classes &
oo principles
class overview
- Homework Overview
-
Overriding Methods
- Abstract Classes
- Interfaces
- Object Oriented Principles
- Shape Class Refactor
overriding methods
- Method overriding occurs when you re-define a method that is already defined in a parent-Class.
- You'll typically override methods from Object like equals() and toString().
- The @Override tag helps to make the overriding explicit. The Java compiler will catch you if it's not overriding.
public class Starship {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "I'm a Spaceship!";
}
}abstract classes
- Add "abstract" modifier to a class
- Cannot be instantiated, only sub-Classed
- Methods can also be abstract (but the Class has to be abstract as well), and have no definition
- If a sub-class does not implement the abstract methods, it must also be abstract
public abstract class Animal {
public abstract void breathe();
}
public class Dog extends Animal {
public void breathe() {
//breathe stuff
}
}interfaces
- Interfaces are similar to Classes, but only contain constants and method declarations, no implementations.
- Cannot be instantiated, only implemented by Classes.
- Implementing Classes must define any Interface methods, unless Abstract
public interface Feedable {
public void feed(String food);
}
public class Dog implements Feedable {
public void feed(String food) {
//feed implementations
}
}oo principles review
-
Package - used to group related sets of classes together, and give them a namespace. The fully qualified name of a class is it’s package name + class name. The fully qualified name of the class must be unique.
-
Interface - contains only method declarations and static properties. Used for communicating expected method signatures between integration projects.
-
Abstract class - Cannot be instantiated. May contain properties, methods, or abstract methods (abstract methods are only declaration). Any subclasses that inherit from the Abstract class must implement those abstract methods.
-
Aggregation - A class defined as having a reference to one or more objects of another class.
-
Inheritance - A class that inherits from another class. Inherits all it’s properties and functions. It extends a base class.
- Encapsulation - Hiding properties or functions of the class that you don’t want everyone to be able to invoke.
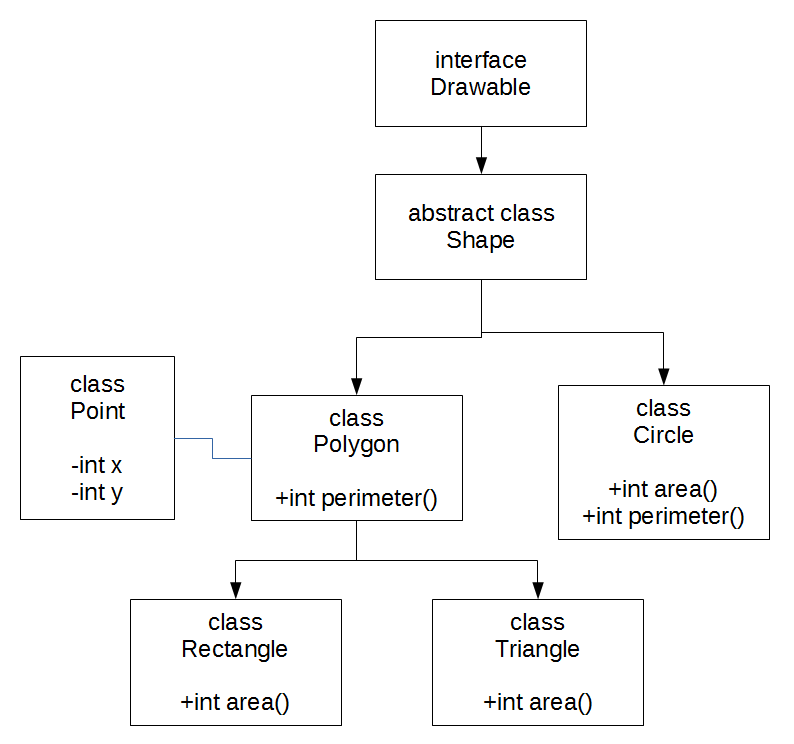
shape class refactor
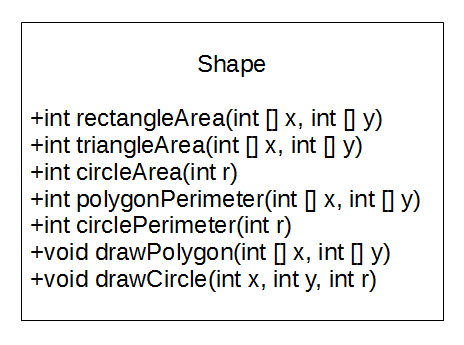
better shape