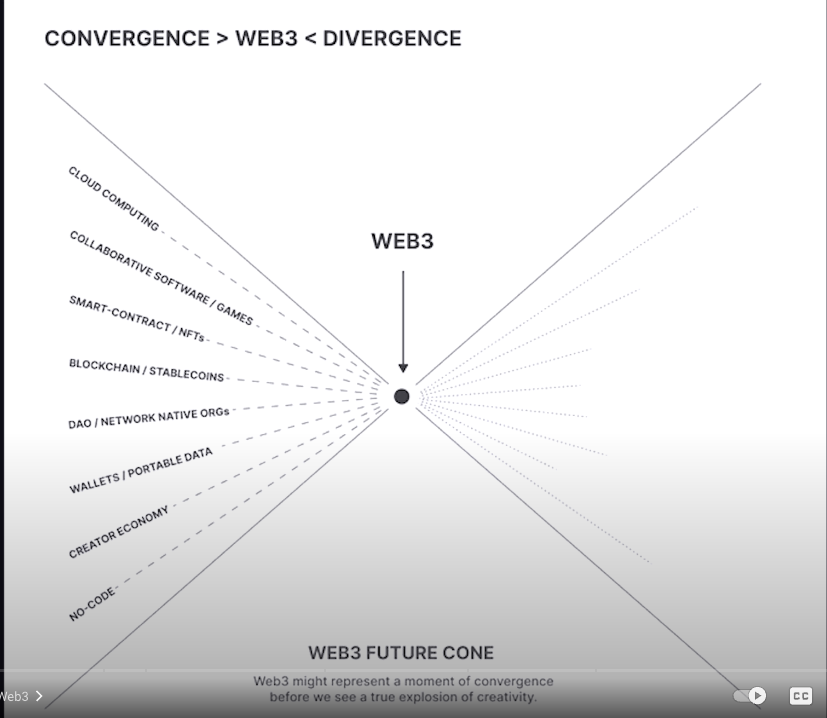
Web3

Saad Bin Amjad
Lead Backend Engineer I
Monstarlab Bangladesh
and the future..

Deep Thinking Book Image
Agenda
1. Evolution of Web
2. Web3 Expectations
3. Blockchain
4. Smart Contracts
5. Token Economy
6. Daos
7. Dapps
8. Metaverse and beyond
7. Developer Tools
8. FAQs and Trends
Evolution of the Web
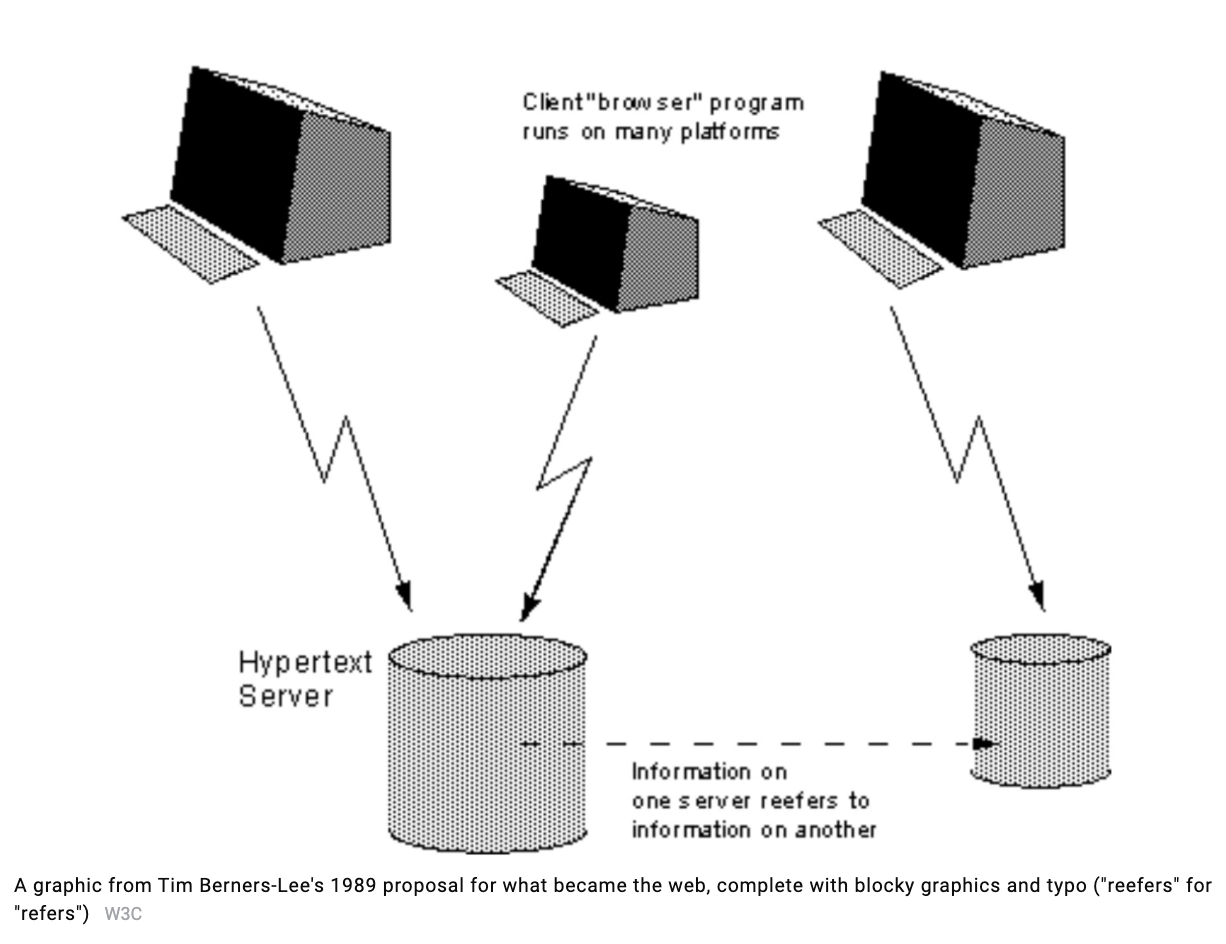
https://worldwideweb.cern.ch/browser/
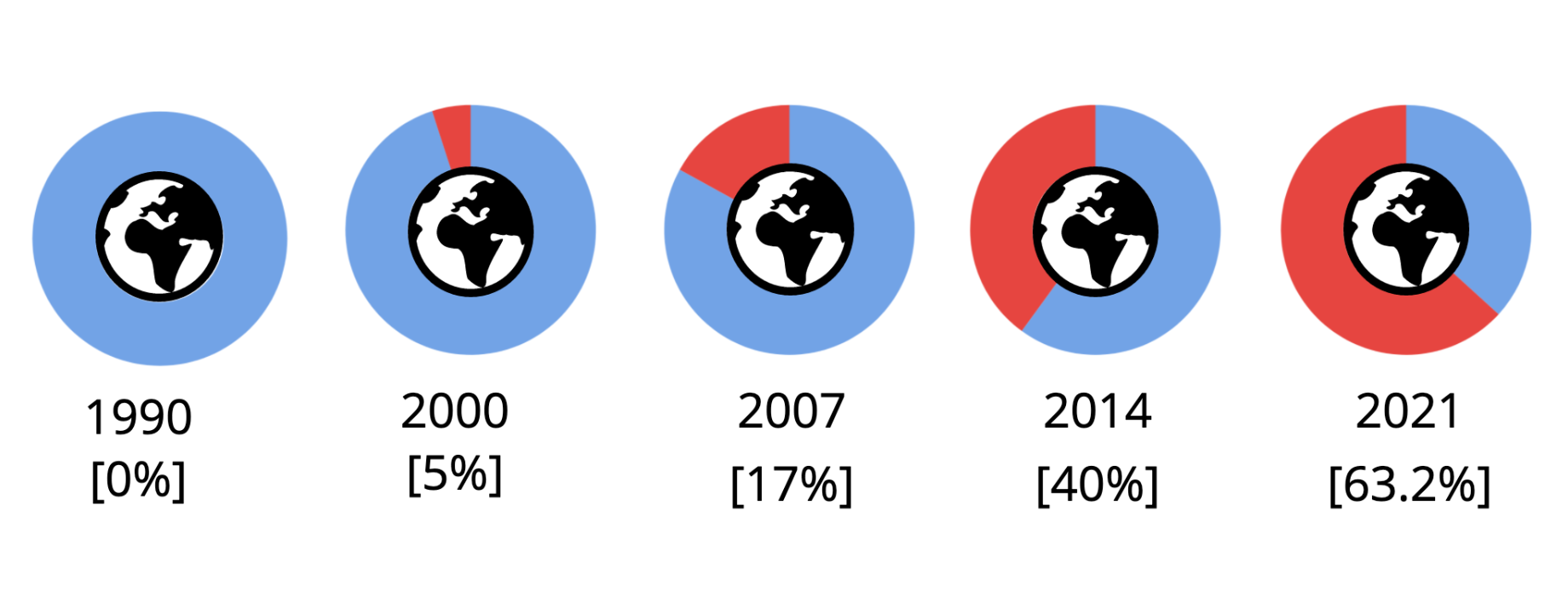
People connected to the internet.
Link: https://www.ted.com/talks/tim_berners_lee_a_magna_carta_for_the_web#t-30157
https://www.broadbandsearch.net/blog/internet-statistics
-
1990s-2003
- 1990: First website
- 1991: Linux, free operating system kernel was born.
- 1992: First Image was posted online
- 1993: Mosaic 1.0 Graphical Browser, Landing page MTV Website
- 1994: Netscape launched to the public, Yahoo, PHP, W3C Common Standard for Web Development.
- 1995: Table format website, JS was introduced.
- 1996: CSS invented, JS used for affects, Google was launched in Stanford Uni's network.
- 1998: Google was founded
- 1999: Web 2.0 was coined, and Zend was found, IoT was also coined.
- 2000: Flash 5 and ActionScript 1, animated content and flash games.
- 2003: Wordpress, dynamic content instead of static.
-
2004-till date
- 2004: First Web 2.0 Conference Held, Facebook was born.
- 2008: Chrome Browser was launched, so was Github.
- 2007: iPhone was launched.
- 2005: Ruby on Rails was released.
- 2006: Sass was created, css with superpowers.
- 2009: Node.js was born, Blockchain was born
- 2010: Responsive Design, Google Fonts, and Laravel was released, AngularJS was born.
- 2011: Bootstrap, React.js
- 2012: Media Query, parallax..
- 2013: React.js was born
- 2014: 3D WebGL, Transform, Web3 was coined
- 2015: HTML5 and dropped YouTube dropped Adobe Flash Player, PWA was introduced, TensorFlow.
- 2016: Google Assistant was released.
- 2018: NestJS released.
- 2021*
Link: https://www.webdesignmuseum.org/web-design-history
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XYTwYmOjqQs&list=LL
https://www.theverge.com/2018/9/5/17823490/google-20th-birthday-anniversary-history-milestones
Web 1.0
the “read-only web.” In other words, the early web allowed us to search for information and read it.
The era of decentralised, open protocols, in which most online activity involved navigating to individual static webpages.
Link:
https://www.practicalecommerce.com/Basic-Definitions-Web-1-0-Web-2-0-Web-3-0

Web 2.0
also know was Participative (or Participatory) and Social Web) refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, ease of use, participatory culture and interoperability for end users.
"The era of centralization, in which a huge share of communication and commerce takes place on closed platforms owned by a handful of super-powerful corporations—think Google, Facebook, Amazon—subject to the nominal control of centralized government regulators"
Link:
https://www.practicalecommerce.com/Basic-Definitions-Web-1-0-Web-2-0-Web-3-0
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_2.0
https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/Web-30

Web 3.0 or Web3
Gavin Wood, coined Web3 term in 2014.
is supposed to break the world free of the web 2.0 monopolistic control.
Decentralized online ecosystem based on the blockchain. Platforms and apps built on Web3 won’t be owned by a central gatekeeper, but rather by users, who will earn their ownership stake by helping to develop and maintain those services.

Are we really talking about a failure of technology? Or are we talking about a failure of governance and regulation and competition policy? It sounds like you’re saying: Yes, it’s a failure of regulation, but the answer isn’t better regulation; there needs to be a new layer of technology, because regulatory failures are inevitable. Am I characterizing your view correctly?
Yeah, absolutely. The model is broken.
Link:
https://www.wired.com/story/web3-gavin-wood-interview/

Web3 Expectations
"Hanging out with cool people, changing the world for the better, and becoming a millionaire are three of my top interests, as well".
"To technologists and cryptographers, Web3 has remained a theoretical grand vision for years. But in recent months, the push for a blockchain-powered future has come to dominate tech conferences and social media chatter in certain circles. It's even forced major tech companies to assemble teams dedicated to Web3."
"where, for instance, every time you post a message, you earn a token for your contribution, giving you both ownership stake in the platform and one day a way to cash in.".
Blockchain
Decentralised And Distributed
A decentralized system is a subset of a distributed system.
Decentralized means that there is no single point where the decision is made. Every node makes a decision for it’s own behaviour and the resulting system behaviour is the aggregate response.
A distributed network is similar to a decentralized network in the sense that it forgoes a single centralized master server in favor of multiple network owners. However, distributed networks are composed of equal, interconnected nodes, meaning that data ownership and computational resources are shared evenly across the entire network. T
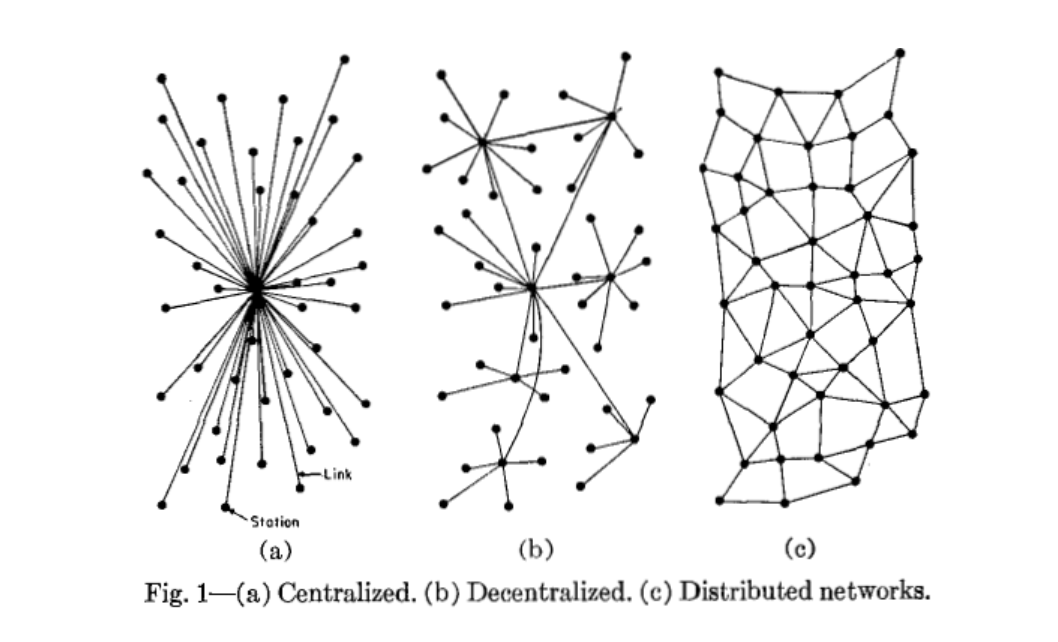
Link: https://medium.com/@VitalikButerin/the-meaning-of-decentralization-a0c92b76a274
https://medium.com/distributed-economy/what-is-the-difference-between-decentralized-and-distributed-systems-f4190a5c6462
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/blockchain-network-decentralized-distributed-centralized
Blockchain
Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
Different way of architecting the internet.
Blockchain technology uses both cryptography and certain game theory economics to deliver its service.
Link:https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchain.asp
https://www.theverge.com/22654785/blockchain-explained-cryptocurrency-what-is-stake-nft
https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/02/19/239592/once-hailed-as-unhackable-blockchains-are-now-getting-hacked/
A blockchain is a cryptographic database maintained by a network of computers, each of which stores a copy of the most up-to-date version.
A blockchain protocol is a set of rules that dictate how the computers in the network, called nodes, should verify new transactions and add them to the database.
The protocol employs cryptography, game theory, and economics to create incentives for the nodes to work toward securing the network instead of attacking it for personal gain.
Link: https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain
Blockchain
Imagine Git where you commit once and never update/delete it.
All changes are new commits.
And all the git commits are present to all members, so they verify your before you can commit.
And then your commit is added in the chain.
Image: https://about.gitlab.com/blog/2018/06/07/keeping-git-commit-history-clean/
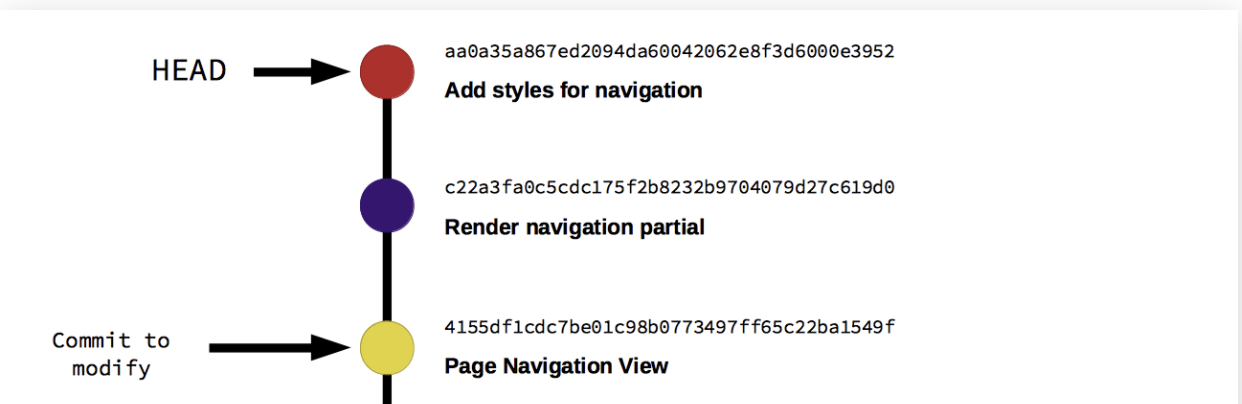
Git is a Merkle Tree (hash tree) without a predefined consensus algorithm.
Blockchains are Merkle Trees (hash tree) with a predefined consensus algorithm.
While Git offers you complete full freedom of choice, Blockchains are a highly political system, where you are forced to trust in others
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46192377/why-is-git-not-considered-a-block-chain
Consensus Algoritm
Blockchain lets you agree about data with strangers on the internet
Link: https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain
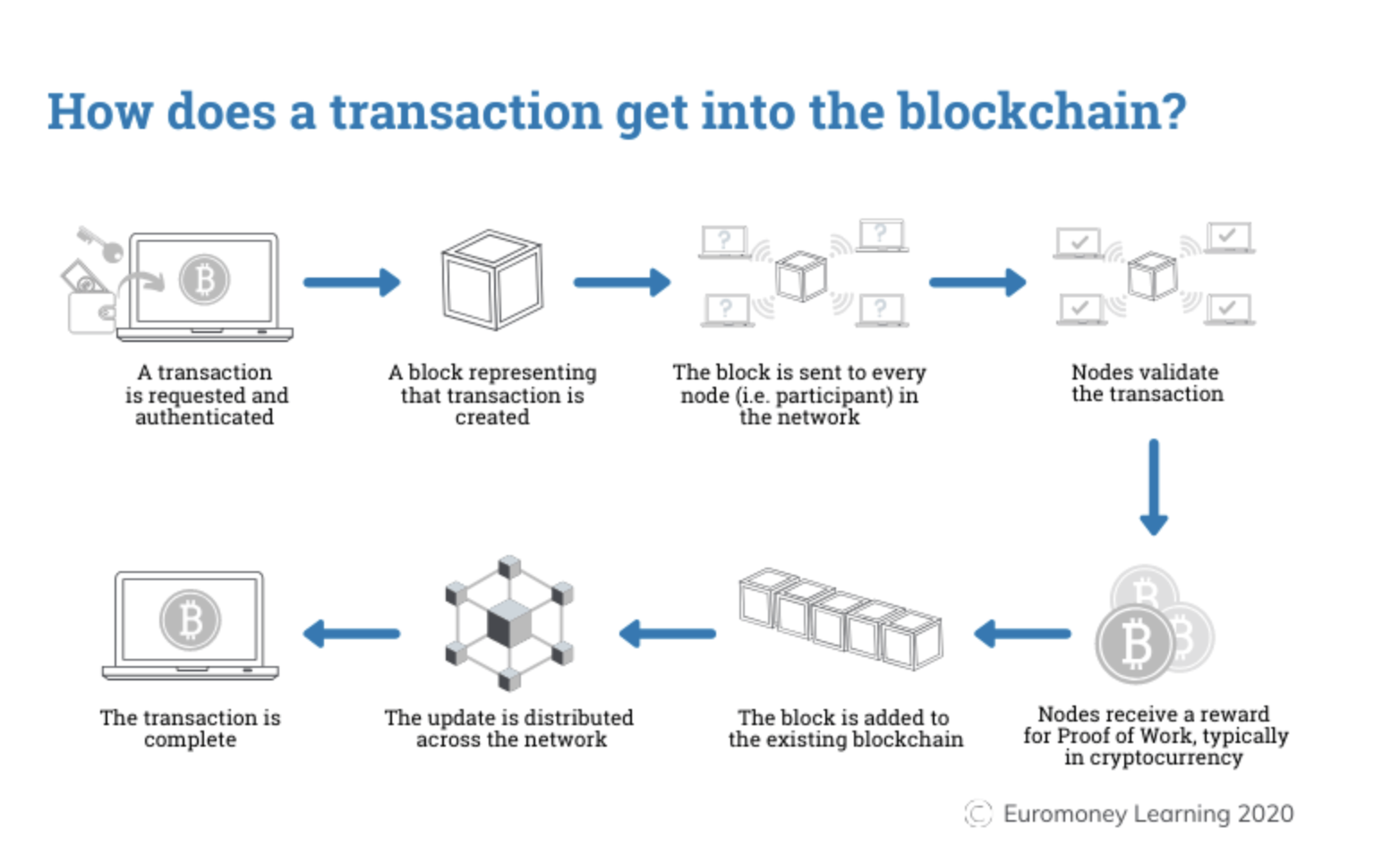
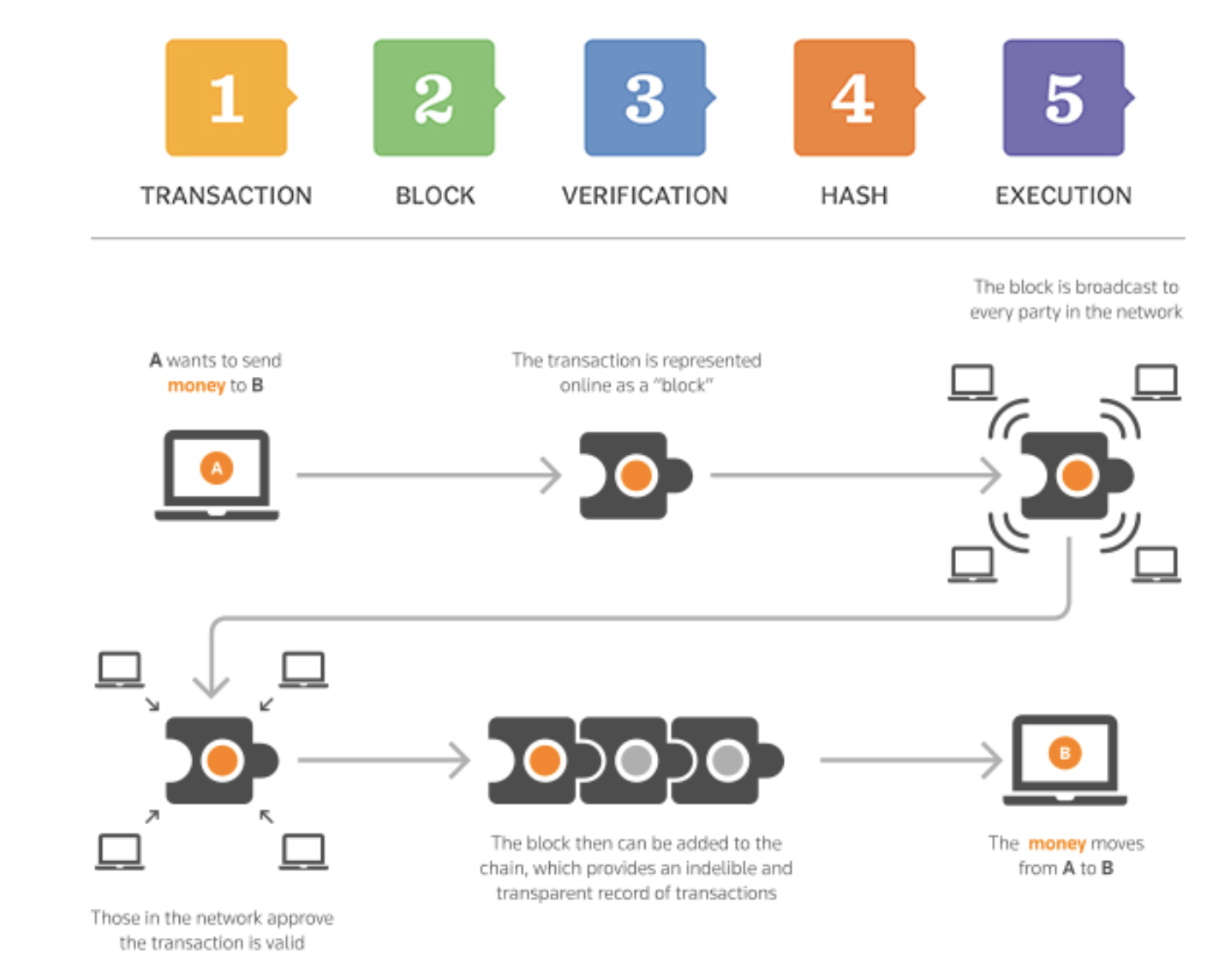
Proof of Work
Proof of State
Hashing is a cryptographic technique that’s been essential to all sorts of computing since the 1950s and ‘60s, and blockchains use it to prevent tampering.
In blockchains, hashes basically act as unique tags that prevent someone from changing data in a block, or even swapping in a fake block.
Link: https://www.theverge.com/22654785/blockchain-explained-cryptocurrency-what-is-stake-nft
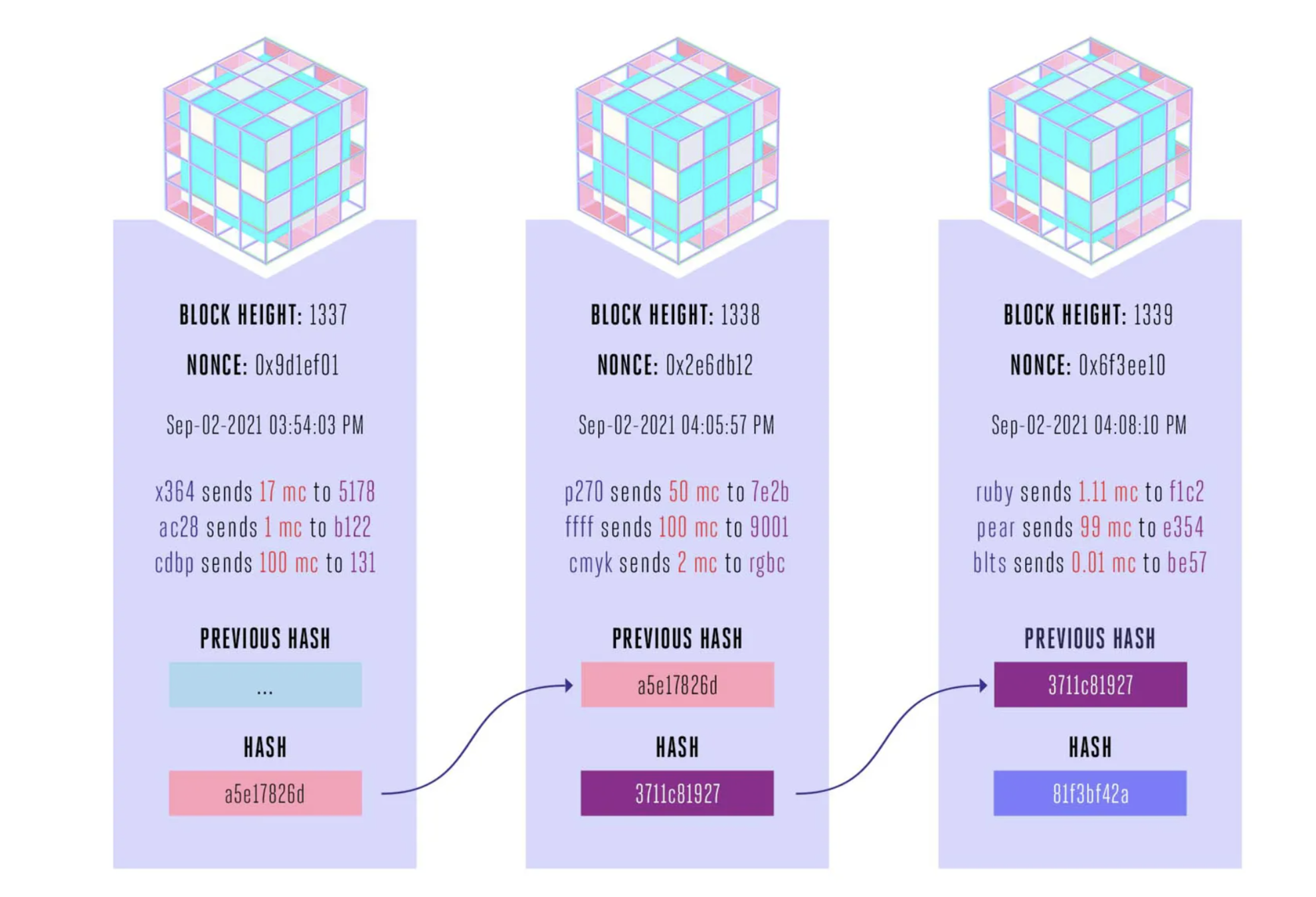
Link: https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain
PoW algorithms demand work from the computers around the world that comprise decentralized networks.
In the case of Bitcoin, this work is the computer processing power that solves a computational puzzle and the computers that carry out this process are called miners.
When miners solve the computational puzzle, their block of data is deemed valid and added to all copies of the blockchain, thus achieving consensus.
As a reward for their efforts, miners are granted a block reward in the form of bitcoin and then turn their attention to the next block of data.
While this method is energy intensive, it has proven very successful at ensuring the security and stability of various blockchain networks.
Proof of Work
Elements
Distributed ledger technology
Immutable records
Smart contracts
Types
Public
Private
Permissioned
Consortium
Link: https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain
Benefits
Greater Trust
Greater Security
More Efficient
Crypto
At its core, cryptocurrency is typically decentralized digital money designed to be used over the internet.
CryptoCurrencies
At its core, cryptocurrency is typically decentralized digital money designed to be used over the internet.
For eg, 3 cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin. All three run on their own, separate blockchains, and there’s way more where those came from, just in the cryptocurrency space alone.
GAS Fees
“Gas fees” are the transaction fees that users pay to miners on a blockchain protocol to have their transaction included in the block. The system works on a standard supply and demand mechanism.
If there is more demand for transactions, miners can choose to include the transactions that pay more, compelling users to pay more to have their transactions processed quickly and efficiently. Users of Ethereum can also choose to pay more for faster transactions.
Link: https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/article/what-are-gas-fees
Blockchain Issues
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/blockchain-trilemma-decentralization-scalability-definition
Visa, on the other hand, processes approximately 1,700 TPS.
Blockchain Issues
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/blockchain-trilemma-decentralization-scalability-definition
Bitcoin processes between 4–7 transactions per second (TPS). Ethereum processes 30 transactions per second (tx/s).
Blockchain Issues
https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/02/19/239592/once-hailed-as-unhackable-blockchains-are-now-getting-hacked/
Hack
An attacker had somehow gained control of more than half of the network’s computing power and was using it to rewrite the transaction history. That made it possible to spend the same cryptocurrency more than once—known as “double spends.”
In total, hackers have stolen nearly $2 billion worth of cryptocurrency since the beginning of 2017, mostly from exchanges, and that’s just what has been revealed publicly.
The 51% rule
This new version is called a fork. The attacker, who controls most of the mining power, can make the fork the authoritative version of the chain and proceed to spend the same cryptocurrency again.
Blockchain Issues
https://www.technologyreview.com/2019/02/19/239592/once-hailed-as-unhackable-blockchains-are-now-getting-hacked/
An attacker stole more than $60 million worth of cryptocurrency by exploiting an unforeseen flaw in a smart contract.
In essence, the flaw allowed the hacker to keep requesting money from accounts without the system registering that the money had already been withdrawn.
Blockchain Issues
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/blockchain-trilemma-decentralization-scalability-definition
Blockchain trilemma
While blockchain technology is proving itself to be a new pillar of the global economy, its underlying structure of decentralized networks faces a unique challenge known as the Blockchain Trilemma: the balancing act between decentralization, security, and scalability within a blockchain infrastructure.
This trilemma refers to a widely held belief that decentralized networks can only provide two of three benefits at any given time with respect to decentralization, security, and scalability.
Kind of like CAP.
That a distributed system can deliver only two of three desired characteristics: consistency, availability, and partition tolerance (the 'C,' 'A' and 'P' in CAP).
Scaling Solutions
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/polygon-crypto-matic-network-dapps-erc20-token#section-polygon-crypto-network-basics
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/proof-of-stake-delegated-pos-dpos
Scaling solutions:
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus algorithms make blockchain networks more efficient by eliminating the energy-intensive computational mining process inherent in Proof-of-Work protocols.
In PoS blockchains, an individual or group is algorithmically chosen to verify transactions with computer hardware based on the tokens they have staked, or locked up, in the network as a form of collateral.
Proof of Stake
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/polygon-crypto-matic-network-dapps-erc20-token#section-polygon-crypto-network-basics
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/proof-of-stake-delegated-pos-dpos
No energy-intensive mining is required on PoS networks.
Instead, the PoS mechanism randomly chooses a validator to validate blocks of data where the cost of an intended malicious error is greater than the block reward. PoS algorithms use several methods to select who will validate the next block.
DeleteGated Proof of Stake
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/polygon-crypto-matic-network-dapps-erc20-token#section-polygon-crypto-network-basics
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/proof-of-stake-delegated-pos-dpos
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a popular evolution of the PoS concept, whereby users of the network vote and elect delegates to validate the next block. Delegates are also called witnesses or block producers. Using DPoS, you can vote on delegates by pooling your tokens into a staking pool and linking those to a particular delegate.
Ethereum 2.0
Link:
https://consensys.net/knowledge-base/ethereum-2/faq/
Ethereum 2.0, also called Eth2, refers to a set of upgrades that will make Ethereum more scalable, more secure, and more sustainable.
Shard chains will give Ethereum more capacity to store and access data, but they won’t be used for executing code.
Rollups are a Layer 2 technology that takes much of the burden of computation and storage out of the blockchain, and uses the chain just enough to benefit from its security guarantees.
RollUps
Link:
https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/article/what-are-gas-fees
Many different technical approaches are being developed in parallel in order to scale the capacity of Ethereum, increase throughput and lower Ethereum gas fees. Out of these, rollups are beginning to show themselves as a promising solution.
By using Ethereum as the base layer and inheriting its security and decentralization, rollups allow users to make transactions without congesting the Ethereum network. We call Ethereum “Layer 1,” while a rollup is built “on top of it” as a Layer 2, expanding its original capabilities.
SmART COntracts
Smart COntracts
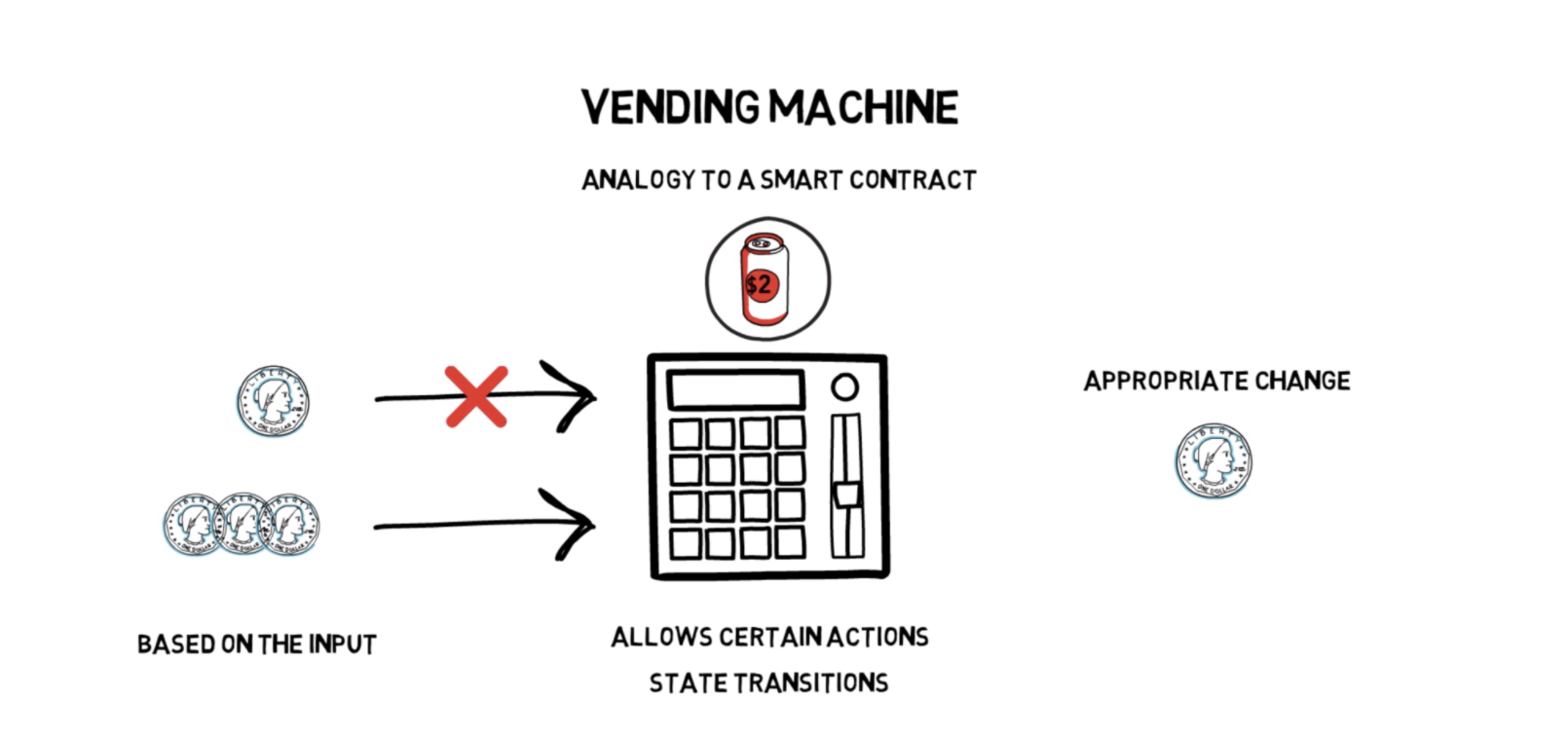
Smart contracts are simply programs stored on a blockchain that run when predetermined conditions are met.
They typically are used to automate the execution of an agreement so that all participants can be immediately certain of the outcome, without any intermediary’s involvement or time loss. They can also automate a workflow, triggering the next action when conditions are met.
Link: https://www.ibm.com/topics/smart-contracts
A DIGITAL VENDING MACHINE
Link: https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/smart-contracts/
https://finematics.com/smart-contracts-explained/
Code
SOLIDITY


Token ECONOMY
Token Economy
Cryptographic tokens represent programmable assets or access rights, managed by a smart contract and an underlying distributed ledger such as a blockchain network.
Token contracts are a specific type of smart contract.
Its age old. Eg. vouchers, gift cards, bonus points in a loyalty program
Link: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/what-is-the/9781492072973/ch01.html
Token Economy
Token economies refer to the economics of goods and services that have been tokenized.
Blockchain technology enables these economies to function without the need for intermediaries and third parties. Blockchain and token economies offer a solution to bridge the physical and digital gap between our increasingly global and virtual worlds.
In a token economy, blockchain technology is used to take physical assets, digitize them, prove their ownership, and potentially trade them. The same principles apply to tokenizing an asset that is already in digital form.
The four tools you need to work with tokens, sometimes called digital assets, are Documentation, Tokenization, Governance, and Trading.
Link: https://coinmarketcap.com/alexandria/glossary/token-economy
Types of Token
Link: https://www.metaco.com/digital-assets-glossary/cryptographic-tokens/
https://blog.makerdao.com/the-different-types-of-cryptocurrency-tokens-explained/
Payment tokens
Utility tokens
Security tokens
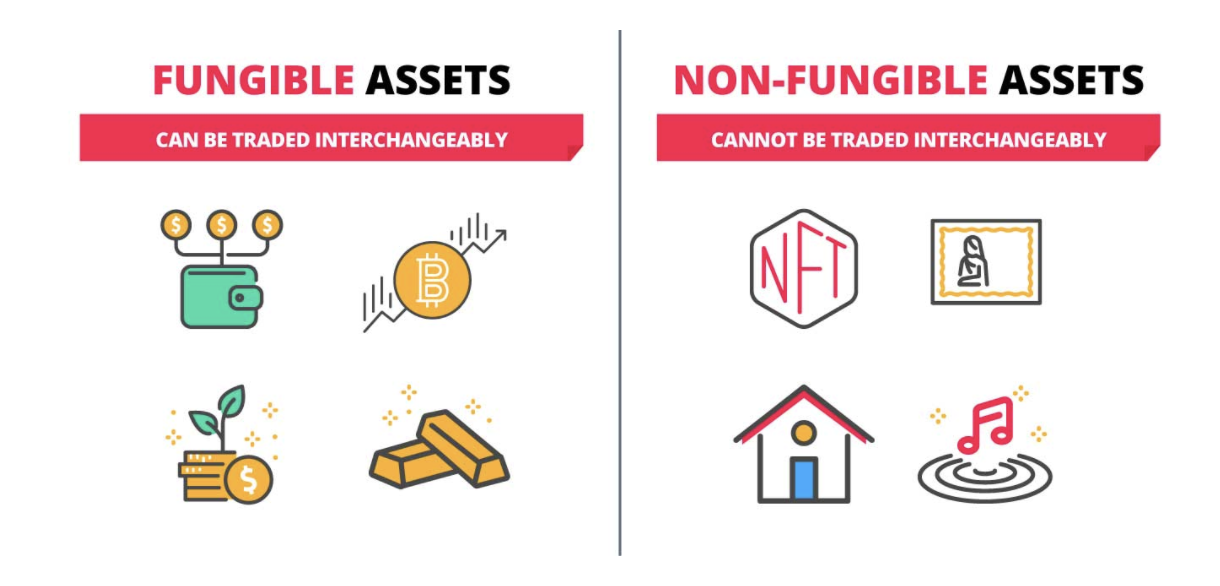
Non-fungible tokens
Platform tokens
Transactional tokens
Governance tokens
Link: https://edition.cnn.com/2021/03/17/business/what-is-nft-meaning-fe-series/index.html
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/nft-non-fungible-t
https://www.dbs.com.sg/personal/articles/nav/investing/nfts-explainedoken/
Link: https://edition.cnn.com/2021/03/17/business/what-is-nft-meaning-fe-series/index.html
https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/nft-non-fungible-t
https://www.dbs.com.sg/personal/articles/nav/investing/nfts-explainedoken/
NFT
NFTs are like physical collector’s items, only digital.
Artists no longer have to rely on galleries or auction houses to sell their art.
Instead, the artist can sell it directly to the consumer as an NFT, which also lets them keep more of the profits.
In addition, artists can program in royalties so they’ll receive a percentage of sales whenever their art is sold to a new owner. This is an attractive feature as artists generally do not receive future proceeds after their art is first sold.
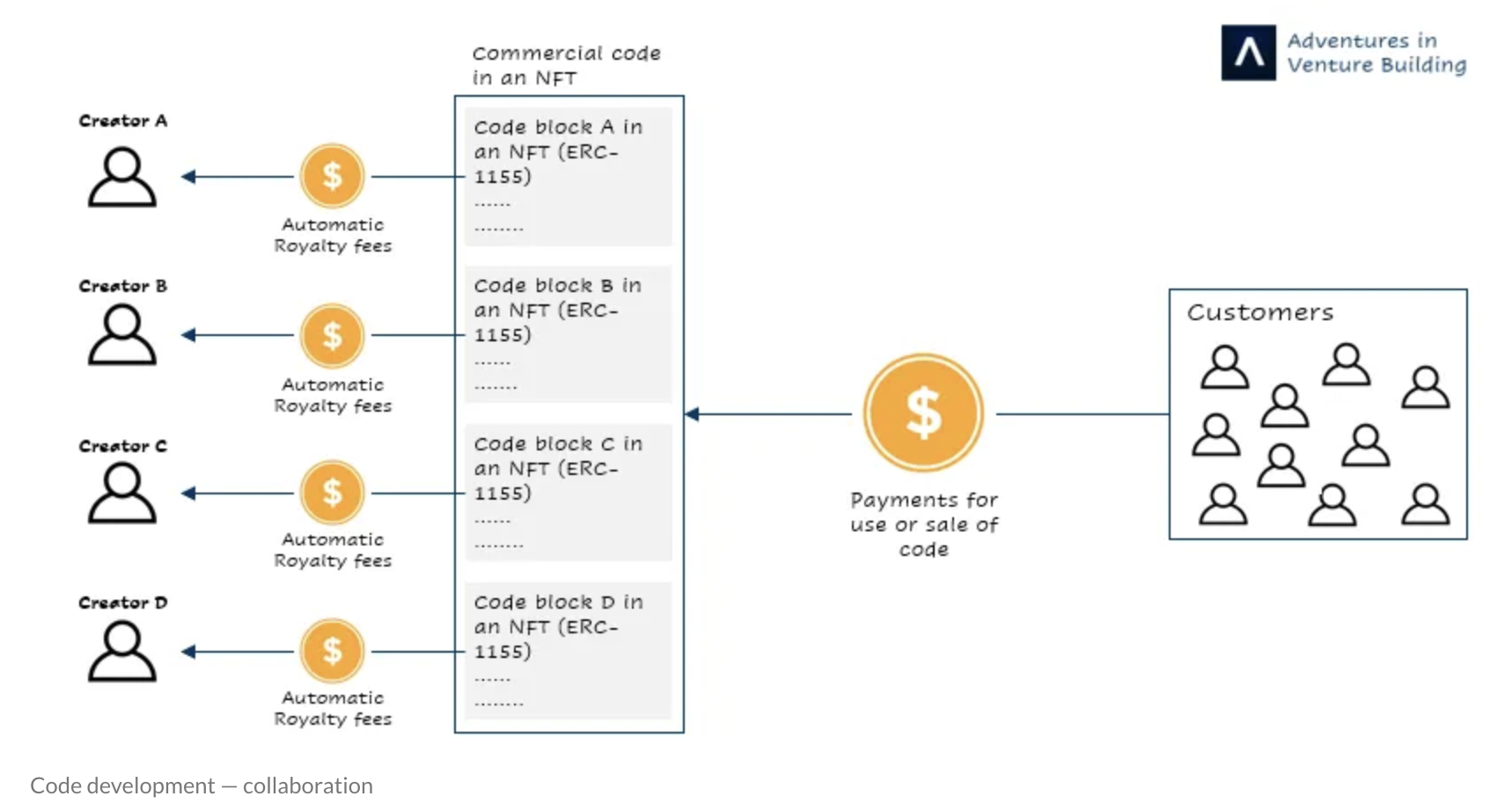
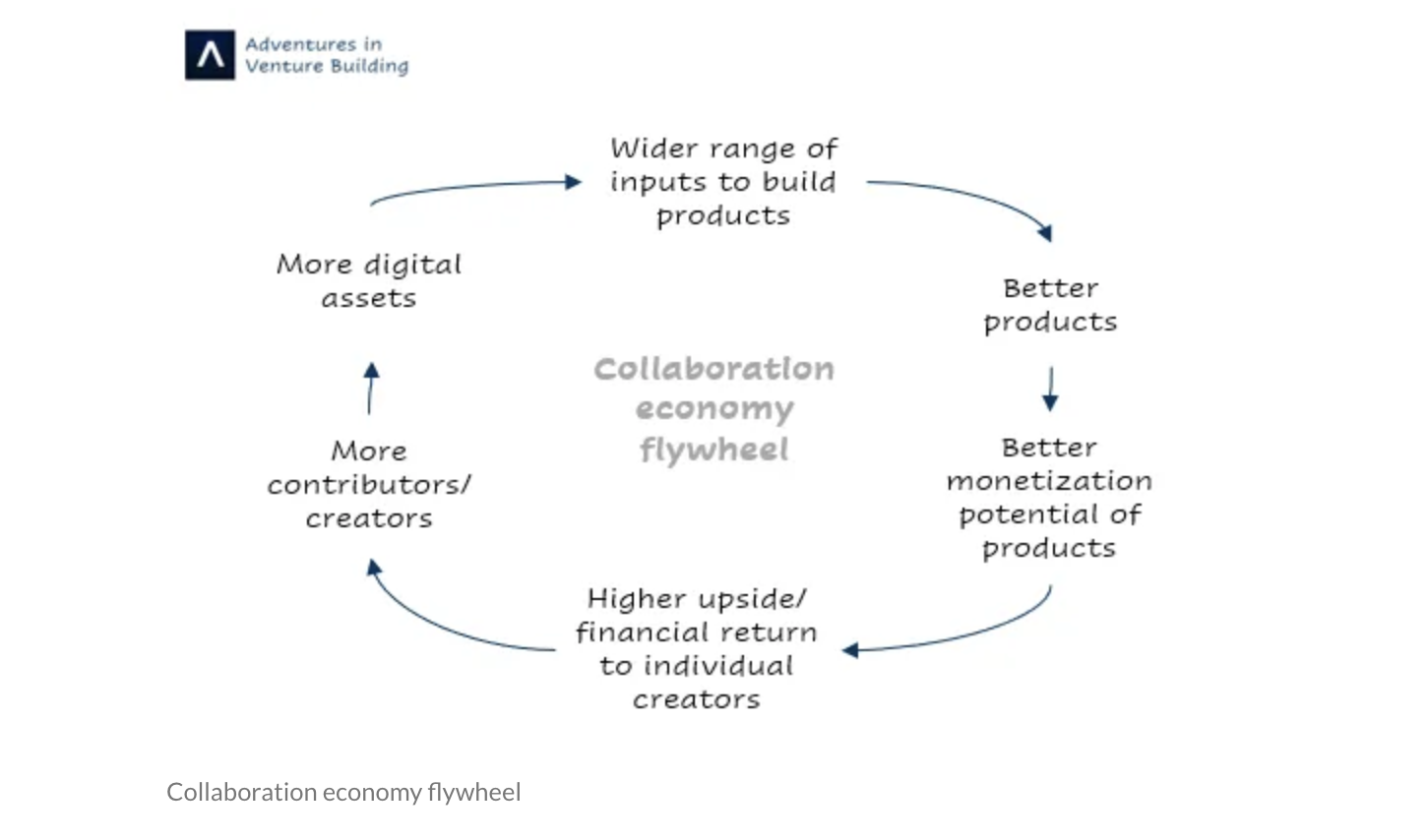
Link: https://www.menabytes.com/rise-of-nfts/
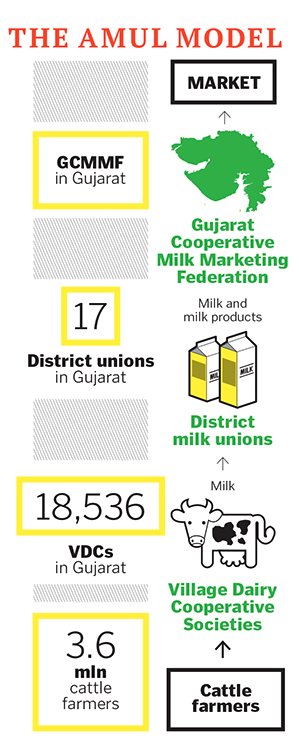
DaOs
Autonomous
Link: https://www.forbesindia.com/article/leadership-awards-2015/cow-to-consumer-beyond-profit-for-gujarat-cooperative-milk-marketing-federation/41207/1

Daos
Decentralised Autonomous Organization
The DAO was an organization created by developers to automate decisions and facilitate cryptocurrency transactions.
A DAO’s financial transactions and rules are recorded on a blockchain. This eliminates the need to involve a third party in a financial transaction, simplifying those transactions through smart contracts.
The firmness of a DAO is a smart contract. The smart contract represents the rules of the organization and holds the Organization’s storage.
No one can edit the rules without people noticing, because DAOs are transparent and public.
Link: https://www.forbesindia.com/article/leadership-awards-2015/cow-to-consumer-beyond-profit-for-gujarat-cooperative-milk-marketing-federation/41207/1
https://medium.com/coinmonks/defi-nft-and-dao-49b07e7c7119
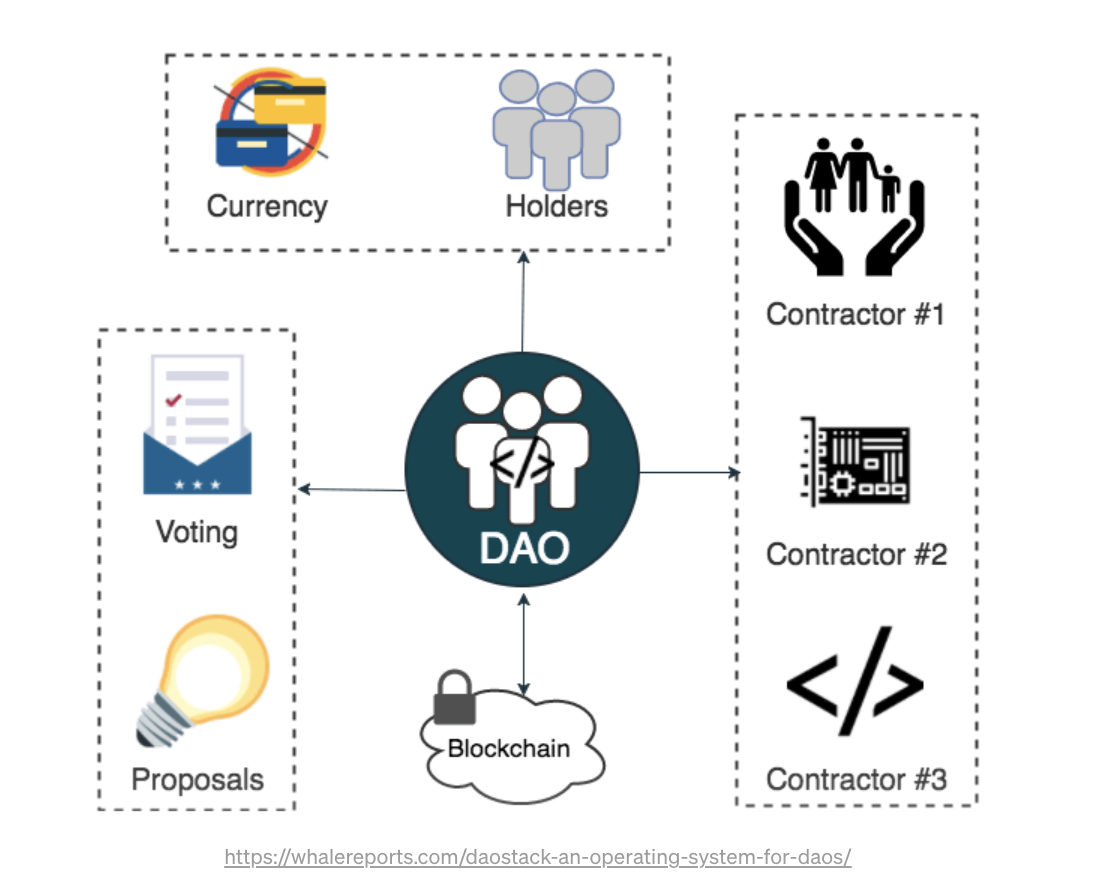
DAOs envision a collective organization owned and managed by its members with all of them having a voice.
‘An internet community with a shared bank account’
Link:
https://www.cnbc.com/2021/10/25/what-are-daos-what-to-know-about-the-next-big-trend-in-crypto.html
https://ethereum.org/en/dao/
https://thedefiant.io/what-is-a-dao-mapping-out-the-ecosystem/
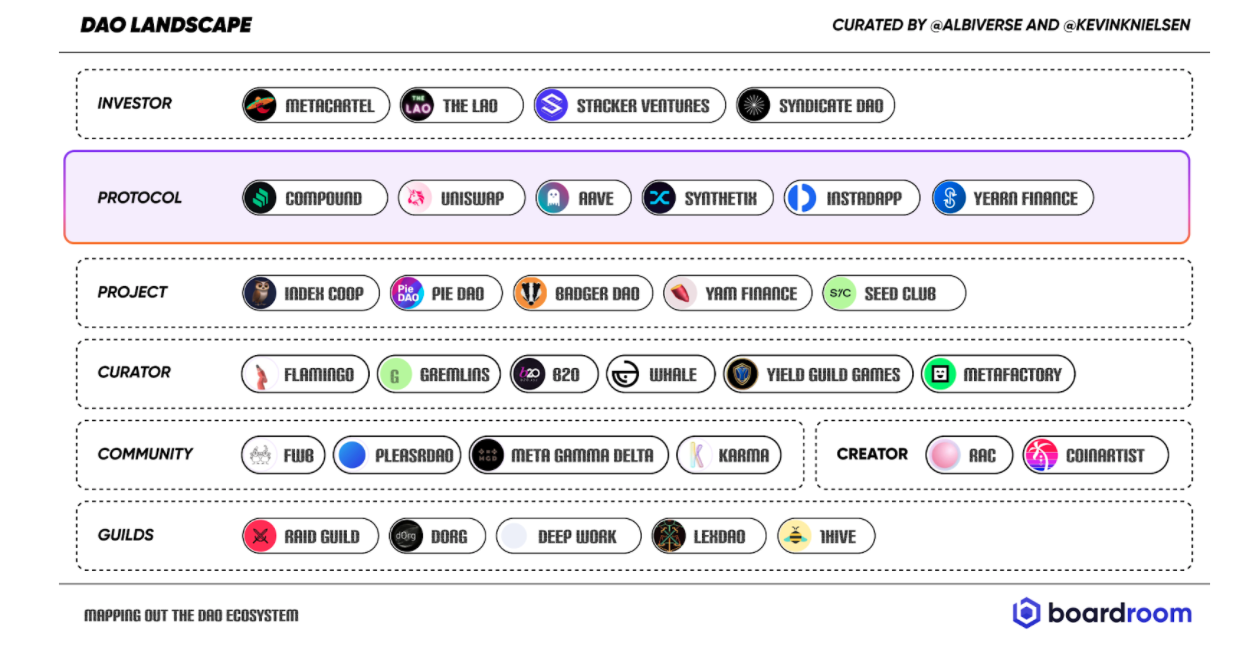
Link: https://www.forbesindia.com/article/leadership-awards-2015/cow-to-consumer-beyond-profit-for-gujarat-cooperative-milk-marketing-federation/41207/1
DAPPS
Dapps
Link:
https://medium.com/centrality/what-even-is-a-dapp-and-why-are-they-useful-10f64c13d454
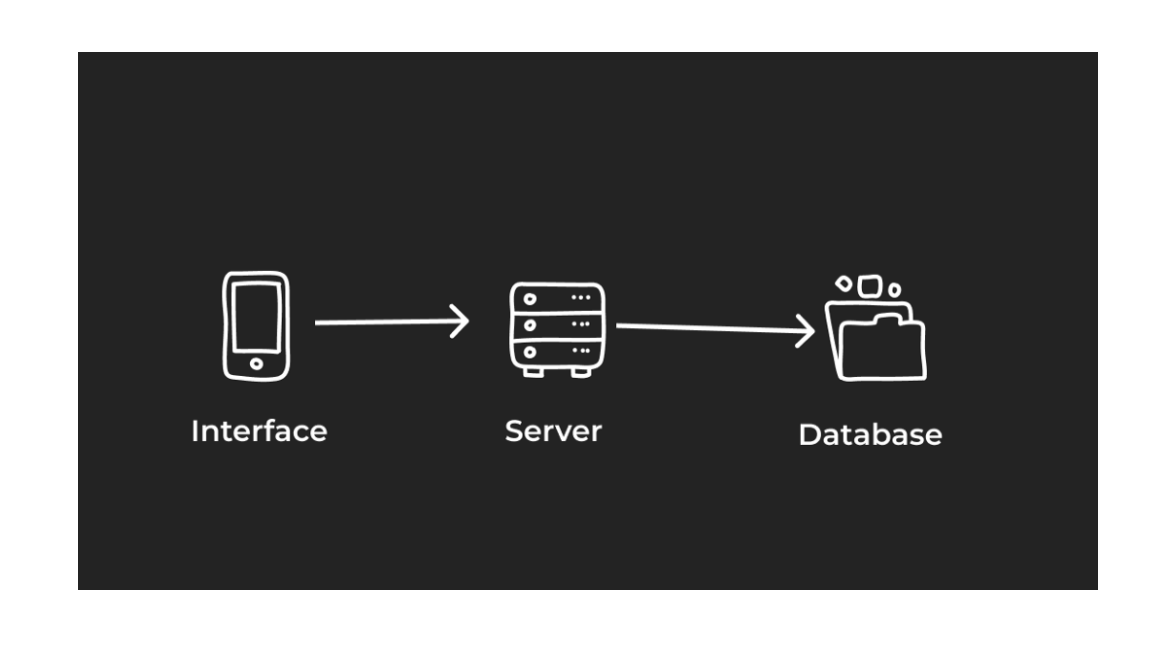
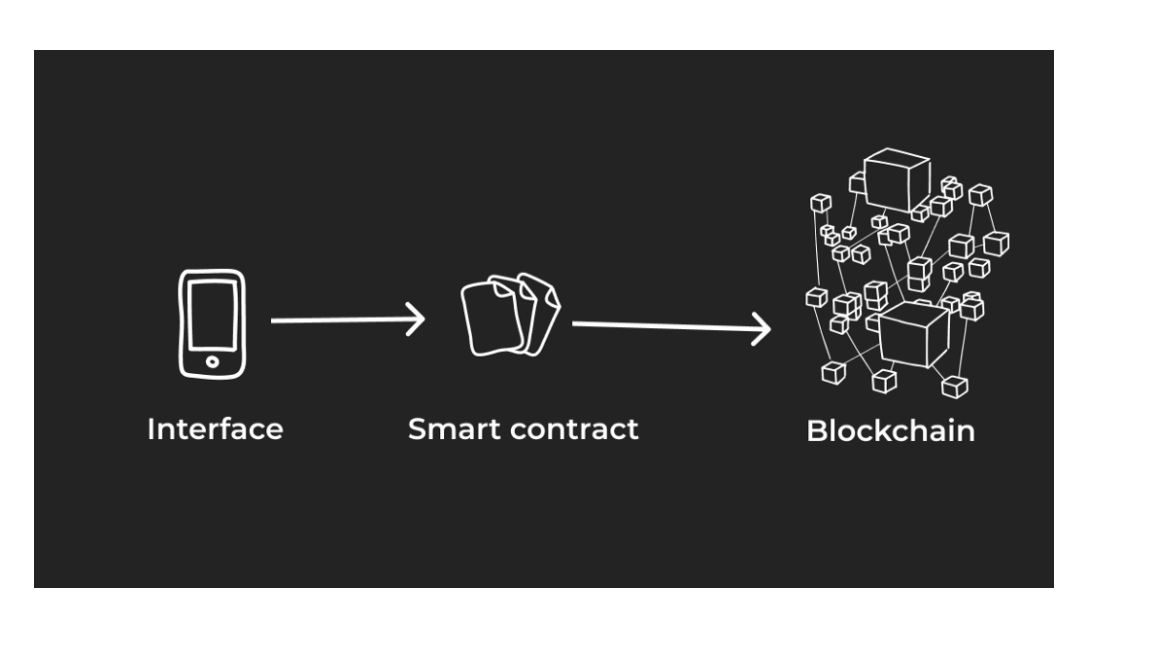
Dapps
Decentralized applications (dApps) are built on blockchain networks and use smart contracts to create platforms that streamline and democratize the entry into industries ranging from finance to gaming — all without intermediaries and centralized authorities.
In terms of front-end user experience, dApps appear nearly identical to traditional web applications. However, on the back-end, dApps function much differently than their conventional counterparts.
Instead of employing the HTTP protocol to communicate with the broader network, dApps connect to the blockchain in a decentralized manner rather than routing through centralized servers.
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/dapps-ethereum-decentralized-application#section-why-ethereum-for-d-apps
Link:
https://ethereum.org/en/dapps/
https://limechain.tech/blog/what-are-dapps-the-2021-guide/
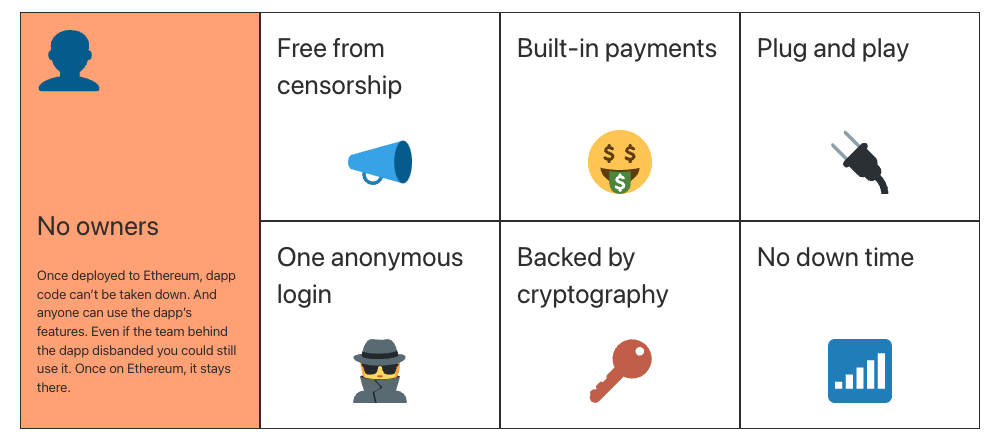
Dapps
-
A dApp is entirely open source, with no entity owning the majority of the coins or tokens. By way of its open-source nature, changes to the protocol must be decided via consensus of its network users.
-
A dApp's data must be stored on a decentralized blockchain.
-
A dApp needs to generate digital assets that act as a proof of value.
-
A dApp's assets are distributed as rewards on the network.
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/decentralized-applications-defi-dapps#section-decentralized-app-criteria
In this basic explanation, the front end communicates with the smart contract using an API (in reality this happens via a blockchain wallet and gets a bit more complicated).
-
A dApp is entirely open source, with no entity owning the majority of the coins or tokens. By way of its open-source nature, changes to the protocol must be decided via consensus of its network users.
-
A dApp's data must be stored on a decentralized blockchain.
-
A dApp needs to generate digital assets that act as a proof of value.
-
A dApp's assets are distributed as rewards on the network.
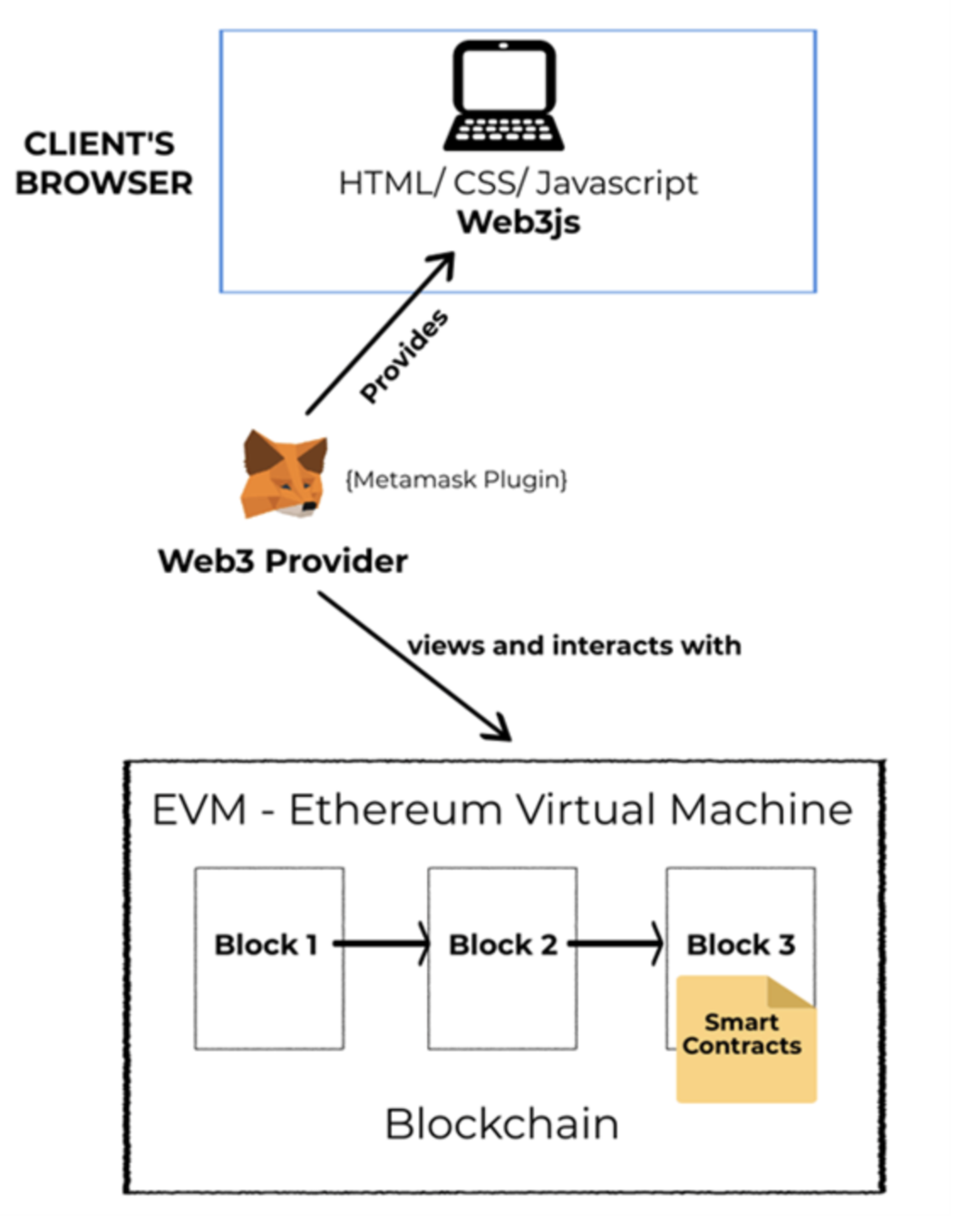
THE ETHEREUM VIRTUAL MACHINE (EVM)
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a development interface accessible through a web browser.
The EVM enables developers to deploy decentralized applications (dApps) more effectively by providing a suite of development kits, application templates, and other tools. The EVM improves accessibility by eliminating the need for developers to purchase costly hardware, and allowing developers to launch a dApp regardless of the underlying coding language.
The EVM is a primary driver of the trend that dApps exist almost exclusively on the Ethereum blockchain thus far.
Ethereum also uses a network-native language known as Solidity for coding smart contracts. This network architecture eliminates the need to develop an entirely new blockchain for every dApp.
Link:
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/decentralized-applications-defi-dapps#section-decentralized-app-criteria
https://www.gemini.com/cryptopedia/glossary#ethereum-virtual-machine-evm
THE ETHEREUM VIRTUAL MACHINE (EVM)
By combining application templates, MetaMask integration, and the EVM, the overall Ethereum development kit allows companies to focus on refining their applications and developing on top of open-source code among a global, mission-based developer community that prioritizes cooperation over competition.
Link:
https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/build-your-ethereum-dapp-on-windows-with-truffle-ganache-and-metamask-beginne/
Types of DAPP
Johnston states that there are three types of dapps.
Type I decentralized applications have their own block chain, such as Bitcoin.
Type II decentralized applications use the blockchain of a type I decentralized application but are “protocols and have tokens that are necessary for their function” like the Omni Protocol.
Type III decentralized applications use the protocol of a type II decentralized application and “are protocols and have tokens that are necessary for their function,” such as the SAFE Network that uses the Omni Protocol to issue ‘safecoins.”
Think of Dapps as an operating system like Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, Android, iOS as a Type I classification. The programs on these systems, such as a word processor or Dropbox, would be Type II. A Type III example would then be a blogging platform that integrates Dropbox.
Link:
https://medium.com/heptagon/step-by-step-guide-to-build-a-dapp-a-homo-sapiens-2-day-love-affair-with-ethereum-dapp-de2b0dea12f1
Link:
https://medium.com/heptagon/step-by-step-guide-to-build-a-dapp-a-homo-sapiens-2-day-love-affair-with-ethereum-dapp-de2b0dea12f1
MetaVerse and BeyonD
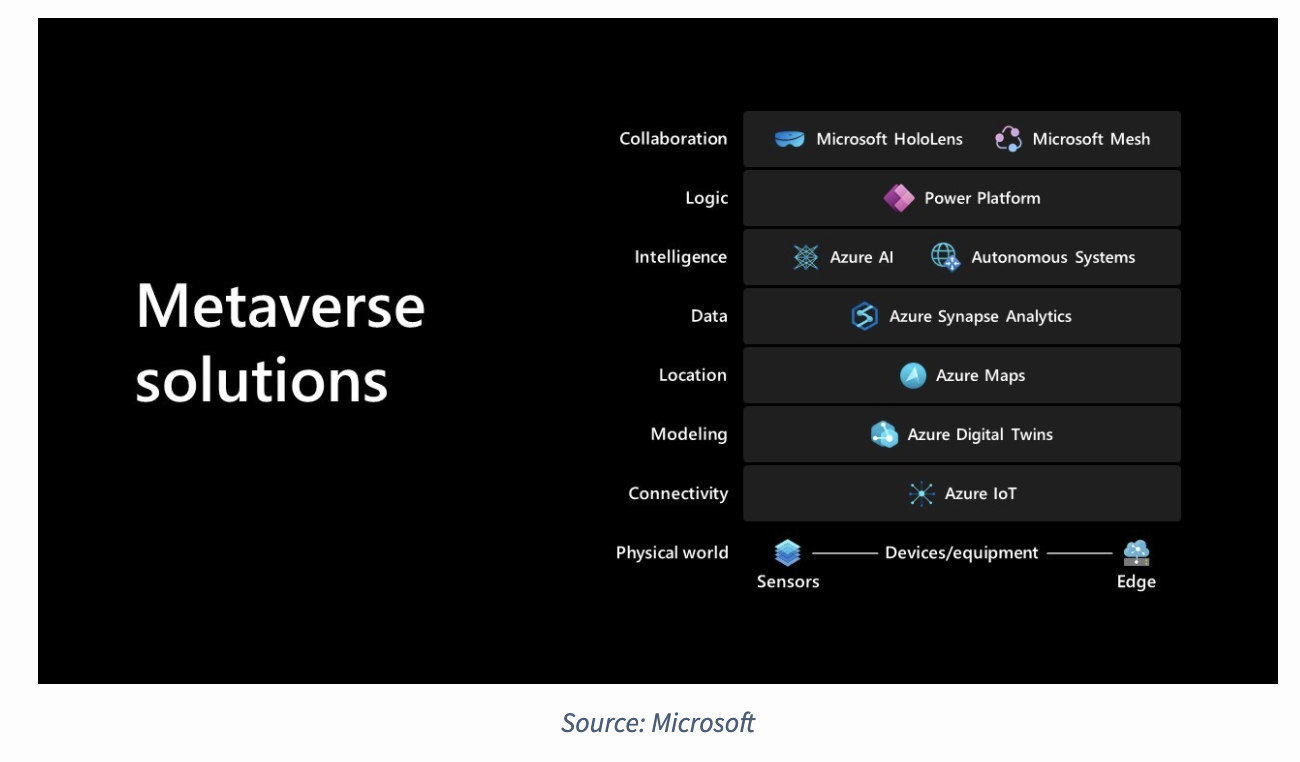
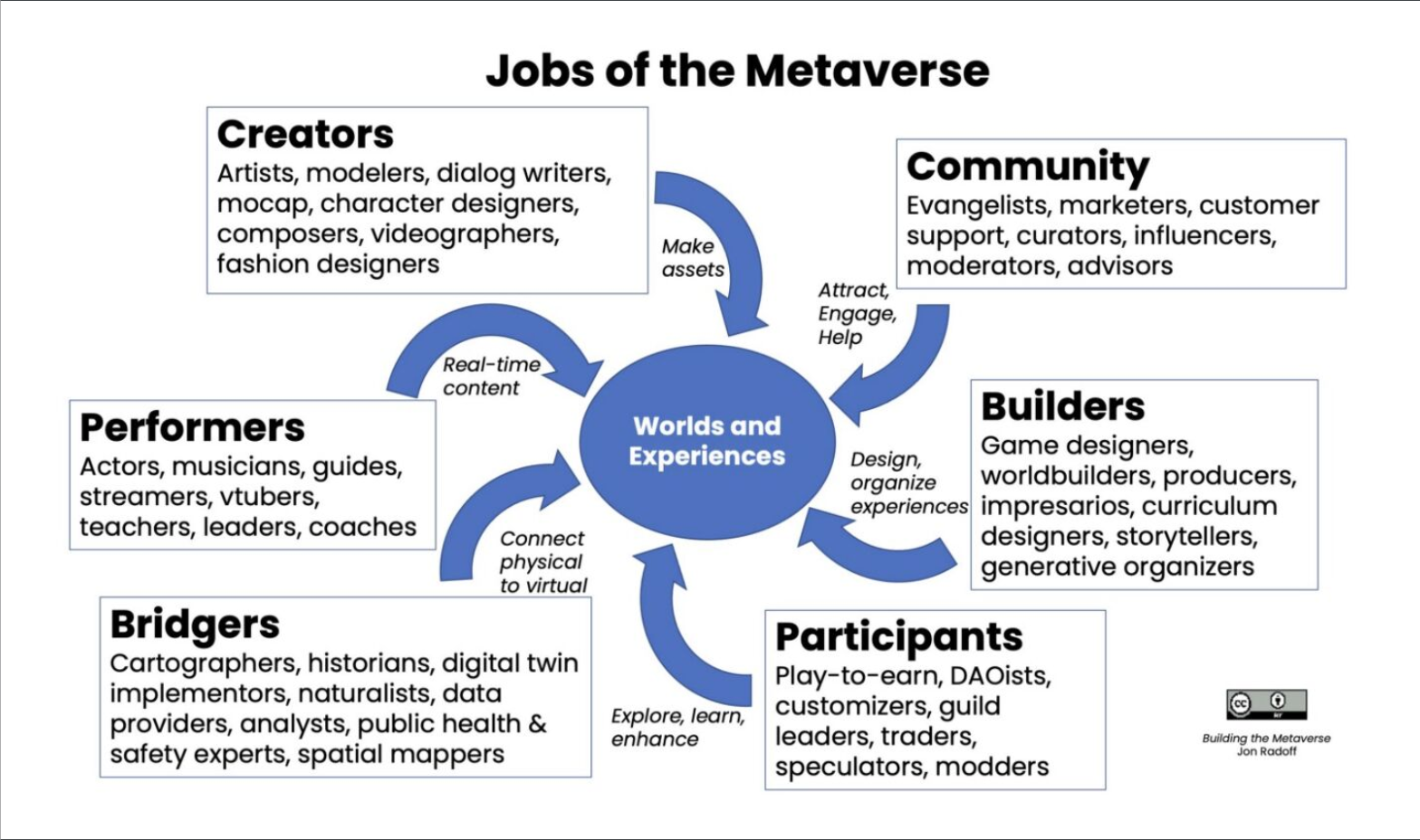
Metaverse and beyond

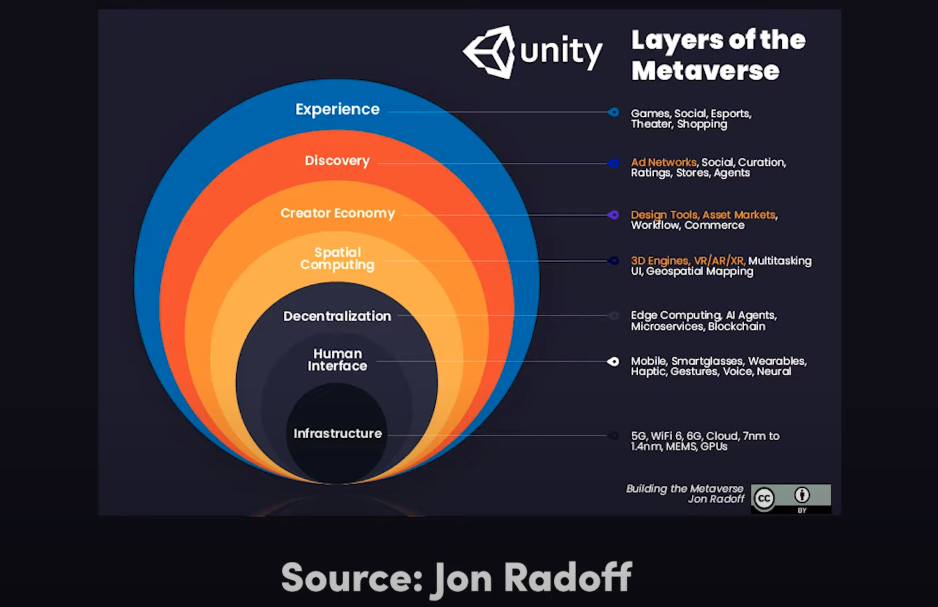

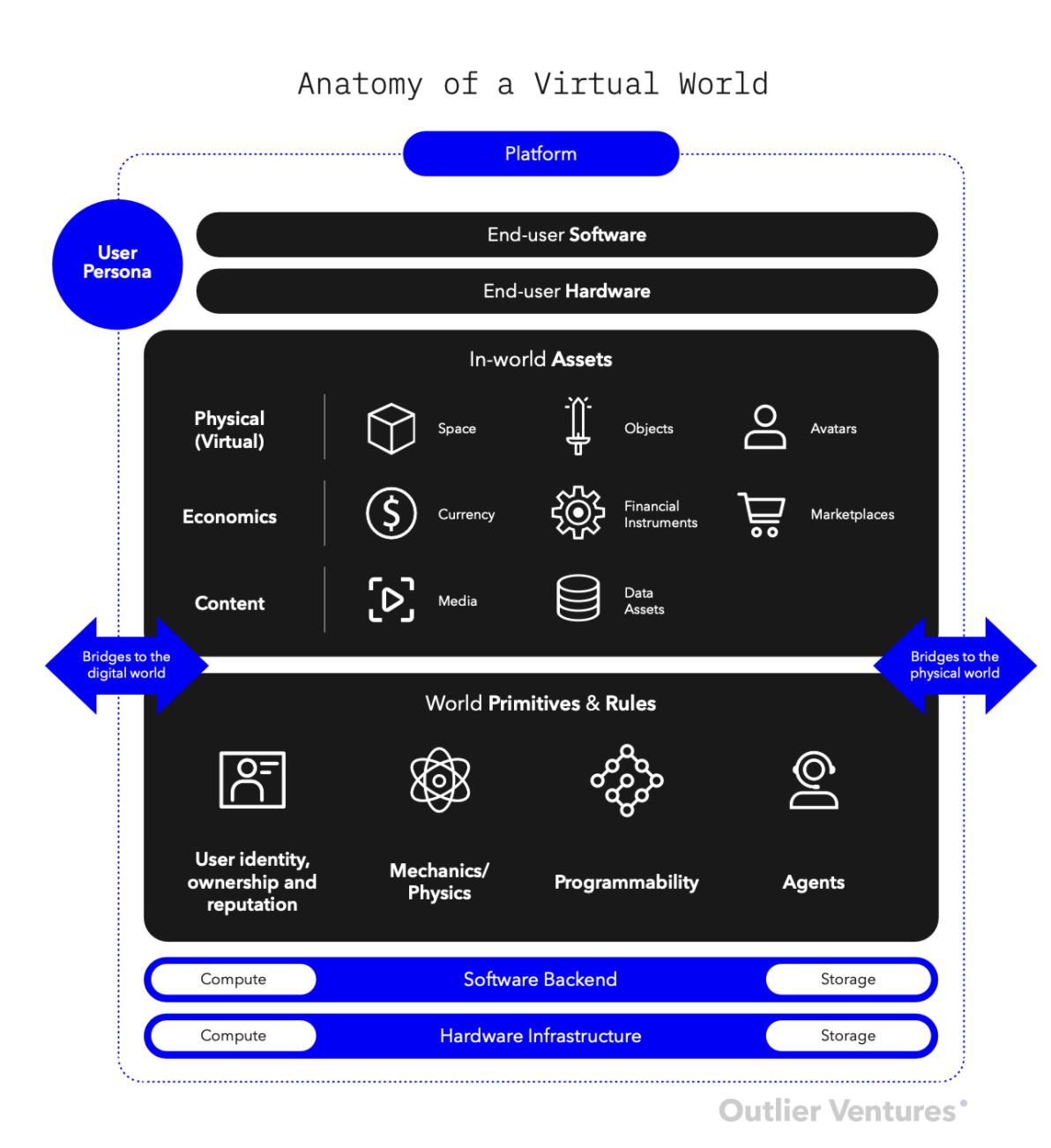
Link:
https://outlierventures.io/research/building-in-the-metaverse/
Link:
https://thenewstack.io/metaverse-developers/
Developer Tools
Link:
https://outlierventures.io/research/the-web-3-toolbox/
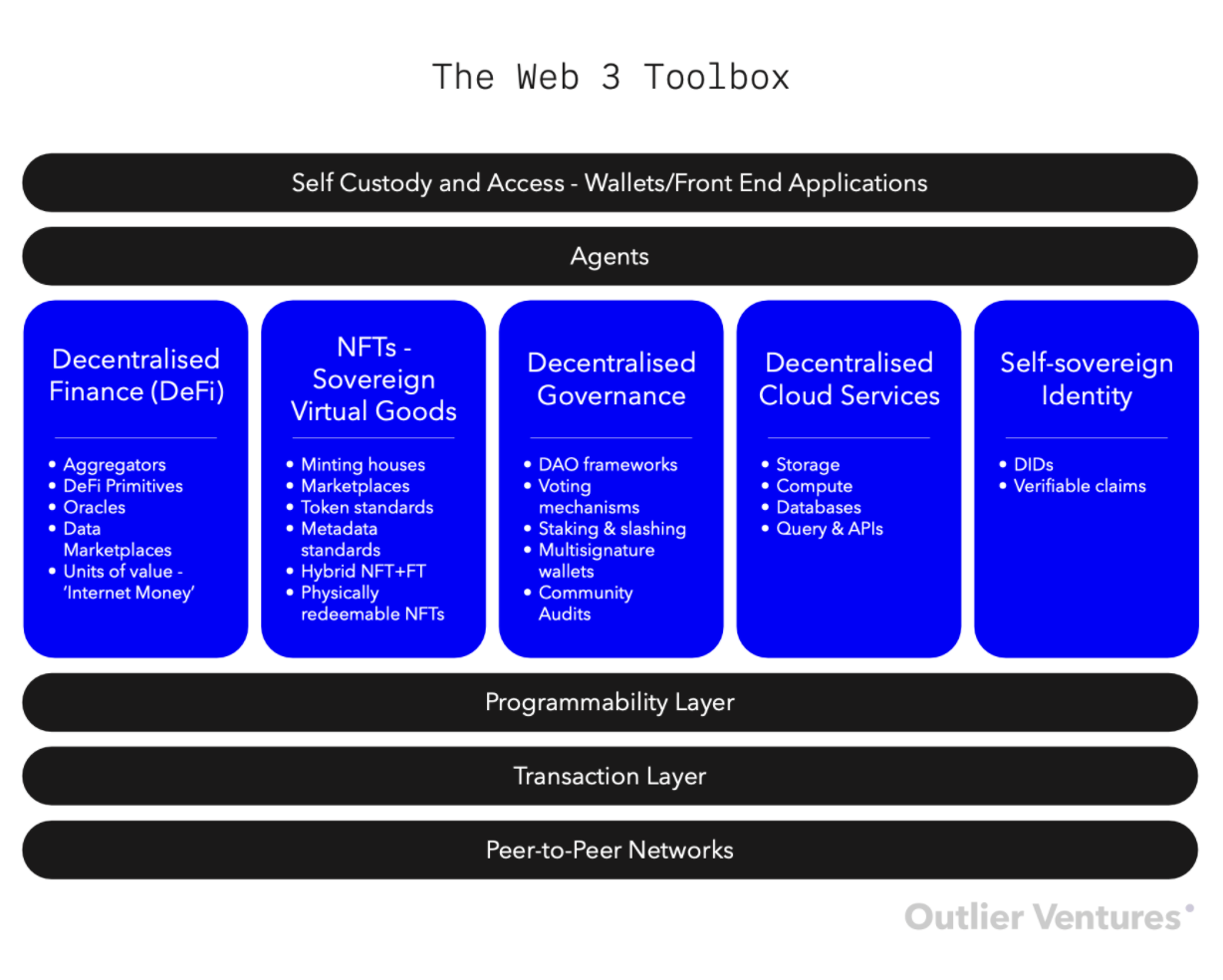
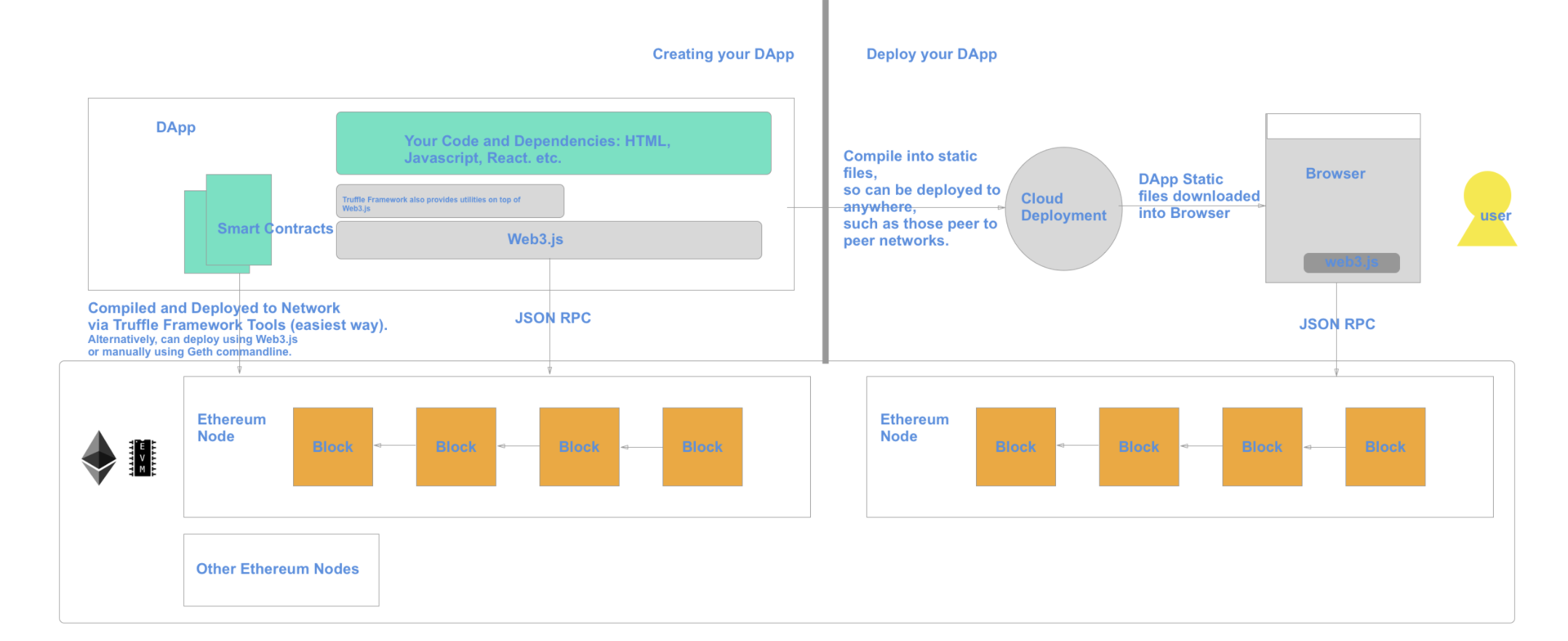
Developer Tools
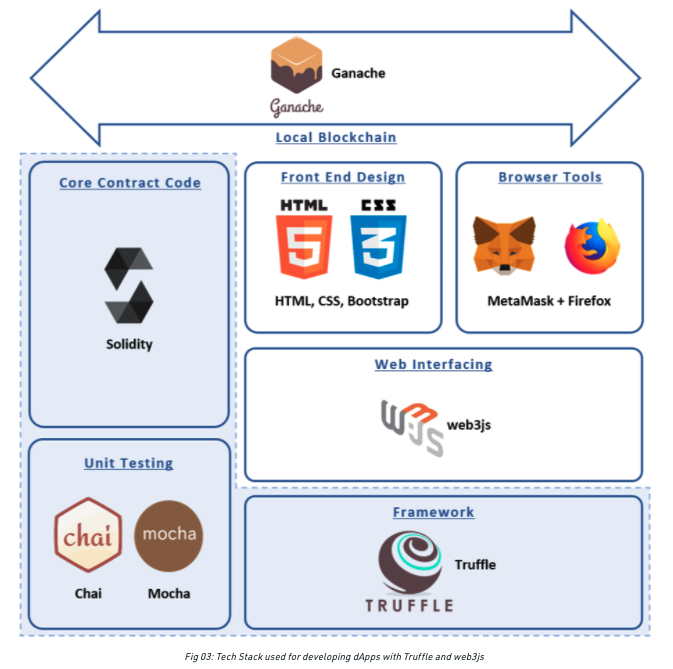
Link:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/creating-dapps-using-the-truffle-framework/
FAQs and TRENDs
India
India gov preparing Cabinet Note (soon to be bill) with these given NOs for crypto.
NO 1. Not as a legal tender.
No 2. No mining allowed
No. 3 Payments in Crypto wont be allowed.But Crypto would be treated as asset class.
Indian Digital Currency will be regulated with RBI and nothing to do with Crypto.
Muslim World
Muslim World

- BLOOMBERG
One thing is for sure,
ChANGE will HAPPEN.
The opening slide picture is from the book Deep Thinking. Do read!