Hello! React.js!
Coupang
Travel CX (Brussel)
김태희(로토/roto)
about me
- Travel CX (Brussel) Web Developer
- Couband Bassist
오늘 우리가 배울 것
- react.js 개요
- react.js를 이용하여 Component 만들기
- es6 style
- react.js에서 css 로딩하기
React.js
- facebook이 만든 View Engine
- MVC 패턴에서 V만 담당
- V만 담당하므로 backbone, angularjs 등의 framework들에 적용가능
- !== framework
React.js
- Declarative
- Component-Based
- Learn Once, Write Anywhere




대표적인 사용처
그외에도...
특징
- Component Base
- Virtual DOM
- One way data binding
- JSX
JSX
- JAVASCRIPT 내에서 XML을 사용하는 문법
- React에선 JSX 를 이용해 UI를 표현
- XML이므로 HTML 보다 엄격하며 DOM API 기반
- (아직까지는) 브라우저가 알아먹지 못하는 문법.
- 브라우저가 알아먹게 하기 위해 babel 등을 이용해서 tranpiling
JSX
var HelloMessage = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <div>Hello {this.props.name}</div>;
}
});
ReactDOM.render(<HelloMessage name="John" />, mountNode);"use strict";
var HelloMessage = React.createClass({
displayName: "HelloMessage",
render: function render() {
return React.createElement(
"div",
null,
"Hello ",
this.props.name
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(HelloMessage, { name: "John" }), mountNode);Transpiling
Try Babel
Component Base
- UI의 모든 요소는 Component를 기준으로 함
- Component 단위로 UI 요소를 만들고, 해당 Component들을 조합해서 화면을 렌더링
Component Base
- Component는 상태(state)를 가질 수 있고, props를 통해 로 파라메터를 넘겨 받는다.
- state - props를 통해 데이터가 한 방향으로 흐른다.
Component Base
// es5 style
var YourComponent = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<div>Hi?</div>
);
}
});// es6 style
class YourComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>Hi!</div>
);
}
}Virtual DOM
- react.js는 자바스크립트 내에 DOM Tree와 비슷한 구조체를 가지고 있음
- Component를 다시 렌더링 할 때, 해당 구조체의 전후 상태를 비교하여 변경이 필요한 최소한의 요소만 다시 렌더링
- 속도 향상 효과
One Way Binding
- 데이터는 한 방향으로만 흐르는 것을 지향
- Two Way Binding 관련 Helper가 있었으나 v15에서 deprecated 됨
- Two Way Binding에 비해 손이 많이 가지만, 데이터 흐름 추적이 좀 더 용이함
- Component는 상태(state)를 가질 수 있고, 사용하는 곳에서 props로 파라메터를 넘겨 받을 수 있다.
- state - props를 통해 데이터가 한 방향으로 흐른다.
이제 컴포넌트를
만들어봅시다.
작성하기에 앞서..
- intellij를 사용할 경우
-
webstorm 쓰세요
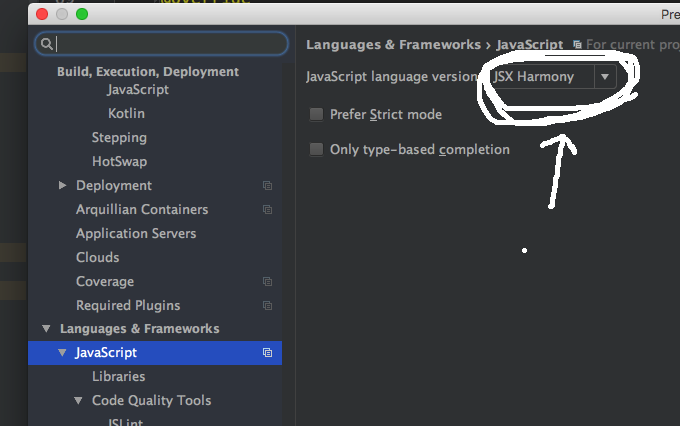
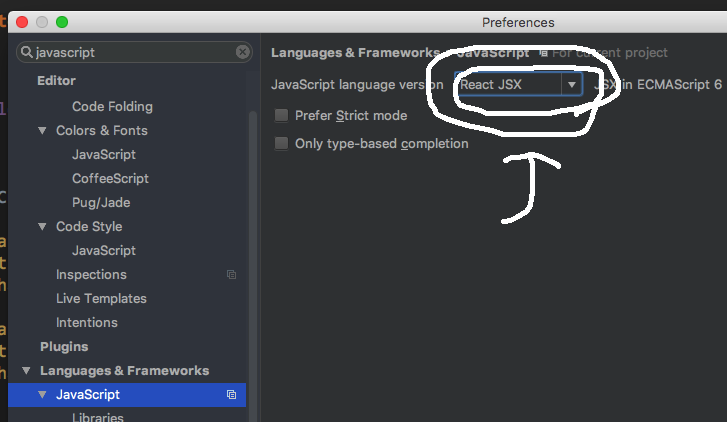
작성하기에 앞서..
혹은 atom 사용
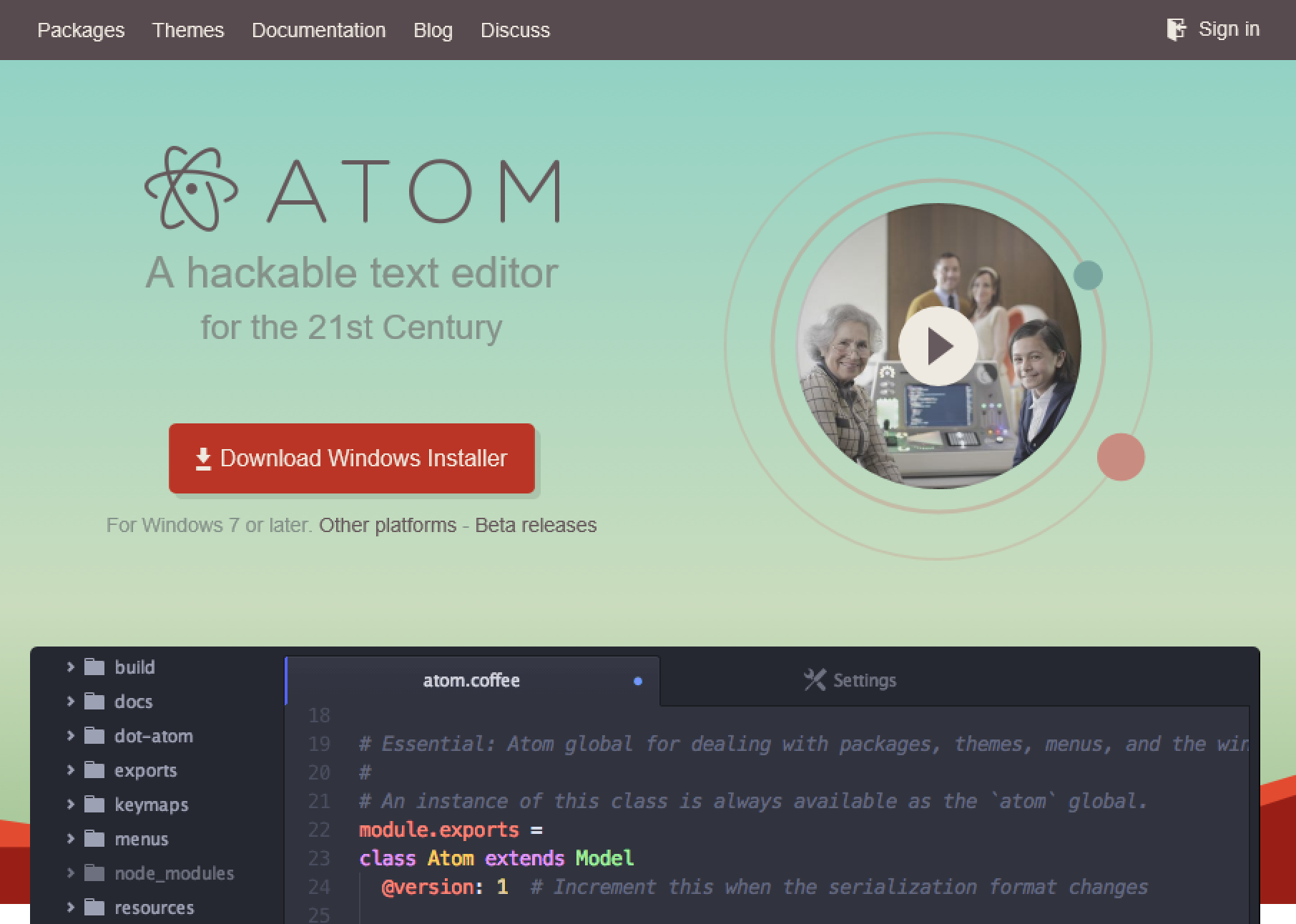
작성하기에 앞서..
React Component
작성 규칙
- component는 render 함수를 구현해야 한다.
// es6 style
class YourComponent extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>Hello! React.js!</div>
);
}
}// 틀린 예
render(){
return (
<div>쿠팡 최고의 동호회</div>
<div>쿠뺀으로 오세요!</div>
);
}
// 올바른 예
render(){
return (
<div>
<div>쿠팡 최고의 동호회</div>
<div>쿠뺀으로 오세요!</div>
</div>
);
}
render 함수가 반환하는 마크업의
최상위에는 단일 Root Node가 있어야 한다.
모든 element는 닫혀야 한다.
// 자주하는 실수
<br>
<img src="bali.png">
<input type="text">
// 올바른 예
<br/>
<img src="bali.png"/>
<input type="text" />attribute는 camelCase로 작성해야한다.
// 잘못된 예
<table cellpadding="5">
<tr rowspan="2">
...
</tr>
</table>
// 올바른 예
<table cellPadding="5">
<tr rowSpan="2">
...
</tr>
</table>class는 className으로
label의 for는 htmlFor로
// 잘못된 예
<div class="wrapper">
<label for="name">이름</label>
<input id="name" />
</div>
// 올바른 예
<div className="wrapper">
<label htmlFor="name">이름</label>
<input id="name" />
</div>Hello React!
Component 만들기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Hello React</title>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-dom-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/babel-core/5.8.34/browser.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="example"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
// 이곳에 코드를 작성합니다.
</script>
</body>
</html>
Component 정의하기
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Hello React</title>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-dom-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/babel-core/5.8.34/browser.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="example"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
// HelloWorld Component 정의
var HelloWorld = React.createClass({
// Component는 render 함수를 기준으로 화면에 그려진다.
render: function () {
return (
<div>Hello React!!!</div>
);
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
브라우저로 열어보면..

React DOM Mounting
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Hello React</title>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://fb.me/react-dom-15.2.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/babel-core/5.8.34/browser.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="example"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
// HelloWorld Component 정의
var HelloWorld = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return (
<div>Hello World!!!</div>
);
}
});
// HelloWorld Comopnent 마운팅하기
ReactDOM.render(
<HelloWorld />,
document.getElementById('example')
);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Component 쪼개고 조립하기
// Hello Component 정의
var Hello = React.createClass({
render: function (){
return (
<span>Hello!!</span>
);
}
});
// World Component 정의
var World = React.createClass({
render: function (){
return (
<span>World!!</span>
);
}
});
// Hello와 World Component를 조합한 새로운 Component
var ThreeHelloOneWorld = React.createClass({
render: function (){
return (
<div>
<Hello />
<Hello />
<Hello />
<World />
</div>
)
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<ThreeHelloOneWorld />,
document.getElementById('example')
);data binding
var Band = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var bandName = 'Cou Fighters';
return (
<div>
Band Name: {bandName}
</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<Band />,
document.getElementById('example')
);변수명을 {}로 감싼다.
props
Component Props
- Component 렌더링 시 렌더링하는 측에서 렌더링할 Component에 attribute 형태로 넘겨주는 값들이다.
- 함수 파라메터로 생각하면 된다.
- immutable해야 한다. 즉 props를 받아서 사용하는 쪽에선 props를 고치면 안 된다.
- props의 기준이 되는 데이터가 변경되는 경우, 연결된 props도 모두 갱신이 되며 해당 Component가 다시 그려진다.
Component Props
var Band = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var bandName = this.props.bandName;
return (
<div>
Band Name: {bandName}
</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<Band bandName="Cou Fighters"/>,
document.getElementById('example')
);Component Props
var Band = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var bandName = this.props.bandName;
return (
<div>
Band Name: {bandName}
</div>
);
}
});
var BandLineUp = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<div>
<h3>Band Line Up</h3>
<Band bandName="Cou Fighters" />
<Band bandName="삼거리 별다방" />
<Band bandName="AZ Taste" />
<Band bandName="TTB" />
</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<BandLineUp />,
document.getElementById('example')
);State
Component State
- Component의 자기자신의 상태에 대한 값은 state로 정의한다.
- props와는 달리 변경 가능한 값이고 setState를 통해 변경한다.
- setState를 통해 자신의 상태를 변경하면, 해당 상태 기준으로 화면이 다시 그려진다.
Component State
// Timer Component 정의
var Timer = React.createClass({
// Component의 state를 정의하는 함수
getInitialState: function(){
return {
count: 0
};
},
// Component가 화면에 Mount 되면 실행되는 Life cycle 함수
componentDidMount: function(){
setInterval(this.tick, 1000);
},
// setState를 통해 상태를 갱신하는 함수
tick: function() {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
});
},
render: function () {
return (
<div>tick count {this.state.count}</div>
);
}
});
ReactDOM.render(
<Timer />,
document.getElementById('example')
);state & props
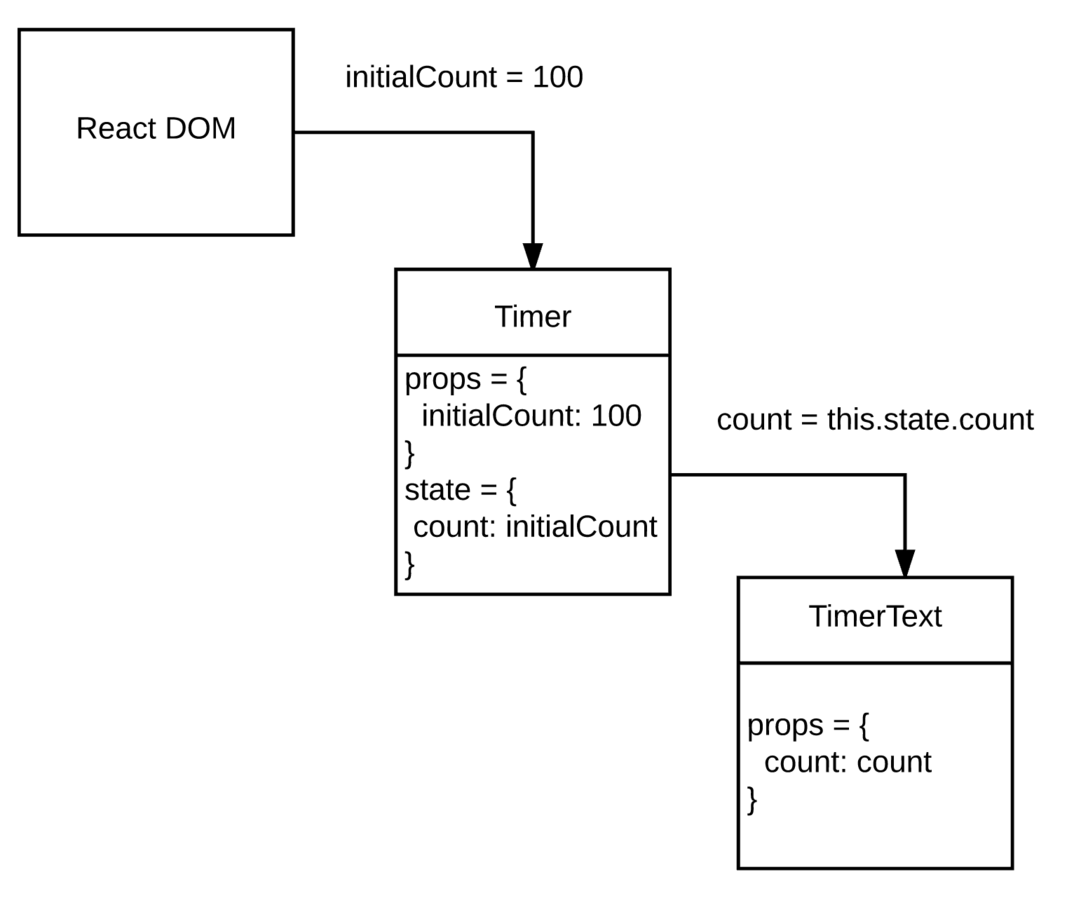
// Timer Component 정의. props로 initialCount를 받아 자신의 state에 설정
var Timer = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function () {
return {
count: this.props.initialCount
};
},
componentDidMount: function (){
setInterval(this.tick, 1000);
},
tick: function() {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
});
},
render: function (){
return (
<div>
<TimerText count={this.state.count} />
</div>
)
}
});
// count를 props로 받아 화면에 뿌려주는 역할
var TimerText = React.createClass({
render: function (){
return (
<span>현재 Count는 {this.props.count} 이다!</span>
);
}
});
// Timer를 렌더링하면서 props로 initialCount를 넘겨줌
ReactDOM.render(
<Timer initialCount={105}/>,
document.getElementById('example')
);
Conditional Rendering
개발자의 단짝 if 처리를 해봅시다.
Case 1
// 각 케이스에 대응하는 컴포넌트 두개를 생성
var CoupangGreeting = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <h1>Welcome to the Coupang!</h1>;
}
});
var GuestGreeting = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <h1>Hello Guest!</h1>;
}
});return 하는 Component를 다르게 하기
Case 1
// 각 케이스에 대응하는 컴포넌트 두개를 생성
var CoupangGreeting = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <h1>Welcome to the Coupang!</h1>;
}
});
var GuestGreeting = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return <h1>Hello Guest!</h1>;
}
});
var Greeting = React.createClass({
render: function(){
var isLoggedIn = this.props.isLoggedIn;
if(isLoggedIn){
return <CoupangGreeting />
}else{
return <GuestGreeting />
}
}
});Case 2
var LoginButton = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<button>로그인 버튼</button/>
)
}
});
var LogoutButton = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<button>로그아웃 버튼</button>
);
}
});
변수를 하나 만들고 condition에 따라 해당 변수에 Component를 넣은 뒤 해당 변수를 binding
Case 2
var LoginButton = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<button>로그인 버튼</button/>
)
}
});
var LogoutButton = React.createClass({
render: function() {
return (
<button>로그아웃 버튼</button>
);
}
});
var LoginControl = React.createClass({
render: function() {
var button = null;
if(this.props.isLoggedIn){
button = <LoginButton />;
}else{
button = <LogoutButton />
}
return (
<div>
Hello! {button}
</div>
);
}
});Case 3
&& 연산자의 특성을 이용하기
var Ticket = React.createClass({
isValidTicket() {
// 유효성 체크한 값 리턴
return true;
}
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<h3>티켓 이름: {this.props.ticketName}</h3>
{!this.isValidTicket() &&
<h2>유효기간이 만료된 티켓입니다!</h2>
}
</div>
);
}
});Case 4
삼항연산자 이용하기
var User = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<h2>{this.props.isLoggedIn ? '로그인 하셨네요!' : '로그인 해주세요 T_T'}</h2>
</div>
);
}
});Loop
Rendering Multiple Component
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
var listItems = numbers.map((number) =>
<li>{number}</li>
);
return (
<ul>
{listItems}
</ul>
);Rendering Multiple Component
render: function() {
var selectedProducts = [
{
id: 1,
name: 'Fender American Standard Jazz Bass',
price: 2000000
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Yamaha Revstar RS620 BRB',
price: 800000
}
];
var products = [];
selectedProducts.forEach(function(selectedProduct, i){
products.push(
<li key={i}>
선택하신 상품 {selectedProduct.name}의 가격은 {selectedProduct.price}원 입니다.
</li>
)
});
return (
<div>
<ul>
{products}
</ul>
</div>
);
}PropTypes
propTypes
- Component 내에 propTypes를 통해 넘어올 props의 형태를 정의할 수 있다.
- 추후 코드 가독성에 매우 도움
- type checking을 통해 버그 사전 방지
propTypes
var Timer = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
initialCount: React.PropTypes.number
},
......
});
var TimerText = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
count: React.PropTypes.number.isRequired
},
....
});propTypes
React.createClass({
propTypes: {
// You can declare that a prop is a specific JS primitive. By default, these
// are all optional.
optionalArray: React.PropTypes.array,
optionalBool: React.PropTypes.bool,
optionalFunc: React.PropTypes.func,
optionalNumber: React.PropTypes.number,
optionalObject: React.PropTypes.object,
optionalString: React.PropTypes.string,
optionalSymbol: React.PropTypes.symbol,
// Anything that can be rendered: numbers, strings, elements or an array
// (or fragment) containing these types.
optionalNode: React.PropTypes.node,
// A React element.
optionalElement: React.PropTypes.element,
// You can also declare that a prop is an instance of a class. This uses
// JS's instanceof operator.
optionalMessage: React.PropTypes.instanceOf(Message),
// You can ensure that your prop is limited to specific values by treating
// it as an enum.
optionalEnum: React.PropTypes.oneOf(['News', 'Photos']),
// An object that could be one of many types
optionalUnion: React.PropTypes.oneOfType([
React.PropTypes.string,
React.PropTypes.number,
React.PropTypes.instanceOf(Message)
]),
// An array of a certain type
optionalArrayOf: React.PropTypes.arrayOf(React.PropTypes.number),
// An object with property values of a certain type
optionalObjectOf: React.PropTypes.objectOf(React.PropTypes.number),
// An object taking on a particular shape
optionalObjectWithShape: React.PropTypes.shape({
color: React.PropTypes.string,
fontSize: React.PropTypes.number
}),
// You can chain any of the above with `isRequired` to make sure a warning
// is shown if the prop isn't provided.
requiredFunc: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired,
// A value of any data type
requiredAny: React.PropTypes.any.isRequired,
// You can also specify a custom validator. It should return an Error
// object if the validation fails. Don't `console.warn` or throw, as this
// won't work inside `oneOfType`.
customProp: function(props, propName, componentName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(props[propName])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
},
// You can also supply a custom validator to `arrayOf` and `objectOf`.
// It should return an Error object if the validation fails. The validator
// will be called for each key in the array or object. The first two
// arguments of the validator are the array or object itself, and the
// current item's key.
customArrayProp: React.PropTypes.arrayOf(function(propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) {
if (!/matchme/.test(propValue[key])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop `' + propFullName + '` supplied to' +
' `' + componentName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
})
},
/* ... */
});propTypes
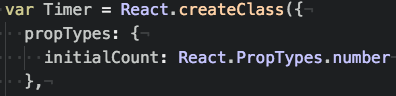
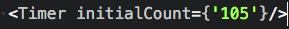

propTypes에 선언된 타입과 props가 다른 경우..
propTypes
isRequired로 선언된 props를 누락한 경우..
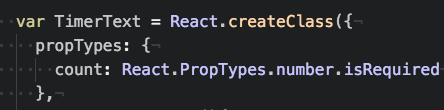

development mode에서만 check
Event System
Event System
- UI Interaction이 일어나는 곳에 onXXX 형태로 Event를 bind
- es5 style 기준으로 이벤트 핸들러에 this가 자동으로 bind 됨
Event System
var ClickCounter = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function() {
return {
clickCounter: 0
};
},
render: function () {
return (
<div>
현재 버튼은 {this.state.clickCounter} 번 눌렸습니다.
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>눌러봅시다!</button>
</div>
)
},
handleClick: function(){
this.setState({
clickCounter: this.state.clickCounter + 1
});
}
});
ReactDOM.render(<ClickCounter/>, document.getElementById('example'));이제 초간단 Todo App을
만들어봅시다.
Todo App
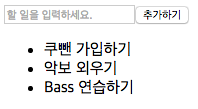
대략 이런 모양새
Component로 생각하기
- TodoApp
- TodoText
- TodoList
우선...TodoApp의 구조
var TodoApp = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function () {
return {
todos: [
{
todoText: '쿠뺀 가입하기'
},
{
todoText: '악보 외우기'
},
{
todoText: 'Bass 연습하기'
}
]
};
},
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<TodoText />
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}/>
</div>
);
}
});그리고 TodoText의 구조
var TodoText = React.createClass({
render: function () {
return (
<form>
<input type="text"
placeholder="할 일을 입력하세요."/>
<button type="submit">추가하기</button>
</form>
);
}
});TodoList의 구조
var TodoList = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
todos: React.PropTypes.array
},
render: function () {
var todoLiComponents = [];
var todos = this.props.todos;
todos.forEach(function(todo, i){
todoLiComponents.push(
<li key={i}>
{todo.todoText}
</li>
);
});
return (
<ul>
{todoLiComponents }
</ul>
);
}
});일단 렌더링은 성공함

TodoText의 input 처리
var TodoText = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function () {
return {
todoText: ''
};
},
render: function () {
return (
<form>
<input type="text"
placeholder="할 일을 입력하세요."
value={this.state.todoText}
onChange={this.handleTodoTextChange}/>
<button type="submit">추가하기</button>
</form>
)
},
handleTodoTextChange: function(e) {
this.setState({
todoText: e.target.value
});
}
});TodoText의 submit 처리
var TodoText = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
onAddTodo: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired
},
getInitialState: function () {
return {
todoText: ''
};
},
render: function () {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input type="text"
placeholder="할 일을 입력하세요."
value={this.state.todoText}
onChange={this.handleTodoTextChange}/>
<button type="submit">추가하기</button>
</form>
)
},
handleTodoTextChange: function(e) {
this.setState({
todoText: e.target.value
});
},
handleSubmit: function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
this.props.onAddTodo(this.state.todoText);
this.setState({
todoText: ''
});
}
});TodoApp에서 onAddTodo 추가하기
var TodoApp = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function () {
return {
todos: [
{
todoText: '쿠뺀 가입하기'
},
{
todoText: '악보 외우기'
},
{
todoText: 'Bass 연습하기'
}
]
};
},
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos} />
</div>
)
},
handleAddTodo: function(todoText) {
// 기존 state의 todos 를 clone
var newTodos = this.state.todos.slice();
newTodos.push({
todoText: todoText
});
this.setState({
todos: newTodos
});
}
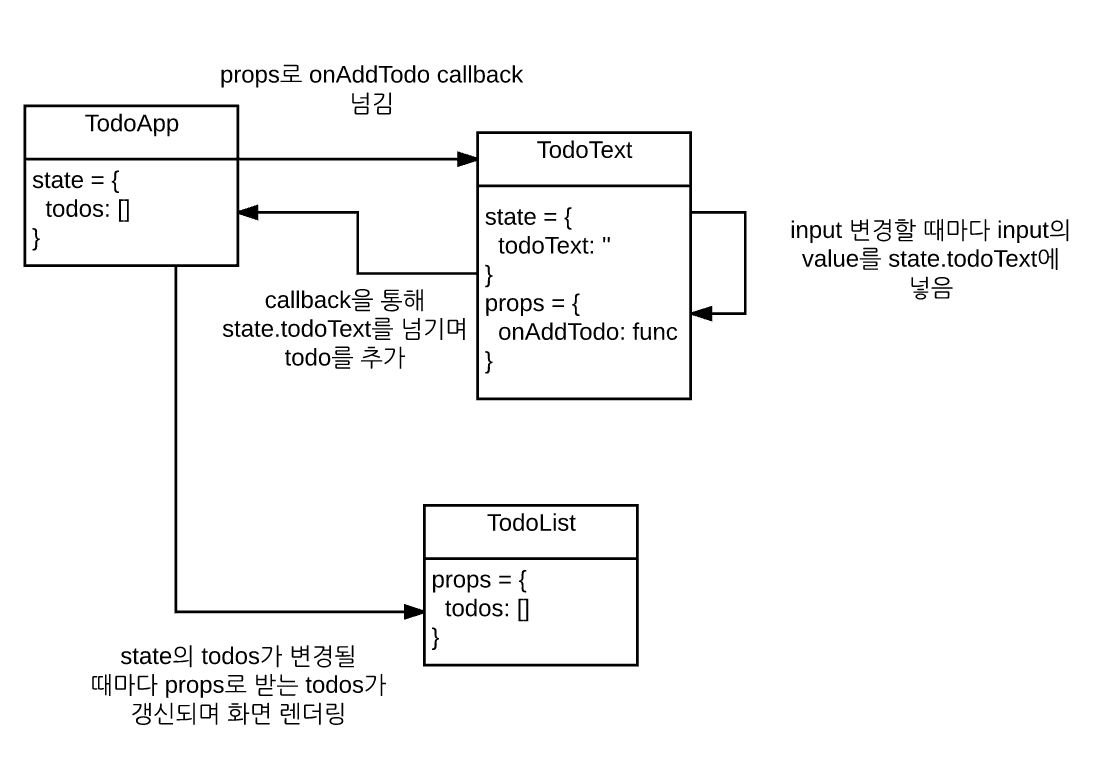
});
todos를 ajax로 fetch해오기
var TodoApp = React.createClass({
getInitialState: function () {
return {
todos: []
};
},
componentDidMount: function() {
$.get('http://demo4539895.mockable.io/todo')
.done(function(result){
this.setState({
todos: result
});
}.bind(this));
},
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos} />
</div>
)
},
handleAddTodo: function(todoText) {
// 기존 state의 todos 를 clone
var newTodos = this.state.todos.slice();
newTodos.push({
todoText: todoText
});
this.setState({
todos: newTodos
});
}
});todo에 새로운 필드를 추가해봅시다.
isCompleted를 추가하기
var TodoApp = React.createClass({
...
render: function () {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
{// onCompleted props 추가 }
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}
onCompleted={this.handleCompleted}/>
</div>
)
},
handleCompleted: function(index) {
// props로 넘어간 이 핸들러가 호출되면서 파라메터로 완료처리할 todo의 index를 넘긴다
// clone 후 값을 바꾸고 setState
var newTodos = this.state.todos.slice();
newTodos[index].isCompleted = true;
// state가 바뀌면서 다시 화면이 그려짐
this.setState({
todos: newTodos
});
}
...
});isCompleted를 추가하기
var TodoList = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
todos: React.PropTypes.arrayOf(React.PropTypes.shape({
todoText: React.PropTypes.string,
isCompleted: React.PropTypes.bool
})).isRequired,
onCompleted: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired
},
render: function () {
var todoLis = [];
var todos = this.props.todos;
todos.forEach(function(todo, i){
// todo의 isCompleted 값에 따라 동적으로 completed className을 설정
todoLis.push(
<li key={i}
className={todo.isCompleted ? 'completed' : ''}
onClick={this.handleClick}>
{todo.todoText}
</li>
)
}.bind(this));
return (
<ul>
{todoLis}
</ul>
)
},
// todo 클릭 시 이벤트 핸들러. 이벤트가 일어난 지점의 index를 구해서 props의 onCompleted Callback 호출
handleClick: function (e) {
this.props.onCompleted($(e.target).index());
}
});새로운 Component를 추가하기
var TodoStatus = React.createClass({
propTypes: {
todos: React.PropTypes.array.isRequired
},
render: function (){
var todos = this.props.todos;
var completedCount = todos.filter(function(todo){
return todo.isCompleted;
}).length;
return (
<div>
{todos.length} 개의 할 일 중에 {completedCount}개가 완료됨
</div>
)
}
});Todo의 상태를 보여주는 TodoStatus Component 추가
새로운 Component를 추가하기
...
render() {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos} onCompleted={this.handleCompleted}/>
<TodoStatus todos={this.state.todos} />
</div>
)
}
...TodoApp render 에 새 Component 추가
ES6 Style Component
ES6 Features
- lexical scope
- class style
- arrow function
- string template
- and more...
create-react-app 를
이용해봅시다.
create-react-app ?
- 기존에는 react.js 관련 프로젝트 세팅을 하려면 이것저것 수작업 할 게 많았는데 그걸 한방에 끝내준다.
- webpack, babel 등이 적용되어 있다.
create-react-app
- node.js 설치
https://nodejs.org/en/ 에서 LTS 버전으로 다운로드 - node.js 설치 후 터미널에서 아래의 커맨드 입력
권한오류 발생 시 sudo chown -R $USER /usr/local 실행
- create-react-app TodoApp 입력
- cd TodoApp
- npm start
npm install -g create-react-appES6 Style Component
class HelloES6React extends React.Component {
render() {
const {name} = this.props;
return (
<div>hi!!!{name}</div>
)
}
}
HelloES6React.propTypes = {
name: React.PropTypes.string.isRequired
};
ReactDOM.render(<HelloES6React name="로토" />, document.getElementById('example'));Component 분리하기
import
export
TodoText.js
import React from 'react';
class TodoText extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
todoText: ''
};
this.handleTodoTextChange = this._handleTodoTextChange.bind(this);
this.handleSubmit = this._handleSubmit.bind(this);
}
_handleTodoTextChange(e) {
this.setState({
todoText: e.target.value
});
}
_handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
this.props.onAddTodo(this.state.todoText);
this.setState({
todoText: ''
});
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<input type="text"
placeholder="할 일을 입력하세요."
value={this.state.todoText}
onChange={this.handleTodoTextChange}/>
<button type="submit">추가하기</button>
</form>
)
}
}
export default TodoText;TodoList.js
import React from 'react';
class TodoList extends React.Component {
render() {
let todoLiComponents = [];
const todos = this.props.todos;
todos.forEach((todo, i) => {
todoLiComponents.push(
<li key={i}>
{todo.todoText}
</li>
);
});
return (
<ul>
{todoLiComponents }
</ul>
);
}
}
export default TodoList;TodoApp.js
import React from 'react';
import TodoText from './TodoText';
import TodoList from './TodoList';
class TodoApp extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
todos: []
};
this.handleAddTodo = this._handleAddTodo.bind(this);
}
_handleAddTodo(todoText) {
var newTodos = this.state.todos.slice();
newTodos.push({
todoText: todoText
});
this.setState({
todos: newTodos
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}/>
</div>
)
}
}
export default TodoApp;index.js
최초 DOM Mounting은 이곳에서.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import TodoApp from './TodoApp';
import './index.css';
ReactDOM.render(
<TodoApp />,
document.getElementById('root')
);
ES6 주의점
- ES5 Style에서 해줬던 auto binding이 없음
- state 선언은 constructor 구문에서
- Event Binding하는 쪽에서 this context에 대해 binding하는 처리를 해줘야 함
http://egorsmirnov.me/2015/08/16/react-and-es6-part3.html - propsTypes는 Component class 선언 이후 넣어줘야 함
ES6 + ES7
ES6 + ES7 Style
class TodoApp extends React.Component {
// constructor 생략
state = {
todos: []
}
componentDidMount () {
$.get('http://demo4539895.mockable.io/todo')
.done((result) => {
this.setState({
todos: result
});
});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<TodoText onAddTodo={this.handleAddTodo}/>
<TodoList todos={this.state.todos}
onCompleted={this.handleCompleted}/>
</div>
)
}
handleAddTodo = (todoText) => {
// 기존 state의 todos 를 clone
var newTodos = this.state.todos.slice();
newTodos.push({
todoText: todoText
});
this.setState({
todos: newTodos
});
};
class TodoList extends React.Component {
static propTypes = {
todos: React.PropTypes.array,
onCompleted: React.PropTypes.func.isRequired
};
render () {
var todoLis = [];
var todos = this.props.todos;
todos.forEach((todo, i) => {
todoLis.push(
<li key={i}
className={todo.isCompleted ? 'completed' : ''}
onClick={this.handleClick}>
{todo.todoText}
</li>
)
});
return (
<ul>
{todoLis}
</ul>
)
}
handleClick = (e) => {
this.props.onCompleted($(e.target).index());
};
}Q & A
and more
-
webpack + babel
-
flux, redux
- Single Page Application
-
react native
