97039: Global Health, Antimicrobial Drugs and Vaccines
Module 1: The antimicrobial resistance pandemic
Russell Lewis, Associate Professor
Infectious Diseases, IRCSS S. Orsola-Malpighi Hospital
Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences

Alma Mater Studiorum
Università di Bologna
10 January 2023
Introduction
-
Module 1: The growing pandemic of antimicrobial resistance
-
Module 2: The public health crisis of new antibiotic development
-
Module 3: Antibiotic and diagnostic test availability, affordability
www.uniboglobalhealth.com


Interactive data visualizations
Expert video explanations
Links to additional reading, case studies, podcasts addressing the topics in the modules
Learning objectives: Module 1
- Review the history and factors that drive antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
- Discuss One Health aspects of antimicrobial resistance
- Compare management challenges of AMR in low and middle-income countries (LMICs)
- Examine problems of managing managing cross-border transmission of AMR (interactive exercise through Microsoft Teams virtual classrooms)

What are the characteristics of a pandemic?
-
Large-scale (exponenetial) outbreak of infectious diseases
-
Crosses international borders
-
Causes disease and death in a large number of people
- epidemic: unexpected increase in the number of disease cases in a specific geographical area
- endemic: consistently present disease but limited to a particular region with predictable disease rates and spread
Currently estimated number of deaths due to antibiotic-resistant infections per year:
Estimated 2.8 million antibiotic resistant infections per year
700,000 deaths (including 230,000 deaths from MDR tuberculosis)
Text
1. Large-scale outbreak of infectious diseases

2. Crosses international borders
3. Disease and death in a large number of people

Deaths per year
WHO report of cumulative COVID-10 deaths: 6.6 million (Dec 22, 2022)
The future of antimicrobial resistance?
-
The estimated total number of deaths due to AMR could climb to 10 million deaths globally per year by 2050
-
Routine medical procedures or surgery will become more dangerous and associated with higher complication rates
-
Immunosuppression, cancer chemotherapy and transplantations may carry unacceptable risk for many patients if infections cannot be effectively prevented and treated
-
Economic and social progress in many countries will be dramatically impacted by increasing AMR leading to political and social instability
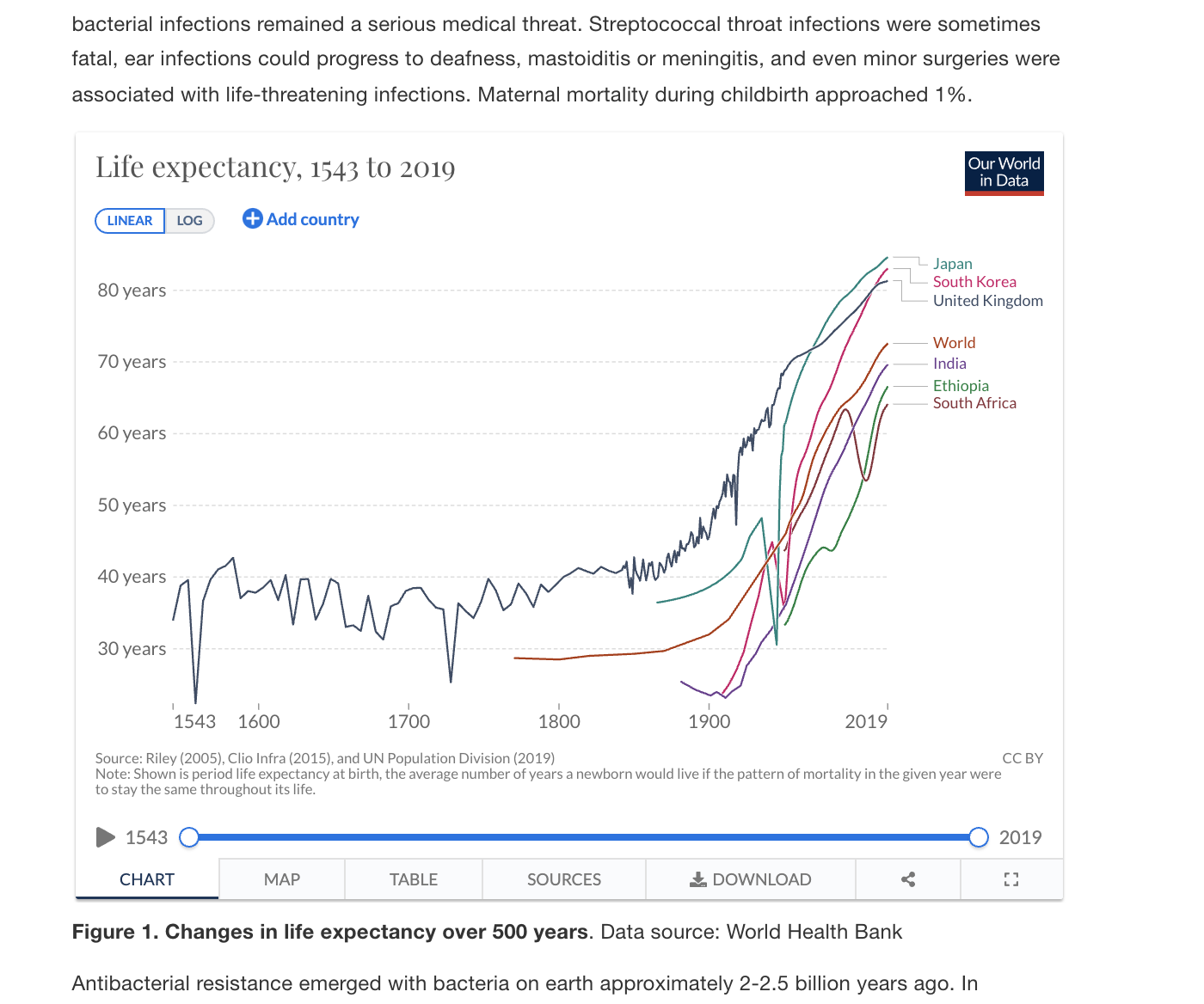
Changes in life expectancy over last 500 years
Source: Our World in Data
What factors reduced premature death due to communicable diseases?
- Improved sanitation and drinking water (Mid 19th century)
- Immunization (Early 20th century)
- Antibiotics (Mid 20th century)
Infectious diseases mortality rates began to fall in the early 1900s, long before antibiotics, on the basis of just implementing better sanitation!

Age-adjusted death rates, U.S. 1900-2018
Antibiotics shifted mortality causes to diseases of old age
A brief history of antibiotics
and antibiotic resistance

Bacteria and antimicrobial resistance:
- Bacteria and antibacterial resistance emerged 2.5 billion years ago...humans 2 million years ago
- It is likely that resistance mechanisms have been developed not only to current but also future antibiotics
-
Any antibiotic use, even appropriate use, will select for resistance...it is biologic destiny
- In terms of Earth's biomass, humans are outnumbered by bacteria by over 1000-fold
- Doubling time of bacteria approximately 20 minutes
PNAS Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018; 115:6506–6511.
See: Youtube video link in handout of resistance developing to ciprofloxacin
Greeks:
myrrh, wine, honey or caustic substances to treat wound infections
Egypt:
moldy bread (Aish baladi) to treat skin lesions
Chinese:
moldy tofu to treat inflammations and infections of the skin
All images: wikipedia
Ancient "Antibiotic" Therapy



Early antibiotics

Paul Ehrlich (1854-1917)
"Magic bullet"- chemotherapy
arsphenamine (Salvarsan) 1909
The first treatment for syphilis
(Treponema pallidum)
Image: Wellcome Library, London
Side effects attributed to Salvarsan, including rashes, liver damage, and risks of life and limb, were thought to be caused by improper handling and administration of the relatively insoluble compound
"the step from the laboratory to the patient's bedside ... is extraordinarily arduous and fraught with danger."
-Paul Erlich

The beginning of the modern antibiotic era
Sir Alexander Fleming (1881-1955)
The serendipitous discovery
of penicillin in 1928
Image: Wellcome Library, London




"It is not difficult to make microbes resistant to penicillin in the laboratory by exposing them to concentrations not sufficient to kill them, and the same thing has occasionally happened in the body.
...The time may come when penicillin can be bought by anyone in the shops. Then there is the danger that the ignorant man may easily under-dose himself and by exposing his microbes to non-lethal quantities of the drug make them resistant."
-Sir Alexander Fleming,
Nobel Prize Lecture, December 11, 1945
Antibiotic development timeline

source: www.react.org
"golden age of discovery"
Why is antibiotic discovery failing?
- Development of truly novel antibiotics is scientifically challenging
-
Antibiotic discovery is time-intensive and high-risk
- 10-15 years, 1 billion dollars investment initially
-
Limited economic incentives for pharmaceutical companies
- Antibiotics are taken for short periods
- Use of newly-approved antibiotics is often discouraged to slow the emergence of resistance
- Extensive post-marketing approval requirements/costs
We will discuss these problems and solutions in Module 2
World Health Organization (WHO)
Establishment of global Antimicrobial Resistance
and Use Surveillance System (GLASS)
2001


2015

2019
Global Research and Development Priorities for AMR
| Priority | Pathogens included |
|---|---|
| Critical |
Acinetobacter baumannii (Carbapenem-resistant) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Carbapenem-resistant) Enterobacterales (3rd generation cephalosporin, carbapenem-resistant) |
| High |
Enterococcus faecium, vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin intermediate and resistant Helicobacter pylori, clarithromycin-resistant Campylobacter, fluoroquinolone-resistant Salmonella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, 3rd gen. cephalosporin-resistant, fluoroquinolone-resistant |
| Medium |
Streptococcus pneumoniae, penicillin-non-susceptible Haemophilus influenzae, ampicillin-resistant Shigella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant |
This table does not include Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which was already recognized as a global health priority pathogen
Source: World Health Organization
WHO Priority pathogens for future pandemics.
Global burden of antimicrobial resistance

Murray CJ et al. The Lancet. 2022 Feb 12;399(10325):629–55.
Murray CJ et al. The Lancet. 2022 Feb 12;399(10325):629–55.

Global burden of antimicrobial resistance
-
In 2019- estimated 4.95 million deaths with AMR;
-
Excess mortality estimated vs. susceptible infections estimated at 1.27 million deaths
- 3rd leading cause of death behind heart disease and stroke
-
Excess mortality estimated vs. susceptible infections estimated at 1.27 million deaths

Murray CJ et al. The Lancet. 2022 Feb 12;399(10325):629–55.
Murray CJ et al. The Lancet. 2022 Feb 12;399(10325):629–55.

Common definitions of resistance used in literature
| Resistance type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Multi-drug resistance (MDR) | Resistance to one agent in at least 3 antibiotic categories |
| Extreme drug resistance (XDR) | Resistant except to 2 or fewer antibiotic categories |
| Pan-drug resistance (PDR) | PDR- resistant to all agents in all antibiotic categories |
| Difficult-to-treat resistance (DTR) | DTR-requires the use of less-effective or more toxic "reserve" antibiotics |
Magiorakos A-P et al. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2012:268–81.
Kadri SS et al. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2018:1803–14.
Murray CJ et al. The Lancet. 2022 Feb 12;399(10325):629–55.
AMR situation in a HIC:
Gram negative bacteria in Italy
Southern Europe has among the highest resistance rates on the WHO priority pathogen list
- 26.4% of Escherichia coli are resistant to 3rd generation cephalosporins
-
29.5% of Klebsiella pneumoniae are resistant to carbapenems
- Including 33.1% resistant to multiple drug classes
- 15.9% of Pseudomonas aeruginosa are resistant to carbapenems
-
80.8% of Acinetobacter spp. are resistant to carbapenems
- 78.8% of species resistant to multiple drug classes
- Overall, higher antimicrobial resistance rates (around 40%) are observed in ICUs versus general medical wards
Source: Micronet Resistance Surveillance
Carbapenem-resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae in EU, 2020
Source: ECDC


Regional CRE bacteremia incidence per 100,000
Italian residents by region
Source: Micronet
Sicilia > Toscana >
Piemonte > Umbria
Southern Europe has among the highest resistance rates on the WHO priority pathogen list
- Staphylococcus aureus, the percentage of methicillin-resistant isolates (MRSA) remained stable around 34%, while a worrying trend continues to increase in the percentage of Enterococcus faecium isolates resistant to vancomycin, which in 2020 was equal at 23.6%
- Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates resistant to penicillin (13.6%) and those resistant to erythromycin (24.5%).
Source: Micronet Resistance Surveillance
AMR situation in Italy-Gram positive bacteria

Cassini et al. Lancet Infect Dis 2019;19:55-66.
AMR situation in Italy-Predicted deaths
AMR situation in Italy-Predicted deaths
AMR in low-middle income countries (LMICs)

Photo: Chandan Khanna/AFP/Getty Images
What factors may contribute to AMR severity in LMICs?
- High population density
- Limited of access to clean water, suboptimal sewage systems, poor sanitation
- Poor healthcare infection control practices
- Limited microbiology laboratory testing/ surveillance
- Increasing consumption of antimicrobials in humans and animals
- Lack of regulation on antimicrobial use in farming, and pharmaceutical industry pollution

Image: Water Aid/Tom Saator
How are LMICs affected by AMR?
- Increased mortality and health costs
- Antibiotics effective against AMR are more expensive and not affordable for many patients
- Increasing use of antibiotics with efficacy against AMR leads to higher resistance to "last-line" antibiotics
- Carbapenem consumption is increasing at a rapid pace in poor economies
Photo: Chandan Khanna/AFP/Getty Images

Klein, E. Y. et al. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 21, 107–115 (2021).
What are the drivers of
antimicrobial resistance?


Source: U.S. CDC
Factors driving antimicrobial resistance

Source: ECDC
Antibiotic resistance is a
multi-faceted problem
Human antimicrobial misuse: outside hospitals

Source: Pew Research Trust

Human antimicrobial misuse in hospitals

Source:ECDC
Antimicrobial stewardship programs
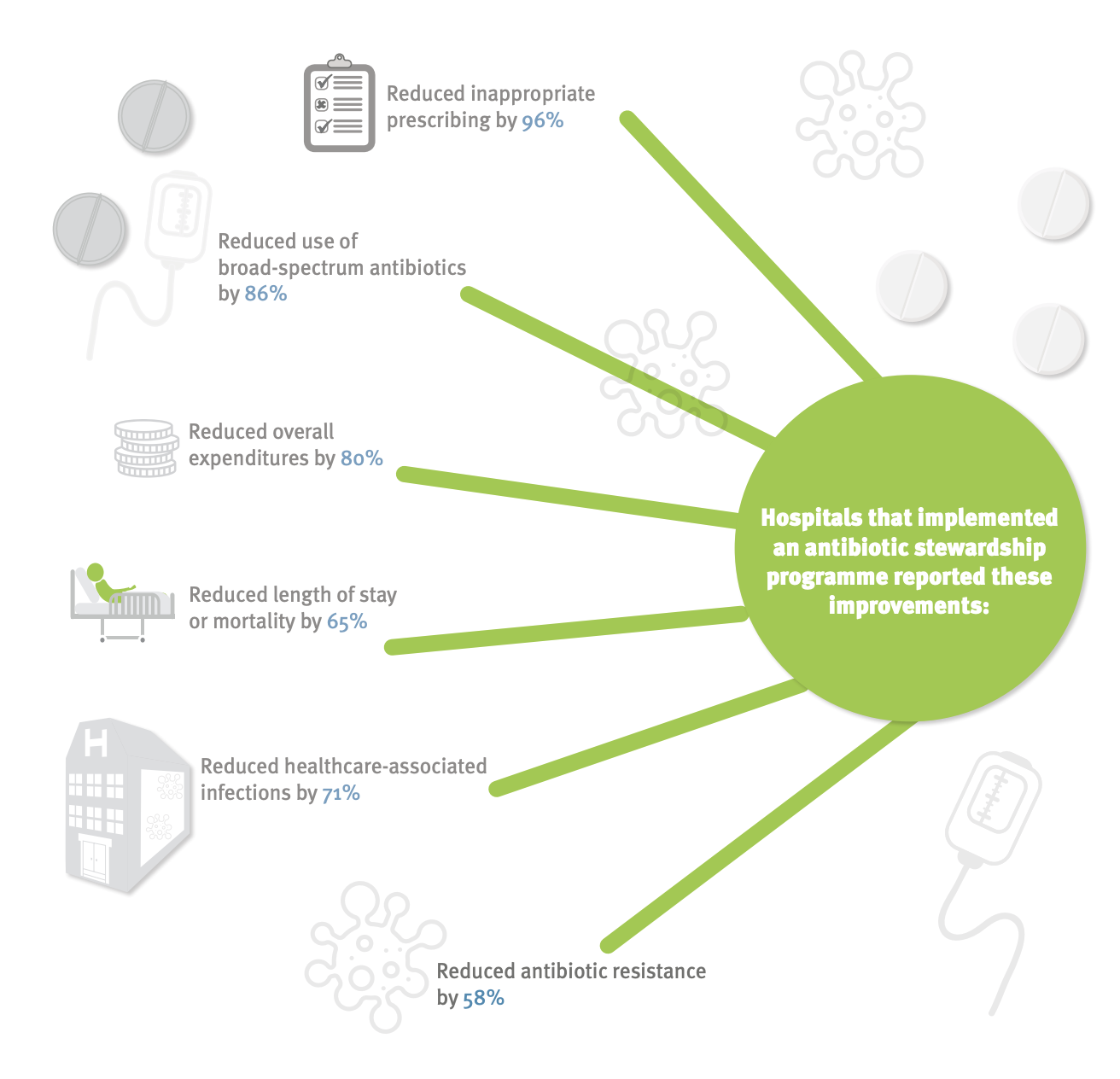
Source:ECDC
Antimicrobial stewardship programs: Success rates (% of studies)
WHO- AWaRe Antibiotic List
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/2021-aware-classification
-
Antibiotics are classified into three groups:
- Access (essential first-line agents)
- Watch (high resistance potential, used in critically-ill)
- Reserve (use only for MDR pathogens-last resort antibiotics)
- Takes into account the impact of different antibiotics and antibiotic classes on antimicrobial resistance, to emphasize the importance of their appropriate use.
- The 2021 update of the AWaRe classification includes an additional 78 antibiotics not previously classified, bringing the total to 258.
Antimicrobial stewardship in Africa-2016
- Only 2 countries had national AMR plans
- 7 had overarching national infection prevention and control (IPC) policies
- 44 had essential medicines lists
- 43 had national medicines policies and treatment guidelines intimating rational use

Essak et al. Journal of Public Health 2016; 39: 8–13
Antimicrobial stewardship in Africa

https://africaguidelines.cddep.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Guidelines_Adults_Peds_English.pdf
Antibiotic Stewardship Programs in Thailand:
Antibiotic Smart Use Program

www.react.org
A self-diagnosis mirror in Thai pharmacies for patients who seek antibiotics for sorethroat
Diagnostic stewardship
Diagnostic stewardship refers to the appropriate use of laboratory testing to guide patient management, including treatment, in order to optimize clinical outcomes and limit the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
Diagnostic stewardship Example:
Urinary Dipstick Tests

The urine dipstick is a rapid semiquantitative assessment of parameters such as pH, heme, albumin, specific gravity, glucose, leukocyte esterase, and nitrite.
- leukocyte esterase may be seen in genitourinary inflammation, irritation from instrumentation or catheterization, glomerulonephritis, UTIs and sexually transmitted infections
- A positive test for nitrite does not diagnose infection in the absence of symptoms
- Given the poor diagnostic utility, current guidelines do not recommend treatment based on the detection of pyuria or bacteruria alone
Advani SD et al. Deconstructing the urinalysis: A novel approach to diagnostic and antimicrobial stewardship. Antimicrob Steward Health Epidemiol. 2021;1(1):e6.
- Widespread indiscriminate use of urinalysis, especially as screening tests in emergency departments, clinics, hospitals and nursing homes, has led to serious downstream consequences (false diagnosis of UTIs and unnecessary courses of antibiotic therapy
- Creates a "reservoir of resistance" for spread in the hospital

Advani SD et al. Deconstructing the urinalysis: A novel approach to diagnostic and antimicrobial stewardship. Antimicrob Steward Health Epidemiol. 2021;1(1):e6.
Diagnostic stewardship:
Example Urinary Dipstick Tests


Modifiable risk factors that
drive antimicrobial resistance
Holmes AH et al. Lancet. 2016 Jan;387(10014):176–87.

One-Health Approach to combatting antimicrobial resistance
What is meant by a One-Health approach?
- Designing and implementing programmes, policies, legislation and research in a way that enables multiple sectors engaged in human, animal, agricultural, and environmental health to communicate and work together to achieve better public health outcomes

Antibiotic use in animals
73% of all antibiotic use is in animals; 66% of human infections are zoonotic in origin
Chicken farm in the United States of America. Image source: The Guardian
Factors influencing animal health
used in food production
-
The genetic stock of the animals
-
Adequate nutrition
-
Hygiene/stress of living conditions
-
Adequate veterinary care
Prophylaxis- antibiotic therapy administered to a single animal to prevent infections
Metaphylaxis- Antibiotic therapy administered to a population to prevent an infection
antibiotics are often used as low-cost substitutes for expensive hygiene measures
Long-term, low-dose mass antibiotic treatment for purposes of growth promotion
- Practice started in 1960's with observation of increased weight gain in cattle and chickens fed antibiotics ...now used to increase profits
- While antibiotic use has stabilized and decreased in HICs, it is increasing in LMICs where meat and milk consumption is increasing as poverty decreases

Boeckel, T. P. V. et al. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112, 5649–5654 (2015).
Only in the last 10 years has antibiotics in livestock begun to be reduced. New EU regulations banning metaphylaxis in 2022
www.resistancebank.org

Chicken Farm in San Diego, California. Image: The Guardian


ceftriaxone
ceftiofurum
Used for
Metaphylaxis in animals
Essential antibiotic in humans
Example- Cephalosporins

Outbreaks of multidrug resistant (MDR) Salmonella Heidelberg infections have been reported in humans working with cattle and chickens- assocaited with cetifior (3rd generation cephalosporin) injection in young hatchlings
Publich Health Authority of Canada - UPDATE - Salmonella Heidelberg Ceftiofur-Related Resistance in Human and Retail Chicken Isolates - 2006 to 2008. (2009).

Pigs in cages, Quanzhou, China. Van Boeckel et al. Science 357, 1350–1352 (2017).

- Colistin-used in veterinary and human medicine for 50 years
- Intravenous colistin has surged in the last decade with the increase in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Even as human use has increased, colistin continues to be used in Brazil, (formally Europe) and rencently banned in China as growth promoting and antibiotic treatment for pigs, poultry and calves.
Example- Colistin
Liu, Y.-Y. et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 16, 161–168 (2016).


Countries reporting plasmid-mediated colistin resistance
encoded by mcr-1
Frost, I, Van Boeckel, T. P., Pires, J., Craig, J. & Laxminarayan, R. Global geographic trends in antimicrobial resistance: The role of international travel. Journal of Travel Medicine 26, taz036 (2019).

Environmental factors driving antimicrobial resistance
Singer, A. C., Shaw, H., Rhodes, V. & Hart, A. Review of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Environment and Its Relevance to Environmental Regulators. Frontiers in Microbiology 7, 1728 (2016).
Cross-border spread of AMR

World airline travel routes 2014. Photo credit Jpatokal/Wikimedia (CC BY-SA 2.5)

WHO Pandemic Treaty 2024
Summary
- AMR is a persistent and growing global health threat that threatens to reverse a half-century or medical and economic progress
- Multiple modifiable risk factors are fueling an increase in AMR, with human and animal antimicrobial use/misuse a major driver-One Health Approach is Needed
- The dissemination of AMR is increasingly more rapid and does not respect boarders- international cooperation is essential
Microsoft Teams Exercise
This simulation exercise was organised by ECDC with the cooperation of the Italian Ministry of Health.
The Exercise sought to bring two themes together, the emergence of a pandrug resistant bacteria in a healthcare setting as a cross-border threat to heath. The exercise provided an opportunity for countries to share knowledge, capabilities, experiences and best practices on how to respond individually and collectively to the challenges of this type of threat.


How this exercise will be run
-
Each student has been assigned to a group (EU country) in a separate virtual classroom:
- Group 1: Spain/Portugal
- Group 2: Italy
- Group 3: Greece
- Information on an outbreak will be posted in the Virtual classroom group chat; with questions for discussion. You should already find the first posting in your group classroom
- Discussion of questions should preferably be discussed through the chat feature; or if using live audio discussion, post your responses in the chat after discussion
- Every 5-10 minutes information will be updated with a new posting update about the epidemic.
- An instructor/ tutor will monitor the discussion and provide possible suggestions, try to answer answer any possible questions, ask follow-up questions etc.
- At the finish of the exercise (30-45 min) we return to the main classroom for a wrap-up
Key considerations...
- The goal is not provide the "correct" answer
- Information will be incomplete as you try to answer questions or provide recommendations....clarifying information later may come in subsequent postings and could change your recommendations
- The objectives of this exercise are to illustrate how a cross-border epidemic of antibiotic resistance unfolds, and the types decisions that need to be made.
A community-acquired pathogen

Russo and Marr. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2019

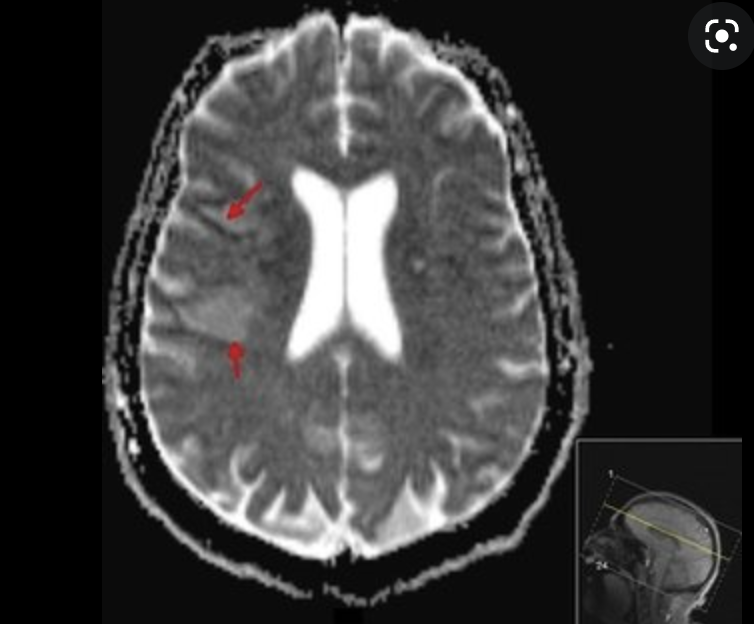

Cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis
endophthalmitis
meningitis, vasculitis, stroke,
brain abscess

Hepatosplenic abscess

Positive "string test"
Hypermucoviscous phenotype seen in Klebsiella pneumoniae -
an indicator of hypervirulence