classes
part 1
class overview
- Homework Solution
- Classes
- Aggregation
- Constructors
- Encapsulation
- Access Modifiers
- Static & Final
- Inheritance
classes
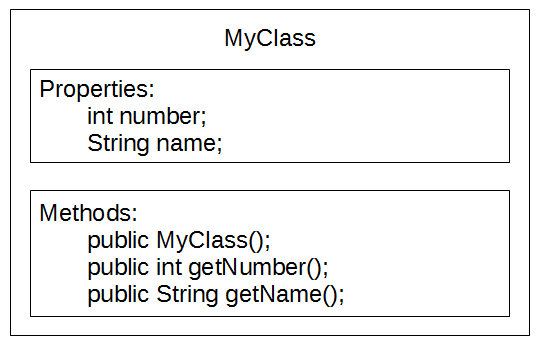
- A Class is a combination of state and behavior
- State: Class properties
- Behavior: Class methods
classes & objects
- An Object is an instance of a Class
- Class is a "blueprint" to build an Object
Class Object
furniture class
- Properties
- int height
- int depth
- int width
- Methods
- int volume()
- String toString()
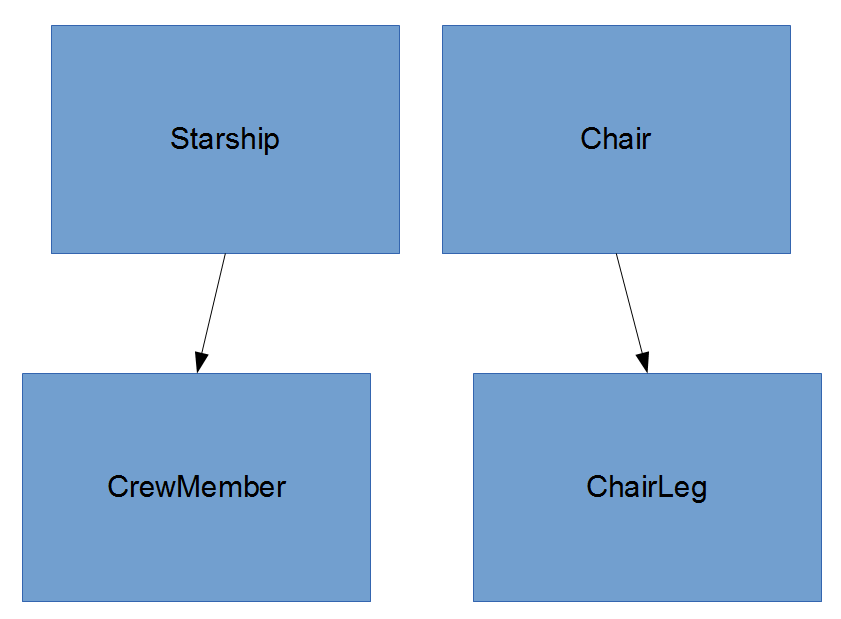
aggregation
- "has-a" relationship
- One Class contains an instance of another Class
aggregation syntax example
Class Starship {
int warpSpeed;
int distanceTraveled;
CrewMember [] crew;
CrewMember captain;
public boolean travelTo(int xCoord, int yCoord, int zCoord);
public void teleport(CrewMember crewMember);
}
Starship enterprise = new Starship();
CrewMember spock = new CrewMember();
enterprise.teleport(spock);
location class
- Properties
- double lat
- double long
- Methods
- void set(double lat, double lng)
- String toString()
constructors
- Java provides a default constructor
- ie. Furniture()
- Best practice to pass required parameters through constructor
//Furniture constructor
public Furniture(int height, int width, int depth) {
//set properties
}
//Table constructor use
Furniture t = new Furniture(3, 5, 3);
System.out.println(t.volume());
constructor rules
- Constructor has the same name as the Class
- No return value is declared
- It can have arguments
- Once you define a constructor, Java does not provide a default
encapsulation
- Concept of restricting access to Class properties by making them private and allowing public access through public methods
- Very common practice in Java
Class Starship {
private int numberOfCrewMembers;
private int crewLimit = 15;
public void setNumberOfCrewMembers(int crew) {
if(crew <= crewLimit)
numberOfCrewMembers = crew;
}
}
access modifiers
- Access Modifiers are used to expose behavior that is useful to the user of a Class.
- public
- Anyone can read or write the property or execute the method
- protected
- Only sub-classes can read or write the property or execute the method.
- private
- Only the current Class can read or write the property or execute the method.
static & final
- static
- Variable/Method isn't tied to an Object instance
- Modifies a variable/method to be at Class level
- final
- Variables can only be set once
- Method can only be defined once (Can't be overridden)
- Classes can't be overridden or extended
public static int aNumber = 3;
public static String convertString(String word);
public final int anotherNumber = 2;
public final void finalMethod(int number);
public final class SomeClass{ }