Annotating
PLANT
genomes
Richard Smith-Unna

What we'll cover
- what annotation is
- what the important steps are
- how those steps work
- what software to use
- what to do with the data
and we'll get our hands dirty
with some real (rice) data
RESOURCES
- these slides
-
software list
- exercises
- recommended pipeline
all online at:
STRUCTURAL ANNOTATION
where are the genes?
what features do they have?
what products do they encode?
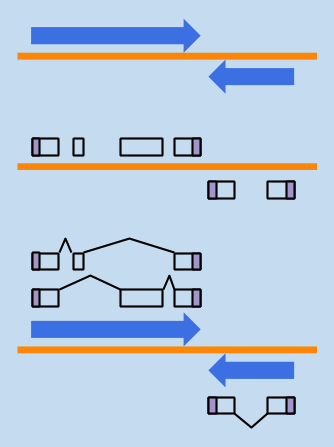
FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION
- what is the biological role of those gene products?
- what should we call them?
- how is the gene regulated?
don't expect too much
Annotation is an imperfect science.
Even the best model genomes (e.g. human)
have very incomplete annotations:
- over 90% of protein loci correctly identified
- ~50% have structure incorrectly annotated
- EGASP 2006
- ~30% lacking any functional annotation
community standards
don't reinvent the wheel

the Generic Model Organism Database project
GMOD TOOLS

THE EVIDENCE TRAIL
annotation is about building evidence to support
our conclusions about structure and function
- GFF3 file format for accumulating and sharing evidence
- CHADO database for storage and querying
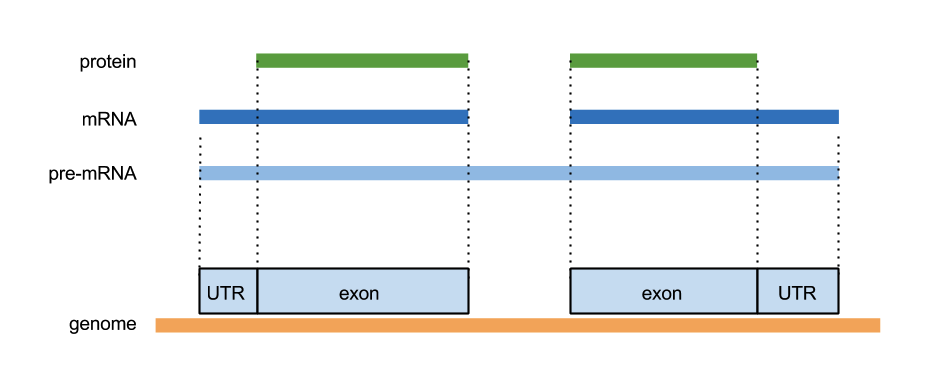
GFF3
ctg123 example gene 1050 9000 . + . ID=EDEN;Name=EDEN;Note=protein kinase ctg123 example mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=EDEN.1;Parent=EDEN;Name=EDEN.1;Index=1 ctg123 example five_prime_UTR 1050 1200 . + . Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example CDS 3000 3902 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example CDS 7000 7608 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example three_prime_UTR 7609 9000 . + . Parent=EDEN.1 ctg123 example mRNA 1050 9000 . + . ID=EDEN.2;Parent=EDEN;Name=EDEN.2;Index=1 ctg123 example five_prime_UTR 1050 1200 . + . Parent=EDEN.2 ctg123 example CDS 1201 1500 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.2 ctg123 example CDS 5000 5500 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.2 ctg123 example CDS 7000 7608 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.2 ctg123 example three_prime_UTR 7609 9000 . + . Parent=EDEN.2 ctg123 example mRNA 1300 9000 . + . ID=EDEN.3;Parent=EDEN;Name=EDEN.3;Index=1 ctg123 example five_prime_UTR 1300 1500 . + . Parent=EDEN.3 ctg123 example five_prime_UTR 3000 3300 . + . Parent=EDEN.3 ctg123 example CDS 3301 3902 . + 0 Parent=EDEN.3 ctg123 example CDS 5000 5500 . + 1 Parent=EDEN.3 ctg123 example CDS 7000 7600 . + 1 Parent=EDEN.3 ctg123 example three_prime_UTR 7601 9000 . + . Parent=EDEN.3
TYPICAL workflow
REPEATS
refers to multiple different biological phenomena
- low complexity sequences
- AAAAATTTTTTAAAAAAAAACCAAAA
- short tandem repeats
- ACACACACACACACAACACACACAC
- transposable elements
- LINEs, SINEs and viruses
REPEATS ARE IMPORTANT
GOOD
- useful in population genetics, phylogenetics and forensics
- fascinating to study in their own right
- cause genome expansions
- affect evolution of genes and regulatory elements
REPEATS ARE IMPORTANT
bad
-
sometimes look like real genes
-
cause spurious alignments
- want to prevent them affecting analysis
REPEATS ARE IMPORTANT
69% of the Gossypium arboreum genome
IDENTIFYING REPEATS
homology
do they look like known repetitive sequences?
DE-NOVO
compare a genome to itself and cluster
OR
use regular expressions
MASKING REPEATS
SOFT: ACAGTAAaaaattttaaaaACTGCATGCAAAT
HARD: ACAGTAANNNNNNNNACTGCATGCAAAT
exercise 1
GENES
shared structure allows de-novo prediction
- start and stop codons
- splice-sites
- promoter elements

low accuracy (~30%)
GENES

GENES
using data from biological experiments
gives evidence-based predictions
- align proteins from related species
- ESTs, cDNAs from same or very close spp.
- assembled transcripts
- RNAseq reads
much more accurate (~90%)
WHAT DOES THE EVIDENCE SAY?
STRUCtURAL aNNOTATION PIPELINES
-
take in multiple sources of evidence
-
balance them based on confidence
-
create a merged annotation
examples:
- MAKER (runs all the tools for you!)
- AUGUSTUS
- PASA-EVM
MAKER-P

THE EVIDENCE TRAIL
however you annotate,
you need to record the evidence
pipelines do this for you
present the evidence in a genome browser
exercise 2
FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION
homology (sequence alignment)
- use predicted protein sequences
- perform pairwise alignment against related spp.
- transfer functional info between species
THE CUTOFF PROBLEM
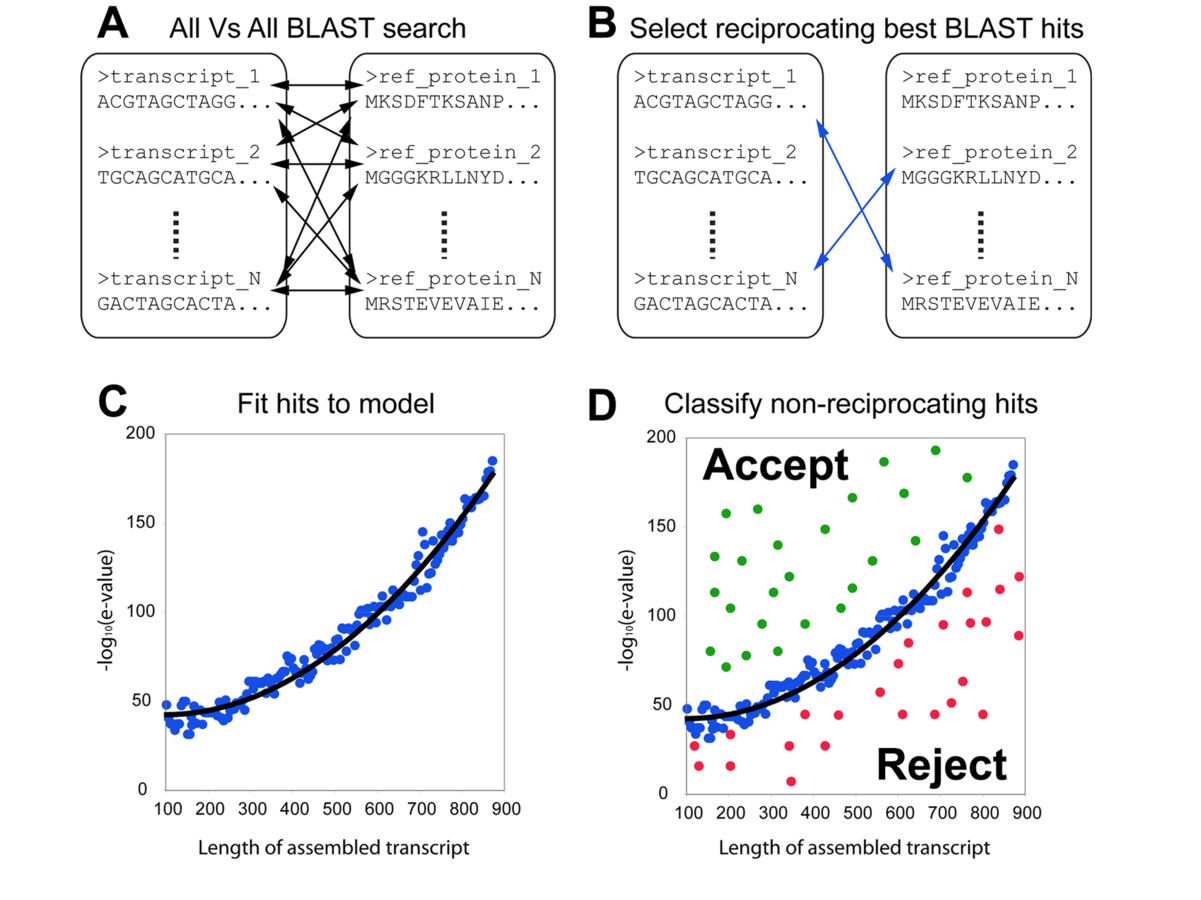
FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION
homology (sequence profiles)
-
search the sequence into a database of models
- can be whole-sequence or domain specific
 PROTEIN PROFILES
PROTEIN PROFILES
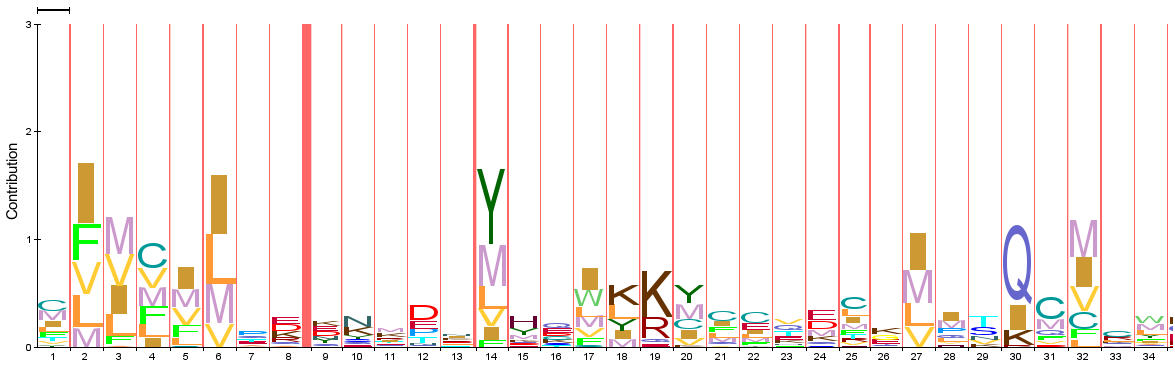
Piwi domain
FunCTIONAL ONTOLOGIES
- GO
- KEGG
- MapMan
FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION PIPELINES
-
use multiple methods
-
search multiple databases and references
-
collect the evidence
example tools:
- InterProScan
- Mercator
- Trinotate
exercise 3
STANDARD PIPELINE
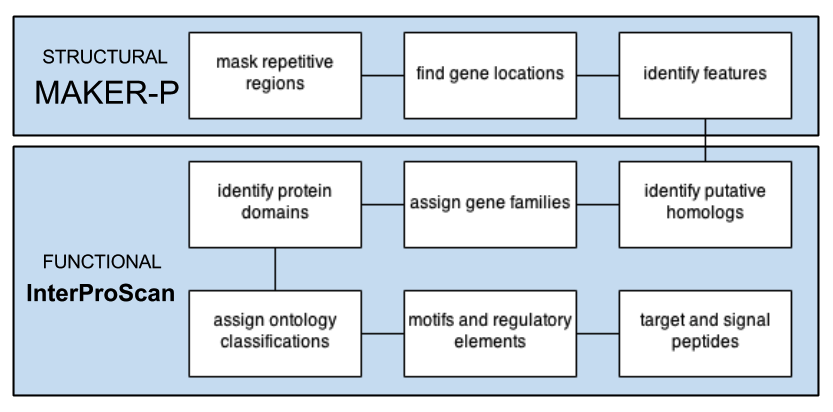
MANUaL CURATION
important to keep the evidence trail
gene family experts required for high confidence
exercise 4
MAKING THE ANNOTATION USEFUL
create a public genome database to
present all your work and allow expert curation
GMOD tools make this (fairly) easy:
- WebApollo (community annotation editor)
- Tripal (genome data browser, BLAST server)
- G/JBrowse (genome track browser)
- biomart (data mining system)
- PathwayTools (metabolic pathway server)
THANKS!
Don't forget the resources:
