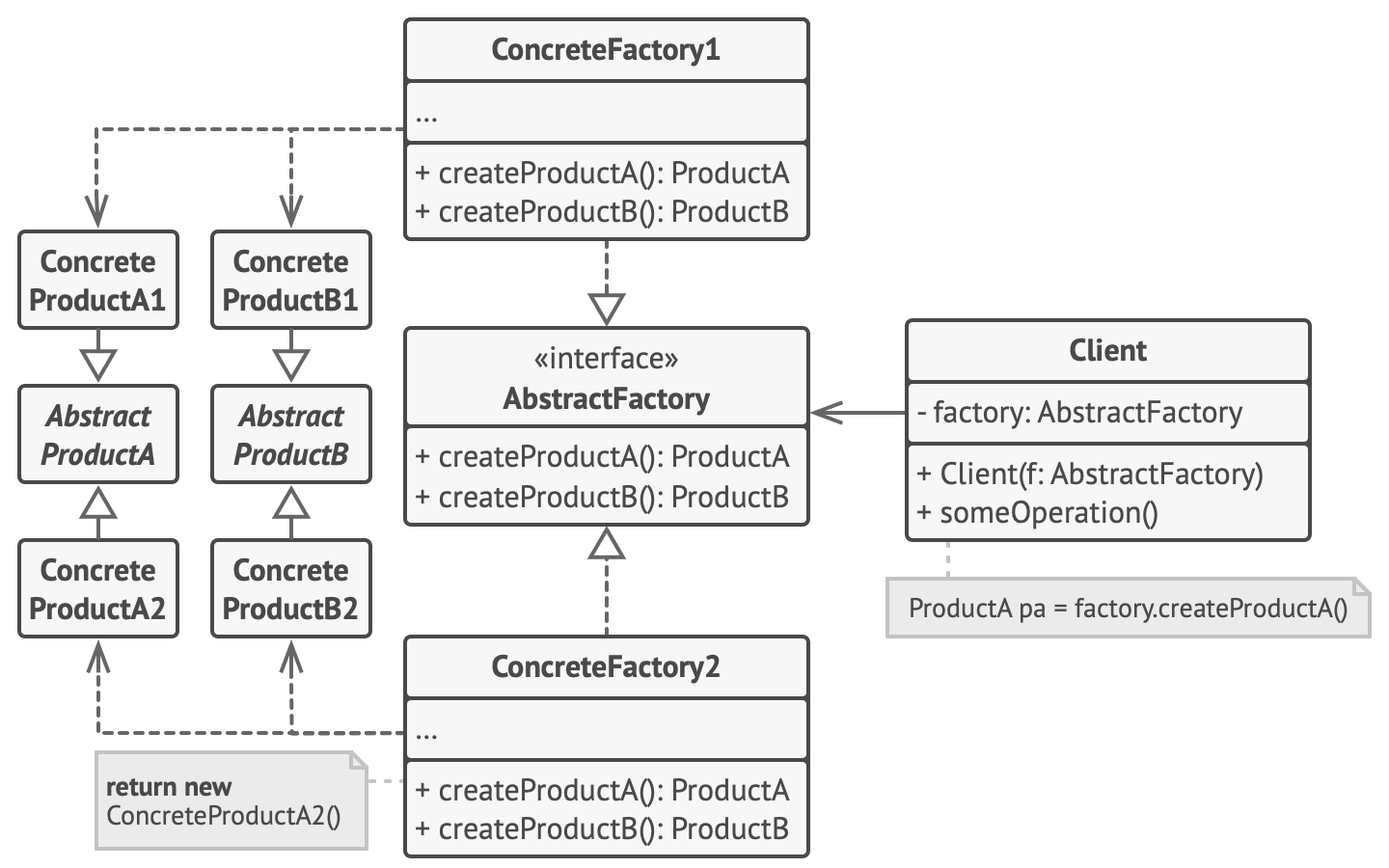
Abstract Factory Pattern
Abstract Factory Pattern
When to use it?
- When code needs to work with variants of each family of products
- Many designs start by using the Factory Pattern and evolve towards Abstract Factory
What is it?
Creational design pattern that lets you produce families of related objected without specifying concrete classes.
Abstract Factory Pattern
Say we decide to further extend our game, so that we have several variants.
For example, products King + Queen + Knight + Dragon are available in different variants:
KingdomA, KingdomB
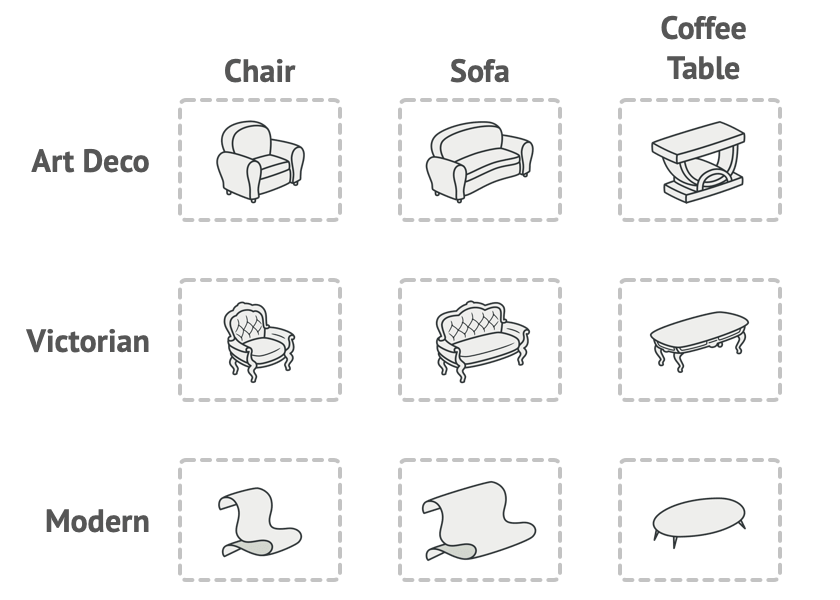
Abstract Factory Pattern
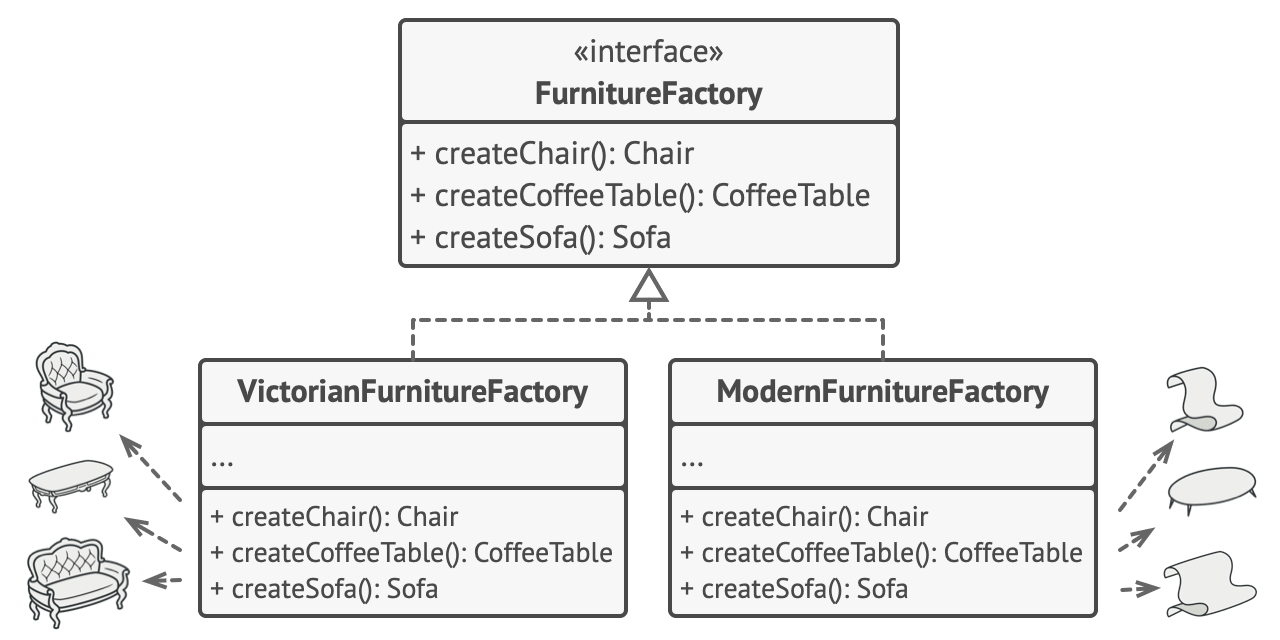
The abstract factory is the interface with all the creation methods in the product family.
For each family variant, we create a separate factory class
Abstract Factory Pattern
KingdomACharacterFactory
KingdomBCharacterFactory
CharacterFactory
KingdomAKing
KingdomBKing
King