Building
STARTUP IDEAS
by Salman Ansari
About Me
- Software developer by trade (mostly Ruby/Rails and iOS)
- Teach lots of web development (BEWD, iXperience)
- Founding engineer of involver (acquired by Oracle)
- DJ for fun (progressive house, techno)
NOT RELATED TO
AZIZ ANSARI


GOALS
- Learn why ideation is important
- Develop familiarity with tactics of idea planning
- Get hands-on experience working on ideas
Why IS IDEATION IMPORTANT?
FACT 1:
Most startups jump straight to development stage,
without investing enough in planning stages.
FACT 2:
Most startups fail to gain significant customer adoption.
This is NOT a coincidence.

Measure twice, cut once.

Agenda:
5 Steps to Build IDEAS
- Inspiration [finding problems]
- Evaluation [market research]
- Research [understanding users]
- Validation [prototyping ideas]
- MVP [focus, focus, focus]
INSPIRATION
What problem should I solve?
Typical Sources of Ideas
- Spontaneous [lightbulb moment in shower]
- Insider [working in an industry for a long time]
- Deliberate [purposefully seeking change]
How Do I Find Problems?
- Make product discovery a habit
- producthunt.com #allday #errday
- Keep a list of potential problems to solve
- Discuss ideas with peers regularly
- Networking is key to discovering opportunities
- Be open-minded, let ideas flow freely
Ideas can come from any source, at any time.
The key is to look for them constantly, learn to compare and measure them effectively, and to act quickly.
ALWAYS. BE. IDEATING.
- You should be able to identify a specific set of users who are affected by the problem you describe
- The primary purpose of this stage is to give you an area of focus, not a solution
- Ideal (but not necessary) that you have a personal interest
- Example problem statement:
- "It's extremely difficult to find the nearest hospital that has specialists for patients suffering from X."
Define the Problem
- Spend 5-10 minutes thinking of 2-3 problems.
- These can be problems you've thought about before, or new ones you think of today.
- For each problem, define:
- the specific users you are targeting
- how big is this group?
- the exact problem you are solving for them
- how severe is this problem? (e.g. where does it land in Maslow's heirarchy of needs)
- the specific users you are targeting
- Do not worry about the solution. Focus on the problem.
ACTIVITY:
BRAINSTORMING PROBLEMS
EVALUATION
Is there a market for this problem?
In order to evaluate the viability of your business idea,
you need to do some competitive analysis,
and establish a business model that you can pursue.
Try and understand the reasons for success/failure outcomes for
as many products/businesses as you can.
It's worth your time.
P.S. That's what an MBA is (thousands of case studies).
StudYING Outcomes
GROUP ACTIVITY
STUDYING OUTCOMES
ACTIVITY
STUDY AN OUTCOME
- Pick any business outcome to study (either a significant failure or significant success).
- Identify what the problem was and who the users who that they were solving for.
- Brainstorm reasons why it failed/succeeded.
- Do some research to help inform your conclusions.
- Share with class.
Competitive Analysis
- Find and study existing competitors thoroughly
- Try and understand why they are successful (or why not)
- Collect metrics about their business model:
- yearly revenue
- # of employees
- # of transactions (e.g. sales)
- Learn about their founders and their mission
ACTIVITY
FIND COMPETITORS TO YOUR IDEA(S)
- Review your list of 2-3 ideas, and find competitors for as many of them as you can.
- Pick a set of 2-3 competitors that you'd like to research, and perform an analysis on them
- For each competitor:
- founder story & mission
- size of business (# employees, $ annual revenue)
- business model (how do they make money?)
- "secret sauce"
ACTIVITY:
CreatE a Business Model
- Choose one idea that you feel has the highest likelihood of gaining traction in the market
- Using existing templates from successful business models
- Numbers can be rough, accuracy is not critical for this exercise.
- Share with class.
- Example:
- Product that helps patients find specialists in area
- Partner with hospitals, and earn revenue through referrals
- Hospitals distribute / market app to existing patients
- 3 million patients with specialist needs / year
- $3/referral -> $9mil annual revenue
RESEARCH
Who is affected by this problem, and how?
User Research: Steps
- Identify your target users
- e.g. emergency patients
- Make some rough estimations as to the market size
- e.g. how many per day? per hospital? per city?
- Develop a plan to conduct user research
- excellent book: just enough research
- Identify data patterns, establish user personas
- creating a "post-it wall" of data can help visualize the data
- Let the data sink in. It might take a while.
- Spend time and effort to make sense of the data, discover the hidden insights.
- Don't bias your questions, or ask leading questions.
- e.g. Don't ask "Would you use a product that did X?"
- If you look for a pre-determined answer, you are sure to find it.
- Don't interview friends... instead look for friend-of-friends, or better yet, complete strangers. They will speak the truth.
- Learn to asses the value of each interview, cut short if necessary
User Research: Tips
- Why do you travel?
- How many trips do you typically take in a year?
- Roughly how much do you spend on a given trip?
- How long are your typical trips?
- How many people usually travel with you?
- How do you plan / book your travel?
- What kind of accommodations do you typically stay at?
- Have you booked with AirBnB?
- What interested you about them?
- What was your experience like?
- What has your experience been like with hotels?
- Tell me about your best & worst travel experiences.
SAMPLE INTERVIEW: TRAVEL
- With the idea you've chosen in mind, spend some time thinking further about the target users
- Try to identify what your unknowns are
- Create a set of questions you'd like to interview users with
- Share with class
ACTIVITY
DESIGN A USER INTERVIEW
User research is an exhausting process,
but it is a critical step.
Keep talking to users, keep following the data, and eventually it will lead you to a solution.
User research will normally lead you much closer to a solution, but unfortunately we don't have time for that in this workshop.
So, for now just do your best to let your intuition (and everything you've learned this session) to lead you to the simplest and most effective solution.
LET's IMPROVISE
Key: What is the simplest way to solve your problem?
- Continuing with the idea you chose to build a business model around, think of potential solutions to the problem
- If possible, focus on one key area of the solution flow
- Write down a few alternative solutions, if they come to you
ACTIVITY
BRAINSTORMING SOLUTIONS
VALIDATION
Testing your solution through prototyping.
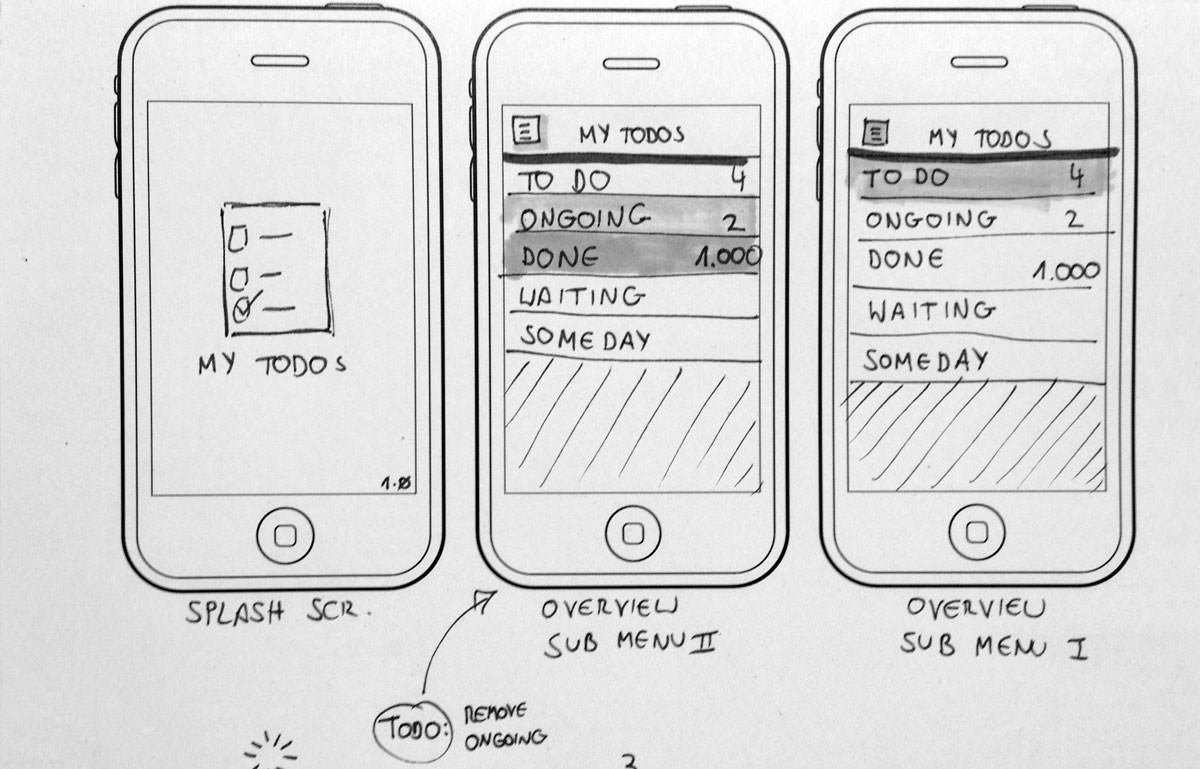
TYPES OF Prototypes
- Prototypes don't have to be complicated
- we will use short-hand sketching today
- Many fantastic tools out there to help make interactive web and mobile prototypes quickly & easily
- Simple goal: convey your idea in an interactive way so users can visualize it and give you quick feedback
SAMPLE SKETCH PROTOTYPE
ACTIVITY
SKETCH A SCREEN
- Pick a screen (or a few) in a critical flow of your solution
- Sketch out the key components
- Consider also sketching out alternative flows
- Share with class
MVP
What is the minimum needed to satisfy user needs?
Building an MVP
- The key to building an MVP is deciding which features to build
- use feedback from prototypes to determine which features are the "must-haves" vs the "nice-to-haves"
- If you do it right, your MVP will feel like it's missing a lot of features, and you'll feel like it's not ready. But it will ship.
- Only you (and your founding team) can determine which features are required. Trust your (well-informed!) intuition.
The key to a great MVP is focus.
REVIEW:
5 STEPS TO BUILD AN IDEA
- Inspiration [finding problems]
- Evaluation [market research]
- Research [understanding users]
- Validation [prototyping ideas]
- MVP [focus, focus, focus]
MORE RESOURCES
- [Inspiration] Founder/Market Fit
- [Inspiration] The Golden Circle
- [Outcomes] Why Google Glass Broke
- [Outcomes] Why did the Segway Fail?
- [Outcomes] The Four Horsemen
- [Prototyping] Google Design Sprint
- [Prototyping] Prototyping with Sketch
- [MVP] How do to MVPs Right
A thing is a thing,
not what is said of the thing.
-Susan Sontag
THANKS!
slides | bit.ly/idea-workshop
twitter | @daretorant
web | salman.io
newsletter | laughlearnletter.com