97039: Global Health, Antimicrobial Drugs and Vaccines
Module 3: Antibiotic and diagnostic test availability, affordability and access: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic
Russell Lewis, Associate Professor
Infectious Diseases, IRCSS S. Orsola-Malpighi Hospital
Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences
russeledward.lewis@unibo.it

Alma Mater Studiorum
Università di Bologna
Follow-up: X-1 antibiotic exercise
X-1
+
ertapenem
placebo
+
meropenem
Hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia/associated pneumonia HABP/VAP
non-inferiority trial, -Δ 30%
- 600 screened
- 192 (x-1, 69 P. aeruginosa)
- 96 (meropenem, 34 P. aeruginosa)
The trial program was implemented over a 36-month period at 250 sites in 20 countries.

Pseudomonas-positive patients

met -Δ 30
This was all Pseudomonas aeruginosa-
not MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Do you think this study provides sufficient evidence for approving X-1 for the treatment of HABP/VABP caused by Pseudomonas pneumonia?
Do you think this study provides sufficient evidence for approving X-1 for the treatment of HABP/VABP caused by MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia?
What do you think would be the effect of 1-2 patients changing outcome on the overall trial results?
Consensus answer: With such small numbers it could change the outcome/interpretation of the trial

with 3 fewer responses in X-1 arm, (Δ -8.2; -30.1 to 14.6)
X-1 would not be approved!
consider the trial probably cost at least 25 million dollars. A similar size trial for carbapenem-resistant organisms (based on Achaogen experience may cost as much as 350 million)
What is your impression about the possible effect of prior antibiotic therapy? Should it have been allowed?...Does it obscure evaluation of the efficacy of X-1 for Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Do you think this therapy would be immediately available in LMICs?
What might affect its availibility?

Antibiotic new chemical entities introduced into country markets,
1999–2014.
97039: Global Health, Antimicrobial Drugs and Vaccines
Module 3: Antibiotic and diagnostic test availability, affordability and access: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic
Russell Lewis, Associate Professor
Infectious Diseases, IRCSS S. Orsola-Malpighi Hospital
Department of Medical and Surgical Sciences
russeledward.lewis@unibo.it

Alma Mater Studiorum
Università di Bologna
Learning objectives
- Current access challenges of COVID-19 vaccine, therapeutics and diagnostic access in HICs vs. LMICs
- Strategies used to improve vaccine and therapeutics access in LMICs
- The problems of counterfeit medications
- Applying lessons learned from COVID-19 thusfar to the epidemic of antimicrobial resistance

Image: World Health Organization

COVID-19 has brought into sharp focus the impact of pandemics:
- More than 5.5 million deaths
- Trillions of dollars lost
- A generation of economic and development goals in jeopardy

"There are vital lessons to learn from this tragedy. Now more than ever, governments have the opportunity to make robust and comprehensive investments into the way they prepare and respond to pandemics..."
...including the silent but potentially more deadly epidemic of antimicrobial resistance.
GARDP. Learning from COVID-19 to Tackle Antibiotic Resistance 2020
Current COVID-19 Situation
Collateral effects of COVID-19
- Tuberculosis deaths also climbed worldwide for the first time in a decade.
- Measles outbreaks may be more likely in the near future, after the number of infants missing their first vaccination jumped by 3 million last year—the largest increase in 20 years.
- Malaria’s 241 million cases and 627,000 deaths in 2020 reflect increases of 14 million and 69,000 respectively—both were largely attributed to pandemic disruptions.
WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2021; WHO Interim Guidance for Country Validation of Hepatitis Elimination;
WHO Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2021

11 billion people worldwide must be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2
Currently, just over half have received the vaccine
Image: Lancet Infectious Diseases; Vaccine data: WHO
Ten countries account for 77% of administered vaccines

Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant
Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant
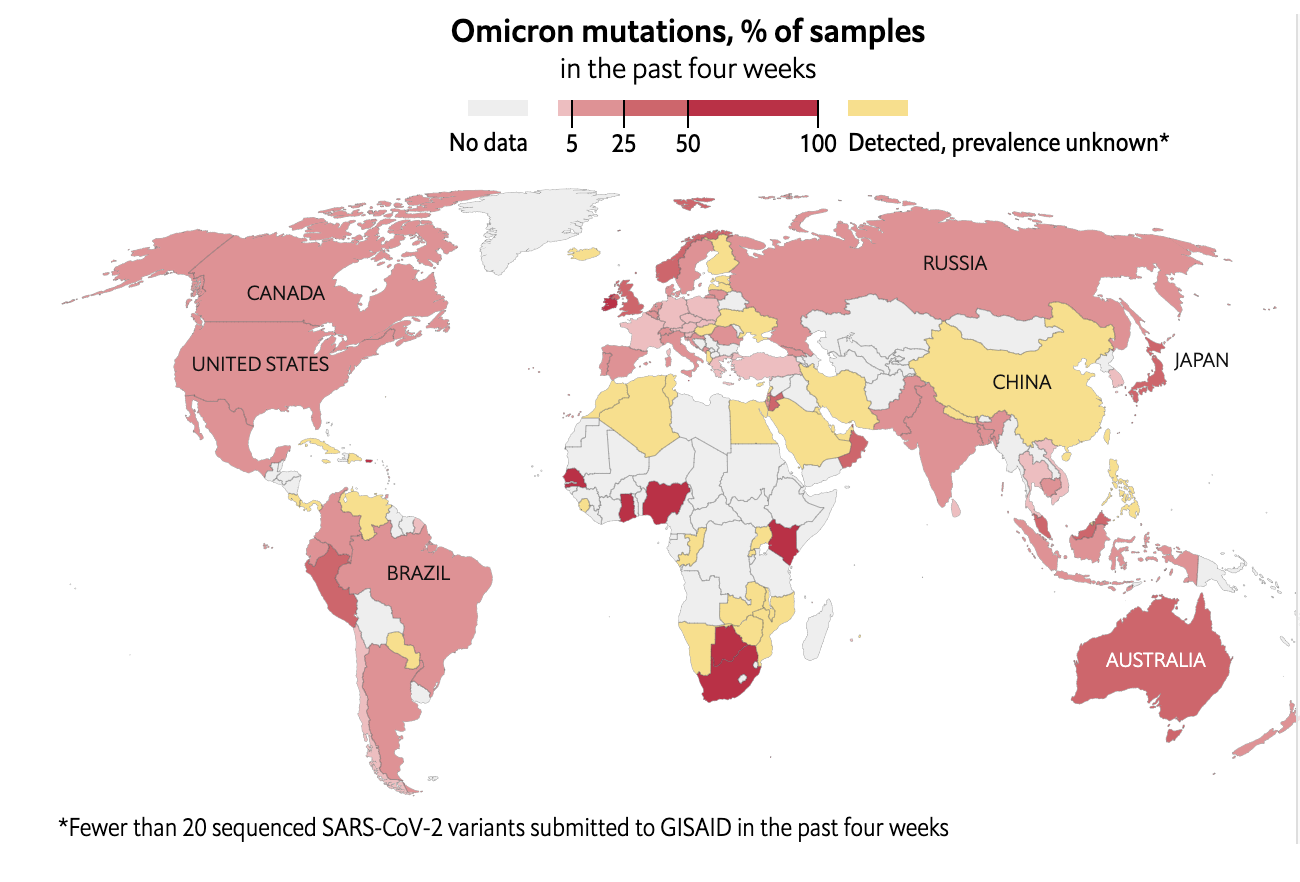
Data source: The Economist December 26, 2021

"It is rather simplistic and naïve to assume that by imposing travel bans and travel restrictions on a few countries reporting the new variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, will prevent importation of the virus, or limit establishment of significant clusters of the Omicron VOC. "
Petersen et al. Int J Infect Disease 2022;114:268-272

"The emergence the VOC Omicron variant and its rapid spread reflects the legacy of wealthy nations’ failure to equitably distribute COVID-19 vaccines globally. This failure also contributes to prolonging the pandemic, and has placed the whole world at continued risk of COVID-19 and continuing impact on their economies."
Petersen et al. Int J Infect Disease 2022;114:268-272


COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access Facility
COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access Facility (COVAX)
High-income
countries (HIC)
Low-income
countries (LIC)
pool resources to back development of multiple vaccine candidates

HICs subsidize vaccine manufacturing
Initial COVAX goals
- Doses for at least 20% of countries' populations
- Diverse and actively managed portfolio of vaccines
- Vaccines delivered as soon as they are available
- End the acute phase of the pandemic
- Rebuild economies
How did COVAX fare during the first
phases of the pandemic?
-
To reach 20% vaccination target, 100 million doses of COVID-19 vaccine were required by the end of March 2021
- This goal was not reached until 6 July 2021. By mid-August of 2021, COVAX delivered 200 million vaccine doses to nearly 140 countries instead of the 600 million doses initially projected.
- Currently, less than 12% of population of sub-Saharan Africa are still vaccinated against COVID-19 (25% in South Africa)
- In some regions, health officials are still struggling to receive enough vaccines to protect workers on the front lines of the pandemic
UN Dashboard for Global Vaccine Equity
COVAX problems
-
WHO set a target for all countries to vaccinate 10% of their populations by the end of September.
-
56 countries effectively excluded from the global vaccine marketplace were not able to reach this target – and most of them in Africa
-
-
Even more countries are at risk of missing the WHO targets of vaccinating 40% of the population of every country by the end 2021, and 70% by the middle of next year
-
A key initial source of vaccine for LMICs was the Astra-Zeneca/Oxford vaccine (less cold-storage requirements) manufactured by the Serum Institute of India (cost $4 dollars per dose vs. $20 per dose-Pfizer)
COVAX problems cont.
- When a third COVID-19 (delta variant) wave hit India, over 400 million doses of the Oxford--AstraZeneca vaccine were diverted for domestic use and not shipped to other LMICs
-
High-income countries ultimately did not surrender their negotiating power to international organizations such as COVAX.
- The US, EU, Canada, UK, Australia, and New Zealand secured >200% population coverage worth of vaccine doses, leaving insufficient doses for LMICs and COVAX
-
Most manufacturers have spurned the opportunities to share technology for vaccine manufacturing
- recent approval of mRNA vaccine technology transfer hub in South Africa
What can be done to address COVID-19 vaccine dose inequity?
- Bilateral donation of COVID-19 vaccine (e.g., U.S.A. → Haiti)
- Multilateral donation of COVID-19 vaccine (e.g., U.S.A, E.U., Australia → Gavi, WHO, COVAX)
-
Creation of manufacturing capacity in LMICs (e.g., Africa)
- Temporary intellectual property waiver from producer
-
Improvements in allocation and vaccine delivery infrastructure
- Donating only almost-expired vaccine



But there’s a glimmer of hope. Covax ended the year strong: December brought a last-minute surge of deliveries, with about 300 million doses of Covid-19 vaccines shipped to 144 mostly low- and middle-income countries. That is roughly a third of the total of vaccine doses Covax delivered in 2021 — in only one month
Planned Phase 2 of COVAX
- Epidemiological approach: consisting of weighted allocation depending on the proportional coverage requested by countries and consideration of vulnerability and ongoing severity of the COVID-19 threat.
- This would require sophisticated country level data collection that will take time to establish.
Other SARS-CoV-2 Challenges in both HIC and LMICs
Diagnostic testing
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Social distancing/restrictions

Example: Dense urban housing in Mumbai, India
(73% of households reported living in two rooms)

Sustenance farmers, or a high percentages of workers who must work "no matter what" to survive
Hospital beds and medical professionals:
LMIC vs. HICs

-
Hospital beds/1000 residents:
- 0.8-2.3 in LMICs vs. 30-80 in HIC
-
Fewer than 10 doctors per/10,000 residents
- 90% of LICs vs. 5% of HICs.
-
Fewer than 40 nursing personnel/10,000 residents
- Up to 93% of LICs vs.19% of HICs
Source: WHO Hospital Bed Survey
Intensive Care
LMIC vs. HICs
-
Beds per 1 million inhabitants:
- Africa: 5 beds
- Europe: 4000 beds
- Equipment in LMICs often older, may not have appropriate service or lack oxygen or medical gas
- Long distances and high transportation costs may delay arrival to ICU
Source: WHO Hospital Bed Survey


LMIC access to COVID-19 Therapeutics:
(oxygen, antiviral therapies, IL-6 inhibitors, MoAb)
COVID-19 Tools Accelerator (ACT)-includes COVAX program
COVID-19 therapeutics availability in LMICs
- Corticosteroids: Dexamethasone, budesonide (available)
- Antivirals: Remdesivir, molnupiravir, ritonavir/nirmatrelvir
- IL-6 pathway inhibitors: (e.g., tocilizumab) (not available)
- JAK inhibitors (e.g., baricitinib) (not available)
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and convalescent plasma (not available)
- Other agents with less data (e.g., fluvoxamine)

Pharmaceutical company/
patent holder (innovator)
Manufacturing in
LMIC
Distribution
Image:Medicines Patent Pool

Addressing the intellectual property (IP)
manufacturing barrier
Medicines patent pool-Advantages

Image:Medicines Patent Pool

MPP-COVID-19
- mRNA Vaccine Technology Transfer Hub initiated in July 2021.
- The first COVID-19 mRNA vaccine technology transfer hub has been established in South Africa.
- The MPP has also entered into license agreements agreements for:
- Merck's molnupiravir
- Pfizer ritonavir/nirmatrelvir oral COVID-29 therapies
- ELISA technology platforms for diagnostics

MPP-Other therapeutic areas
-
HIV/AIDS
-
One- third of the people requiring treatment for HIV/AIDS have access to therapy.
-
The MPP has signed agreements with 10 patent holders for 13 HIV antiretrovirals and a technology for injectable long-acting HIV drug combination technology.
-

MPP- Hepatitis B (HBV) & Hepatits C (HCV)
- 58 million people live globally with HCV, many of them in LMICs, with the vast majority remaining undiagnosed and untreated.
-
New direct-acting antivirals (DAA) that are effective across all major HCV strains (95% effective) can cure millions.
-
Approximately 84% of the people infected with HCV are not receiving treatment- 290,000 deaths per/year from cirrhosis and liver cancer.

MPP- Hepatitis B (HBV) & Hepatits C (HCV)
-
MPP signed licence agreements for three HCV treatments: daclatasvir (DAC) in 2015, ravidasvir (RAV) in 2017 and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (G/P) in 2018.
-
Licenses also secured for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) for patients with HIC and chronic HBV infection

MPP- Tuberculosis
-
Tuberculosis (TB) is a global pandemic affecting around 10 million people worldwide.
-
In 2018, the disease caused 1.5 million deaths, and it is the leading killer of people living with HIV.
-
Almost 90% of TB deaths occur in LMIcs
-
The World Health Organization's post-2015 Global TB Strategy sets ambitious targets aimed at reducing TB deaths by 95% between 2015 and 2035, and to end TB.
-
To meet these targets, faster acting, better therapies to treat TB are urgent, particularly for multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).

MPP- Tuberculosis
- The MPP's focus is to secure access to new treatments for MDR-TB and drug-susceptible tuberculosis.
-
The MPP also facilitates the development of new regimens by licensing TB drugs that are still under development.
- In early 2017, MPP signed its first agreement with the Johns Hopkins University to facilitate the clinical development of sutezolid, a promising investigational treatment for tuberculosis.
- It was followed by a second agreement with Pfizer in October 2019 to access Pfizer's preclinical, phase I and phase IIa clinical study data and results on sutezolid.

Is the Medicines Patent Pool Working?




"38-year-old man in Birmingham, UK has been arrested in connection with the sale of fake COVID-19 testing kits which were sold online."
source: SkyNews UK
"There is a growing online trend of fake websites that mimic real pharmaceutical websites where COVID-19 vaccines are sold up to $1000 and vaccine certificates for $200"

Source: BBC news
What is a counterfeit medication?
According to Interpol:
-
Contains too much or too little of one or more ingredients, or containing different ingredients
-
Claiming to have different properties or side effects
-
Having a different shape, size, taste, or colour
-
Being not correctly labelled or not labelled at all
-
Having an out-of-date or missing expiry date
-
Not including information on how to store the medicine
-
Having packaging that looks poorly constructed, is labelled with spelling or grammar errors, or appears to have been interfered with
How common are counterfeit medications?
- Limited data suggest estimated prevalence HICs: 1% vs. 10% in LMICs; however data are limited
- Nearly 170,000 children die annually of pneumonia from falsified antibiotics worldwide
- Substandard or fake anti-malarial medications are estimated to cause 116,000 deaths annually in sub-Saharan Africa
- Antibiotics are the most commonly counterfeited medications -account for 28% of seized medications

Delepierre A et al. Update on counterfeit antibiotics worldwide; Public health risks. Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses. 2012 Jun;42(6):247–55.
Where do counterfeit medications come from?

Figure source: Financial Times

What is the motive for selling counterfeit medications?
- Counterfeit pharmaceuticals are 25x more profitable than heroin and 5x more profitable than cigarettes
-
Many legal systems do not consider public health consequences of counterfeit prescription drugs
- Less severe penalties than selling illicit drugs
-
Similar penalties as counterfeiting luxury handbags or T-shirts
- Fine in India: $108
Specific problems for antibiotics
- Typically "older" antibiotics from the WHO essential medicines list; beta-lactams, tetracyclines, trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol
- Increased risk of adverse effects because of different active ingredients, toxic chemicals or contaminants
- Increased risk of resistance if counterfeit antibiotic has expired or inadequate drug concentrations

An agent stands next to a container full of illegal and false drugs seized by Ivorian authorities in Abidjan, Ivory Coast November 6, 2018. Picture taken November 6, 2018. REUTERS/Luc Gnago

How is the problem of countnerfit medications being addressed?
- Guidance for legal reforms in heavily impacted countries
- Implementation of new regulations for improving control, tracking, procedures
- Coordination with international policing and customs
- Development of new technology for tracking and monitoring drug supply chains, traceability and verifications (i.e. RFID tags)-now mandated by new European Medicines Agency regulations
- Medicrime convention-multinational judicial organization that prosecutes drug counterfeiting

Lessons for
antibiotic resistance?
Summary: COVID-19 and lessons for the AMR crises

- Invest and prepare now for future crises
- Collaboration and international coordination are critical
- We cannot rely on markets to ensure global access to medical treatment, vaccines and diagnostic tests
- Equitable and affordable access to medical therapies is essential for controlling a pandemic response:
- None of use are safe until all of use are safe
GARDP. Learning from the COVID-19 to Tackle Antibiotic Resistance

