Introduction to Transfer Learning

@sachinkmr_
sachink.it@nsit.net.in

Sachin Kumar
About Me
-
Sophomore at NSIT,Delhi University-
B.E. in Information Technology
-
-
Teaching Assistant at Coding Blocks. -
Independent study on Deep Learning and its applications.
Outline
-
Recap : Convolutional neural network -
Deep Convolutional neural network Architecture
-
What is transfer Learning? -
Pre-trained Models -
Why to use pre-trained models? -
How to use pre-trained models-
Feature Extraction -
Fine Tuning
-
-
Ways to fine tune -
Code Implementation
Recap : Convolutional Neural Network
Convolutions as Features Generators
-
A neural network that use convolution in place of general matrix multiplication in at least one of their layers. -
Its a popular approach for image feature generation (detect edges, show differences in adjacent pixel values in a particular direction etc.) -
Extract spatial features of the image.



Edge Detection
Sharpen
\begin{bmatrix}
-1 & -1 & -1 \\
-1 & 8 & -1 \\
-1 & -1 & -1
\end{bmatrix}
⎣⎡−1−1−1−18−1−1−1−1⎦⎤
\begin{bmatrix}
0 & -1 & 0 \\
-1 & 5 & -1 \\
0 & -1 & 0
\end{bmatrix}
⎣⎡0−10−15−10−10⎦⎤
So the Convolution Arithmetic works like :
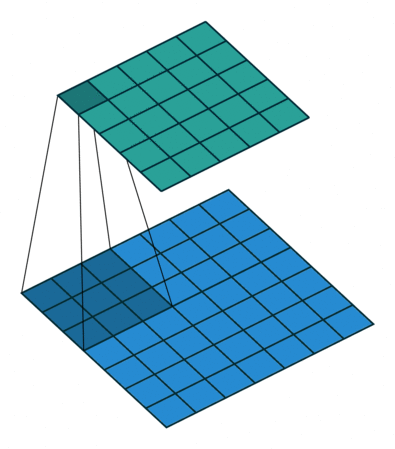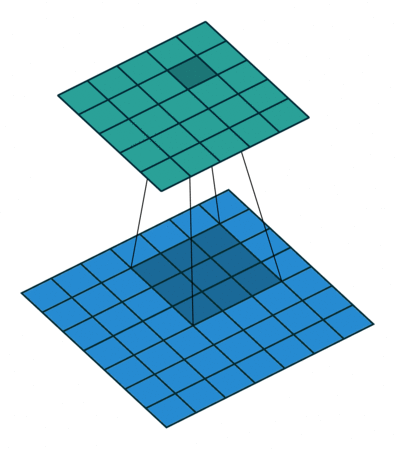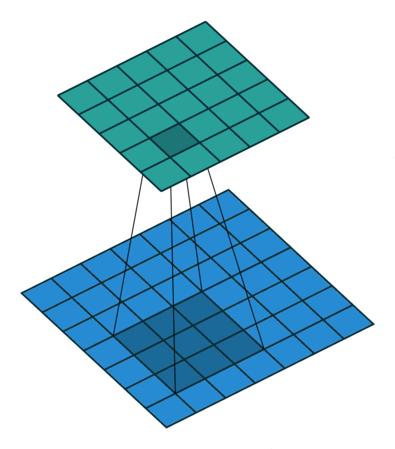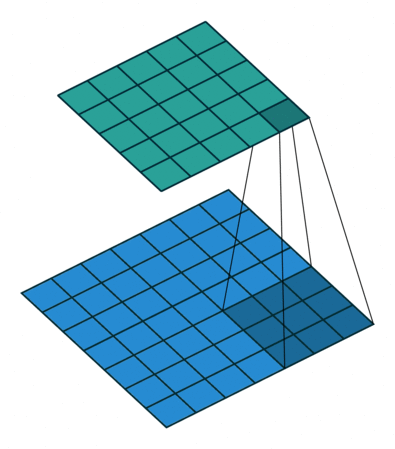
Deep Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
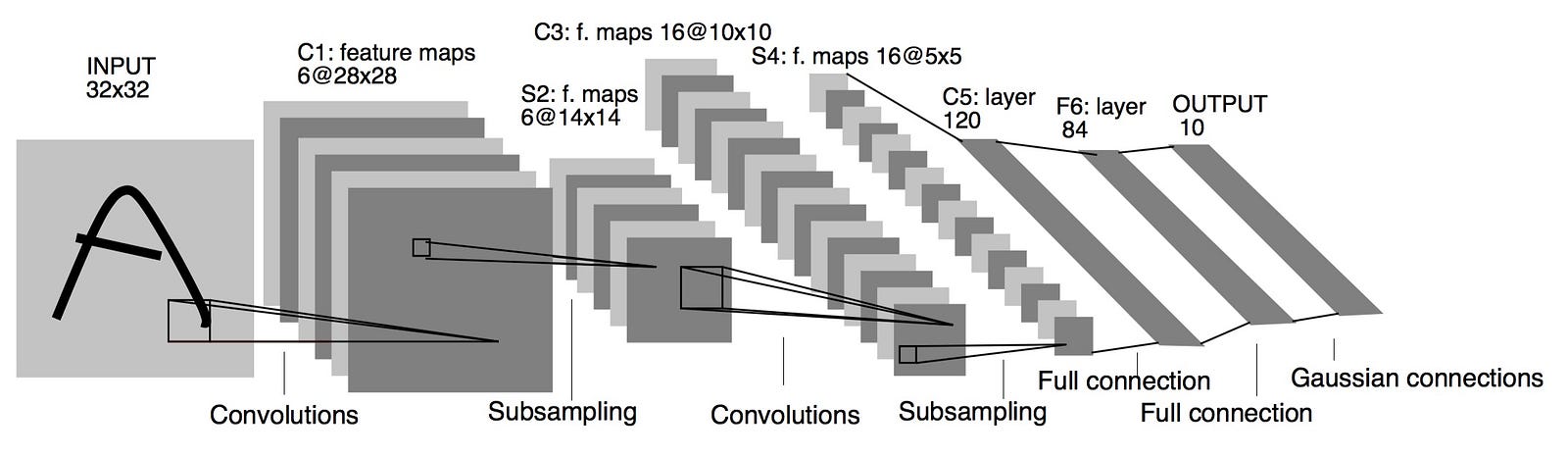
-
Consists of alternating layers of convolution and pooling. -
Each layer initialized with random filter weights. -
Multiple filters combined at each pooling layer. -
Number of filters increases from left to right. -
Terminated by one or more fully connected layers. -
Filter weights updated by back-propagation during training.
What is Transfer Learning?
-
C++ => Java
-
Mathematics/Physics => Computer Science
We often transfer knowledge to novel situations:

The ability of a system to recognize and apply knowledge and skills learned in previous tasks to novel tasks (or new domains).

Performance vs Training Plot
Transfer Learning:

Why Transfer Learning?
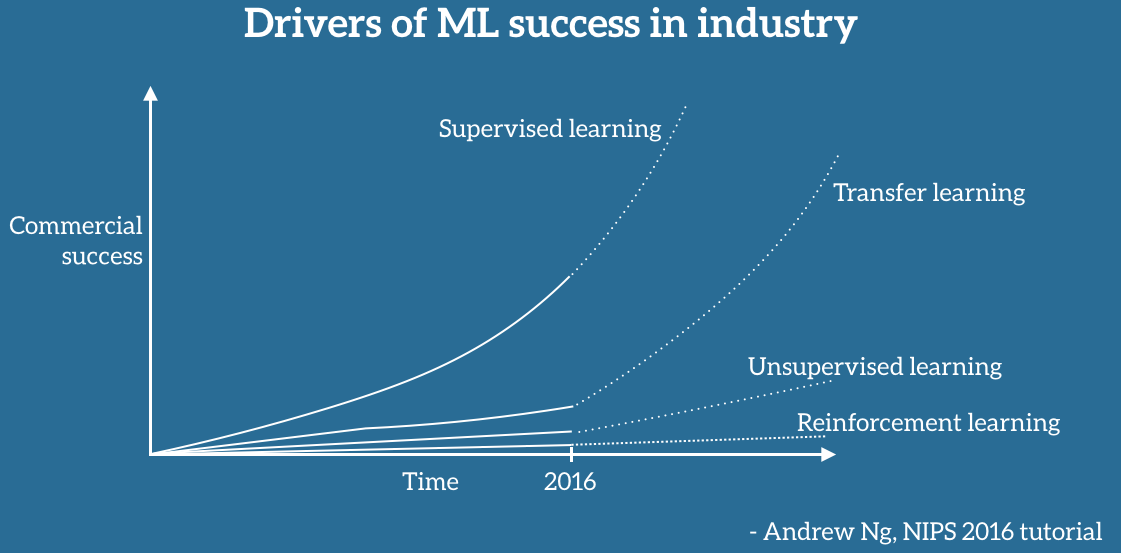
Andrew Ng, chief scientist at Baidu and professor at Stanford, said during his widely popular NIPS 2016 tutorial that transfer learning will be (after supervised learning) the next driver of ML commercial success.
He sketched out a chart on a whiteboard. According to Andrew Ng, transfer learning will become a key driver of Machine Learning success in industry.
Keras Pre-trained Models
-
Keras - High-level neural networks API, written in Python. -
Modular, minimalistic and easy to use.
-
Runs on top of Theano, Tensorflow, CNTK.
-
Keras applications (Model Zoo) contains following pre-trained models:
-
Xception -
VGG16 -
VGG19 -
ResNet50 -
InceptionV3
-
We will use VGG-16 for our talk.

-
Very simple and homogeneous.
-
Better accuracy because of increased depth of the network by adding more convolutional layers.
-
Which is feasible due to the use of very small (3 × 3) convolution filters in all layers.
Keras VGG-16 Model
So, lets try some hands on code:
We'll predict labels of random images using VGG16 model
Why to use pre-trained models ?
-
It is relatively rare to have a dataset of sufficient size. -
Instead, it is common to use pretrained ConvNet which was trained on a very large dataset (e.g. ImageNet, which contains 1.2 million images with 1000 categories), and then use the ConvNet either as an:-
Initialization or -
A fixed feature extractor for the task of interest.
-
-
Greater Accuracy
-
And training of model from scratch requires more time then training the dense layers of pre-trained models.

How to use pre-trained models ?
1. Feature extractor :
• Remove the Fully Connected (Bottleneck layer) from pre-trained VGG16 model. • Run images from Dataset through this truncated network to produce image vectors. • Use these vectors to train another classifier to predict the labels in training set. • Prediction is made with second classifier against image vector.

New
Classifier
2. Fine Tuning :
• We train the model partially.
• Remove the Fully Connected (Bottleneck layer) from pre-trained VGG16 model.
• Make weights of all convolution blocks non-trainable(frozen)except the last few convolutional layers. • Attach our own classifier to the bottom. • Train the resulting classifier with very low learning rate. • Computationally more expensive but still cheaper than training network from scratch. • More robust model.

New
Classifier
Size of data set
Data similarity
Train the model
from scratch
Fine Tune the pre-trained model
Fine tune the lower lower layers
Fine tune the output dense layer
How to proceed using pre-trained models :
Results
• Pre-trained model has learned to pick out features from images that are useful in distinguishing one image (class) from another. • Initial layer filters encode edges and color, while later layer filters encode texture and shape.
So, Cheaper to "transfer" that learning to new classification scenario than training a classifier from scratch.



Code on GitHub
Thank You!
Any Questions?
@sachinkmr_
