Microcontrollers
(for web developers)
Rex St. John

Our goal today is to understand what is going on here
Why Microcontrollers?

By 2020, there will be 50 billion computers on earth
Moore's Law: They will keep getting smaller, cheaper and faster
Many of these devices will lack user interfaces
Often communicating via low-energy wireless protocols
They will rely on sensors to understand their environment
Heat, temperature, sound, light, smoke, steam, LiDAR...
And form "the edge" of large internet connected systems...
These computers will often take the form of Microcontrollers
Small computers specializing in real-time operations
Increasingly we are using web development tools and techniques to program these devices
GitHub, Containers, Node.js etc
"Hybrid" developers will be needed who are capable of understanding these systems
Are you up for the task?
Full-Stack Developer, n: Person who is comfortable programming both front and back-end systems
Full-Stack Developer, n: Person who is paid once to do the work of four people
(actual definition)
(technical definition)
Now that we can run Linux on our IoT devices, full-stack developer takes on a whole new meaning!
Example Projects
What can we do with microcontrollers?
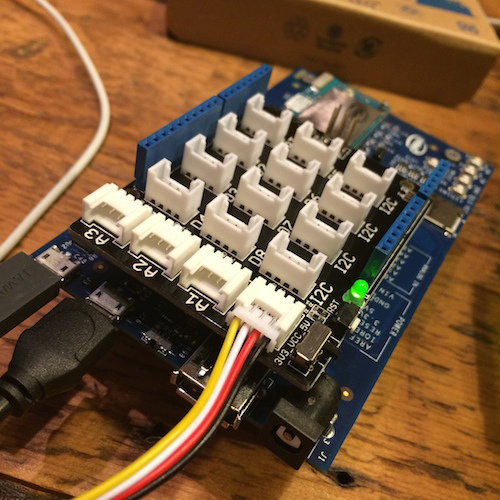

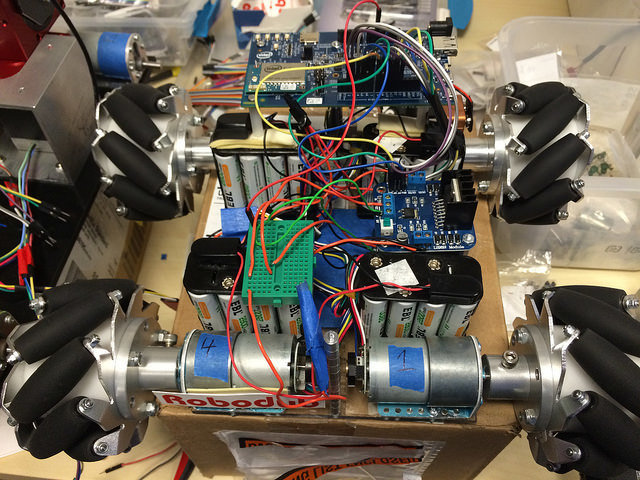
RamBot
Gamification of drones and robots
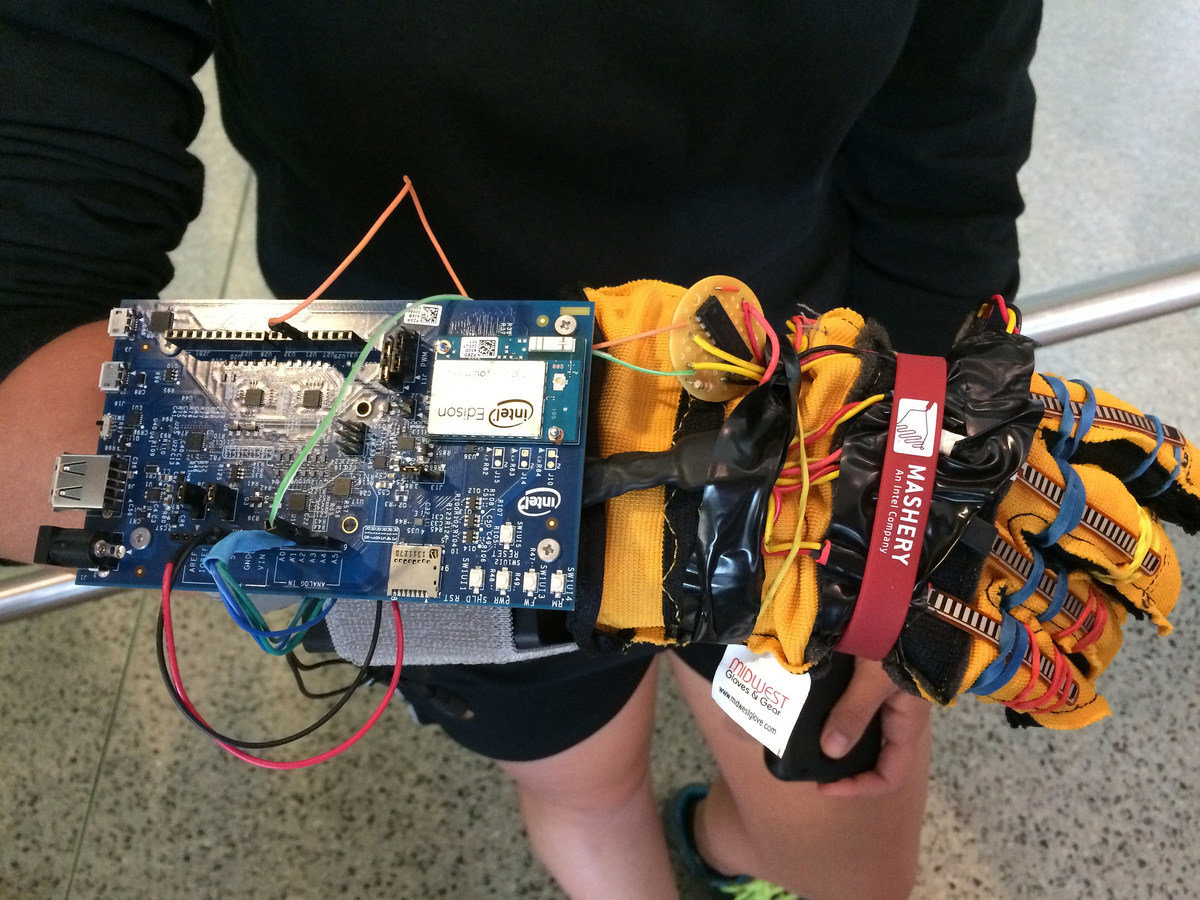
Sign++
Sign language translation glove
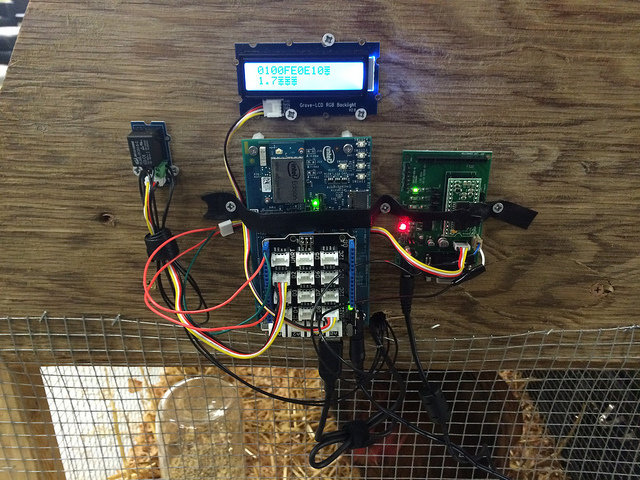
Smart Chicken Coop
Smart chicken tender
TinyCheese
Makes tiny cheese
A Microcontroller (MCU) is a small computer with a processor, memory, and programmable input/output peripherals.

They specialize in real-time behavior
They are used everywhere (automotive, industrial etc)
They are contained on an integrated circuit
Microprocessor
Microcontroller
- Microprocessor
- Plus other stuff*
- On integrated circuits (IC)
- Often on a PCB*
- Programmable device
- Accepts digital IO
- Processes data
- Provides results as output
*Other stuff may vary
*Printed Circuit Board
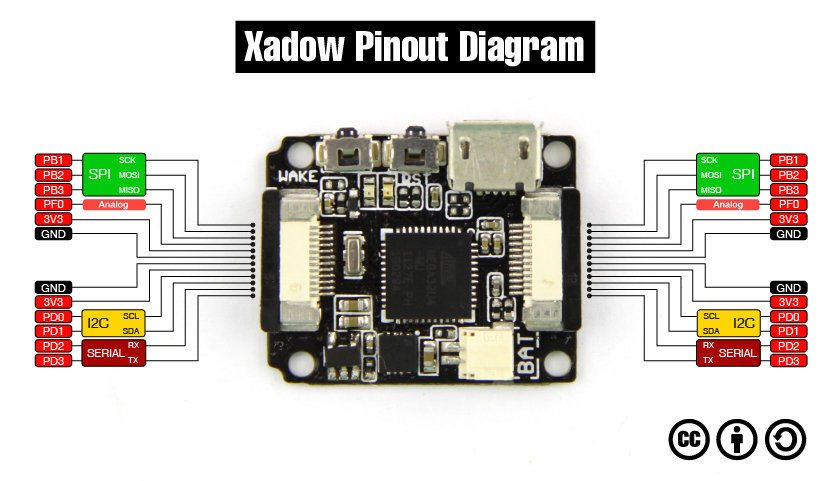
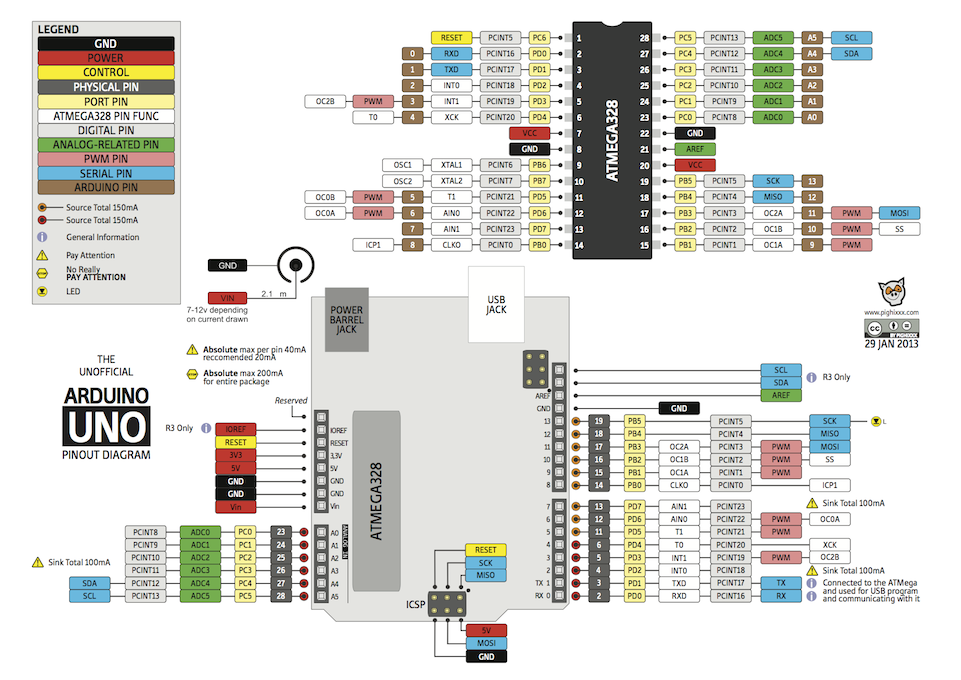
PCB with microcontroller pinout
Example Uses
- Home appliances
- Industrial
- Automotive
- Drones
- Everything, really
Anywhere you need cheap, highly reliable, event-driven computers
Sensors attached to PCB boards are the "user interface" for microcontrollers, lets learn how that works
Web Development For Things
Firmata is a protocol for communicating with microcontrollers from software on a computer (based on MIDI).
LibMRAA is a C/C++ library with bindings to javascript & python to interface with the IO on Galileo, Edison etc.

We can now talk to our microcontrollers without writing assembly language!
Johnny-Five
Digital and Analog Sensors

Communication for basic data
Digital I/O
- GPIO: General purpose input / output
- High or Low depending on voltage level (1 or 0)
- Frequently come in "ports" of 8 (a byte)
- Can alternate as analog pins (but not both!)
- Good for LEDs, buttons, buzzers, relays
Example: LED with MRAA
var m = require('mraa'); //require mar
//write the mraa version to the console
console.log('MRAA Version: ' + m.getVersion());
//LED hooked up to digital pin 13 (or built in pin on Galileo Gen1 & Gen2)
var myLed = new m.Gpio(13);
myLed.dir(m.DIR_OUT); //set the gpio direction to output
var ledState = true; //Boolean to hold the state of Led
periodicActivity(); //call the periodicActivity function
function periodicActivity()
{
//if ledState is true then write a '1' (high) otherwise write a '0' (low)
myLed.write(ledState?1:0);
ledState = !ledState; //invert the ledState
//call the indicated function after 1 second (1000 milliseconds)
setTimeout(periodicActivity,1000);
}Analog I/O
- GPIO pins for digital can often be used for analog
- Good for sensing light, temperature, sound etc
- We must translate digital signals to analog signals (PWM)
Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off.
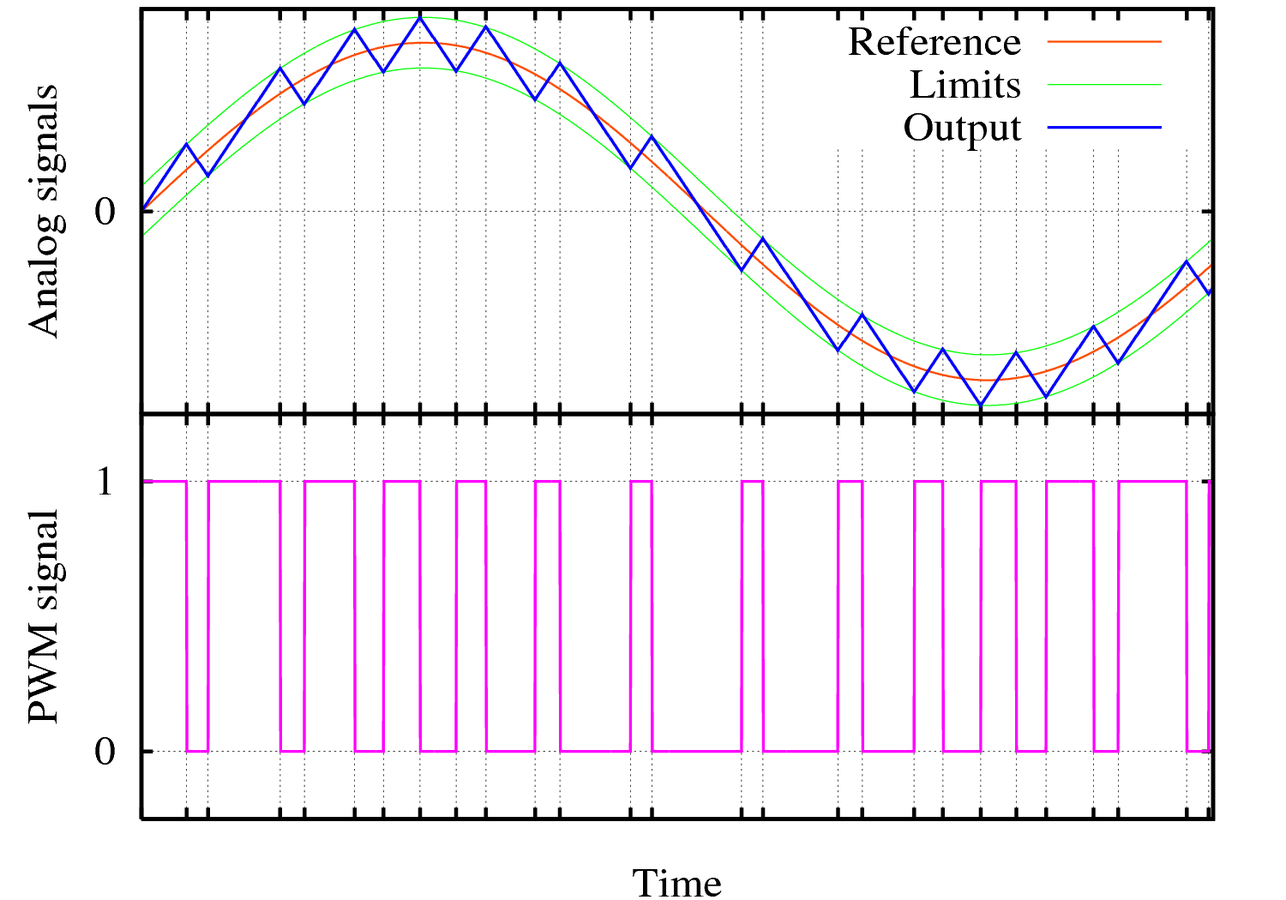
Let us turn a jaggy thing into a squiggly thing
Example: 3-Axis Accelerometer
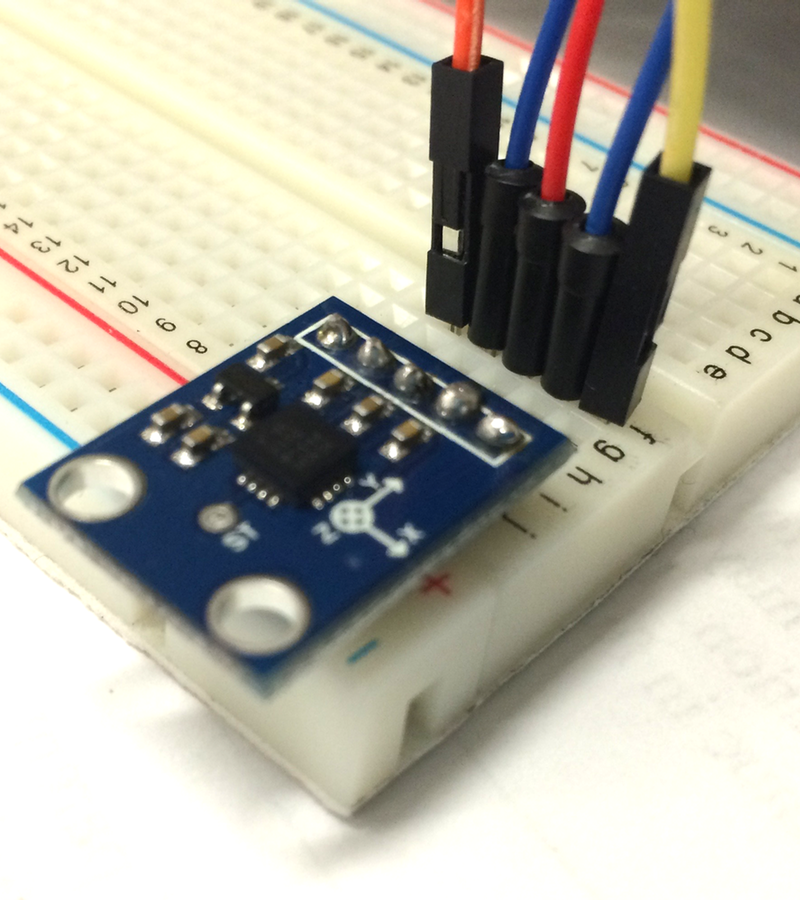
Has a ground wire, power wire and 3-analog wires
// "ADXL335"
var five = require("johnny-five");
var Edison = require("edison-io");
var board = new five.Board({
io: new Edison()
});
board.on("ready", function() {
var accelerometer = new five.Accelerometer({
controller: "ADXL335",
pins: ["A0", "A1", "A2"]
});
accelerometer.on("change", function() {
console.log(" x : ", this.x);
console.log(" y : ", this.y);
console.log(" z : ", this.z);
});
});Johnny-Five Syntax
Serial Communications
Communication for fancy data
"Serial" aka "Time Division Multiplexed"
Data is sent one chunk at a time based on a clock signal
Errors and noise occur when sending data via wire requiring safeguards.
Common Serial Communications
Example: I2C LCD

// How to write to the Seeed LCD Screen
// NOTE: You *MUST* plug the LCD into an I2C slot or this will not work!
var Cylon = require('cylon');
function writeToScreen(screen, message) {
screen.setCursor(0,0);
screen.write(message);
}
Cylon
.robot({ name: 'LCD'})
.connection('edison', { adaptor: 'intel-iot' })
.device('screen', { driver: 'upm-jhd1313m1', connection: 'edison' })
.on('ready', function(my) {
writeToScreen(my.screen, "Ready!");
}).start();Cylon Syntax

A master sends a clock signal, and upon each clock pulse it shifts one bit out to the slave, and one bit in, coming from the slave. Signal names are therefore SCK for clock, MOSI for Master Out Slave In, and MISO for Master In Slave Out.
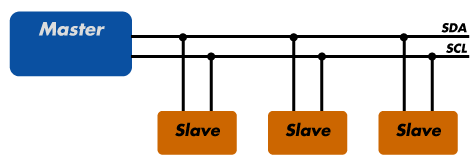
SCL and SDA. SCL is the clock line. It is used to synchronize all data transfers over the I2C bus. SDA is the data line. The SCL & SDA lines are connected to all devices on the I2C bus.
Common Synchronous Protocols
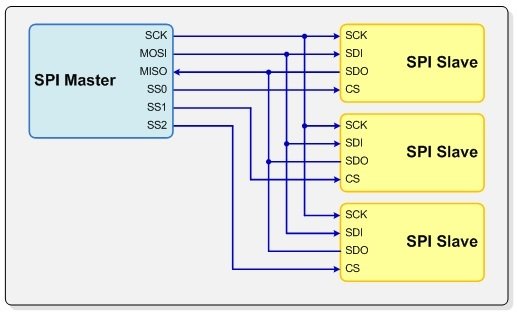
- Faster, 1-20MHz
- Requires 3+ physical lines
- Less worry about "noise"
- All lines are unidirectional
- Chip-select lines required
- Slower, 100 - 400MHz
- 2 lines only, easier to wire
- Noise an issue
- All lines are bi-directional
- For chaining devices
Common Synchronous Protocols Compared
Many microcontrollers support both protocols.
UART (or SCI) uses two wires (TX / RX) to transmit data asynchronously at an agreed-upon baud rate
Uses start and stop bits for primitive error correction
Buad Rate: Transmission speed (9600, 115200 etc)
Long history, common on PCs before USB
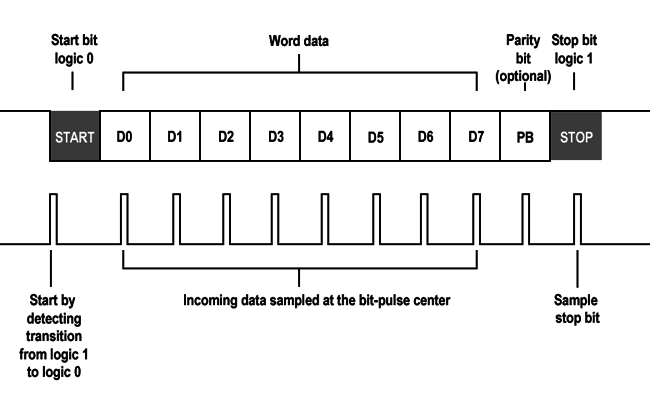
UART Notes
- UART is a hardware module, not a protocol
- Can run in a synchronous mode called USART
- Slow: 9 - 56 kHz (vs. 1 - 20 MHz for SPI)
- Used for sending ASCII characters
- Also: Keyboard, LCD monitor data

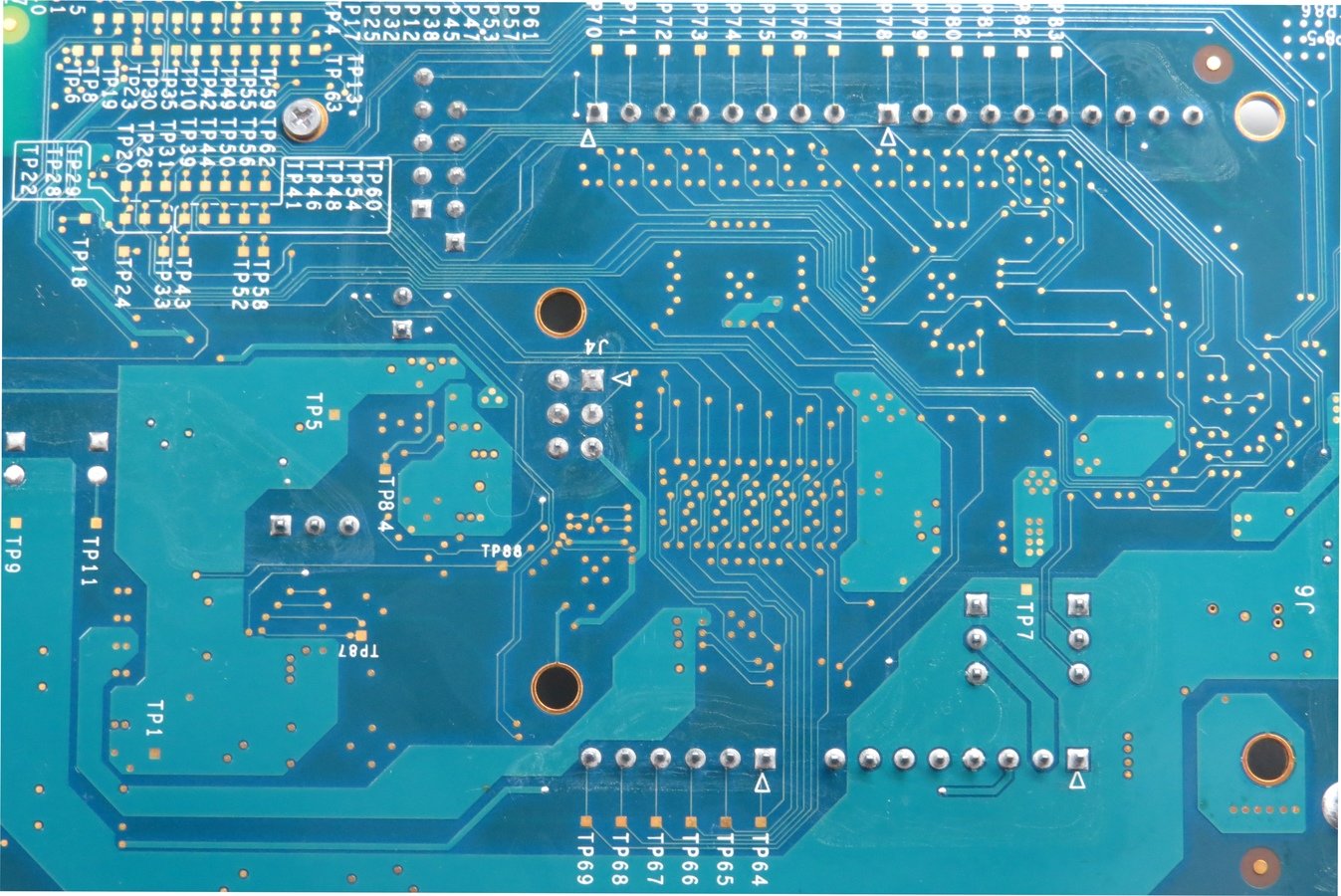
Test Time: Xadow Main Board with ATmega32U4
Lets find: SPI, UART, I2C, Analog I/O

Test Time: Find GPIO, Analog, PWM, UART, SPI
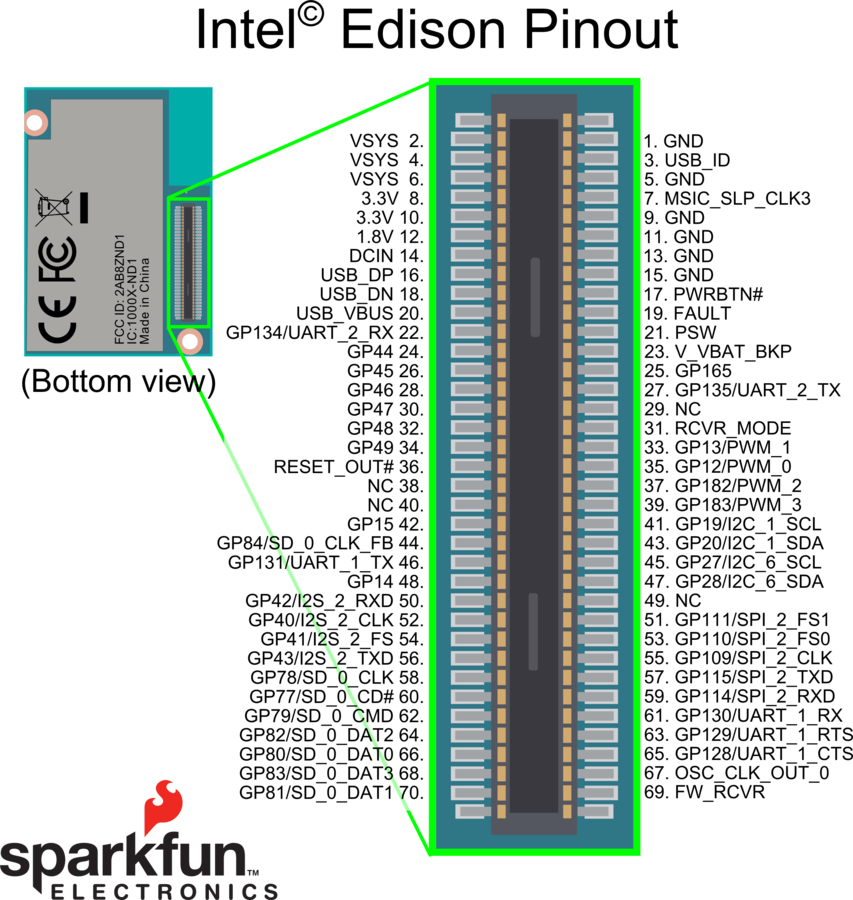
Test Time: Find SPI, UART, I2C, USB, PWM, GPIO, Clock lines
Further Reading