Scrum, Yay or Nay
Riza Nugraha
Happy

What is Scrum?
- a process framework
- consist of powerful set of principles and practices
- short cycles
- fast feedback
- continual improvement
- adaptation to change.
Scrum Theory
-
Transparency
Process must be visible to those responsible for the outcome. -
Inspection
Frequently inspect Scrum artefacts and progress toward a Sprint Goal to detect undesirable variances. - Adaptation
Adjust as soon as possible when aspects of process deviate outside acceptable limit.
Inspect & Adaptation Tools (Scrum Events):
Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective
Scrum Important Elements
- 3 Roles
- 3 Artefacts
- 3 Ceremonies
3 Roles
Product Owner
Development Team
Scrum Master



Where's the Project Manager?
Product Owner
- Clearly expressing Product Backlog items;
- Ordering the items in the Product Backlog to best achieve goals and missions;
- Optimizing the value of the work the Development Team performs;
- Ensuring that the Product Backlog is visible, transparent, and clear to all, and shows what the Scrum Team will work on next; and,
- Ensuring the Development Team understands items in the Product Backlog to the level needed.

Development Team
- 3 - 9 team members
- Self-organizing
- Cross-functional
- No titles, only developer
- No sub-teams
- Individual Development Team members may have specialized skills and areas of focus, but accountability belongs to the Development Team as a whole.



Scrum Master
- Responsible for ensuring Scrum is understood and enacted.
- Ensure Scrum team adheres to Scrum theory, practices & rules.
- Helps those outside the Scrum Team understand which of their interactions with the Scrum Team are helpful and which aren’t.
- Helps everyone change these interactions to maximize the value.

Scrum Master Service to Product Owner
-
Finding techniques for effective Product Backlog management;
-
Helping the Scrum Team understand the need for clear and concise Product Backlog items;
-
Understanding product planning in an empirical environment;
-
Ensuring the Product Owner knows how to arrange the Product Backlog to maximize value;
-
Understanding and practicing agility; and,
-
Facilitating Scrum events as requested or needed.


Scrum Master Service to Development Team
-
Coaching the Development Team in self-organization and cross-functionality;
-
Helping the Development Team to create high-value products;
-
Removing impediments to the Development Team’s progress;
-
Facilitating Scrum events as requested or needed; and,
-
Coaching the Development Team in organizational environments in which Scrum is not yet fully adopted and understood.




Scrum Master Service to Organization
-
Leading and coaching the organization in its Scrum adoption;
-
Planning Scrum implementations within the organization;
-
Helping employees and stakeholders understand and enact Scrum and empirical product development;
-
Causing change that increases the productivity of the Scrum Team; and,
-
Working with other Scrum Masters to increase the effectiveness of the application of Scrum in the organization.


Project Manager's New Role
-
Scrum Master
- Facilitator
-
Product Owner
- Don't manage, but work with them
-
Stay as PM (if project is Big)
- Budget etc
- As stake holder
3 Artefacts
Product Backlog
Sprint Backlog
Burndown Chart
Product Backlog Item
Product Backlog Item
Product Backlog Item
Product Backlog Item
Product Backlog Item



Product Backlog
-
List of items need to be built or done. (PBI's)
-
Prioritised.
-
PBI's are consulted by PO to the stakeholders & team to make sure what they want and what can be built.
-
Refined & estimated by people who are going to do it.
-
Only single product backlog exists.

Product Backlog Item
-
Can be features, bug-fixes, non-functional requirements.
-
Articulated in any way that is clear and sustainable.
-
Able to be demonstrated & potentially shippable.
-
Estimated in story points (e.g. t-shirt sizes or Fibonacci numbers).
-
Has clear Definition of Done that everyone agrees and creates visible values.

As a < ... >
I want to be able to < ... >
so that < ... >
Sprint Backlog
-
Set of PBI's selected for the Sprint.
-
A forecast by the Development Team about what functionality will be in the next Increment.
-
Only the Development Team can change its Sprint Backlog during a Sprint.
-
Once is committed, no additional work can be added to the Sprint Backlog except by the team.
-
The amount of completed PBI's becoming the Team's Velocity

Monitoring Sprint Backlog
- Development Team tracks this total work remaining
- As work is performed or completed, the estimated remaining work is updated
- Remove elements of the plan are deemed unnecessary
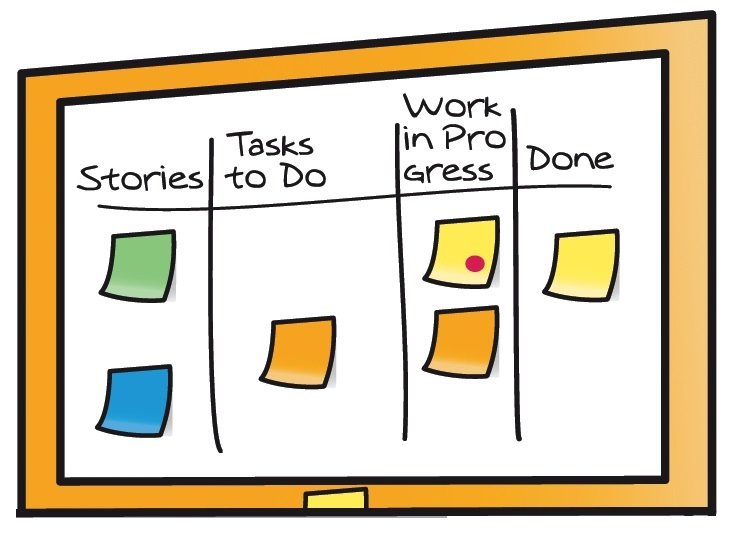
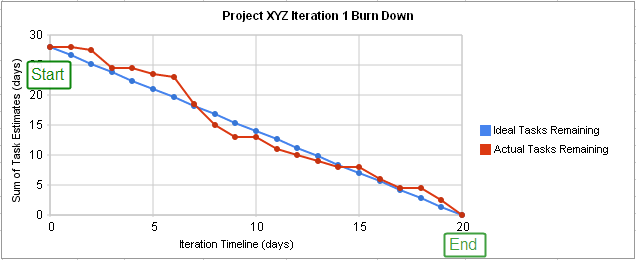
Burndown Chart
-
Graphical representation of work left to do versus time.
-
Useful for predicting when all of the work will be completed.
3 Ceremonies
Sprint Planning
Daily Standup
Sprint Review
Sprint Retrospective
Backlog Refinement
Sprint Planning
-
Collaborative meeting among Scrum team.
-
Look at top of backlog and forecast how much of it they can complete in this sprint
-
Should take number of points (Velocity) from last sprint
-
Time-boxed to a max of 2 hrs for a 2 weeks Sprint.
-
Committed items should not be changed.












2h
Daily Standup
-
Everyday <= 15 minutes
-
Development Team & Scrum Master
-
To answer following
-
What did you do to help the team finish the Sprint?
-
What will you do today to help the team finish the Sprint?
-
Is there any obstacle blocking you or team from achieving Sprint Goal?
-





15'
Sprint Review/Demo
-
Time boxed to 2h for 2 weeks sprint.
-
Attended by not only everyone but also stakeholders, customers, managers, whoever.
-
PO shows what's been accomplished (and not).
-
Dev team summarised what's going well and what's problem ran into.
-
Dev Team demonstrates the work that it has “Done” and answers questions about the Increment;






2h
Sprint Review/Demo
cont'd
- The PO discusses the Product Backlog as it stands, projects completion dates based on progress.
- Review what is the most valuable thing to do next; and,
- Review of the timeline, budget, potential capabilities, and marketplace for the next anticipated release of the product.
- Resulted a revised Product Backlog that defines the probable Product Backlog items for the next Sprint.






2h
Putting them all together



























PBIs
Sprint Planning
Sprint
Daily Standup
Potentially Shippable Product
Sprint Review/Demo
Backlog Refinement
Sprint Retrospective

Backlog Refinement
-
The act of adding detail, estimates, and order to items in the Product Backlog.
-
Ongoing process between Product Owner & Development Team.
-
Product backlog can be updated by Product Owner anytime with his own discretion





Sprint Retrospective
-
1,5h duration for 2 weeks sprint
-
Inspect how the last Sprint went with regards to people, relationships, process, and tools;
-
Identify and order the major items that went well and potential improvements; and,
-
Create a plan for implementing improvements to the way the Scrum Team does its work.
-
Solution oriented, emotional maturity in order to be effective.

Are we Scrum enough?
Challenges
- Difficulties on promoting Scrum to potential clients.
- Most clients want to know how long one project will take upfront.
- Developer involves in multiple projects.
- Stakeholders reluctancy to participate in Scrum ceremonies.
- Our knowledge of Scrum.
Where do we go from here?
- Training
- Books
- Youtube Videos
Common Values from the Agile Manifesto
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
Scrum Values
- Focus
- Courage
- Openness
- Commitment
- Respect
Summary
- Scrum is a simple yet powerful set of principles and practices that help teams deliver products in short cycles, enabling fast feedback, continual improvement, and rapid adaptation to change.
-
Three important elements in Scrum:
- Roles: Product Owner, Development Team & Scrum Master.
- Artefacts: Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog & Burndown Chart.
- Ceremonies: Sprint Planning, Daily Standup & Sprint Review
- Scrum Values : Focus, Courage, Openness, Commitment & Respect.

References
-
https://www.scrumalliance.org
-
https://www.scrum.org/
-
https://www.scruminc.com/