Adventures in Software Craftsmanship
Day 1 - Afternoon
- Design Patterns
- Core Principles
- Test-Driven Development
Software Design Patterns
-
Helps developers reuse successful designs by basing new designs on prior experience.
-
Improves understandability for developers familiar with the pattern.
-
Identifies participating classes and instances, their roles and collaborators, and the distribution of responsibilities. This helps ensure adherence to Design Principles.
A design pattern is a general reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within software design. It is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations.
Software Design Patterns
Creational
- Factory
- Builder
- Singleton
Structural
- Adapter
- Decorator
- Facade
Behavioral
- Iterator
- Command
- Observer
Creation of objects for you rather than instantiating objects directly
Composition of classes and objects to obtain new functionality
Communication and interaction between objects
Software Design ANTI-Patterns
Common processes or solutions that, although might seem effective, have been found to be ineffective.
- Lasagna code: consisting of too many layers
- God object: granting and object too much control
- Sequential coupling: requiring methods to be called in order
- Gold plating: working on a project past the point of adding value
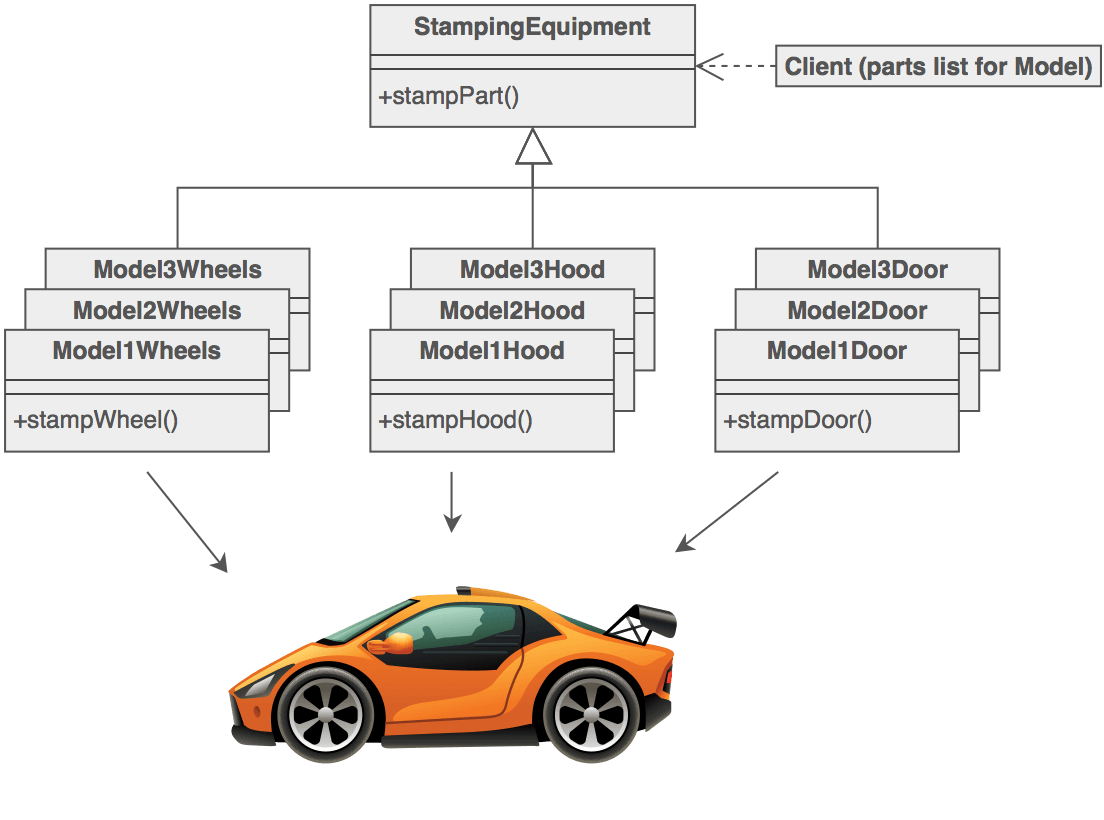
Factory Pattern
Encapsulates object creation logic by delegating to implementations of a common Factory interface without specifying the exact class of object to create.
Use when
- creation of a concrete object is complex
- the type of a concrete object is one of any sub-classes and determined by application state
- framework classes are expected to be overridden
sourcemaking.com
interface Account {
String getAccountNumber();
}
interface AccountFactory {
Account createAccount();
}
class BankAccountFactory implements AccountFactory {
Account createAccount() {
Account account = new BankAccount("01234567890");
account.setInterestRate(0.01);
return account;
}
}
class CreditCardAccountFactory implements AccountFactory {
Account createAccount() {
Account account = new CreditCardAccount("0000123456789999");
account.setCreditLimit(5000);
return account;
}
}
...
switch (accountType) {
case BANK:
return new BankAccountFactory();
case CREDIT:
return new CreditCardAccountFactory();
}
...Builder Pattern
Solves the "telescoping constructor" problem by encapsulating individual construction steps that can be invoked individually.
Use when
- class has too many or too complex constructors
- creation logic is highly conditional
- the algorithm for creating a complex object should be independent of the parts of object and how they're assembled

sourcemaking.com
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/login.jsp").permitAll()
.anyRequest().hasRole("USER")
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedPage("/login.jsp?authorization_error=true")
.and()
.csrf()
.requireCsrfProtectionMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/oauth/authorize"))
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login.jsp")
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.failureUrl("/login.jsp?authentication_error=true")
.loginPage("/login.jsp");
JobDetail job = newJob(HelloJob.class)
.withIdentity("myJob", "group1") // name "myJob", group "group1"
.build();
Trigger trigger = newTrigger()
.withIdentity("myTrigger", "group1")
.startNow()
.withSchedule(simpleSchedule()
.withIntervalInSeconds(40)
.repeatForever())
.build();
// Tell quartz to schedule the job using our trigger
sched.scheduleJob(job, trigger);Singleton Pattern
Restricts the number of instantiations of a class to one single instance.
Use when
- a single global point of access is required
- an object needs to maintain a shared state
Better than static methods
- Supports OO principles such as Polymorphism and Inheritance
- Compatible with DI frameworks
- Can be instantiated lazily and can be thread safe
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance = null;
private Singleton() { }
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
@Configuration
public class TdpAppSpringConfig {
@Inject
org.apache.commons.configuration.Configuration epfApplicationConfigUtil;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
String postgresUrl = epfApplicationConfigUtil.getString("postgresql.jdbcurl");
String postgresUsername = epfApplicationConfigUtil.getString("postgresql.username");
String postgresPassword = epfApplicationConfigUtil.getString("postgresql.password");
BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl(postgresUrl);
dataSource.setUsername(postgresUsername);
dataSource.setPassword(postgresPassword);
return dataSource;
}
}
@Repository
public class QuestionsDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@InjectLogger
private Logger logger;
@Inject
public QuestionsDao(final DataSource dataSource) {
setDataSource(dataSource);
}
...Facade Pattern
A facade object provides a simplified interface to a larger body of code to make a subsystem easier to use.
Use when
- a simpler to use interface is desired
- making a software library easier to use
- using a poorly designed API or legacy code that is difficult to understand

sourcemaking.com
public boolean createNewFile() throws IOException {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) security.checkWrite(path);
return fs.createFileExclusively(path);
}
public boolean delete() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkDelete(path);
}
return fs.delete(this);
}
public String getName() {
int index = path.lastIndexOf(separatorChar);
if (index < prefixLength) return path.substring(prefixLength);
return path.substring(index + 1);
}
}Iterator Pattern
Encapsulates and decouples the algorithm for traversing a data structure, providing a way to access the elements sequentially without exposing the structure's underlying implementation.
Use when
- a uniform traversal interface is required
- a complex data structure is traversed in multiple places
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
E next = get(i);
lastRet = i;
cursor = i + 1;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void removeNaughtyWords(final List<String> words) {
Iterator<String> wordIter = words.iterator();
while (wordIter.hasNext()) {
String next = wordIter.next();
if (NAUGHTY_LIST.contains(next)) {
wordIter.remove();
}
}
}Command Pattern
Uses a command object to represent the information needed to call a method at a later time. Command information includes the method's name, object that owns the method, and values for the method's parameters.
Use when
- a sequence of various method calls needs to occur at a later time
- a collection of different method calls needs to be handled by a shared invoker
- a history of actions is needed

sourcemaking.com
interface TransactionExecutor {
void addTransactionCommand(TransactionCommand transaction);
}
interface TransactionCommand {
void execute();
}
class DepositCommand implements TransactionCommand {
Account account;
double amount;
void execute() {
account.addFunds(amount);
}
}
class WithrawalCommand implements TransactionCommand {
Account account;
double amount;
void execute() {
account.removeFunds(amount);
}
}Observer Pattern
An object (the subject) maintains a list of its dependents and notifies them of any state changes.
Use when
- changes to one object requires notifying numerous dependent objects
- and object should be able to notify other objects without making assumptions about who those objects are
- process is event-driven

sourcemaking.com
Test-Driven Development
- Write a failing unit test
- Write the minimum amount of code to make the test pass
- Refactor the new code to acceptable standards while keeping the test passing
Requirements must be completely understood through use cases and user stories.
- "Keep it simple, stupid"
- "You aren't gonna need it"
- "Fake it till you make it"
TDD Benefits
- TDD means writing more tests and programmers who write more tests are more productive.
- Beyond standard unit testing, TDD also drives the design of the application, allowing developers to consider how the API will be used by clients and writing for the interface instead of the implementation (DIP).
- Resulting code tends to be more modular because developers think in terms of smaller, testable units of code as they only write code to pass a testable unit. Using mock objects also helps contribute to modularity because it requires swapping out modules.
Unit Testing Conventions
Test structure
- Setup
- Execution
- Validation
- Clean up
- Treat your test code with the same respect as your production code
- Separate common set up and clean up logic
- Work with your team to review your tests and test practices
Avoid
- unnecessary or useless tests
- depending on external environments
- depending on system state manipulated by previously executed test cases
- dependencies between test cases
- testing execution timing or performance
@Before
public void setUp() {
bill = new Bill(2, new Server("gtb012", "Reid"));
calculator = new BillCalculator(.05);
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
bill = null;
calculator = null;
}
@Test
public void testCalculateTax() {
bill.addItem(new Item("milk", 1.23));
bill.addItem(new Item("cereal", 2.13));
double tax = calculator.calculateTax(bill);
assertEquals(0.17, tax);
}Unit Test Mocking
Mock objects can simulate the behavior of complex, real objects when the real object is impractical or impossible to incorporate in a unit test.
Creating a mock object will stub the method implementations.
Usage of a mock object by the unit under test (UUT) allows control and verification of the invocation of the mock by the UUT.
@Test
public void testReadConfigurationFromPropertiesFile_OneHttpStream() {
when(appConfig.getProperty(StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_STREAM_COUNT)).thenReturn(1);
when(appConfig.getString(StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_STREAM_PREFIX + 1 + "." + StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_TYPE)).thenReturn("http");
when(appConfig.getString(StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_STREAM_PREFIX + 1 + "." + StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_NAME)).thenReturn("http1");
Iterator mockIter = mock(Iterator.class);
when(appConfig.getKeys(StreamEmitterFactory.PROPS_KEY_STREAM_PREFIX + 1)).thenReturn(mockIter);
//Iterate 4 times for 4 different property keys for http configuration
when(mockIter.hasNext()).thenReturn(true, true, true, true, false);
when(mockIter.next()).thenReturn("upf.dfs.stream1.type",
"upf.dfs.stream1.name",
"upf.dfs.stream1.host",
"upf.dfs.stream1.port");
when(appConfig.getString("upf.dfs.stream1.type")).thenReturn("http");
when(appConfig.getString("upf.dfs.stream1.name")).thenReturn("http1");
when(appConfig.getString("upf.dfs.stream1.host")).thenReturn("localhost");
when(appConfig.getString("upf.dfs.stream1.port")).thenReturn("9000");
streamFactory.readConfigurationFromPropertiesFile();
verify(mockIter, times(5)).hasNext();
verify(mockIter, times(4)).next();
verify(appConfig, times(6)).getString(anyString());
StreamEmitter emitter = streamFactory.getEmitter("http1");
assertNotNull(emitter);
StreamMessageEntryPoint entryPoint = emitter.getStreamMessageEntryPoint();
assertNotNull(entryPoint);
}Pair Programming
Driver
- Less experienced
- Focused on tactical decisions ("What code do I need to write right now to solve the problem?")
Navigator
- More experienced
- Focused on strategic decisions ("Is the driver writing effective code?" Where are we heading next?")
Exercise Requirements
Restaurant order and transaction system.
- Add orders to bills
- Finalize bill and add tax
- Table management
- Support for gratuity
- Coupons and comps
- Splitting bills