COMP2511 Tute01
Introduction
- My name is Rebecca
- I have been tutoring COMP2511 since 23T3
- Graduated last T2 last year! Completed degree in Computer Science and Maths
- Full time software engineer
-
Fun fact(s):
- Here is a photo of my cat named Tuna
- I like going on hikes, most recently went to the Blue Mountains



Introduction
Hi, my name is ...
I study ...
Choose one
- What I did over the holidays / weekend
- Hobbies / what you like doing in your spare time
- Other courses I am taking this term
- Anything random :D
Course Overview
-
Tutorial (1 hour)
- Consolidate recent lecture topics
- Good to attend for the labs
-
Lab (2 hours)
- Lab exercises, marking & general help
- All marking for labs are completed manually by tutor and lab assistant (no automarking)
- Must be pushed on Gitlab before due date
- 8 labs, each worth 10 marks. Total lab marks are capped at 70, leaving one lab as buffer
- lab09 is an attendance and participation task
Tutorial + Lab
Lab Marking
- Labs MUST be marked within two weeks after the due date.
- i.e. lab01 must be marked in week 2 and 3 only
- Labs are marked off the marking branch mainly
Assignments
- Due Friday of Week 5
- Individual
- Can be quite a bit of a learning curve, learning both Java and good design principles
- Due Friday of Week 10
- Individual!
Assignment 1
Assignment 2
35% of the course
Both assignments involve are quite large.
It is crucial that you start these early, at least a week before to comfortably finish the assignment on time.
Course Overview
- Final exam
- Exam hurdle of 40%
- Tutorial/lab content make up at least 50% of exam
- In person in CSE labs
Final Exam
My Advice
-
Make sure to keep up with lecture / lab content
- A lot of content is taught in this course
- Most students learn the most completing the labs
- Plan out your term, COMP2511 can take up a lot of time!
- Please start assignments/projects early! (Looking at assignment 1)
- Ask lots of questions
- Prepare to learn how to read documentation & google on your own
- Make a cheatsheet for the different design patterns, code smells and software architecture
Cheers to a great term ahead!


Part B
Solving Design Problems
UNSW students say walking across campus is slow and too energy-intensive (especially up those stairs 😮💨).
UNSW has decided that they want to create their own light rail, which takes students from upper campus to lower campus.
Design a solution for this - how will it work? What will need to be changed about the campus layout for it to work?

Object-Oriented Programming
- OOP is a programming paradigm.
- It organises code into objects, these objects combine data + behaviour
- So far, most of you would have only encountered procedural programming (like C) where code is organised into procedures/functions
#include <stdio.h>
struct Car {
char brand[20];
int speed;
};
void drive(struct Car c) {
printf("%s is driving %d km/h\n", c.brand, c.speed);
}
int main() {
struct Car myCar = {"Toyota", 100};
drive(myCar); // function acts on struct
return 0;
}class Car {
String brand;
int speed;
void drive() {
System.out.println(
brand + " is driving at " + speed + " km/h"
);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car();
myCar.brand = "Toyota";
myCar.speed = 100;
myCar.drive(); // method belongs to the object
}
}Part C
Hello World
Part D
Java Programming

Java Programming
- Think of classes as like a blueprint or recipe for creating objects
- If you imagine building a car, the blueprint is the class, the physical car that you build is the object/instance
- Classes are like modules that contains data (fields) and behaviour (methods) for everything related to an object
Classes
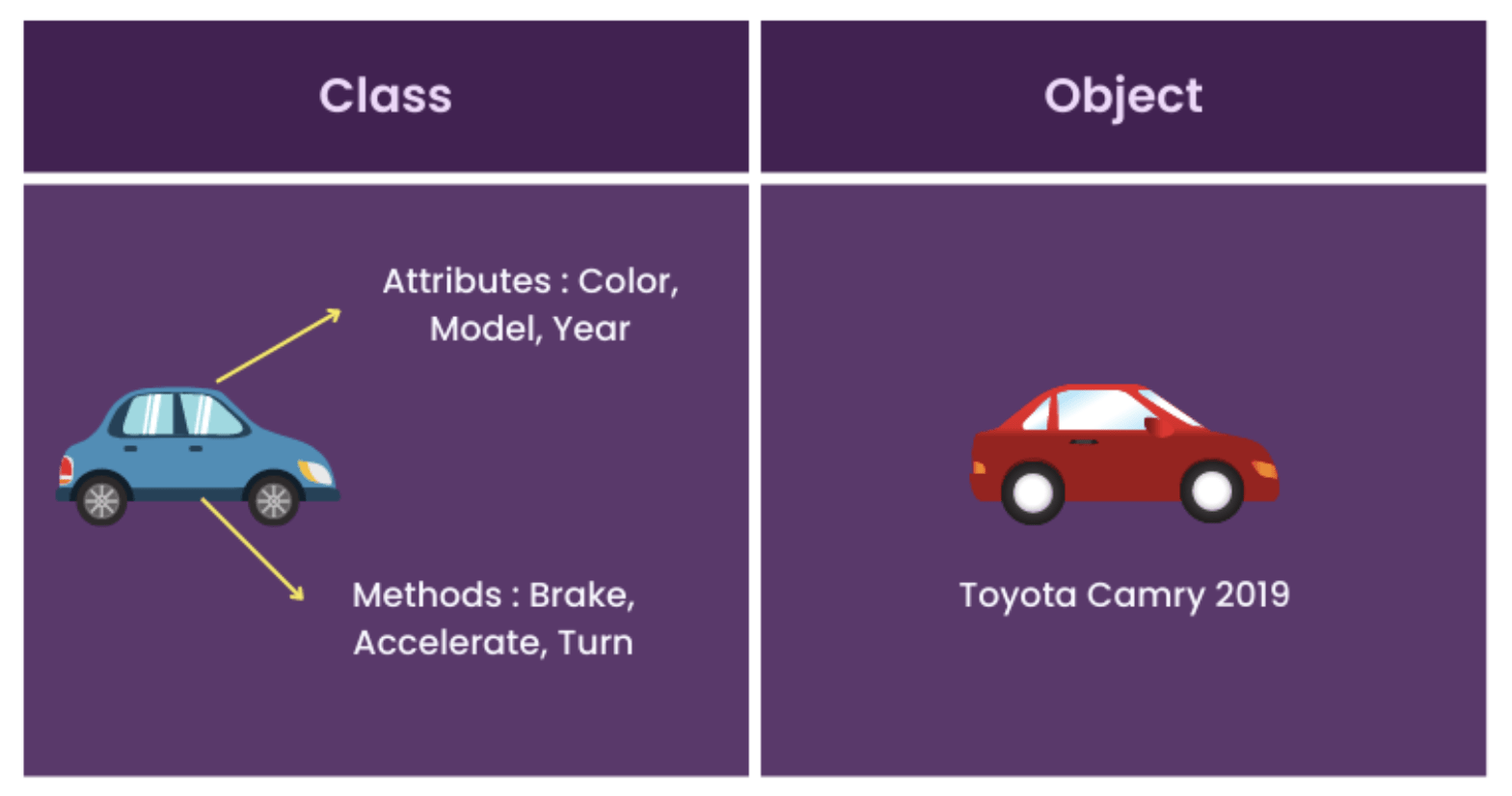
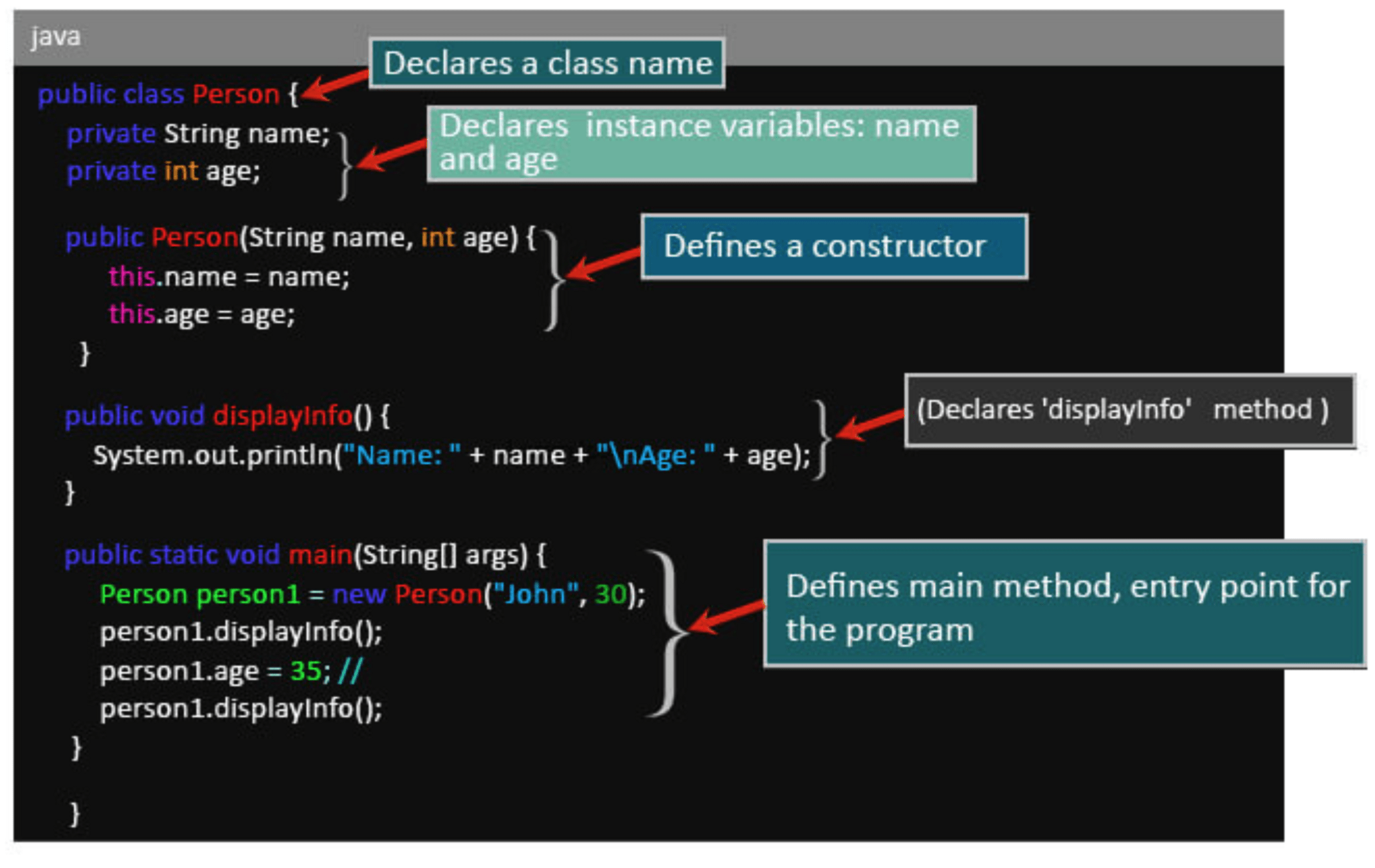
Structure of a Java Class
Classes
Part E
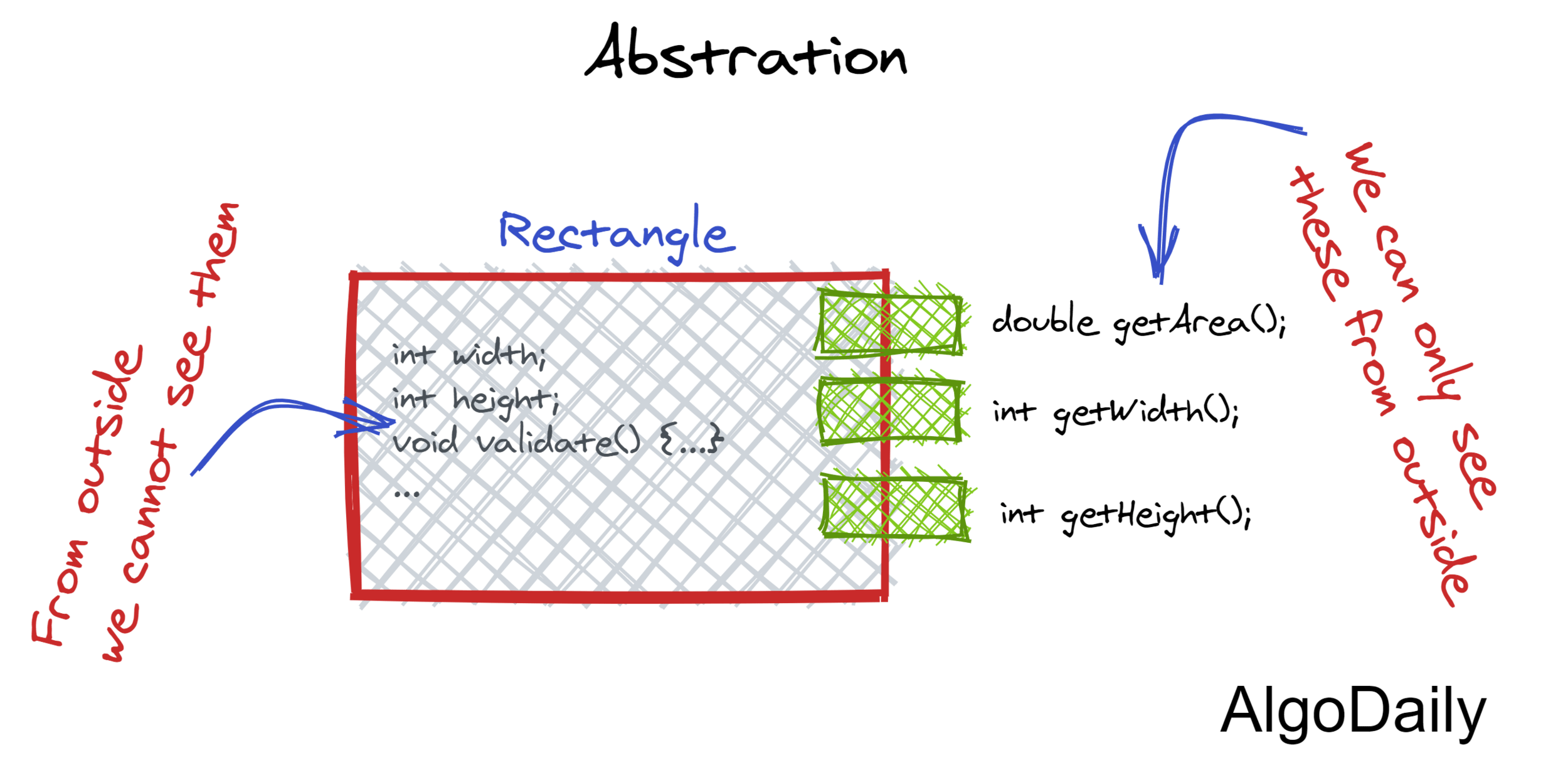
Abstraction
What is abstraction?
How is abstraction used in Java or other object oriented languages?
Abstraction
What examples of abstraction have we seen in previous courses?
Abstraction
What examples of abstraction have we seen in previous courses?
2521
#include “list.h”
int main(void) {
List l = newList();
l.insert(20);
l.insert(10);
l.pop();
}Typedef list* List;
List newList();
// insert an element at the end of the list
void insert(List list, int element);
// get the last element of the list
int pop(List list);typedef _list {
int element;
List next;
} list
List newList () {
List l = malloc(sizeof(list));
return l;
}
....listClient.c
list.h
list.c
Abstraction
What examples of abstraction have we seen in previous courses?
1531
/auth/register
/auth/login
/channels/create
/admin/auth/remove
/message/sendfunction authRegister (
email: String, name: String) {
return true;
}
....function channelCreate
(uid: number) {
const c: Channel = {
owner: uid;
}
}
....Routes (server.ts)
auth.ts
channel.ts
Frontend
OOP encapsulates data (attributes) and behaviour (methods) into classes, hiding the internal state.
All interaction with this data and behaviour is hidden from the outer world through access modifiers with access only permitted to certain functions/properties (e.g. getters/setters)