Data Communications and Networking
Introduction
RS Maniaol
What hath God wrought?
- Samuel F.B. Morse
First telegraph message on 24 May, 1844 from Supreme Court chamber in Washington, D.C. to the B&O's Mount Claire Station in Baltimore, Maryland
Definition of Terms
Communication
Telecommunication
Data Communication
Communicating devices must be part of a data communicating system (DCS), a combination of hardware and software
Data



Components of a Data Communication System
Protocol
Sender
Receiver
Medium
Message
Effective DCS
- Delivery
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
- Jitter
Data Representation
- Text
- Numbers
- Images
- Audio
- Video
Data Flow
Simplex
Half-duplex
Full-duplex/duplex




Direction of data at time 1
Direction of data at time 2


Network
set of devices (nodes) connected by communication links
uses distributed processing
Network Criteria
- Performance
- Transmit time
- Response time
- More throughput, less delay
- Reliability
- Security
Physical Structure: Type of Connection
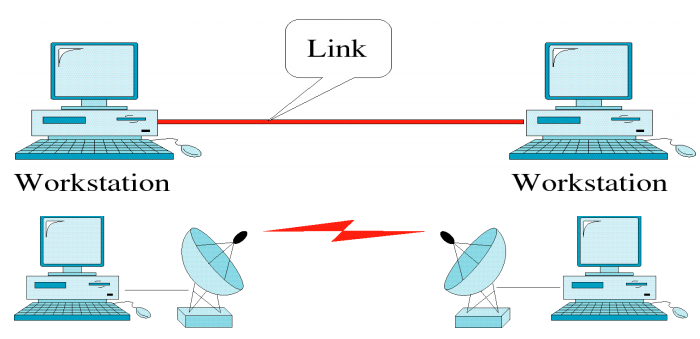
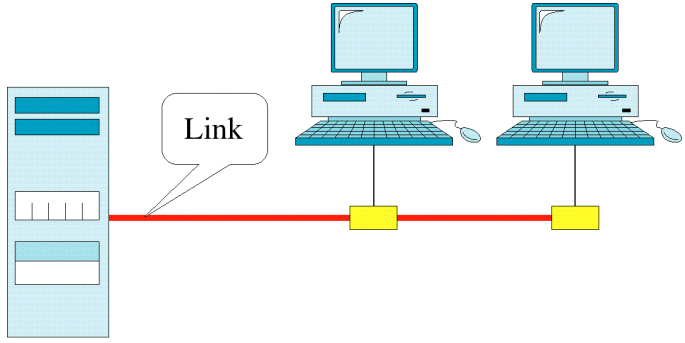
Point to Point
Multipoint/Multidrop
Physical Structure: Topology
refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically
geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and nodes to one another
Mesh









Hub
Star
Bus



Tap
Drop line
Cable end
Cable end
Ring





Repeater
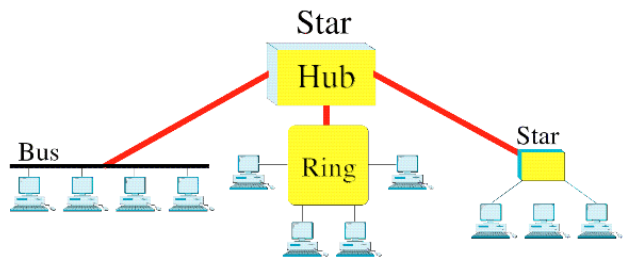
Hybrid
Daisy Chain





Tree Topology






Network Models
Allows heterogeneous networks created by different entities to communicate
OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model defines a seven-layer network
Internet model defines a five-layer network
Categories of Network:
Local Area Network (LAN)
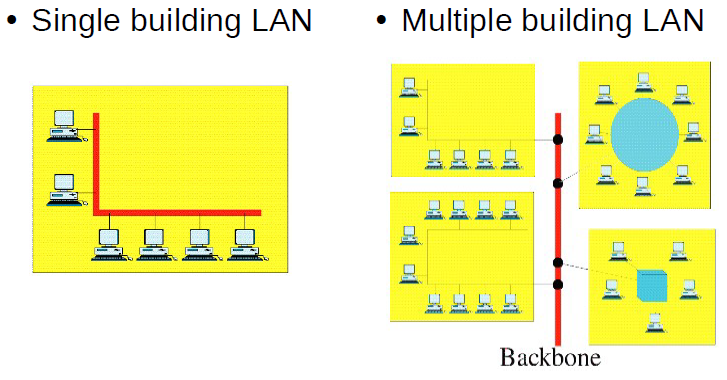
Categories of Network:
Wide Area Network (WAN)
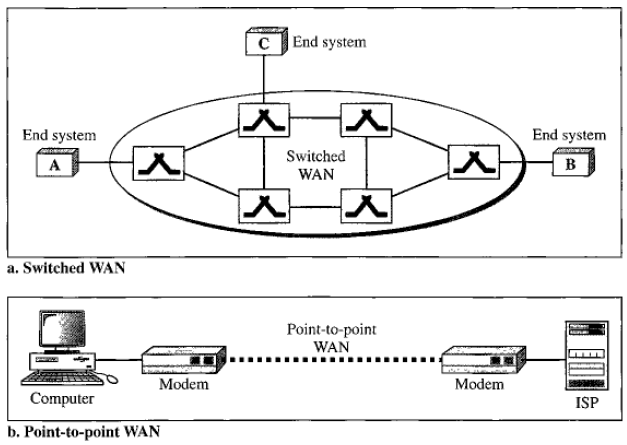
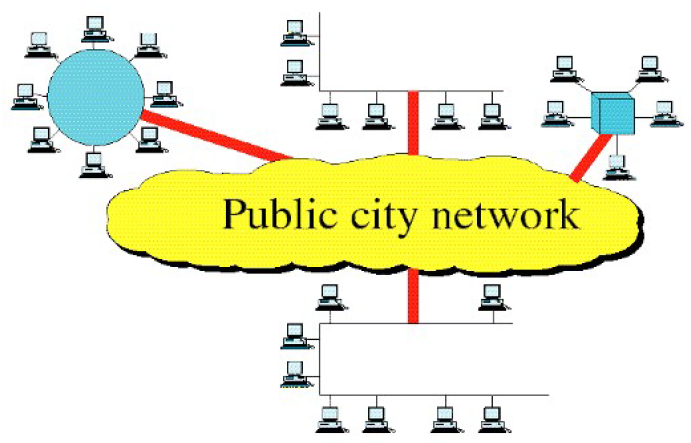
Categories of Network:
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Interconnection of Networks:
Internetwork
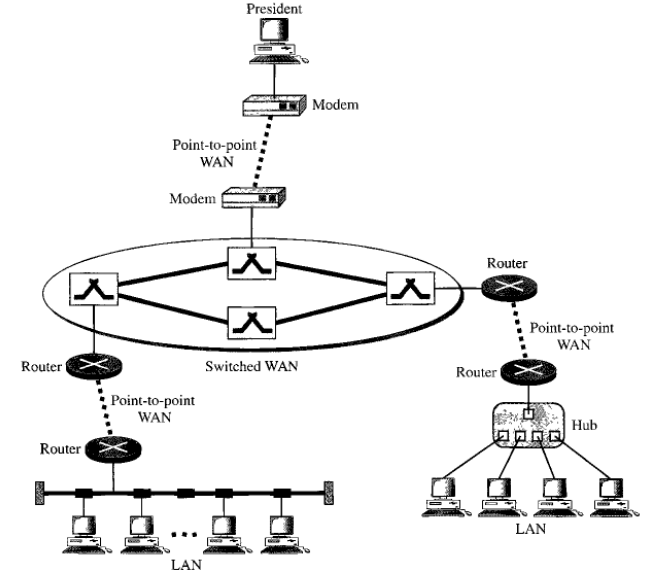
The Internet: History
internet
Internet
two or more networks that can communicate with each other
collaboration of more than thousands of interconnected networks
1967 - at an ACM meeting, Advanced Research Projects Agency presented ARPANET
small network of computers which used Interface Message Processors
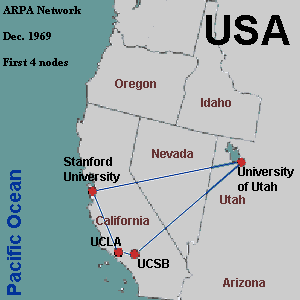
UCLA, UCSB, SRI and UU connected in 1969 via software called Network Control Protocol
http://projet-arpanet.over-blog.com
The Internet: History
1972 - Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn worked on the Internetting Project
1973 - paper on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
protocols to achieve end-to end delivery, encapsulation, the datagram and functions of a gateway
split into TCP and IP
TCP responsible for higher-level functions such as segmentation, reassembly and error detection
IP handles datagram routing
The Internet: Today
Made up of many wide- and local-area networks joined by connecting devices and switching stations
Internet Service Providers provide Internet access to users
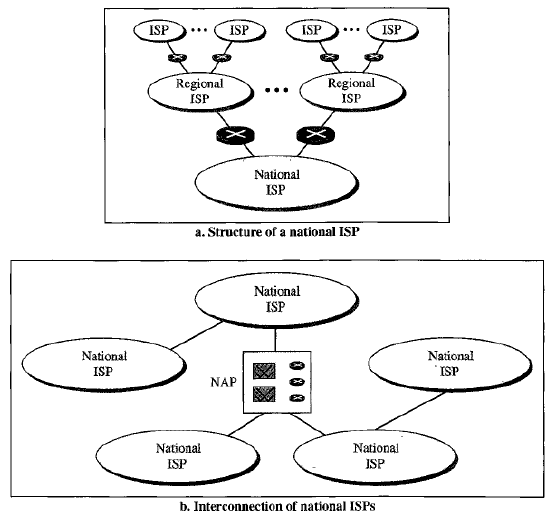
Peering vs Transit
Autonomous Systems (AS)
collection of routers whose prefixes and routing policies are under common administrative control
Peering - two or more autonomous networks interconnect directly with each other to exchange traffic
Transit - one autonomous network agrees to carry the traffic that flows between another autonomous network and all other network
Peering vs Transit




A
B
Peering
Peering vs Transit




A
B
C
Transit
Transit
Peering vs Transit




A
B
C
Transit
Transit
D
Peering
Peering vs Transit




A
B
C
Transit
Transit
D
Transit
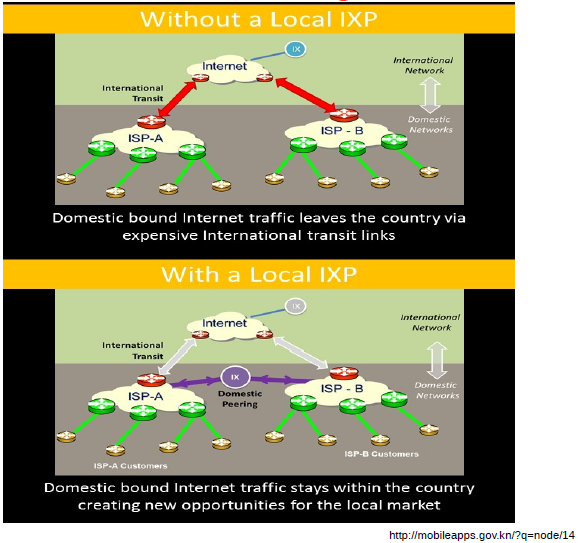
Internet Exchange Point
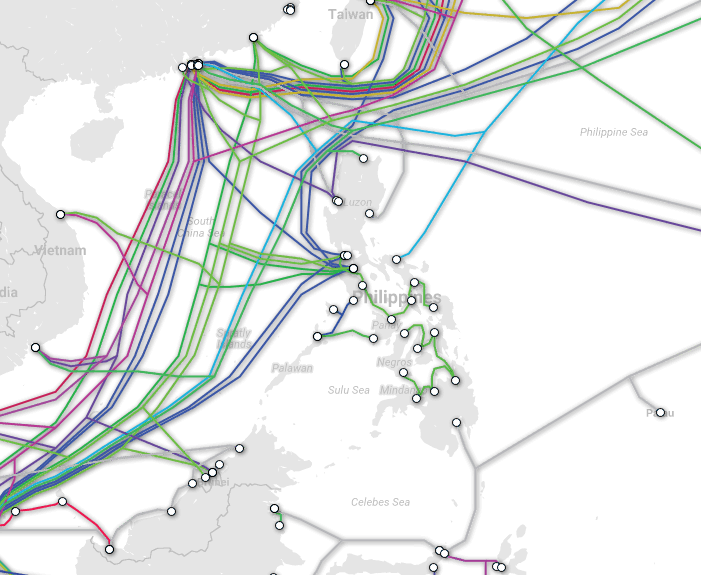
Submarine Cable Map
https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
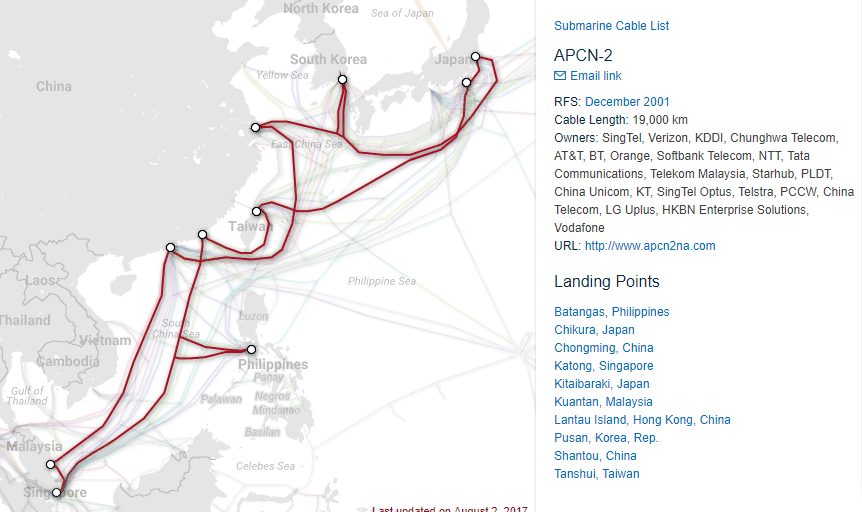
Asia-Pacific Cable Network 2 (APCN-2)
https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
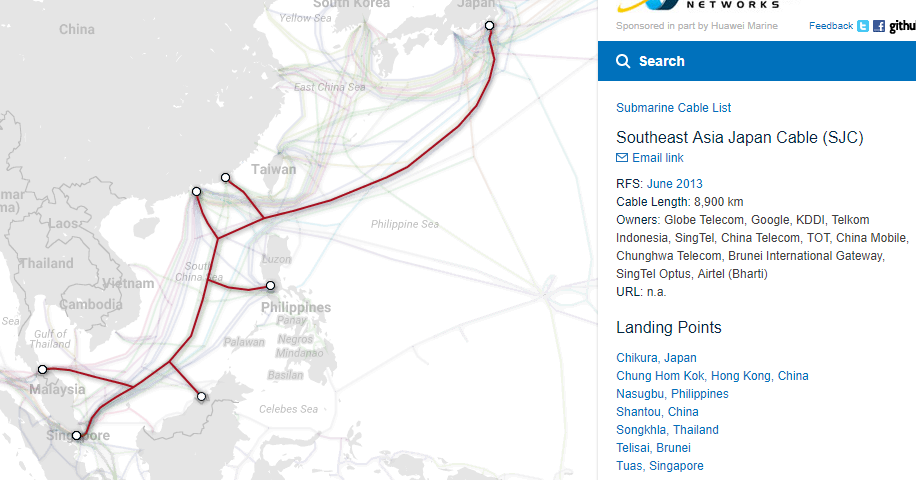
Southeast Asia Japan Cable (SJC)
https://www.submarinecablemap.com/
Protocols
Communication occurs between entities in different systems
Entity - anything capable of sending or receiving information
Protocol - set of rules that govern data communications
Elements of a Protocol
Syntax - structure and format of data
Semantics - meaning of each section of bits
Timing - when data should be send and how fast they can be sent
Standards
creates and maintains an open and competitive market for manufacturers
guarantees national and international operability of data and telecommunications technology and processes
De facto ("by fact") - have not been approved by an organized body but have been adopted as standards through widespread use
De jure ("by law") - have been legislated by an officially recognized body
How are standards developed?
Standard creation committees
ISO, ITU-T, CCITT, ANSI, IEEE
Slow approval process
Forums
speeds up acceptance and use of technology
conclusions presented in standards bodies
Government Regulatory Agencies
FCC/NTC
To protect public interest
Standard Creation Committees
- ISO - International Organization for Standardization
- CCITT - Consultative Committee for International Telegraphy and Telephony
- ITU-T - International Telecommunication Union - Telecommunication Standards Sector
- ANSI - American National Standards Institute
- IEEE - Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
- EIA - Electronic Industries Association
Internet Standards
A thoroughly tested specification that is useful to and adhered to by those who work with the Internet
Specification begins as an Internet draft
work in progress, 6 month lifetime
Upon recommendation, may be published as Request for Comment
edited, assigned a number, made available to interested parties
Request for Comments
Invented by Steve Crocker to provide record of
Network Working Group's (NWG) design of the ARPANET
RFC 1 - “Host Software”
RFC 1000 - “Request for Comments Reference Guide”

RFC 1
References
- Forouzan, B.A. 2007. Data Communications and Networking, 4th Ed.McGraw-Hill, New York
- https://arstechnica.com/features/2008/09/peering-and-transit/
- https://www.cs.rutgers.edu/~pxk/352/notes/autonomous_systems.html