Load Balancing Containers

we'll explore how you can use the NGINX web server to load balance requests between two containers running on the host.
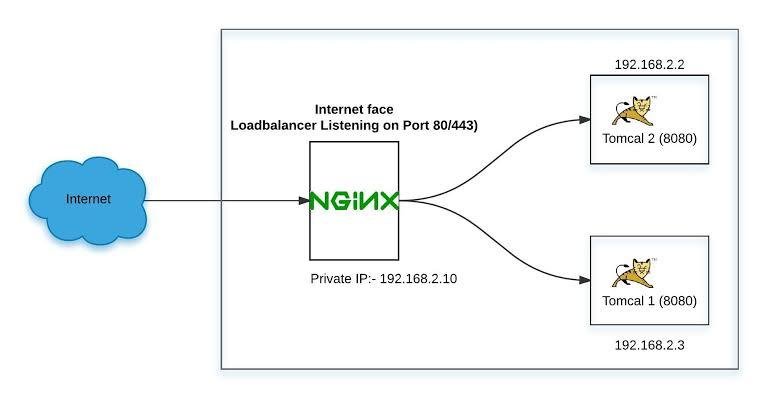
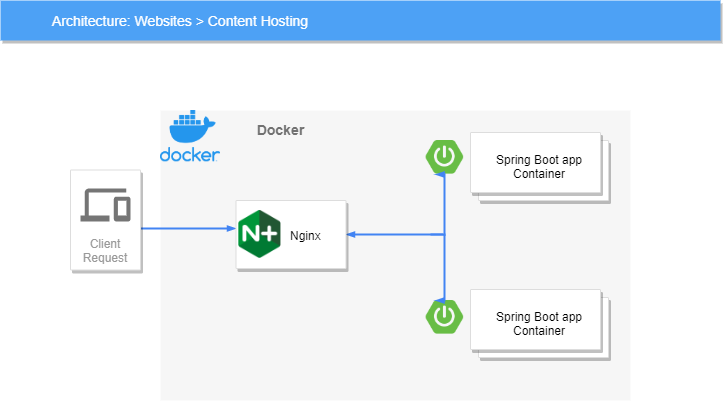
Step 1:-NGINX Proxy
Nginx-proxy accepts HTTP requests and proxies the request to the appropriate container based on the request Hostname. This is transparent to the user with happens without any additional performance overhead.
In this scenario, we want to have a NGINX service running which can dynamically discovery and update its load balance configuration when new containers are loaded.
Use the command below to launch nginx-proxy.
docker run -d -p 80:80 -e DEFAULT_HOST=proxy.example -v /var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock:ro --name nginx jwilder/nginx-proxy
DEFAULTHOST: we can set an optional _-e DEFAULTHOST=<domain>. If a request comes in and doesn't make any specified hosts, then this is the container where the request will be handled. This enables you to run multiple websites with different domains on a single machine with a fall-back to a known website
Sock: This is a connection to the Docker daemon running on the host and allows containers to access its metadata via the API. Nginx-proxy uses this to listen for events and then updates the NGINX configuration based on the container IP address. Mounting file works in the same way as directories using -v /var/run/docker.sock:/tmp/docker.sock:ro. We specify :ro to restrict access to read-only.
Lunch Your App Container with below command
docker run -d -p 80 -e VIRTUAL_HOST=servicediscovery.com