Elevator: OMS
Metabolism
Saj Arora
Big Picture
- Catabolism vs. Anabolism
- Anaerobic vs. Aerobic Reactions
- Glycolysis
- TCA Cycle
- ETC (Nitrogen, Oxygen, Sulfur, Carbonate)
- Obligates, Facultative, Microaerophilic, Capnophilic
- Oral Cavity (OA)
Big Picture
- Radicals, Superoxides
- NAD+ Recycling and Fermentation
- Acetoin*: Voges-Proskauer Test
- Temperature Dependence
- Minimal Media (Prototrophs v. Auxotrophs)
- Transport Processes
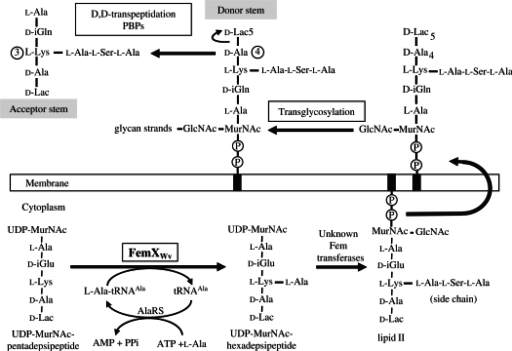
- Synthesis of Peptidoglycan
Catabolism V. Anabolism
- Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytosol while ETC is in the outer mitochondrial matrix
- All catabolic pathways can occur in anaerobic conditions except the Electron Transport Chain
- 4 ATP are generated through Glycolysis with a net of 2 ATP
- Substrate level phosporylation is the end step of ETC
- Regeneration of NAD+ occurs through the lactic acid pathway using the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase
Answers Slide Down!!!
Catabolism V. Anabolism
- Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytosol while ETC is in the outer mitochondrial matrix - False (inner MM)
- All catabolic pathways can occur in anaerobic conditions except the Electron Transport Chain - False (TCA cycle requires oxygen)
- 4 ATP are generated through Glycolysis with a net of 2 ATP - True
- Substrate level phosporylation is the end step of
ETC - False (Oxidative) - Regeneration of NAD+ occurs through the lactic acid pathway using the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase - False (Lactate dehydrogenase)
Pathways and Oxygen use
- Each Acetyl-CoA processed through the TCA Cycle produces 3 NADH and 2 FADH2
- Oxygen is the only possible final electron acceptor for NADH and FADH2 oxidation
- Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen due to the lack of Superoxide Dismutase
- Microaerophilic bacterial like >10% oxygen but
< 15 % oxygen
Pathways and Oxygen use
- Each Acetyl-CoA processed through the TCA Cycle produces 3 NADH and 2 FADH2 - False (1 FADH2)
- Oxygen is the only possible final electron acceptor for NADH and FADH2 oxidation - False
- Obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen due to the lack of Superoxide Dismutase - True
- Microaerophilic bacterial like >10% oxygen but
< 15 % oxygen - False
Fermentation
- Ethanolic or lactic acid fermentation pathways are ways of regenerating Electron Carriers such as NADH
- Pyruvate is the final electron acceptor in lactic acid fermentation
- Fermentation reaction that produce Acetoin can be tested using Voges-Proskauer test (e. coli is - ive and enterobacteria are + ive)
- Pyruvic acid is the final electron acceptor in
ethanol fermentation reaction
Fermentation
- Ethanolic or lactic acid fermentation pathways are ways of regenerating Electron Carriers such as NADH - True
- Pyruvate is the final electron acceptor in lactic acid fermentation - True
- Fermentation reaction that produce Acetoin can be tested using Voges-Proskauer test (e. coli is - ive and enterobacteria are + ive) - True
- Pyruvic acid is the final electron acceptor in
ethanol fermentation reaction - False (acetylaldehyde)
Temperature Dependence
- Pyscrophiles like Listeria love to grow at warm temperatures
- Mesophiles were probably the first living organisms on earth
- Minimal media consists of 5 basic substrates required by E. coli to grow hence, it is called a prototroph
- Most use of ATP by bacteria is to synthesize
RNA followed by proteins.
Temperature Dependence
- Pyscrophiles like Listeria love to grow at warm temperatures - False (cold temp.)
- Mesophiles were probably the first living organisms on earth - False (extremophiles/thermophiles)
- Minimal media consists of 5 basic substrates required by E. coli to grow hence, it is called a prototroph - True
- Most use of ATP by bacteria is to synthesize
RNA followed by proteins. - False (50% proteins, 14% RNA)
Transport Processes
- Facilitated Diffusion is a passive process that requires 0 ATP
- Phosphoenolypyruvate Tranferase system is used by bacteria to transport sucrose into the cell
- Sucrose is an inducer of Enzyme II and Su-6-P hydrolase genes
- Peptidoglycan is a repeating polymer N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosame acid and its synthesis is facilitated by pencillin-binding transpeptidase
Transport Processes
- Facilitated Diffusion is a passive process that requires 0 ATP - True
- Phosphoenolypyruvate Tranferase system is used by bacteria to transport sucrose into the cell - True
- Sucrose is an inducer of Enzyme II and Su-6-P hydrolase genes - True
- Peptidoglycan is a repeating polymer N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosame acid and its synthesis is facilitated by pencillin-binding transpeptidase - True
Peptidoglycan synthesis