INTRODUCTION TO AZURE STORAGE
- Azure is cloud storage that allows you to have anywhere and anytime access as long as you have internet connectivity.
- Azure Storage is massively scalable, so you can store and process hundreds of terabytes of data to support the big data scenarios required by scientific, financial analysis, and media applications.
- Or you can store the small amounts of data required for a small business website. Wherever your needs fall, you pay only for the data you're storing.
- Azure Storage currently stores tens of trillions of unique customer objects, and handles millions of requests per second on average.

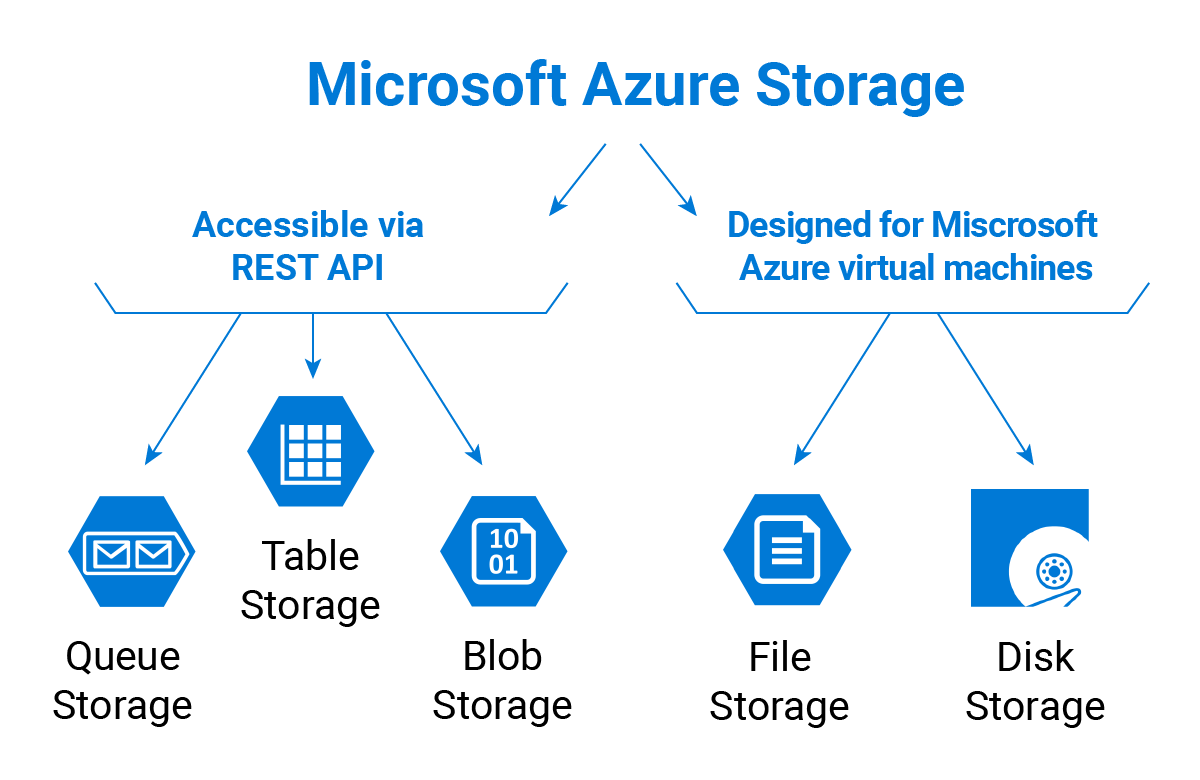
AZURE STORAGE SERVICES
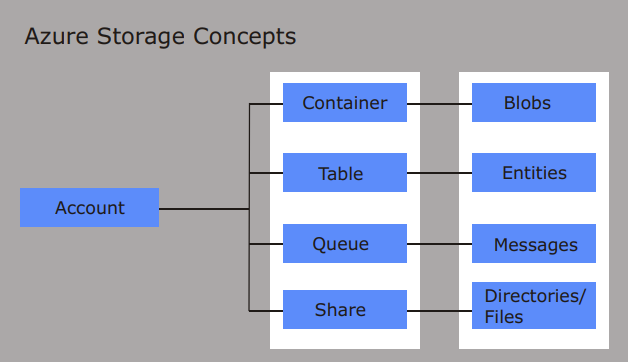

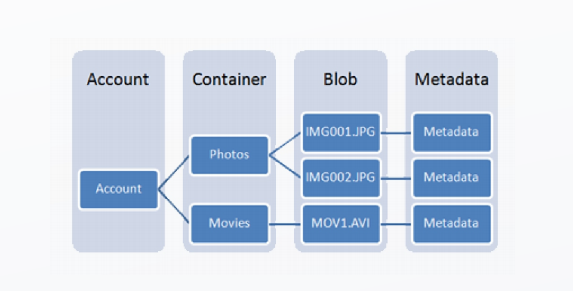
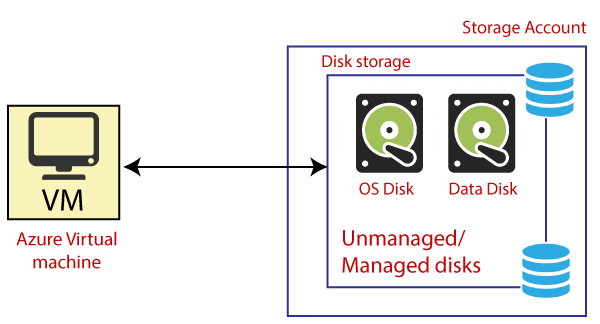
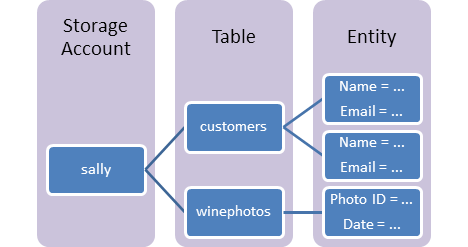
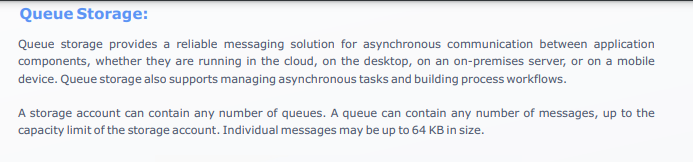
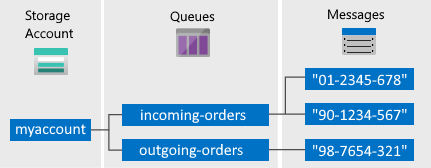
Blob Storage:




Azure Storage redundancy
Azure Storage always stores multiple copies of your data so that it is protected from planned and unplanned events, including transient hardware failures, network or power outages, and massive natural disasters. Redundancy ensures that your storage account meets its availability and durability targets even in the face of failures.
When deciding which redundancy option is best for your scenario, consider the tradeoffs between lower costs and higher availability.
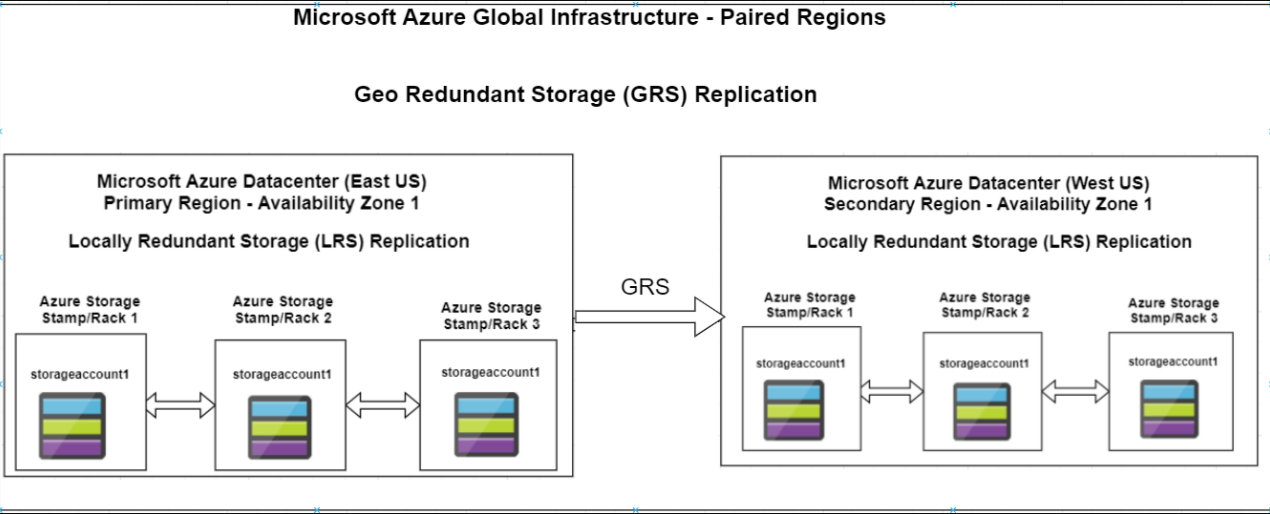
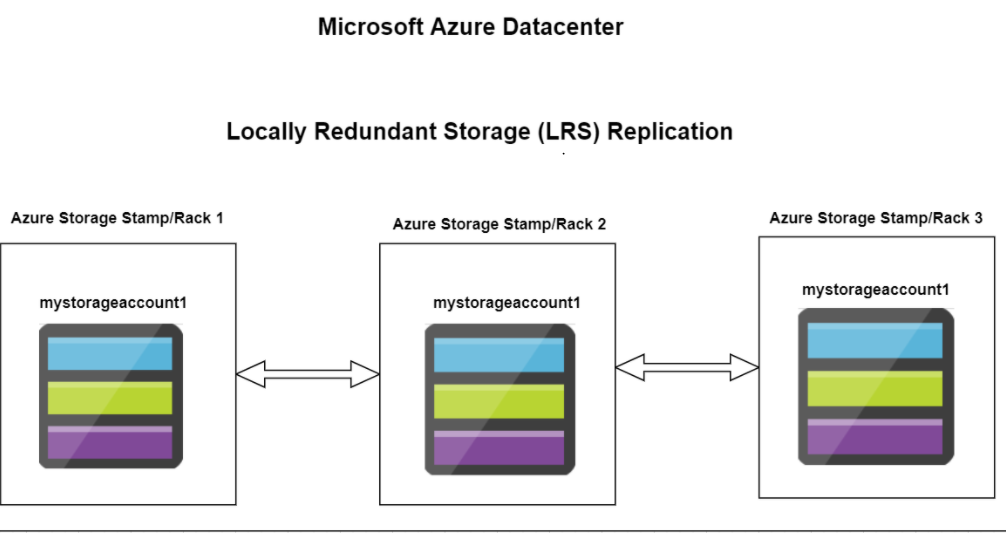
Redundancy in the primary region
Data in an Azure Storage account is always replicated three times in the primary region. Azure Storage offers two options for how your data is replicated in the primary region:
1. Locally redundant storage (LRS) copies your data synchronously three times within a single physical location in the primary region. LRS is the least expensive replication option, but is not recommended for applications requiring high availability.
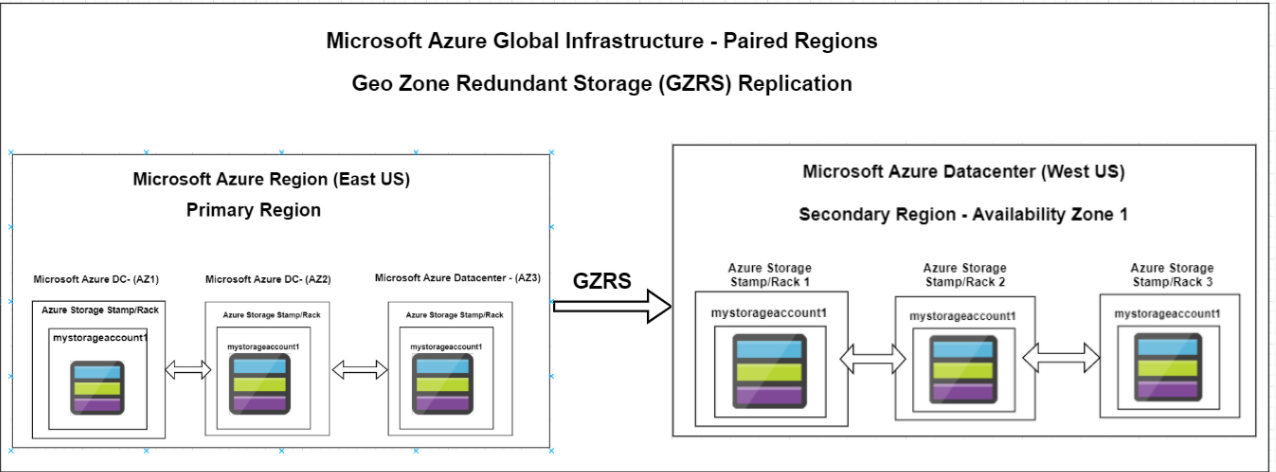
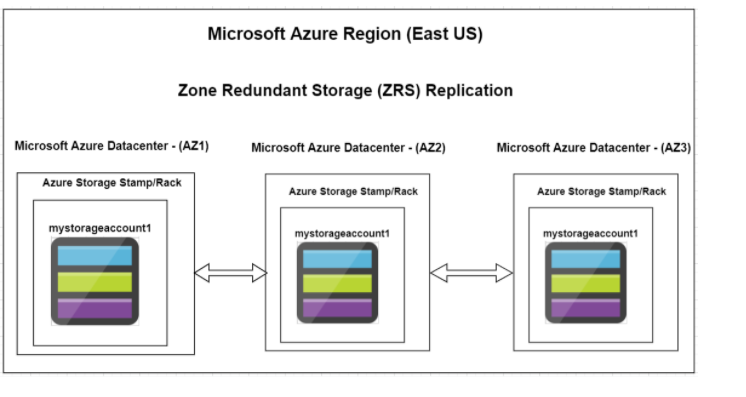
2. Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) copies your data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region. For applications requiring high availability, Microsoft recommends using ZRS in the primary region, and also replicating to a secondary region.
The following table shows which types of storage accounts support ZRS
- General-purpose v21
- BlockBlobStorage1
- FileStorage
Redundancy in a secondary region