Ingeniería de Requerimientos #2
CAPÍTULO 1

Ricardo Antonio Bermúdez Osorio
DOCENTE

Ingeniero de sistemas y computación
Universidad Tecnológica de Pereira, 2008
Especialista en ingeniería del software
Universidad Autónoma de Manizales, 2012
tusk@utp.edu.co
Acronyms
- KA: Knowledge Area
- CIA: Confidenciality, Integrity and Availabilty
- DAG: Directed Acyclic Graph
- FSM: Functional Size Measurement
- INCOSE: International Council on Systems Engineering
- UML: Unified Modeling Language
- SysUML: Systems Modeling Language
- PMI: Project Management Institute
High Level Requirements
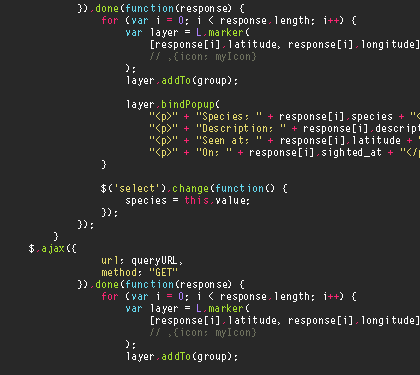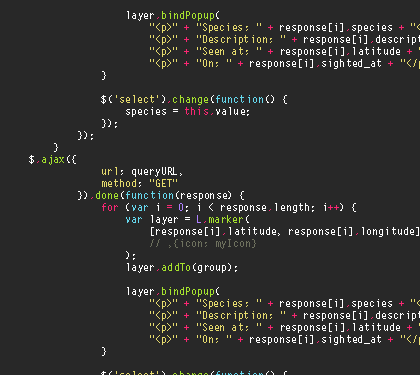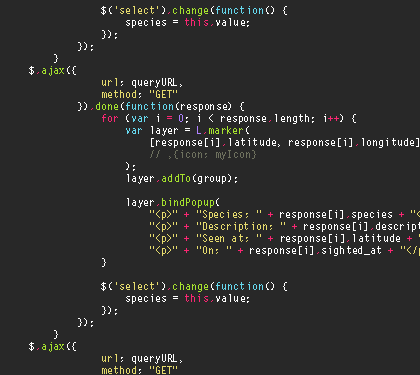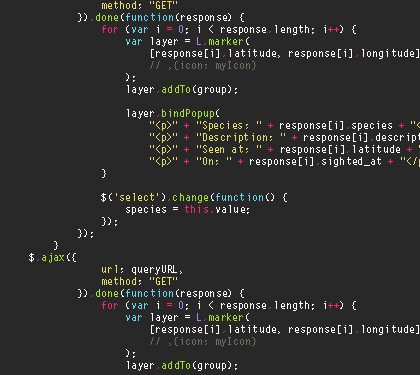
The initial requirements inventory identifies the high level requirements (HLRs) associated with each type of requirement within the project. The HLR level is the most generalized breakdown of requirements of the system. This level corresponds to major system functions or business processes. Source
Total
System
Accounting
Payments
Clients
Low Level Requirements
May be calculations, technical details, data manipulation and processing and other specific functionality that define what a system is supposed to accomplish in order to meet the high-level software requirements from which it is derived through software design analysis
Elicitation
- Software engineering uses this word instead of capturing or acquiring requirements to differentiate this process from just collecting information

Stakeholder
- “individuals and organizations who are actively involved in the project, or whose interests may be positively or negatively affected as a result of project execution or successful project completion” (PMI®), 1996)

Allocation
It is used when a high-level requirement relates to more detailed requirements, then we can deduce which lower-level requirements are necessary to meet the higher-level ones.

Fundamentals
- Definition of Software Requirement
- Product and Process Requirements
- Functional And Nonfunctional requirements
- Emergent Properties
- Quantifiable Requirements
- System Requirements and Software Requirements
Software requirement
At its most basic, a software requirement is a property that must be exhibited by something in order to solve some problem in the real world.



Software requirement
- It may aim to automate part of a task for someone to support business process.
- Correct shortcomings of existing software
- Control a device
- ...

Product Requirement
A product requirement is a need or constraint on
the software to be developed
“The software shall verify that a student meets all prerequisites before he or she registers for a course”
Example:

Process Requirement
A process requirement is essentially a constraint
on the development of the software
“The software shall be developed using
a RUP process”
Example:
Important!
Some software requirements generate implicit process requirements. The choice of verification technique is one example. Another might be the use of particularly rigorous analysis techniques (such as formal specification methods) to reduce faults that can lead to inadequate reliability. Process
requirements may also be imposed directly by the development organization, their customer, or a third party such as a safety regulator.

Functional Requirements
Describe the functions that the software is to execute
Examples:
- Formating some text
- Modulating a signal
- Calculate some taxes
They are described as capabilities or features

Functional Requirements
A functional requirement can also be described as one for which a finite set of test steps can be written to validate its behavior.


Non Functional Requirements
Are the ones that act to constrain the solution.
Sometimes known as constraints or quality requirements.

Non Functional Requirements
They can be further classified according to whether they are:
- Performance
- Maitanibility
- Safety
- Reliability
- Security
- Interoperability
- ...
all ...ilities
Emergent Properties
Some requirements represent emergent properties of software—that is, requirements that cannot be addressed by a single component but that depend on how all the software components interoperate.
The throughput requirement for a call center would, for example, depend on how the telephone system, information system, and the operators all interacted under actual operating conditions.
Emergent Properties
Emergent properties are crucially dependent on the system architecture.
The throughput requirement for a call center would, for example, depend on how the telephone system, information system, and the operators all interacted under actual operating conditions
Example
Quantifiable Requirements
Software requirements should be stated as clearly and as unambiguously as possible, and, where appropriate, quantitatively. It is important to avoid vague and unverifiable requirements that depend for their interpretation on subjective judgment
“The software shall be reliable”
“The software shall be user-friendly”
Quantifiable Requirements
This is particularly important for nonfunctional requirements
Two examples of quantified requirements
are the following:
- A call center’s software must increase the center’s throughput by 20%
- Asystem shall have a probability of generating a fatal error during any hour of operation of less than 1 * 10
-8
System And Software Requirements
In this topic, “system” means
An interacting combination of elements to accomplish a defined objective. These include hardware, software, firmware, people, information, techniques, facilities, services, and other support elements.
As defined by the International Council on Software and Systems Engineering (INCOSE)
System requirements are the requirements for the system as a whole. In a system containing software components, software requirements are derived from system requirements.
System And Software Requirements
This KA defines “user requirements” in a restricted way, as the requirements of the system’s customers or end users. System requirements, by contrast, encompass user requirements, requirements of other stakeholders (such as regulatory authorities), and requirements without an identifiable human source.
Software Requirements

Conclusion
- The requirements are in the people's mind
- All the documents and models are representations
- All stakeholders must understand the shared model
Is not a requirement
- Design or develop details ("How")
- Except client or bussiness constraints
- Testing information
- Planning information
- Budget
- Schedules
Requirements must be
- Complete
- Suitable
- Necessary
- Non ambiguous
- Verifiable
- Can be implemented